Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
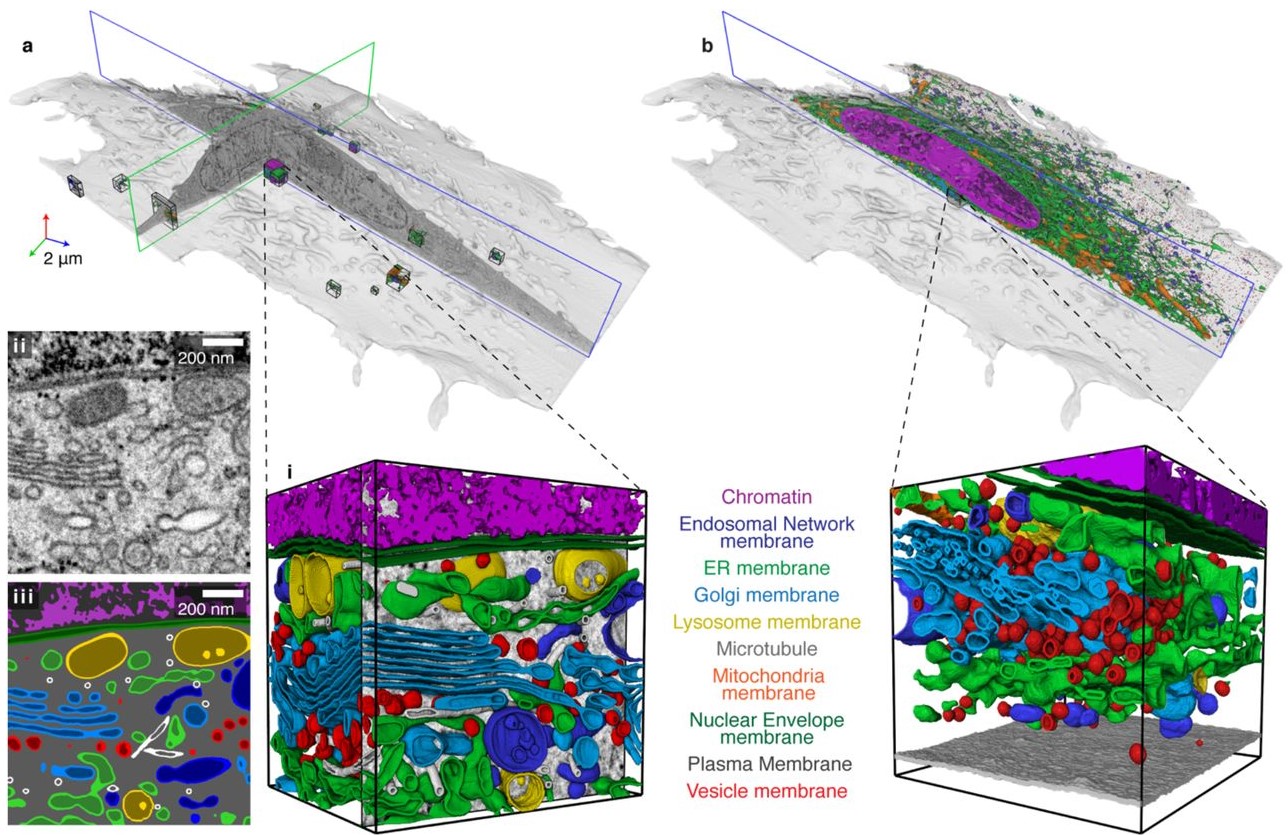
Automatic whole cell organelle segmentation in volumetric electron microscopy
Cells contain hundreds of different organelle and macromolecular assemblies intricately organized relative to each other to meet any cellular demands. Obtaining a complete understanding of their organization is challenging and requires nanometer-level, three-dimensional reconstruction of whole cells. Even then, the immense size of datasets and large number of structures to be characterized requires generalizable, automatic methods.
To meet this challenge, we developed an analy... Read more
Larissa Heinrich, Davis Bennett, David Ackerman, Woohyun Park, John Bogovic, View ORCID ProfileNils Eckstein, Alyson Petruncio, Jody Clements, C. Shan Xu, Jan Funke, Wyatt Korff, Harald F. Hess, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Stephan Saalfeld, Aubrey V. Weigel, COSEM Project Team
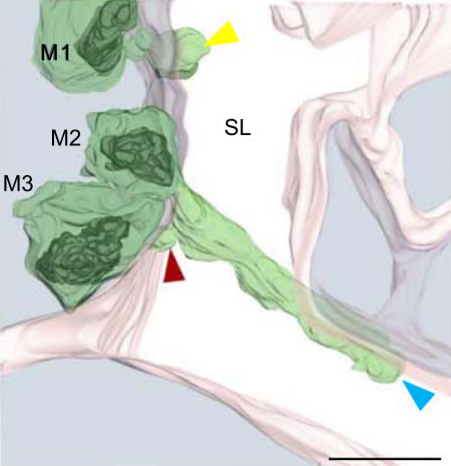
Multiple membrane extrusion sites drive megakaryocyte migration into bone marrow blood vessels
Platelets, cells central to hemostasis and thrombosis, are formed from parent cell megakaryocytes. Although the process is highly efficient in vivo, our ability to generate them in vitro is still remarkably inefficient. We proposed that greater understanding of the process in vivo is needed and used an imaging approach, intravital correlative light electron microscopy, to visualize platelet generation in bone marrow in the living mouse. In contrast to current understanding, we found that most... Read more
Edward Brown, Leo M Carlin, Claus Nerlov, Cristina Lo Celso, Alastair W Poole
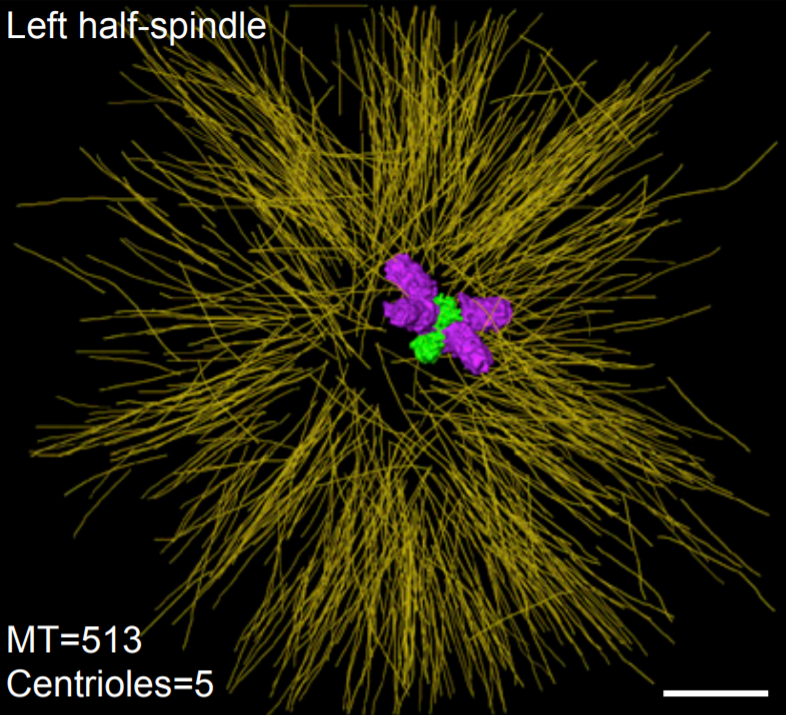
Asymmetric Centriole Numbers at Spindle Poles Cause Chromosome Missegregation in Cancer
Chromosomal instability is a hallmark of cancer and correlates with the presence of extra centrosomes, which originate from centriole overduplication.
Overduplicated centrioles lead to the formation of centriole rosettes, which mature into supernumerary centrosomes in the subsequent cell cycle. While extra centrosomes promote chromosome missegregation by clustering into pseudo-bipolar spindles, the contribution of centriole rosettes to chromosome missegregation is unknown. We us... Read more
Marco R.Cosenza, Anna Cazzola, Annik Rossberg, Nicole L. Schieber, Gleb Konotop, Elena Bausch, Alla Slynko, Tim Holland-Letz, Marc S.Raab, Taronish Dubash, Hanno Glimm, Sven Poppelreuther, Christel Herold-Mende, Yannick Schwab, Alwin Krämer
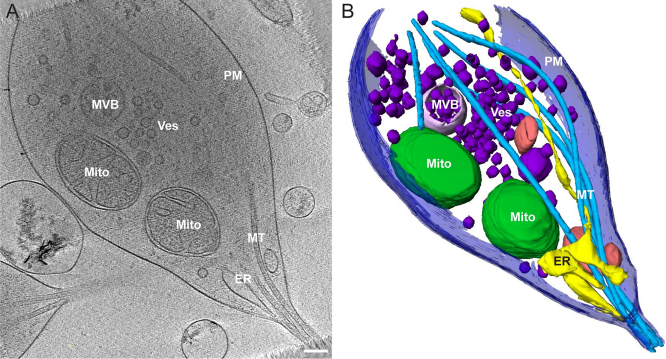
Morphology of mitochondria in spatially restricted axons revealed by cryo-electron tomography
Neurons project axons to local and distal sites and can display heterogeneous morphologies with limited physical dimensions that may influence the structure of large organelles such as mitochondria. Using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET), we characterized native environments within axons and presynaptic varicosities to examine whether spatial restrictions within these compartments influence the morphology of mitochondria. Segmented tomographic reconstructions revealed distinctive morphologi... Read more
Tara D. Fischer, Pramod K. Dash, Jun Liu, M. Neal Waxham
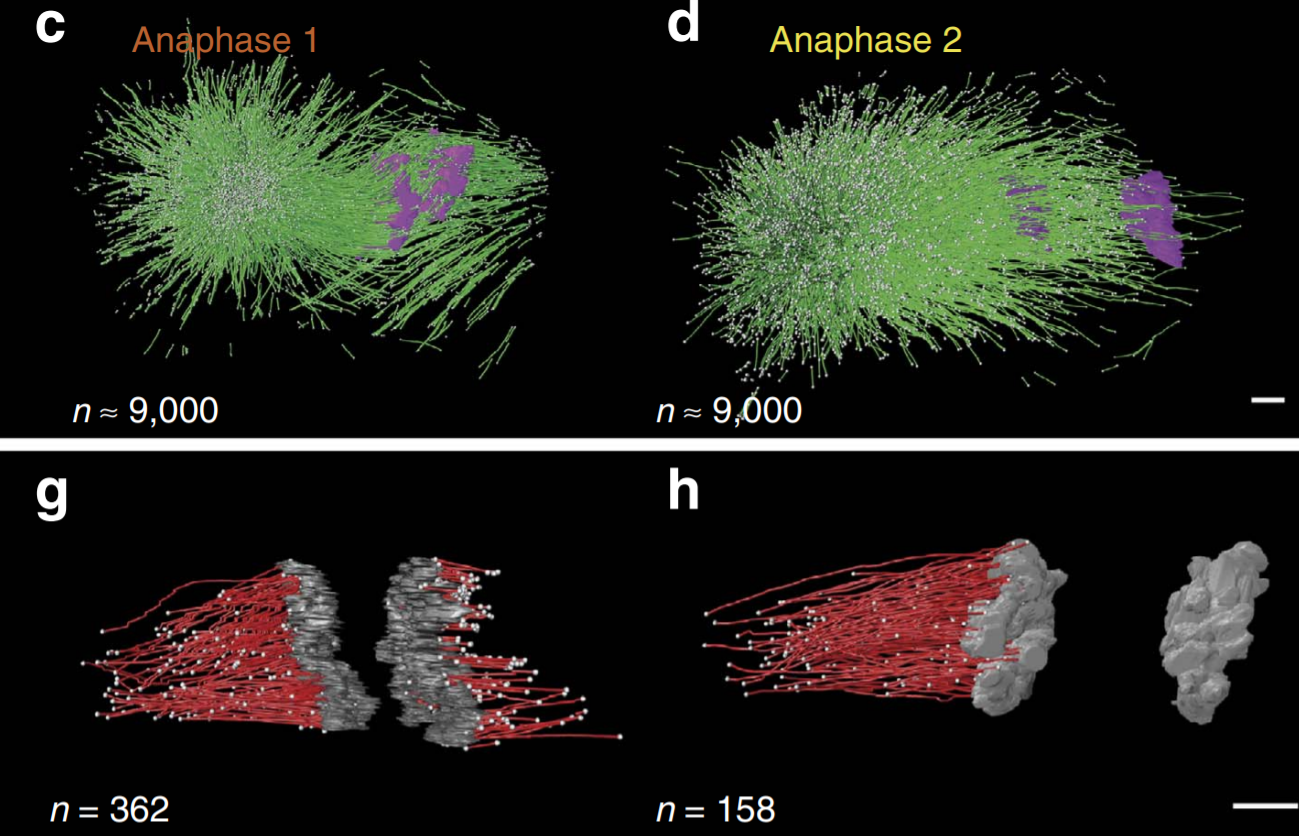
C. elegans chromosomes connect to centrosomes by anchoring into the spindle network
The mitotic spindle ensures the faithful segregation of chromosomes. Here we combine the first large-scale serial electron tomography of whole mitotic spindles in early C. elegans embryos with live-cell imaging to reconstruct all microtubules in 3D and identify their plus- and minus-ends. We classify them as kinetochore (KMTs), spindle (SMTs) or astral microtubules (AMTs) according to their positions, and quantify distinct properties of each class. While our light microscopy and muta... Read more
Stefanie Redemann, Johannes Baumgart, Norbert Lindow, Michael Shelley, Ehssan Nazockdast, Andrea Kratz, Steffen Prohaska, Jan Brugués, Sebastian Fürthauer & Thomas Müller-Reichert
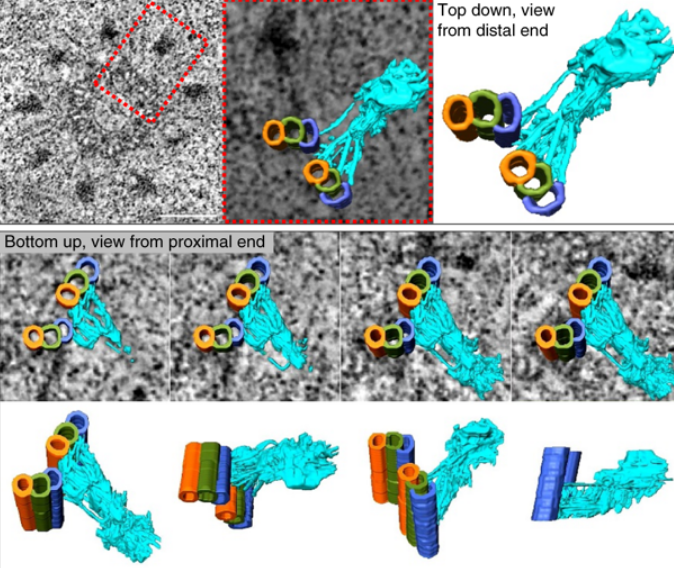
Centrioles are vital cellular structures that form centrosomes and cilia. The formation and function of cilia depends on a set of centriole’s distal appendages. In this study, we use correlative super resolution and electron microscopy to precisely determine where distal appendage proteins localize in relation to the centriole microtubules and appendage electron densities. Here we characterize a novel distal appendage protein ANKRD26 and detail, in high resolution, the initial steps of dist... Read more
Mathew Bowler, Dong Kong, Shufeng Sun, Rashmi Nanjundappa, Lauren Evans, Veronica Farmer, Andrew Holland, Moe R. Mahjoub, Haixin Sui & Jadranka Loncarek
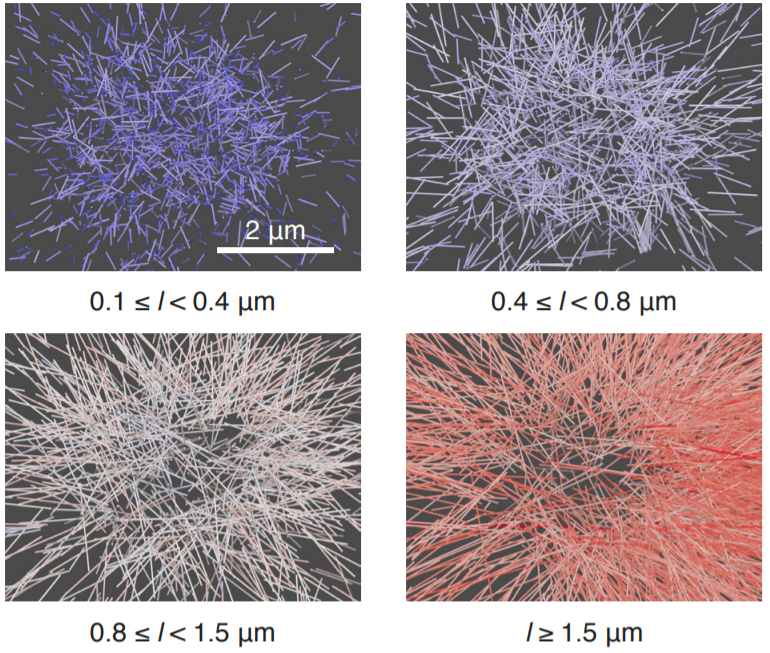
Soluble tubulin is locally enriched at mitotic centrosomes in C. elegans
During mitosis, the centrosome expands its capacity to nucleate microtubules. Understanding the mechanisms of centrosomal microtubule nucleation is, however, constrained by a lack of knowledge of the amount of soluble and polymer tubulin at mitotic centrosomes. Here we combined light microscopy and serial-section electron tomography to measure the amount of dimer and polymer at mitotic centrosomes in early C. elegans embryos. We show that a C. elegans one-cell stage centrosome at metaphase co... Read more
Johannes Baumgart, Marcel Kirchner, Stefanie Redemann, Jeffrey Woodruff, Jean-Marc Verbavatz, Frank Julicher, Anthony Hyman, Thomas Mueller-Reichert, Jan Brugues
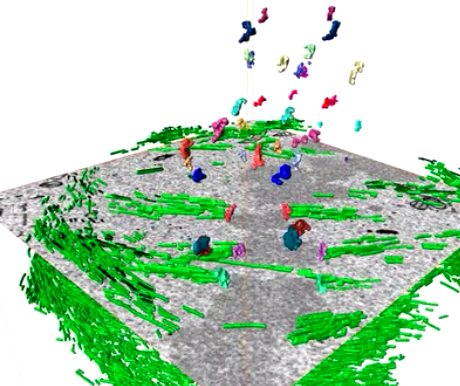
Serial block face scanning electron microscopy (SBF-SEM) is a powerful method to analyze cells in 3D. Here, working at the resolution limit of the method, we describe a correlative light–SBF-SEM workflow to resolve microtubules of the mitotic spindle in human cells. We present four examples of uses for this workflow that are not practical by light microscopy and/or transmission electron microscopy. First, distinguishing closely associated microtubules within K-fibers; second, resolving brid... Read more
Faye M. Nixon, Thomas R. Honnor, Nicholas I. Clarke, Georgina P. Starling, Alison J. Beckett, Adam M. Johansen, Julia A. Brettschneider, Ian A. Prior, Stephen J. Royle
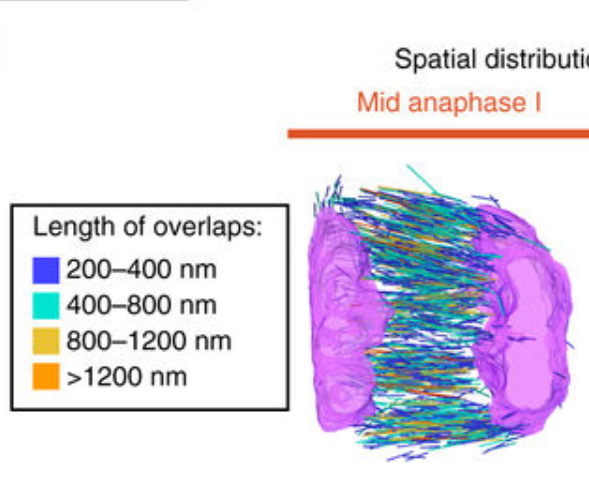
Chromosome segregation occurs by microtubule pushing in oocytes
During cell division, spindle microtubules ensure an equal repartition of chromosomes between the two daughter cells. While the kinetochore-dependent mechanisms that drive mitotic chromosome segregation are well understood, in oocytes of most species atypical spindles assembled in absence of centrosomes entail poorly understood mechanisms of chromosome segregation. In particular, the structure(s) responsible for force generation during meiotic chromosome separation in oocytes is unclear. Usin... Read more
Kimberley Laband, Rémi Le Borgne, Frances Edwards, Marine Stefanutti, Julie C. Canman, Jean-Marc Verbavatz, Julien Dumont