Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
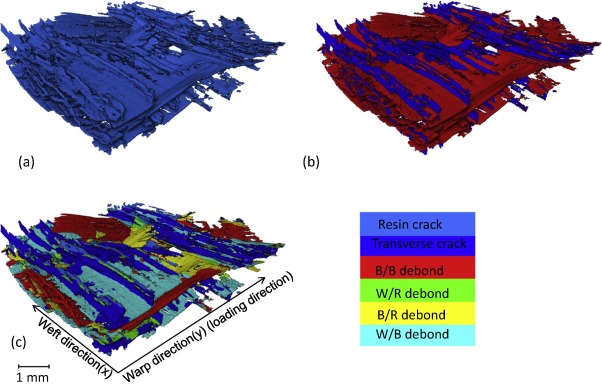
Three dimensional (3D) composites were proposed over 40 years ago in an attempt to overcome the shortcomings of 2D laminates, by incorporating fibres into the through-thickness direction. 3D weaving offer significant manufacturing benefits as well as creating versatile textiles having a range of 3D architectures.
The development of fatigue damage in a glass fibre modified layer-to-layer three dimensional (3D) woven composite has been followed by time-lapse X-ray computed tomograp... Read more
B. Yu, R. Blanc, C. Soutis, P.J. Withers
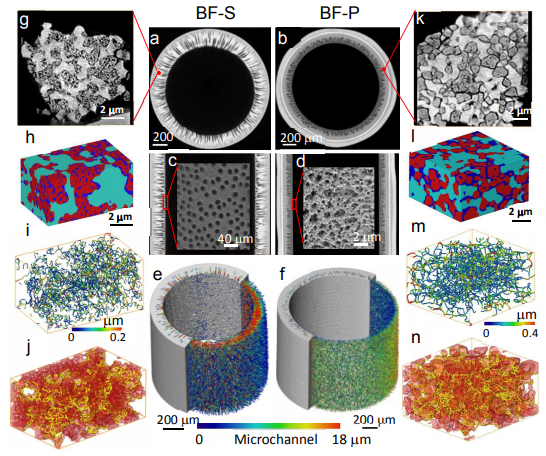
Mass transport can significantly limit the rate of reaction and lead to concentration polarization in electrochemical devices, especially under the conditions of high operating current density.
In this study we investigate hierarchically structured micro-tubular solid
oxide fuel cells (MT-SOFC) fabricated by phase inversion technique and quantitatively assess the mass transport and electrochemical performance improvement compared to a conventional tubular SOFC. We present pioneer... Read more
Xuekun Lu, Tao Li, Antonio Bertei, Jason I S Cho , Thomas M.M. Heenan , Rabuni Mohamad, Kang Li, Dan JL Brett, Paul R Shearing
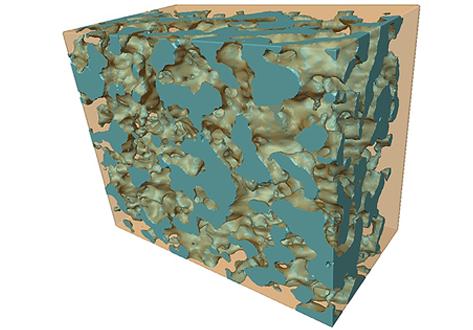
A simple chemical bath deposition is used to coat a complex porous ceramic scaffold with a conformal Ni layer.
The resulting composite is used as a solid oxide fuel cell electrode, and its electrochemical response is measured in humidified hydrogen. X‐ray tomography is used to determine the microstructural characteristics of the uncoated and Ni‐coated porous structure, which include the surface area to total volume, the radial pore size, and the size of the necks between the pores.... Read more
Dr. Enrique Ruiz‐Trejo, Milla Puolamaa, Brian Sum, Dr. Farid Tariq, Dr. Vladimir Yufit, Prof. Nigel P. Brandon
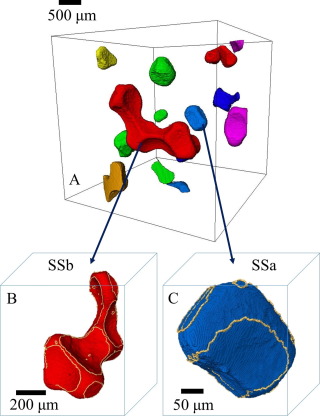
Multiphase flow in porous media is strongly influenced by the wettability of the system, which affects the arrangement of the interfaces of different phases residing in the pores.
We present a method for estimating the effective contact angle, which quantifies the wettability and controls the local capillary pressure within the complex pore space of natural rock samples, based on the physical constraint of constant curvature of the interface between two fluids. This algorithm is ... Read more
Alessio Scanziani, Kamaljit Singh, Martin J. Blunt, Alberto Guadagnini
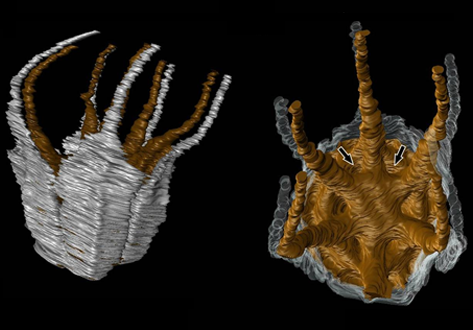
Angiosperm-dominated floras of the Late Cretaceous are essential for understanding the evolutionary, ecological, and geographic radiation of flowering plants.
The Late Cretaceous–early Paleogene Deccan Intertrappean Beds of India contain angiosperm-dominated plant fossil assemblages known from multiple localities in central India. Numerous monocots have been documented from these assemblages, providing a window into an important but poorly understood time in their diversification. On... Read more
Kelly K.S. Matsunaga, Selena Y. Smith, Steven R. Manchester, Dashrath Kapgate, Deepak Ramteke, Amin Garbout, and Herminso Villarraga-Gómez
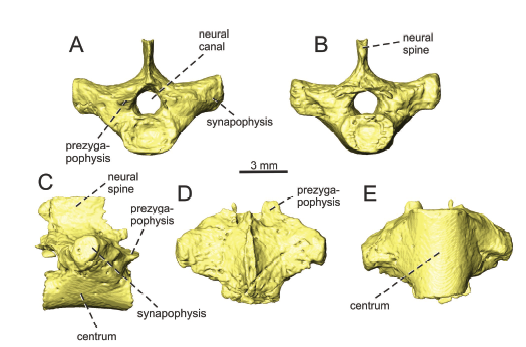
An eosauropterygian skeleton found in the Middle Triassic (upper Anisian) Gutenstein Formation of the Fatric Unit (Demänovská dolina Valley, Low Tatra Mountains, Slovakia) represents the earliest known occurrence of marine tetrapods in the Western Carpathians. The specimen represents a partly articulated portion of the postcranial skeleton (nine dorsal vertebrae, coracoid, ribs, gastral ribs, pelvic girdle, femur and one zeugopodial element). It is assigned to the Pachypleurosauria, more pr... Read more
ANDREJ ČERŇANSKÝ, NICOLE KLEIN, JÁN SOTÁK, MÁRIO OLŠAVSKÝ, JURAJ ŠURKA, and PAVEL HERICH
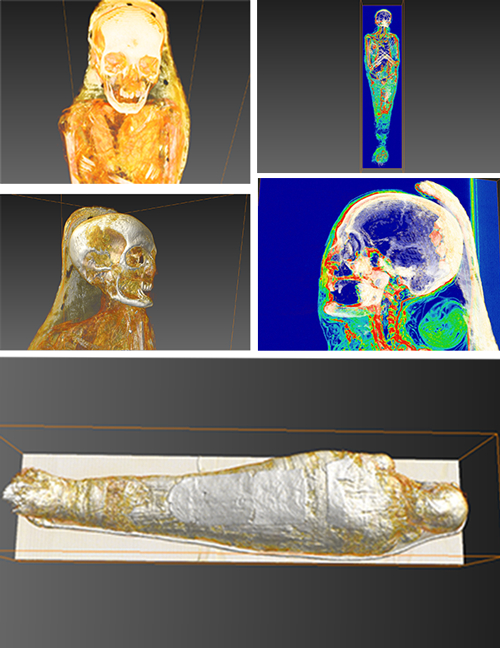
AMSC Research, LLC uses Amira software to understand processes and rituals of Egyptian mummification
“Scanning is important, but it is really just the first step in an immersive exploration of artifacts” says Elias. Raw data from scans taken of mummies (or other archaeological subject matter) is delivered to AMSC Research as files in a language known as DICOM. Next, these are converted into a visually readable form for analytical purposes and to launch the creative modeling process.
Elias uses Amira software to analyze scan data. Mummies are biological entities, so apart f... Read more
Dr. Jonathan Elias, AMSC Research, LLC
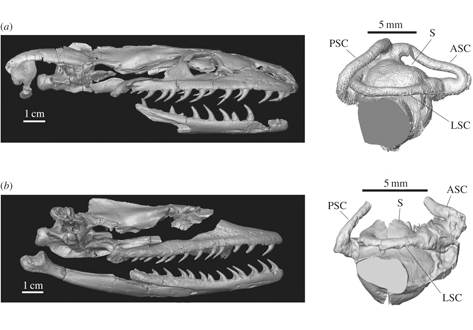
Madtsoiids are among the most basal snakes, with a fossil record dating back to the Upper Cretaceous (Cenomanian). Most representatives went extinct by the end of the Eocene, but some survived in Australia until the Late Cenozoic. Yurlunggur and Wonambi are two of these late forms, and also the best-known madtsoiids to date. A better understanding of the anatomy and palaeoecology of these taxa may shed light on the evolution and extinction of this poorly known group of s... Read more
Alessandro Palci, Mark N. Hutchinson, Michael W. Caldwell, John D. Scanlon, Michael S. Y. Lee
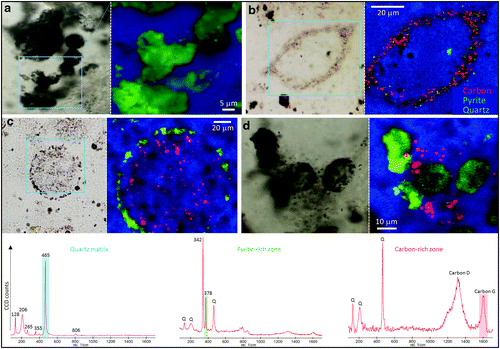
Volcanogenic Pseudo-Fossils from the ∼3.48 Ga
The ∼3.48 billion-year-old Dresser Formation, Pilbara Craton, Western Australia, is a key geological unit for the study of Earth’s earliest life and the habitats it occupied. Here, we describe a new suite of spheroidal to lenticular microstructures that morphologically resemble some previously reported Archean microfossils. Correlative microscopy shows that these objects have a size distribution, wall ultrastructure, and chemistry that are incompatible with a microfossil origin and in... Read more
Wacey David , Noffke Nora , Saunders Martin , Guagliardo Paul , and Pyle David M
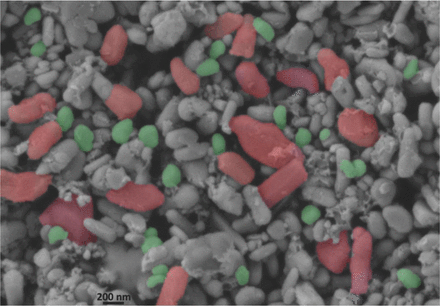
Enhanced Imaging of Lithium Ion Battery Electrode Materials
The authors present for the first time a new methodology of contrast enhancement for 3D imaging, including novel advanced quantification, on a commercial Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) LiFePO4 cathode. The aim of this work is to improve the quality of the 3D imaging of challenging battery materials by developing methods to increase contrast between otherwise previously poorly differentiated phases. This is necessary to enable capture of the real geometry of electrode microstructures... Read more
Moshiel Biton, Vladimir Yufit, Farid Tariq, Masashi Kishimoto and Nigel Brandon
Unilever uses Avizo software to visualize and understand food and detergent structures
Food and detergent products are composed of complex micro structures. With modern microscopic techniques we can make them visible. The microstructure greatly affects macroscopic properties such as appearance, taste, mouth feel and solubility. Making these structures visible and quantifying them is essential to the development of products with optimal product properties. A broad range of imaging techniques is used to visualize microstructure elements at different length scales. For example, X-... Read more
Gerard van Dalen, Unilever R&D Vlaardingen (The Netherlands)
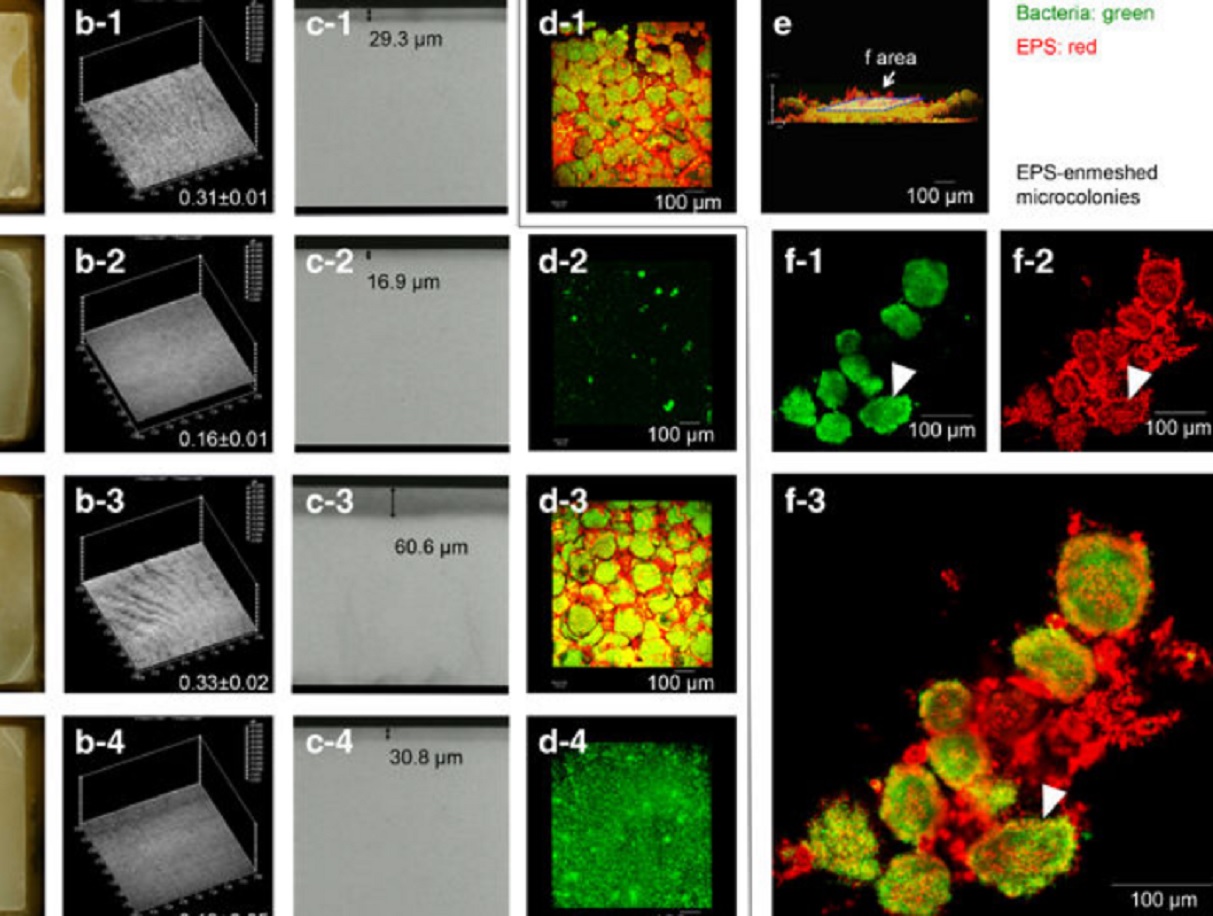
Acidic microenvironments created by bacterial clusters thriving in a polysaccharide matrix could be behind localized tooth decay. Jin Xiao of the University of Rochester Medical Center and Geelsu Hwang of the University of Pennsylvania with colleagues in the US mapped acidity changes across tooth enamel caused by the microstructure of dental plaque: a film of bacteria and the polysaccharide matrix they secrete. Using fluorescence microscopy, they studied the 3D architecture of plaque that for... Read more
Jin Xiao, Anderson T Hara, Dongyeop Kim, Domenick T Zero, Hyun Koo et al.
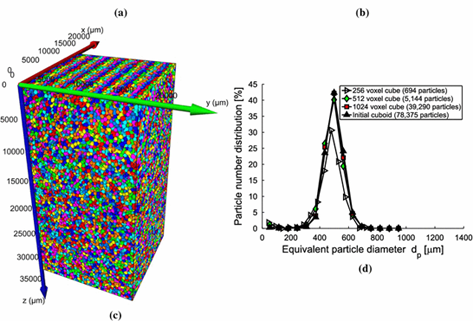
Hydraulic properties of porous sintered glass bead systems
In this paper, porous sintered glass bead packings are studied, using X-ray Computed Tomography (XRCT) images at 16μm16μm voxel resolution, to obtain not only the porosity field, but also other properties like particle sizes, pore throats and the permeability. The influence of the sintering procedure and the original particle size distributions on the microstructure, and thus on the hydraulic properties, is analyzed in detail. The XRCT data are visualized and studied by advanced image fil... Read more
University of Twente, Enschede | Ruhr-University Bochum; Eindhoven University of Technology | Helmholtz Institute Erlangen-Nürnberg for Renewable Energy | University of Stuttgart