Thermo Fisher Scientific › Electron Microscopy › Electron Microscopes › 3D Visualization, Analysis and EM Software › Use Case Gallery
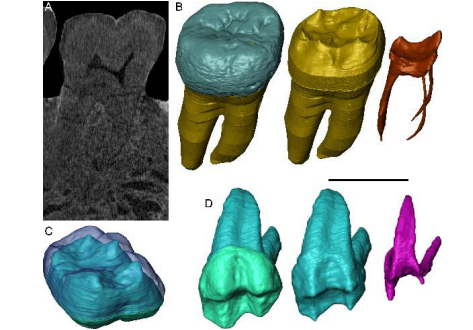
Fossil dental remains are an archive of unique information for paleobiological studies. Computed microtomography based on Xray microfocus sources (X-µCT) and Synchrotron Radiation (SR-µCT) allow subtle quantification at the micron and sub-micron scale of the meso- and microstructural signature imprinted in the mineralized tissues, such as enamel and dentine, through highresolution “virtual histology”. Nonetheless, depending on the degree of alterations undergone during fossilization, X-ray analyses of tooth tissues do not always provide distinct imaging contrasts, thus preventing the extraction of essential morphological and anatomical details. We illustrate here by three examples the successful application of neutron microtomography (n-µCT) in cases where X-rays have previously failed to deliver contrasts between dental tissues of fossilized specimen.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.