Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
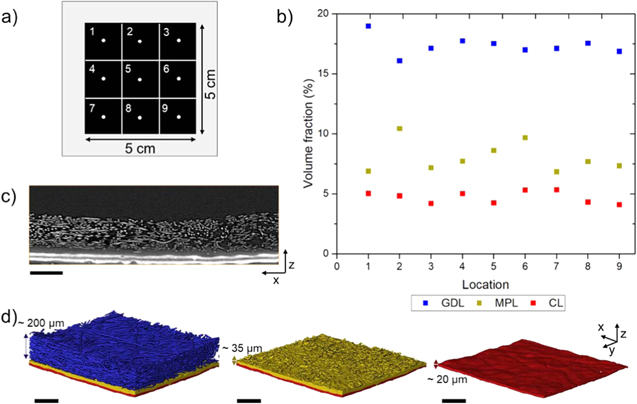
With the growing use of X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) datasets for modelling of transport properties, comes the need to define the representative elementary volume (REV) if considering three dimensions or the representative elementary area (REA) if considering two dimensions. The resolution used for imaging must be suited to the features of interest in the sample and the region-of-interest must be sufficiently large to capture key information. Polymer electrolyte fuel cells have a hier... Read more
Jennifer Hack et al 2020 J. Electrochem.
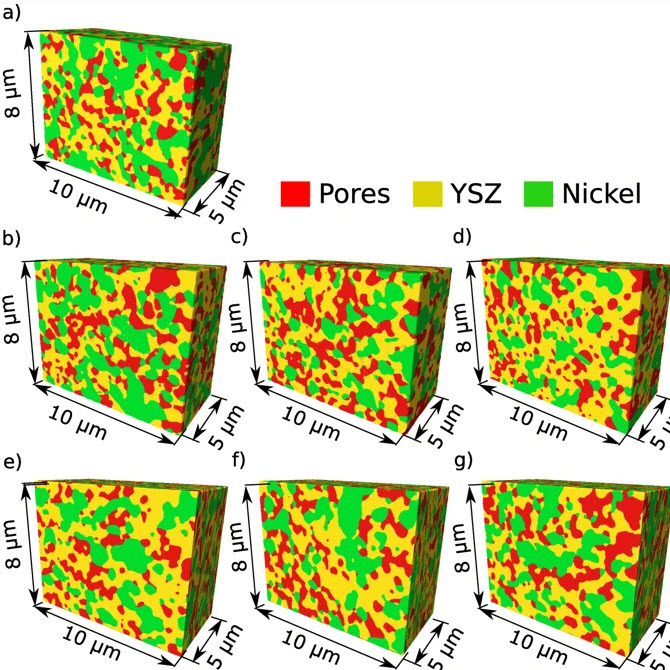
An Anisotropic Microstructure Evolution in a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Anode
A solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) is an electrochemical device that converts the chemical energy of hydrogen directly into electricity. A single cell usually has a form of a flat plate in which an impervious and dense ion-conducting electrolyte is sandwiched between two porous catalytic electrodes: an anode and a cathode. Fuel is fed to the anode side, and the air is supplied to the cathode. The gasses cannot mix to avoid unproductive combustion. Instead, gasses hit catalyst material, lose their... Read more
Grzegorz Brus, Hiroshi Iwai, Janusz S. Szmyd
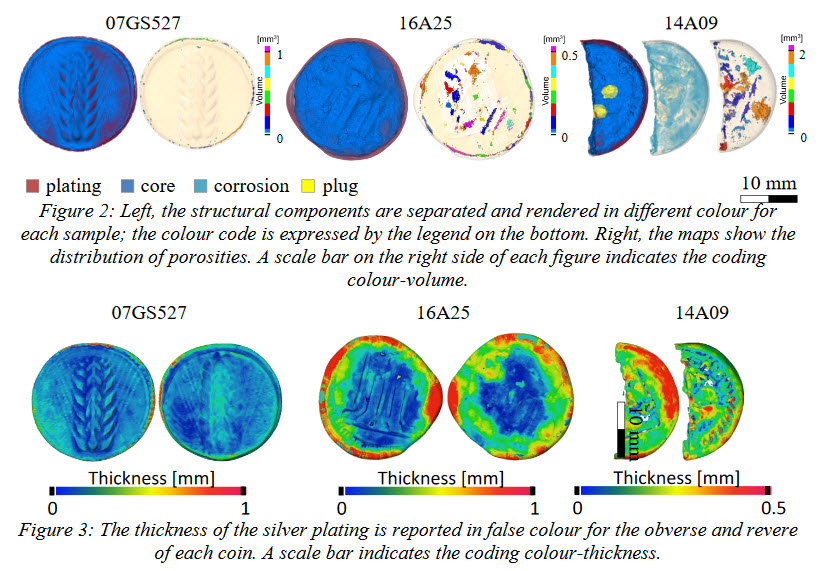
A Neutron Tomographic Analysis of Plated Silver Coins from Ancient Greece Official or Illegal?
In the 6th century BC different techniques of coin manufacture were employed by mints in mainland Greece and in the Greek colonies in Southern Italy. In Greece these techniques were evidently derived from the Lydians and consisted in striking a piece of cast metal of predetermined weight (a ‘blank’ or flan) between two engraved dies made of hardened bronze. Colonies in Magna Graecia, however, uniquely developed another set of minting techniques to produce what today is called incuse coina... Read more
Scott Olsen, Filomena Silvemini, Ulf Garbe, Max Avdeev, Joel Davis, Vladimir Luzin, Ken Sheedy
The microstructure morphologies have been characterized by high resolution laboratory X-ray computed tomography in Carbon Fiber Reinforced Carbon and Silicon Carbide (C/C-SiC) ceramic composites fabricated by Gaseous Silicon Infiltration (GSI) from C/C preforms of three different architectures: 3D stitched cloth fabric; 3D orthogonal woven fabric; and needled short-cut felt. Each composites’ microstructure was influenced by the structure of the C/C preform. By incorporating tomography with ... Read more
Fan Wan, Talha, J. Pirzada, Rongjun Liu, Yanfei Wang, Changrui Zhang, Thomas James Marrow
In this study, various wood material sources were used for the manufacture of wood-polymer composites (WPC). The materials were categorised as virgin wood particles (VWP), reprocessed WPC particles (RWP) and recycled thermoset composite particles (RCP) and derived from two virgin wood sources, three-layer particle boards, medium-density fibre boards (MDF) boards,or two different wood/polypropylene composites. All produced wood-polypropylene compounds contained 60% wood material and were manu... Read more
Kim Christian Krause, D, Philipp Sauerbier, Tim Koddenberg and Andreas Krause
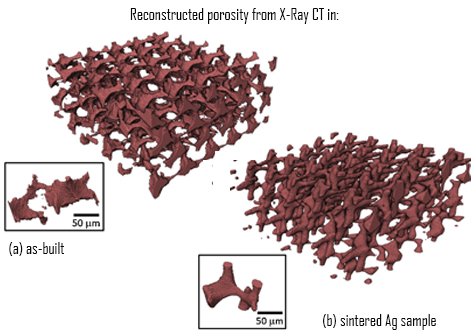
Towards digital metal additive manufacturing via high-temperature drop-on-demand jetting
Drop-on-demand jetting of metals offers a fully digital manufacturing approach to surpass the limitations of the current generation powder-based additive manufacturing technologies. However, research on this topic has been restricted mainly to near-net shaping of relatively low melting temperature metals. Here it is proposed a novel approach to jet molten metals at high-temperatures (>1000 °C) to enable the direct digital additive fabrication of micro- to macro-scale objects. […] ... Read more
Marco Simonelli, Nesma Aboulkhair, Mircea Rasa, Mark East, Chris Tuck, Ricky Wildman, Otto Salomons, Richard Hague
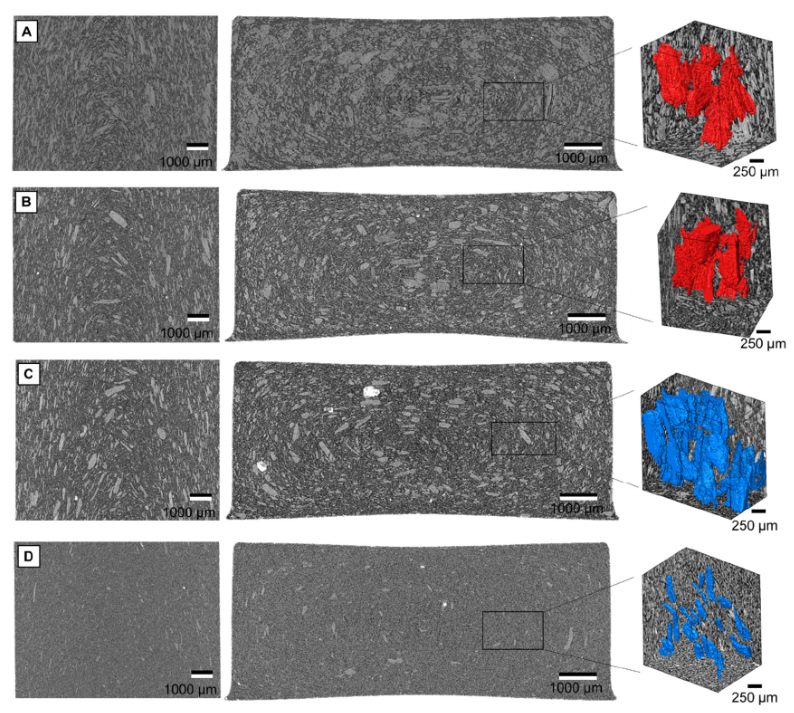
Additive manufacturing (AM) of aluminum alloy components has drawn broad attention from industrial customers in recent years. With the advantages of low cost and high deposition rate, wire + arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) has been recognized as a promising AM technology in producing large-scale aluminum alloy structural parts. However, the adverse effect of internal defects on mechanical properties has limited the application of WAAM aluminum alloys. Micropores, as one of the most harmfu... Read more
Jianglong Gu, Shouliang Yang, Minjie Gao, Jing Bai, Yuchun Zhai, Jialuo Ding
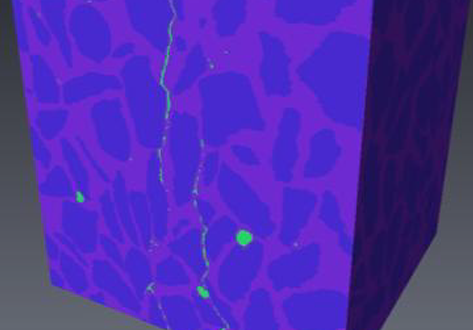
X-ray Computed Tomography (XCT) is a powerful technology that can accurately image the internal structures of composite and heterogeneous materials in three-dimensions (3D). In this study, in-situ micro XCT tests of concrete specimens under progressive compressive loading are carried out. The aim of the observations is to gain a better understanding of 3D fracture and failure mechanisms at the meso-scale. To characterise the fracture evolution as the deformation increases, two methods are use... Read more
College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Zhejiang University | School of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering, the University of Manchester | Manchester X-ray Imaging Facility | Oxford Martin School and Department of Materials
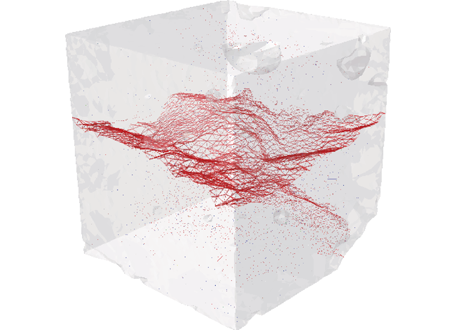
Three-Dimensional In Situ XCT Characterisation and FE Modelling of Cracking in Concrete
An improved understanding of 3D cracking in concrete can be achieved by multiscale experiments and numerical modelling based on realistic microstructures, for the development of materials with higher strength, durability, and fracture resistance.
Three-dimensional (3D) characterisation and modelling of cracking in concrete have been always of great importance and interest in civil engineering. In this study, an in situ microscale X-ray computed tomography (XCT) test was carried out to ... Read more
Wenyuan Ren, Zhenjun Yang, Rajneesh Sharma, Samuel A. McDonald, Paul M. Mummery
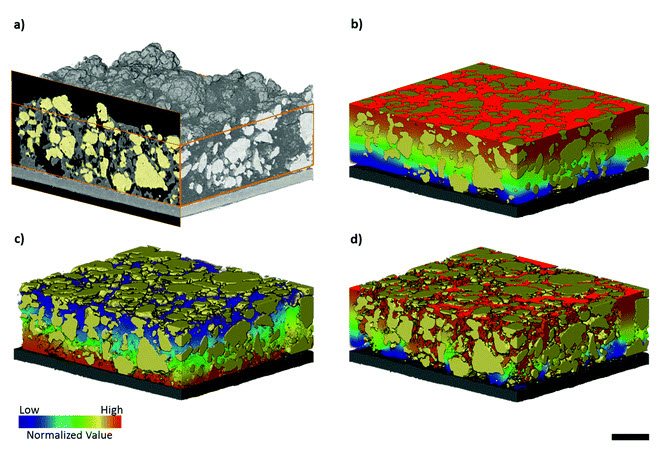
Three-dimensional image based modelling of transport parameters in lithium–sulfur batteries
An elemental sulfur electrode was imaged with X-ray micro and nano computed tomography and segmented into its constituent phases. Morphological parameters including phase fractions and pore and particle size distributions were calculated directly from labelled image data, and flux based simulations were performed to determine the effective molecular diffusivity of the pore phase and electrical conductivity of the conductive carbon and binder phase, D... Read more
Chun Tan, Matthew D. R. Kok , Sohrab R. Daemi , Daniel J. L. Brett and Paul R. Shearing
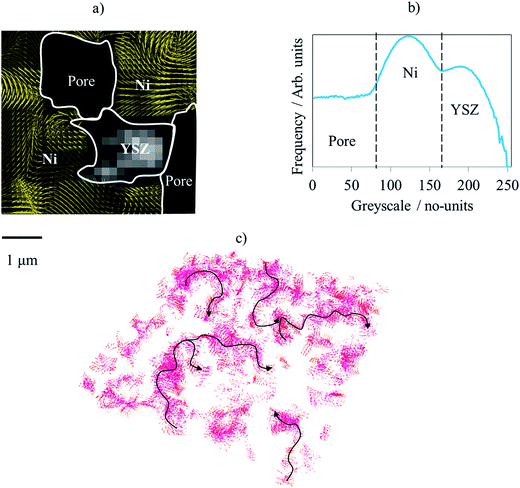
Evaluating microstructure evolution in an SOFC electrode using digital volume correlation
Degradation mechanisms within solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) during thermal cycling limit operational start-up times and cell lifetime, and must therefore be better understood and mitigated. This work explores such mechanisms using digital volume correlation (DVC) techniques applied to lab-based X-ray tomograms where the microstructural evolution is evaluated during the operational cycling of a Ni–YSZ/YSZ cell. To emulate reduced start-up times, five tomograms were collected over four operat... Read more
T. M. M. Heenan, X. Lu,, D. P. Finegan,, J. Robinson, F. Iacoviello, J. J. Bailey, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
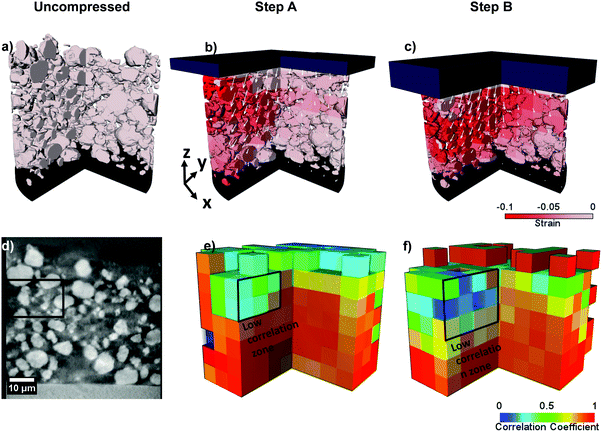
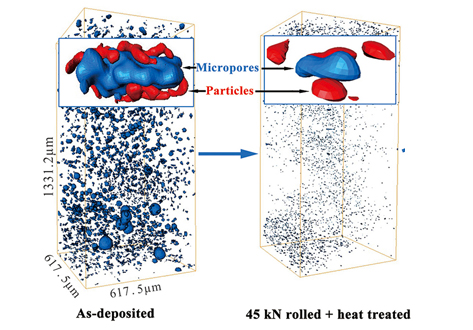
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries operate via electrochemical reactions between positive and negative electrodes, formed by complex porous microstructures. An improved understanding of these materials can lead to a greater insight into the link between microscopic electrode morphology and macroscopic performance. The practice of calendering electrodes after manufacturing has been widely used to increase the volumetric energy density and improve the electrical contact between electrode... Read more
S. R. Daemi,X. Lu, D. Sykes, J. Behnsen, C. Tan, A. Palacios-Padros, J. Cookson, E. Petrucco, P. J. Withers, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
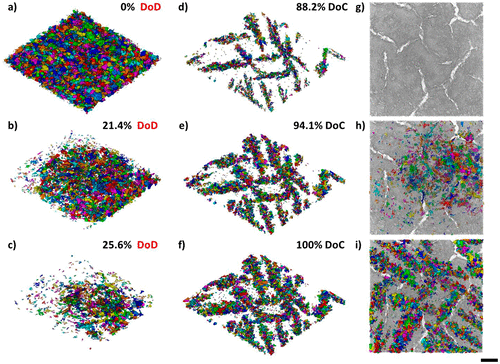
Four-Dimensional Studies of Morphology Evolution in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
Lithium sulfur (Li–S) batteries have great potential as a successor to Li-ion batteries, but their commercialization has been complicated by a multitude of issues stemming from their complex multiphase chemistry. In situ X-ray tomography investigations enable direct observations to be made about a battery, providing unprecedented insight into the microstructural evolution of the sulfur cathode and shedding light on the reaction kinetics of the sulfur phase. Here, for the first time, the mor... Read more
Chun Tan, Thomas M. M. Heenan, Ralf F. Ziesche, Sohrab R. Daemi, Jennifer Hack, Maximilian Maier, Shashidhara Marathe, Christoph Rau, Daniel J. L. Brett, Paul R. Shearing
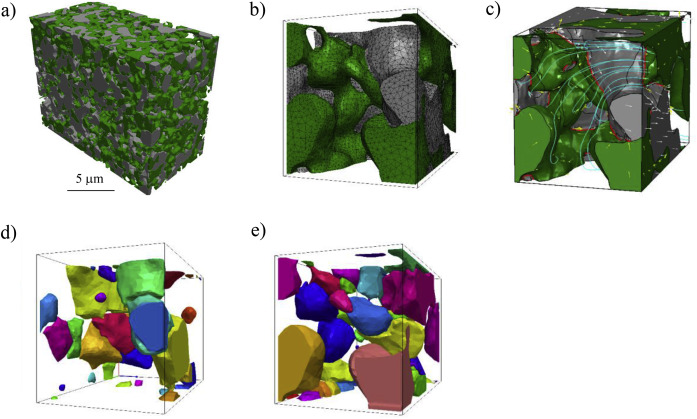
The electrode microstructural properties significantly influence the efficiency and durability of many electrochemical devices including solid oxide fuel cells. Despite the possibility of simulating the electrochemical phenomena within real three-dimensional microstructures, the potential of such 3D microstructural information has not yet been fully exploited. We introduce here a completely new methodology for the advanced characterization of inhomogeneous current distribution base... Read more
A.Bertei, V.Yufit, F.Tariq, N.P.Brandon
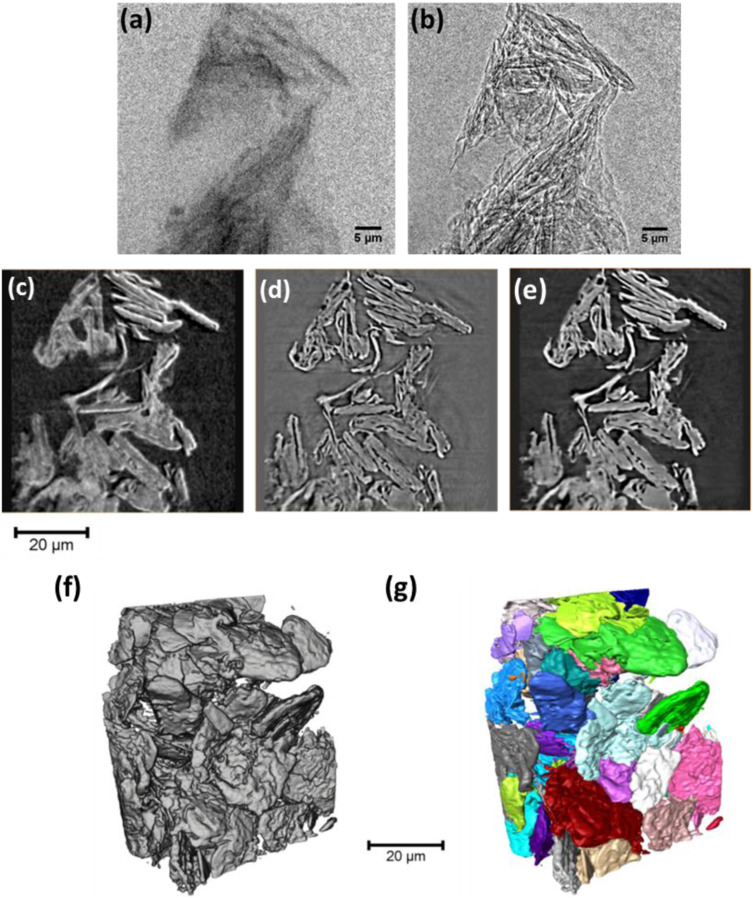
The use of contrast enhancement techniques in X-ray imaging of lithium–ion battery electrodes
Understanding the microstructural morphology of Li–ion battery electrodes is crucial to improving the electrochemical performance of current Li–ion battery systems and in developing next-generation power systems. The use of 3D X-ray imaging techniques, which are continuously evolving, provides a noninvasive platform to study the relationship between electrode microstructure and performance at various time and length scales. In addition to characterizing a weakly (X-ray) absorbing graphite... Read more
Oluwadamilola O. Taiwo , Donal P. Finegan , Jeff Gelb , Christian Holzner , Daniel J.L. Brett , Paul R. Shearing
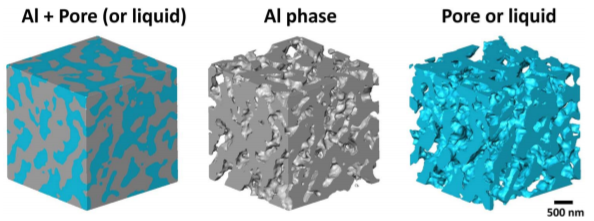
Nanoporous Aluminum by Galvanic Replacement: Dealloying and Inward-Growth Plating
In aqueous solutions, electro/chemically deposited metals usually grow outward into electrolyte. Here we report that the reduced Al grows inward into the sample, surprisingly, while Mg (in pure Mg and Al2Mg3 alloy) is galvanically replaced with Al in an ionic liquid. The galvanic replacement reaction (GRR) of Al2Mg3 involves a dealloying process that generates a nanoporous Al skeleton, and simultaneously the inward-growth plating of Al that thicke... Read more
Wei Yang, Xian-Gui Zheng, Shao-Gang Wang, Hai-Jun Jin
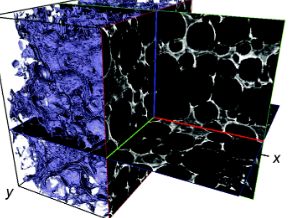
Biodegradable materials, such as collagen scaffolds, are used extensively in clinical medicine for tissue regeneration and/or as an implantable drug delivery vehicle. However, available methods to study biomaterial degradation are typically invasive, destructive, and/or non-volumetric. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate a new method for nondestructive, longitudinal, and volumetric measurement of collagen scaffold degradation. Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) were covalently ... Read more
Tyler A. Finamore, Tyler E. Curtis, James V. Tedesco, Kathryn Grandfield, Ryan K. Roeder
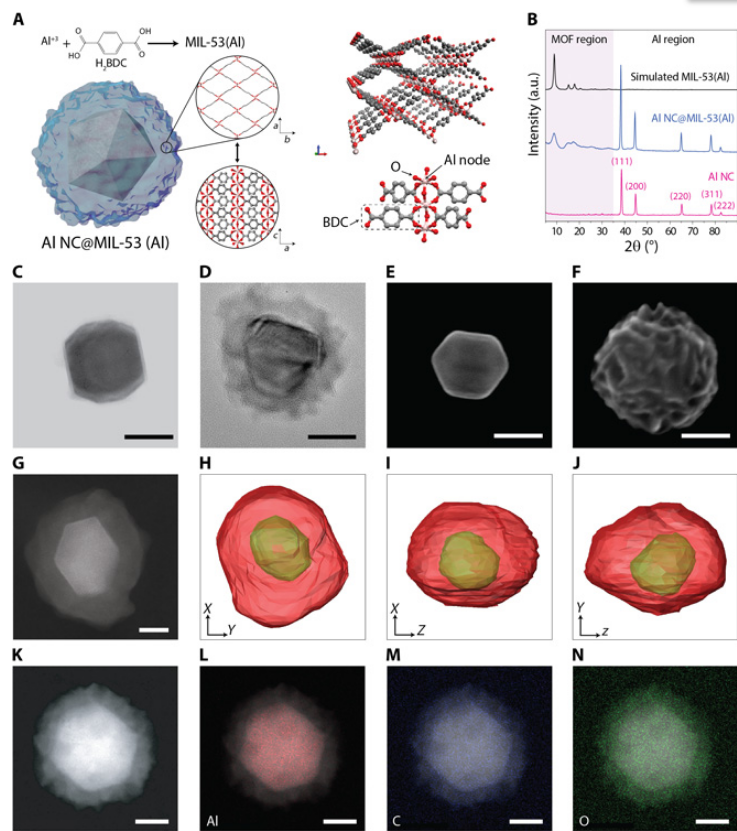
Metal-organic frameworks tailor the properties of aluminum nanocrystals
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and metal nanoparticles are two classes of materials that have received considerable recent attention, each for controlling chemical reactivities, albeit in very different ways. Here, we report the growth of MOF shell layers surrounding aluminum nanocrystals (Al NCs), an Earth-abundant metal with energetic, plasmonic, and photocatalytic properties. The MOF shell growth proceeds by means of dissolution-and-growth chemistry that uses the intrinsic surface oxide o... Read more
Hossein Robatjazi, Daniel Weinberg, Dayne F. Swearer, Christian Jacobson, Ming Zhang, Shu Tian, Linan Zhou, Peter Nordlander, Naomi J. Halas
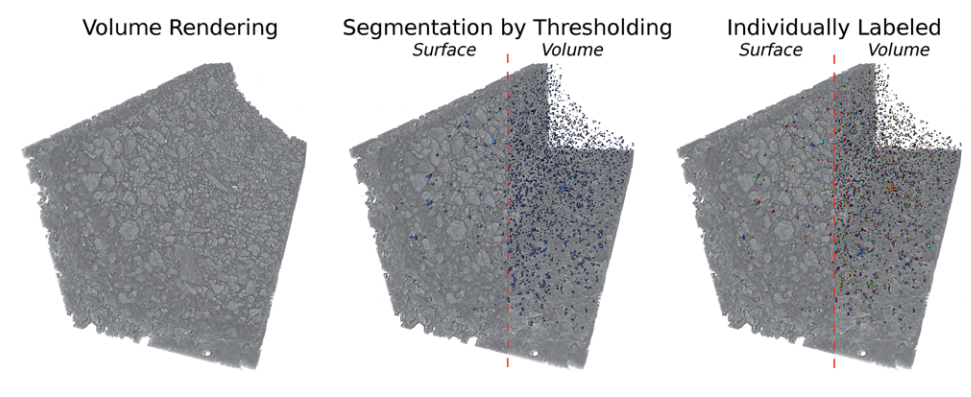
Aging of a Pt/Al2O3 exhaust gas catalyst monitored by quasi in situ X-ray micro computed tomography
Catalyst aging effects were analyzed using X-ray absorption micro-computed tomography in combination with conventional characterization methods on various length scales ranging from nm to μm to gain insight into deactivation mechanisms.
For this purpose, a 4 wt% Pt/Al2O3 model exhaust gas catalyst was coated on a cordierite honeycomb and subjected to sequential thermal aging in static air at 950 °C for 4, 8, 12 and 24 hours. The ag... Read more
Georg Hofmann, Amélie Rochet, Elen Ogel, Maria Casapu, Stephan Ritter, Malte Ogurreck and Jan-Dierk Grunwaldt
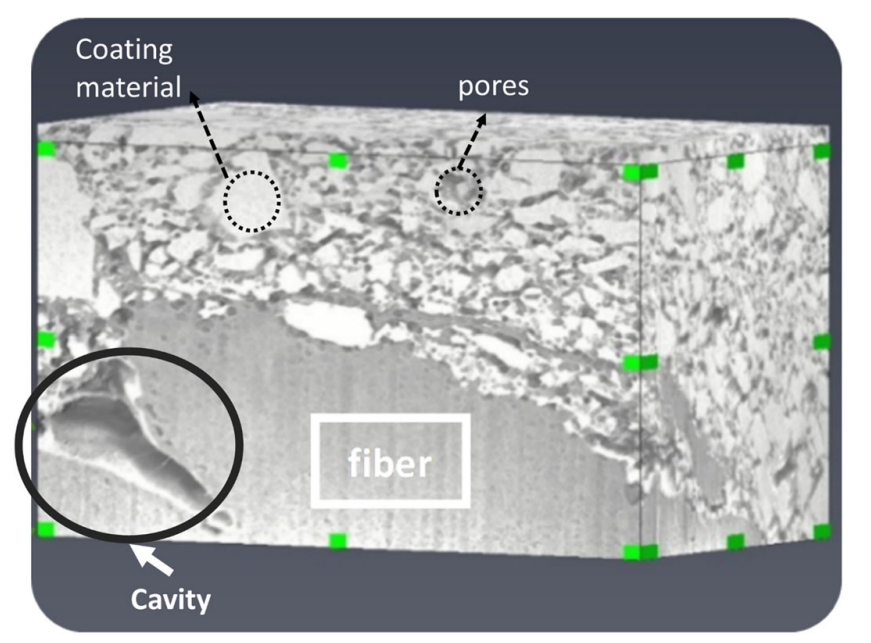
Characterization of the Interface Between Coating and Fibrous Layers of Paper
Coated paper is an example of a multi-layer porous medium, involving a coating layer along the two surfaces of the paper and a fibrous layer in the interior of the paper. The interface between these two media needs to be characterized in order to develop relevant modeling tools. After careful cutting of the paper, a cross section was imaged using focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy. The resulting image was analyzed to characterize the coating layer and its transition to the fibrous ... Read more
H. Aslannejad, S. M. Hassanizadeh, M. A. Celia
The development of focused ion beam-scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) techniques has allowed high-resolution 3D imaging of nanometre-scale porous materials. These systems are of important interest to the oil and gas sector, as well as for the safe long-term storage of carbon and nuclear waste. This work focuses on validating the accurate representation of sample pore space in FIB-SEM-reconstructed volumes and the predicted permeability of these systems from subsequent single-phase flow s... Read more
Department of Chemical Engineering, Qatar Carbonates and Carbon Storage Research Centre, Imperial College London | Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, Cambridge University