Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
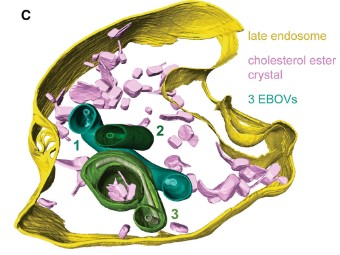
The Ebola virus VP40 matrix layer undergoes endosomal disassembly essential for membrane fusion
Ebola viruses (EBOVs) assemble into filamentous virions, whose shape and stability are determined by the matrix viral protein 40 (VP40). Virus entry into host cells occurs via membrane fusion in late endosomes; however, the mechanism of how the remarkably long virions undergo uncoating, including virion disassembly and nucleocapsid release into the cytosol, remains unknown. Here, we investigate the structural architecture of EBOVs entering host cells and discover that the VP40 matrix disassem... Read more
Sophie L Winter, Gonen Golani, Fabio Lolicato, Melina Vallbracht, Keerthihan Thiyagarajah, Samy Sid Ahmed, Christian Lüchtenborg, Oliver T Fackler, Britta Brügger, Thomas Hoenen, Walter Nickel Ulrich S Schwarz, Petr Chlanda
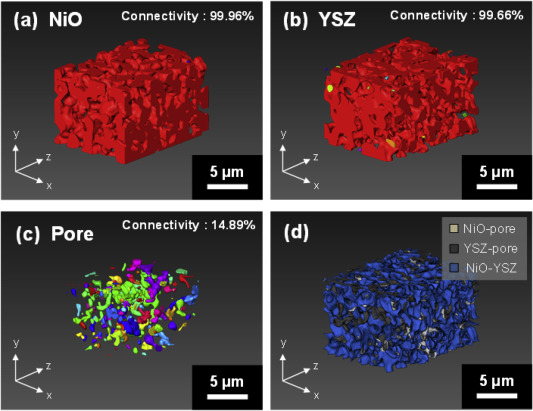
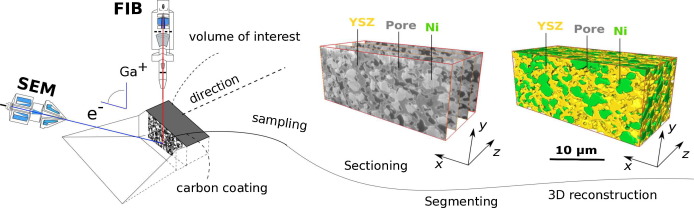
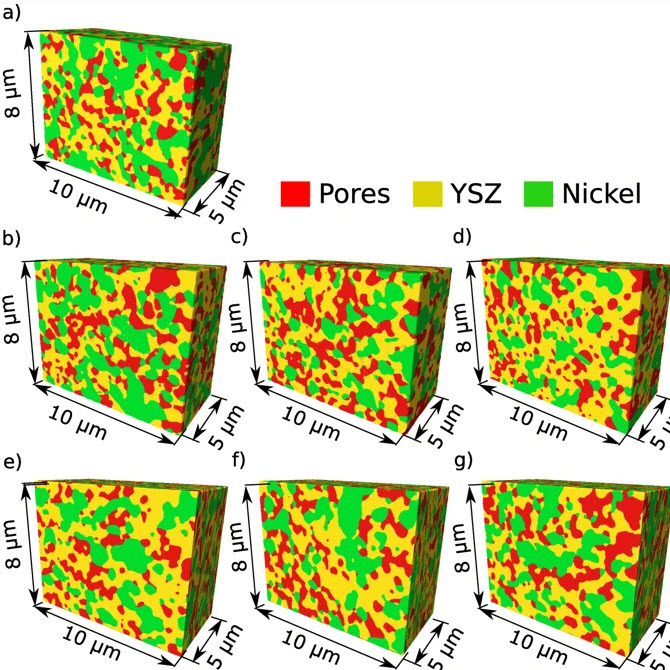
Nickel-yttria-stabilized zirconia (Ni-YSZ) cermet is widely used as an anode material in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs); however, Ni re-oxidation causes critical problems due to volume expansion, which causes high thermal stress. We fabricated a Ni-YSZ anode functional layer (AFL), which is an essential component in high-performance SOFCs, and re-oxidized it to investigate the related three-dimensional (3D) microstructural and thermo-mechanical effects. A 3D model of the re-oxidized AFL ... Read more
Jun Woo Kim, Kiho Bae, Hyun Joong Kim, Ji-won Son, Namkeun Kim, Stefan Stenfelt, Fritz B. Prinz, Joon Hyung Shim
Growing popularity and rapid development of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) stem for their potential to become a gamechanger in the field of clean power generation technologies.
In this paper, a transient microstructure-oriented numerical simulation of a planar Direct Internal Reforming Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (DIR-SOFC) is delivered. The performance criteria in a direct steam reforming for a fuel starvation scenario are analyzed in order to optimize the underlying process. The proposed t... Read more
Maciej Chalusiak, Michal Wrobel, Marcin Mozdzierz, Katarzyna Berent, Janusz S. Szmyd, Shinji Kimijima, Grzegorz Brus
Nickel-rich transition metal oxide materials […] are of great interest for achieving immediate improvements in the energy density of Li-ion batteries and for risk reduction within the Li-ion battery supply chain.
[…] An increase in Ni content in NMC materials leads to accelerated degradation […]. This potentially complicates their adoption in applications requiring extended cycle life such as in electric vehicles.
Recent developments in X-ray characterization to... Read more
ChunTan, Andrew S.Leach, Thomas M.M. Heenan, Huw Parks, Rhodri Jervis, Johanna Nelson Weker, Daniel J.L. Brett, Paul R.Shearing
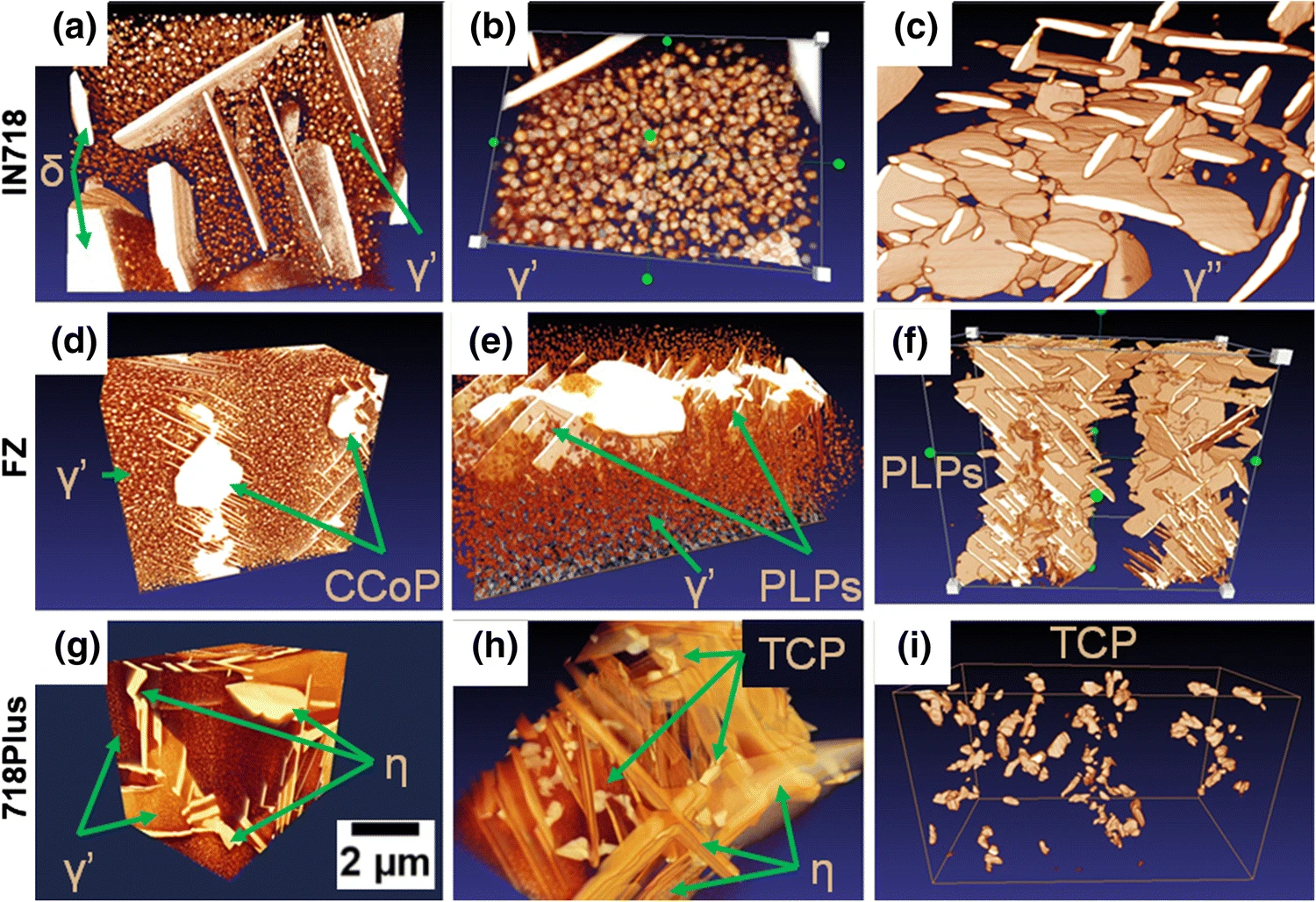
Inconel 718 (IN718) is the most popular precipitation-strengthened nickel-based superalloy introduced by the Huntington Alloys Division of INCO in 1959 (Ref Read more
Oskar Dziuba, Grzegorz Cempura, Agnieszka Wusatowska-Sarnek & Adam Kruk
An Anisotropic Microstructure Evolution in a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Anode
A solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) is an electrochemical device that converts the chemical energy of hydrogen directly into electricity. A single cell usually has a form of a flat plate in which an impervious and dense ion-conducting electrolyte is sandwiched between two porous catalytic electrodes: an anode and a cathode. Fuel is fed to the anode side, and the air is supplied to the cathode. The gasses cannot mix to avoid unproductive combustion. Instead, gasses hit catalyst material, lose their... Read more
Grzegorz Brus, Hiroshi Iwai, Janusz S. Szmyd
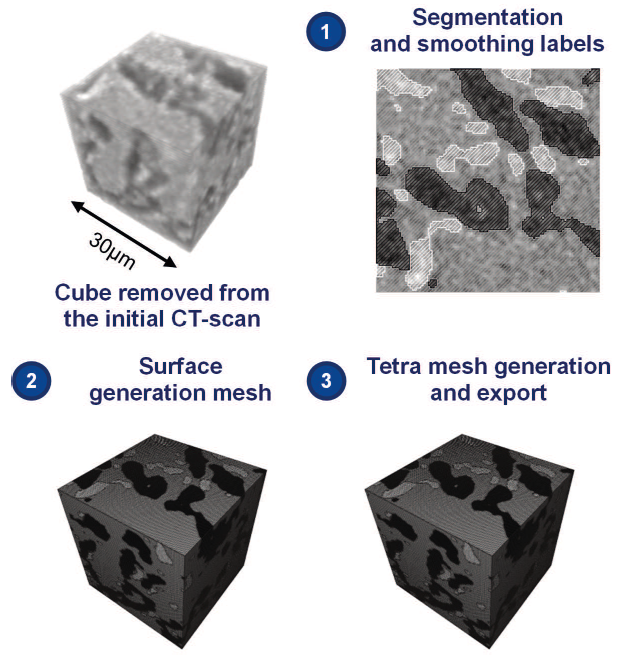
Current materials such nickel based superalloys cannot be used anymore and new materials are thus considered. For the hottest parts of jet engines, eutectic ceramics have potentially interesting features. In order to assess the thermo-mechanical properties of this material, numerical multi-scale analyses may be performed. Thus, a 3D finite element model was generated from a CT scan, representative of the microstructure and with a similar volume fraction. Effective elastic properties were calc... Read more
S. Gourdin, L. Marcin, M. Podgorski, M. Cherif, L. Carroz
Nickel/zirconia-based nanostructured electrodes for solid oxide fuel cells suffer from poor stability even at intermediate temperature.
This study quantifies the electrochemical and microstructural degradation of nanostructured electrodes by combining 3D tomography, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and mechanistic modeling. For the first time, the electrochemical degradation of nanostructured electrodes is quantified according to the fractal nature of the three-phase bounda... Read more
A. Bertei, E. Ruiz-Trejo, K. Kareh, V. Yufit, X. Wang, F. Tariq, N.P. Brandon,
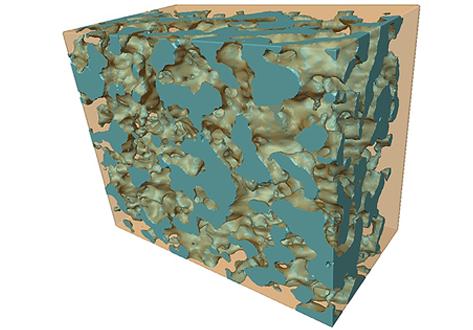
A simple chemical bath deposition is used to coat a complex porous ceramic scaffold with a conformal Ni layer.
The resulting composite is used as a solid oxide fuel cell electrode, and its electrochemical response is measured in humidified hydrogen. X‐ray tomography is used to determine the microstructural characteristics of the uncoated and Ni‐coated porous structure, which include the surface area to total volume, the radial pore size, and the size of the necks between the pores.... Read more
Dr. Enrique Ruiz‐Trejo, Milla Puolamaa, Brian Sum, Dr. Farid Tariq, Dr. Vladimir Yufit, Prof. Nigel P. Brandon
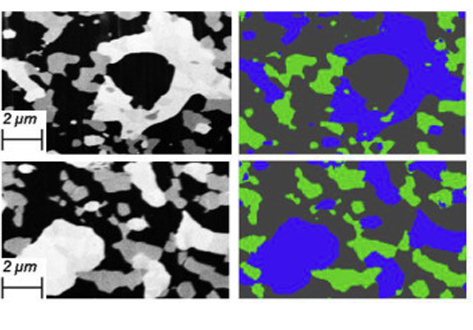
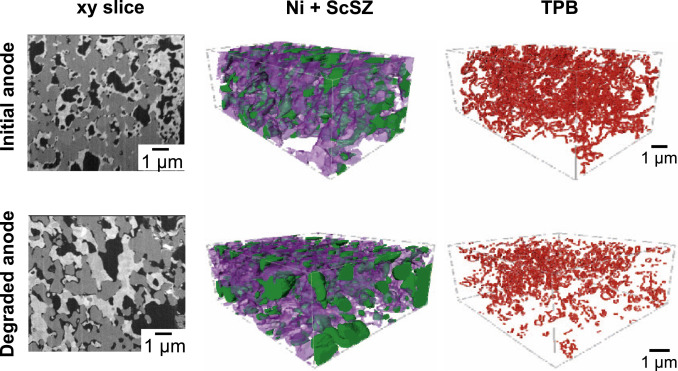
Quantification of the degradation of Ni-YSZ anodes upon redox cycling
Ni-YSZ anodes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells are vulnerable to microstructural damage during redox cycling leading to a decrease in the electrochemical performance.
- Quantification of redox damage by coupling 3D tomography, EIS and nanoindentation.
- YSZ fracture, Ni detachment and agglomeration led to irreversible mechanical damage.
- Ni nanoparticles obtained upon redox cycling improve electrochemical performance.
- Loss in TPB densi... Read more
Bowen Song, Enrique Ruiz-Trejo, Antonio Bertei, Nigel P.Brandon