Thermo Fisher Scientific › Electron Microscopy › Electron Microscopes › 3D Visualization, Analysis and EM Software › Use Case Gallery
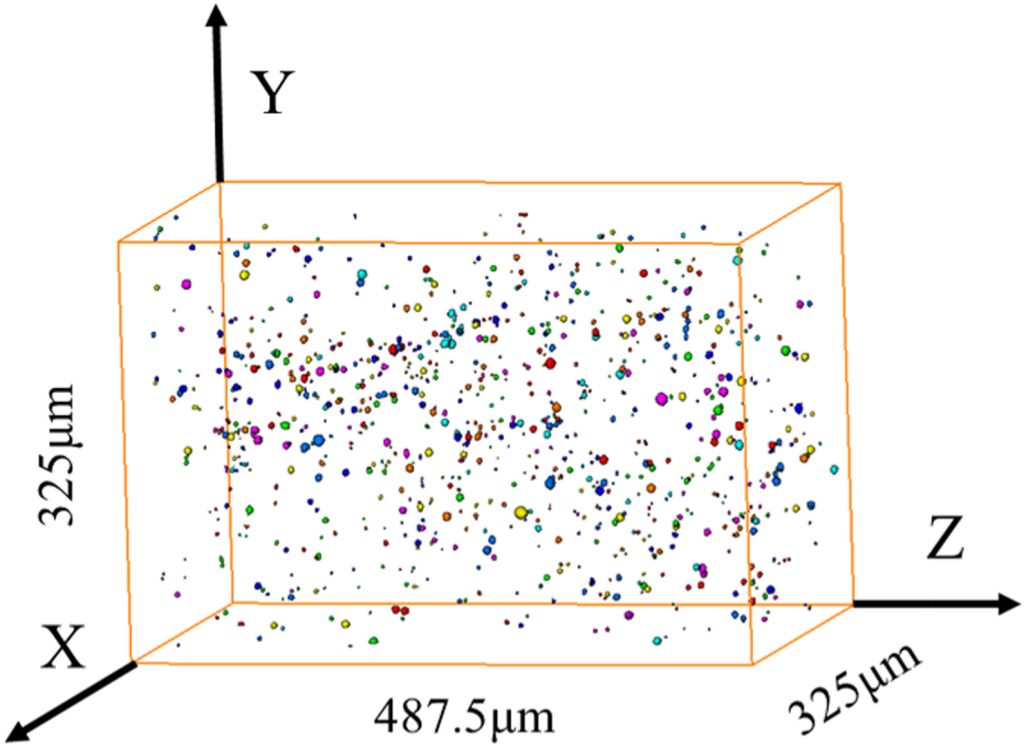
The non-metallic inclusions are mostly harmful to the propertiesof the steel products. The effective characterization of the size, morphology, and distribution of the inclusions in steel is a key issue to remove and control the inclusions in the metallurgical process. However, the conventional methods usually characterize the inclusions on the cross sections of polished samples, which could only reveal the local features of the inclusions. Therefore, the three-dimensional (3D) observation of the inclusions would provide critical information of the inclusions in the steel matrix. However, it is rare to find the reports of the quantitative investigation of the 3D morphology of inclusion particles.
Three-dimensional (3D) observation of the inclusions would provide critical information of the inclusions in the steel matrix. The 3D particles were reconstructed by the commercial software Avizo based on the optimized cross-sectional image slices. A series of parameters were defined to quantitatively express the 3D size and morphology of the inclusions, whose distributions are discussed and analyzed statistically. The method provides a powerful and useful way to observe and analyze inclusion particles in the steel products. Learn more about Avizo Software
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.