Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
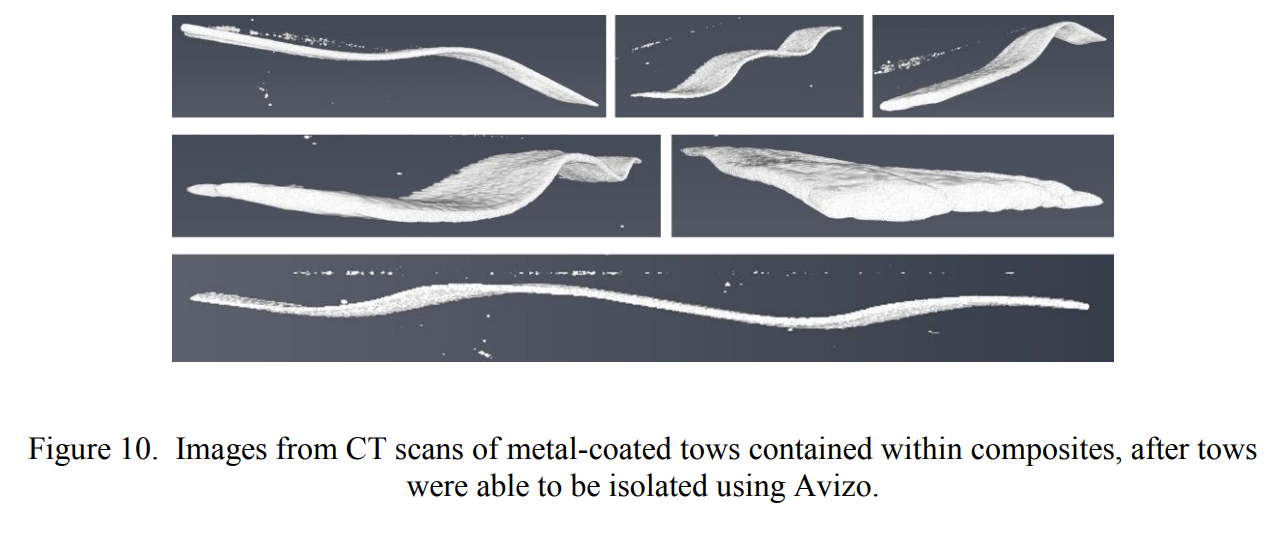
Investigation of Carbon Fiber Architecture in Braided Composites Using X-Ray CT Inspection
During the fabrication of braided carbon fiber composite materials, process variations occur which affect the fiber architecture.
Quantitative measurements of local and global fiber architecture variations are needed to determine the potential effect of process variations on mechanical properties of the cured composite. Although non-destructive inspection via X-ray CT imaging is a promising approach, difficulties in quantitative analysis of the data arise due to the similar densities o... Read more
Daniel J. Rhoads, Sandi G. Miller, Gary D. Roberts, Richard W. Rauser, Dmitry Golovaty, J. Patrick Wilber, Malena I. Español
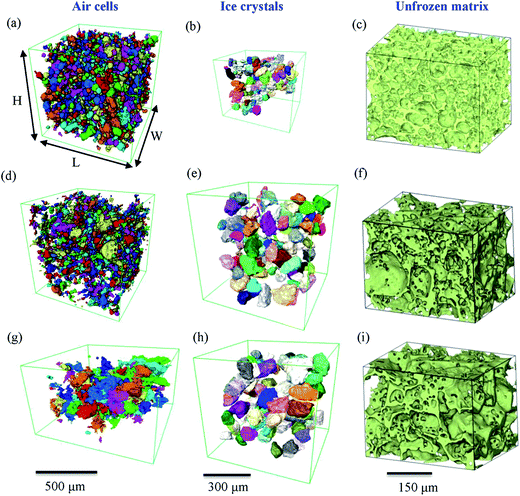
The microstructure of food affects our sensorial perception, its attractiveness, and the manufactured product’s shelf-life.
Microstructural evolution in soft matter directly influences not only the material’s mechanical and functional properties, but also our perception of that material’s taste. Using synchrotron X-ray tomography and cryo-SEM we investigated the time–temperature evolution of ice cream’s microstructure. This was enabled via three adv... Read more
Enyu Guo, Guang Zeng, Daniil Kazantsev, Peter Rockett, Julian Bent, Mark Kirkland, Gerard Van Dalen, David S. Eastwood, David StJohn and Peter D. Lee
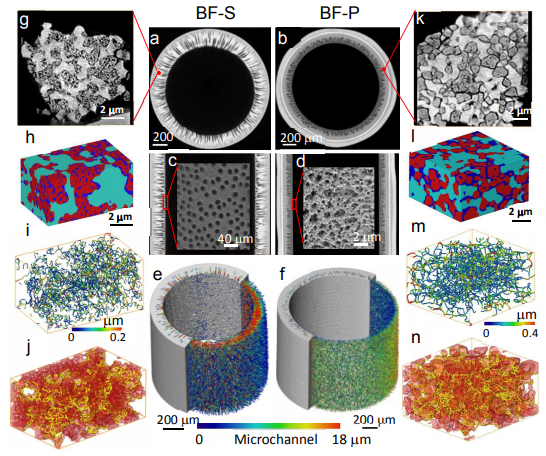
Mass transport can significantly limit the rate of reaction and lead to concentration polarization in electrochemical devices, especially under the conditions of high operating current density.
In this study we investigate hierarchically structured micro-tubular solid
oxide fuel cells (MT-SOFC) fabricated by phase inversion technique and quantitatively assess the mass transport and electrochemical performance improvement compared to a conventional tubular SOFC. We present pioneer... Read more
Xuekun Lu, Tao Li, Antonio Bertei, Jason I S Cho , Thomas M.M. Heenan , Rabuni Mohamad, Kang Li, Dan JL Brett, Paul R Shearing
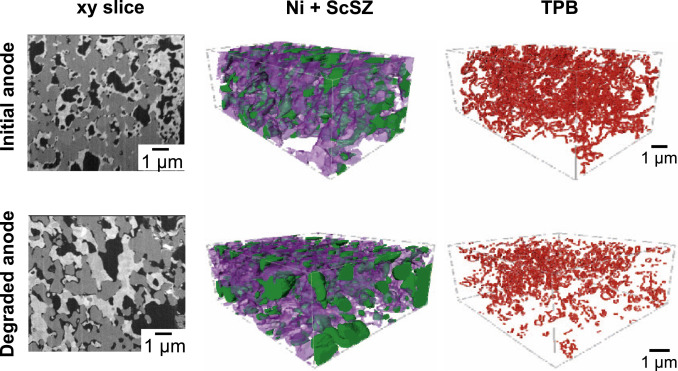
Correlation between triple phase boundary and the microstructure of Solid Oxide Fuel Cell anodes
This study aims to correlate the active triple phase boundaries (TPBs) to the variation of as-prepared anode microstructures and Ni densifications based on the reconstructed 3D volume of an SOFC anode, providing a point of comparison with theoretical studies that reveal the relationship of TPBs and the material microstructure using randomly packed spheres models.
Read more
Xuekun Lu, Thomas M.M. Heenan, Josh J. Bailey, Tao Li, Kang Li, Daniel J.L. Brett, Paul R. Shearing, Electrochemical Innovation Lab, Department of Chemical Engineering, University College London, London
Nickel/zirconia-based nanostructured electrodes for solid oxide fuel cells suffer from poor stability even at intermediate temperature.
This study quantifies the electrochemical and microstructural degradation of nanostructured electrodes by combining 3D tomography, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and mechanistic modeling. For the first time, the electrochemical degradation of nanostructured electrodes is quantified according to the fractal nature of the three-phase bounda... Read more
A. Bertei, E. Ruiz-Trejo, K. Kareh, V. Yufit, X. Wang, F. Tariq, N.P. Brandon,
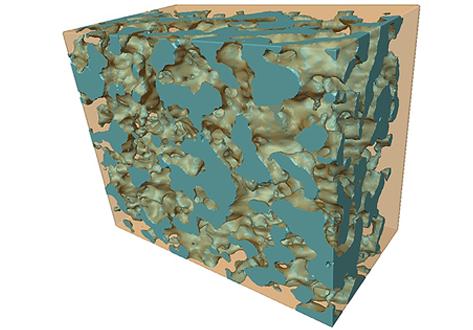
A simple chemical bath deposition is used to coat a complex porous ceramic scaffold with a conformal Ni layer.
The resulting composite is used as a solid oxide fuel cell electrode, and its electrochemical response is measured in humidified hydrogen. X‐ray tomography is used to determine the microstructural characteristics of the uncoated and Ni‐coated porous structure, which include the surface area to total volume, the radial pore size, and the size of the necks between the pores.... Read more
Dr. Enrique Ruiz‐Trejo, Milla Puolamaa, Brian Sum, Dr. Farid Tariq, Dr. Vladimir Yufit, Prof. Nigel P. Brandon
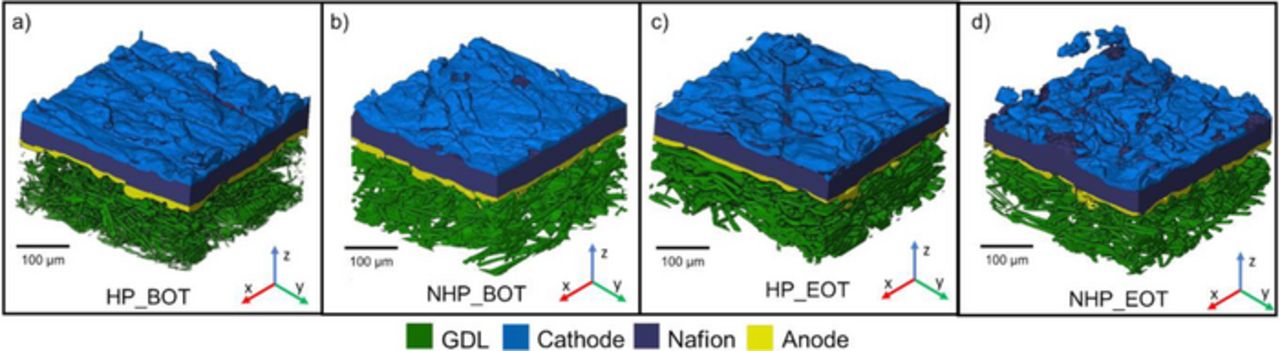
The most common means of fabricating membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs) for polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs) involves a hot-press step. The conditions used to perform the hot-press impacts the performance and durability of the fuel cell.
However, the hot-press process is not essential for achieving operational MEAs and some practitioners dispense with the hot-press stage altogether by using a self-assembled approach. By performing the integration of the components in-situ durin... Read more
Jennifer Hack, T. M. M. Heenan, F. Iacoviello, N. Mansor, Q. Meyer, P. Shearing, N. Brandon and D. J. L. Brett
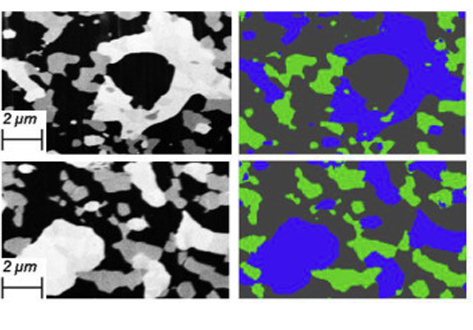
Quantification of the degradation of Ni-YSZ anodes upon redox cycling
Ni-YSZ anodes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells are vulnerable to microstructural damage during redox cycling leading to a decrease in the electrochemical performance.
- Quantification of redox damage by coupling 3D tomography, EIS and nanoindentation.
- YSZ fracture, Ni detachment and agglomeration led to irreversible mechanical damage.
- Ni nanoparticles obtained upon redox cycling improve electrochemical performance.
- Loss in TPB densi... Read more
Bowen Song, Enrique Ruiz-Trejo, Antonio Bertei, Nigel P.Brandon
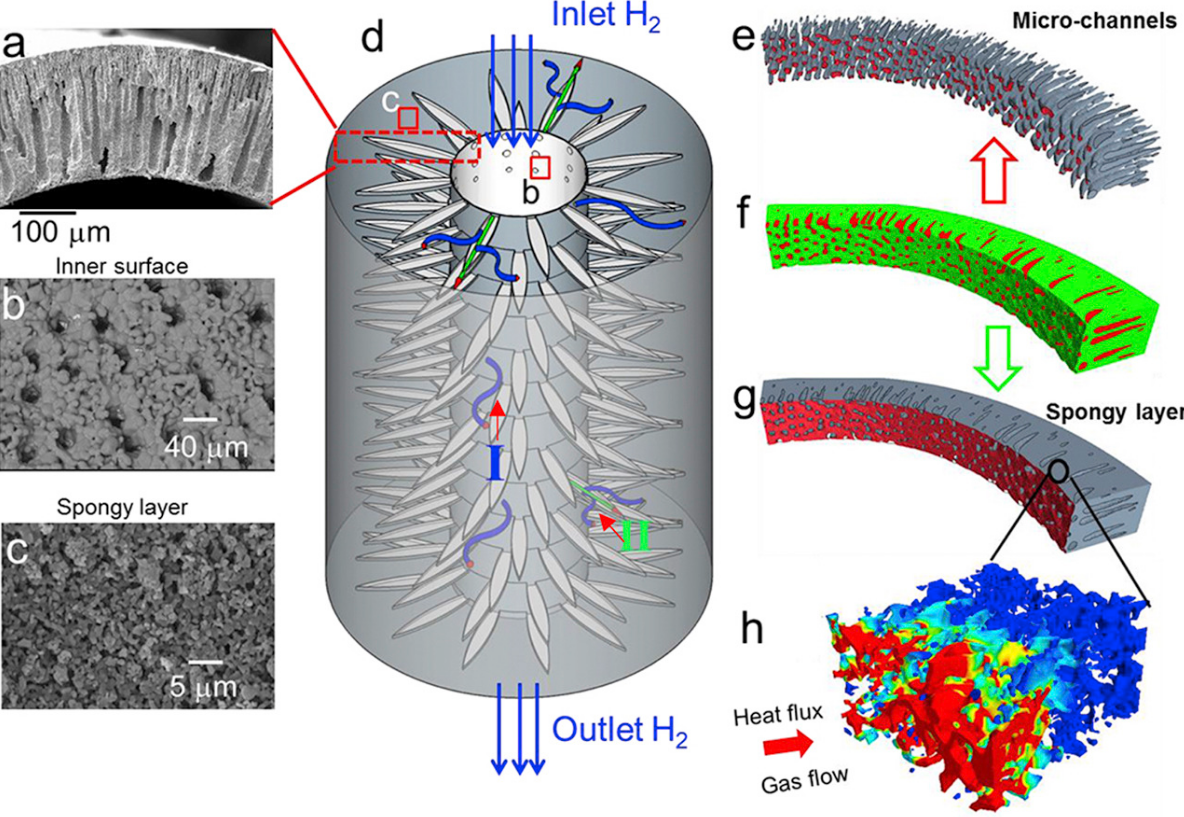
Our parametric study shows that increasing the porosity in the spongy layer beyond 10% enhances the effective transport parameters of the spongy layer at an exponential rate, but linearly for the full anode. For the first time, local and global mass transport properties are correlated to the microstructure, which is of wide interest for rationalizing the design optimization of SOFC electrodes and more generally for hierarchical materials in batteries and membranes.
Read more
Xuekun Lu, Oluwadamilola O. Taiwo, Antonio Bertei, Tao Li, Kang Li, Dan J.L. Brett, Paul R.Shearing
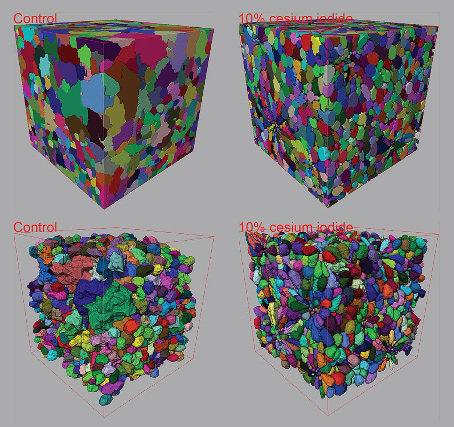
Contrast-enhanced 3D micro-CT of plant tissues using different impregnation techniques
X-ray micro-CT has increasingly been used for 3D imaging of plant structures. At the micrometer reso-lution however, limitations in X-ray contrast often lead to datasets with poor qualitative and quantitative measures, especially within dense cell clusters of plant tissue specimens. The current study developed protocols for delivering a cesium based contrast enhancing solution to varying plant tissue specimens for the purpose of improving 3D tissue structure characterization within plant spec... Read more
Zi Wang, Pieter Verboven and Bart Nicolai, Department of Biosystems KU Leuven – University of Leuven Willem de Croylaan, Leuven Belgium
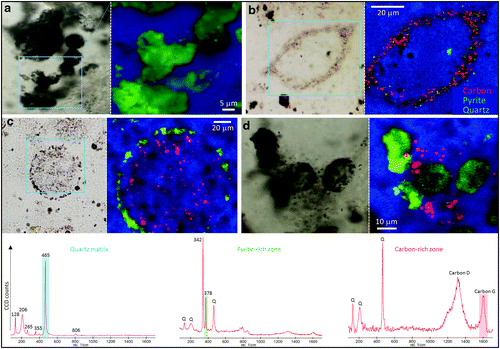
Volcanogenic Pseudo-Fossils from the ∼3.48 Ga
The ∼3.48 billion-year-old Dresser Formation, Pilbara Craton, Western Australia, is a key geological unit for the study of Earth’s earliest life and the habitats it occupied. Here, we describe a new suite of spheroidal to lenticular microstructures that morphologically resemble some previously reported Archean microfossils. Correlative microscopy shows that these objects have a size distribution, wall ultrastructure, and chemistry that are incompatible with a microfossil origin and in... Read more
Wacey David , Noffke Nora , Saunders Martin , Guagliardo Paul , and Pyle David M
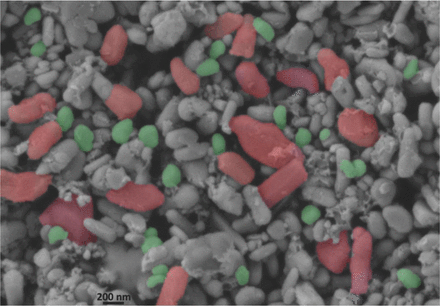
Enhanced Imaging of Lithium Ion Battery Electrode Materials
The authors present for the first time a new methodology of contrast enhancement for 3D imaging, including novel advanced quantification, on a commercial Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) LiFePO4 cathode. The aim of this work is to improve the quality of the 3D imaging of challenging battery materials by developing methods to increase contrast between otherwise previously poorly differentiated phases. This is necessary to enable capture of the real geometry of electrode microstructures... Read more
Moshiel Biton, Vladimir Yufit, Farid Tariq, Masashi Kishimoto and Nigel Brandon
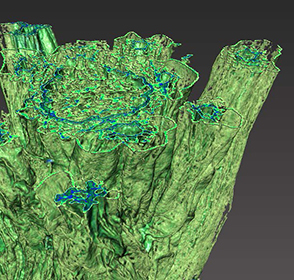
Unilever uses Avizo software to visualize and understand food and detergent structures
Food and detergent products are composed of complex micro structures. With modern microscopic techniques we can make them visible. The microstructure greatly affects macroscopic properties such as appearance, taste, mouth feel and solubility. Making these structures visible and quantifying them is essential to the development of products with optimal product properties. A broad range of imaging techniques is used to visualize microstructure elements at different length scales. For example, X-... Read more
Gerard van Dalen, Unilever R&D Vlaardingen (The Netherlands)
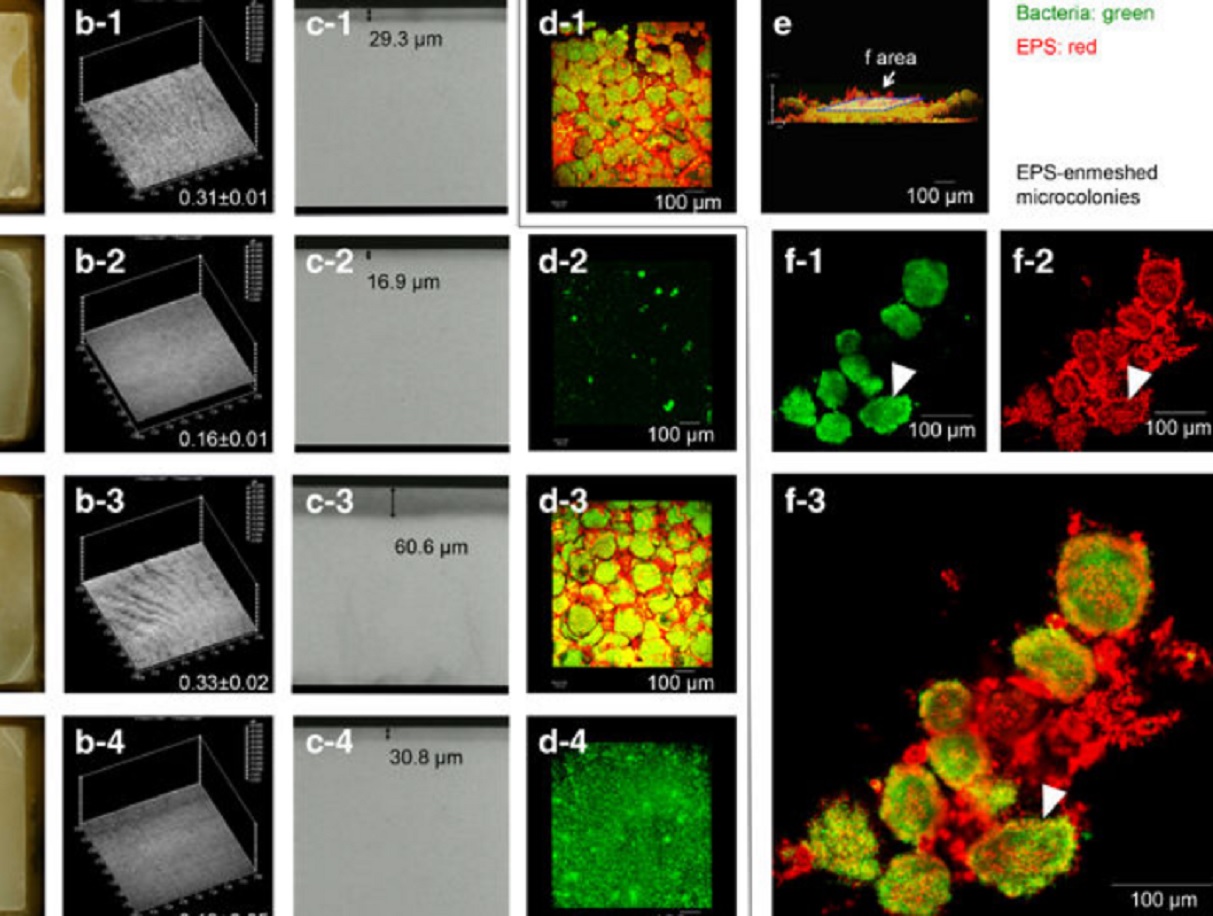
Acidic microenvironments created by bacterial clusters thriving in a polysaccharide matrix could be behind localized tooth decay. Jin Xiao of the University of Rochester Medical Center and Geelsu Hwang of the University of Pennsylvania with colleagues in the US mapped acidity changes across tooth enamel caused by the microstructure of dental plaque: a film of bacteria and the polysaccharide matrix they secrete. Using fluorescence microscopy, they studied the 3D architecture of plaque that for... Read more
Jin Xiao, Anderson T Hara, Dongyeop Kim, Domenick T Zero, Hyun Koo et al.
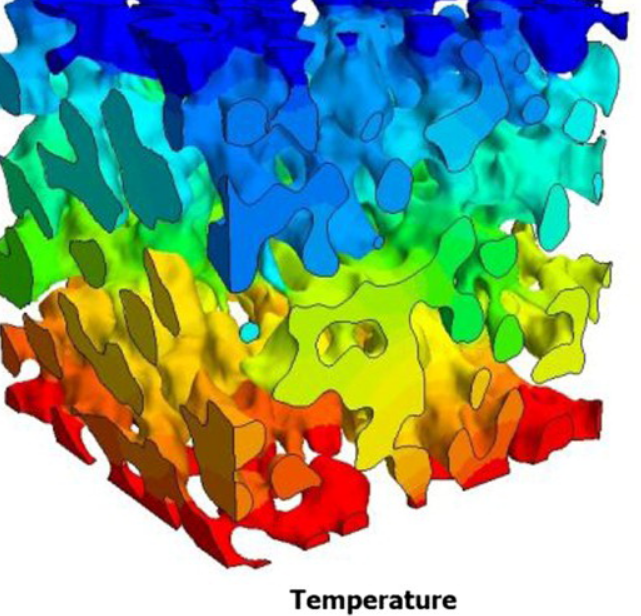
Tortuosity in electrochemical devices: a review of calculation approaches
Here, a review of tortuosity calculation procedures applied in the field of electrochemical devices is presented to better understand the resulting values presented in the literature. Visible differences between calculation methods are observed, especially when using porosity–tortuosity relationships and when comparing geometric and flux-based tortuosity calculation approaches.
Read more
Bernhard Tjaden, Dan J. L. Brett, Paul R. Shearing
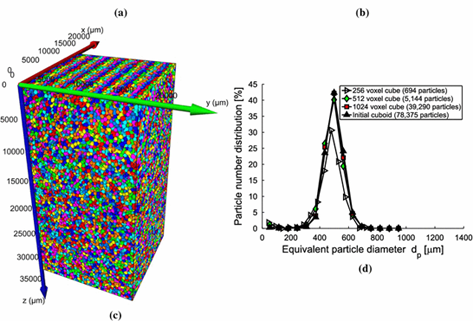
Hydraulic properties of porous sintered glass bead systems
In this paper, porous sintered glass bead packings are studied, using X-ray Computed Tomography (XRCT) images at 16μm16μm voxel resolution, to obtain not only the porosity field, but also other properties like particle sizes, pore throats and the permeability. The influence of the sintering procedure and the original particle size distributions on the microstructure, and thus on the hydraulic properties, is analyzed in detail. The XRCT data are visualized and studied by advanced image fil... Read more
University of Twente, Enschede | Ruhr-University Bochum; Eindhoven University of Technology | Helmholtz Institute Erlangen-Nürnberg for Renewable Energy | University of Stuttgart