Thermo Fisher Scientific › Electron Microscopy › Electron Microscopes › 3D Visualization, Analysis and EM Software › Use Case Gallery
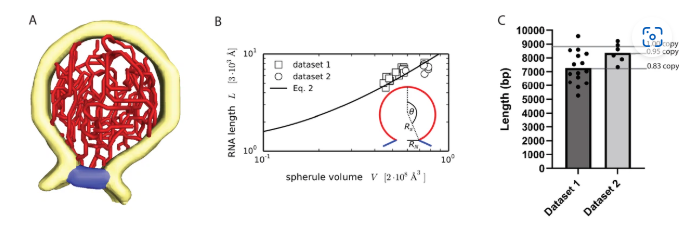
Alphaviruses are mosquito-borne viruses that cause serious disease in humans and other mammals. Along with its mosquito vector, the Alphavirus chikungunya virus (CHIKV) has spread explosively in the last 20 years, and there is no approved treatment for chikungunya fever. On the plasma membrane of the infected cell, CHIKV generates dedicated organelles for viral RNA replication, so-called spherules. Whereas structures exist for several viral proteins that make up the spherule, the architecture of the full organelle is unknown. Here, we use cryo-electron tomography to image CHIKV spherules in their cellular context. This reveals that the viral protein nsP1 serves as a base for the assembly of a larger protein complex at the neck of the membrane bud. Biochemical assays show that the viral helicase-protease nsP2, while having no membrane affinity on its own, is recruited to membranes by nsP1. The tomograms further reveal that full-sized spherules contain a single copy of the viral genome in double-stranded form. Finally, we present a mathematical model that explains the membrane remodeling of the spherule in terms of the pressure exerted on the membrane by the polymerizing RNA, which provides a good agreement with the experimental data. The energy released by RNA polymerization is found to be sufficient to remodel the membrane to the characteristic spherule shape.
The segmentation in Figure 1B was created by manual segmentation in Amira […] , Binned tomograms were filtered using a SIRT-like (simultaneous iterative reconstruction technique) filter with two iterations in IMOD and were imported in Amira where the RNA tracing was performed using its filament tracing functionality, a functionality that has been shown to allow quantification and structural analysis of filaments (Rigort et al., 2012; Dimchev et al., 2021).
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.