Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
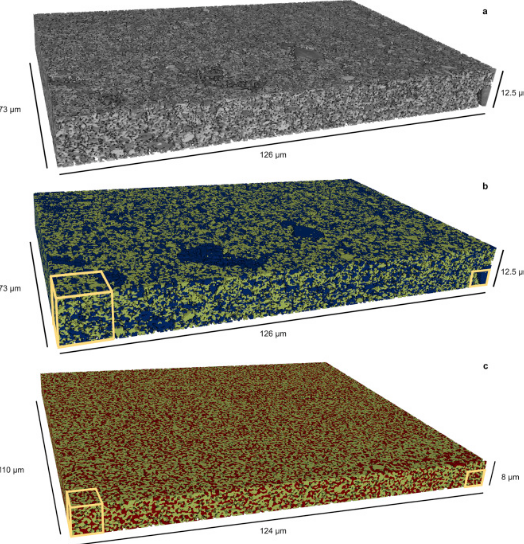
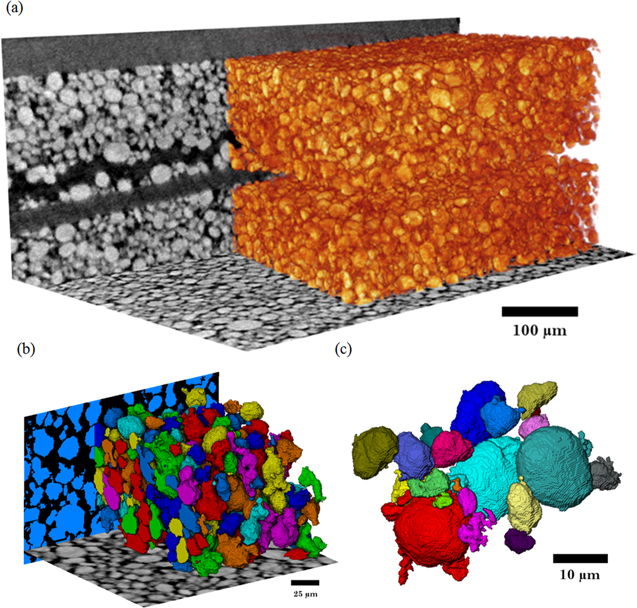
Mesoscale characterization of local property distributions in heterogeneous electrodes
The performance of electrochemical devices depends on the three-dimensional (3D) distributions of microstructural features in their electrodes. Several mature methods exist to characterize 3D microstructures over the microscale (tens of microns), which are useful in understanding homogeneous electrodes. However, methods that capture mesoscale (hundreds of microns) volumes at appropriate resolution (tens of nm) are lacking, though they are needed to understand more common, less ideal electrode... Read more
Tim Hsu, William K. Epting, Rubayyat Mahbub, Noel T. Nuhfer, Sudip Bhattachary, Yinkai Lei, Herbert M. Miller, Paul R. Ohodnicki, Kirk R. Gerdes, Harry W. Abernathy, Gregory A. Hackett, Anthony D. Rollett, Marc De Graef, Shawn Litster, Paul A. Salvador
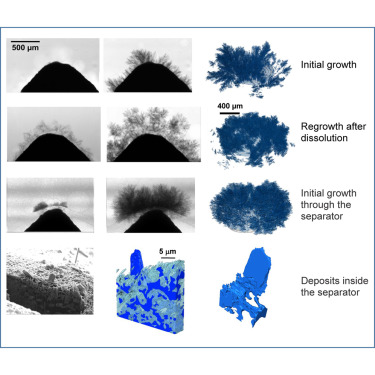
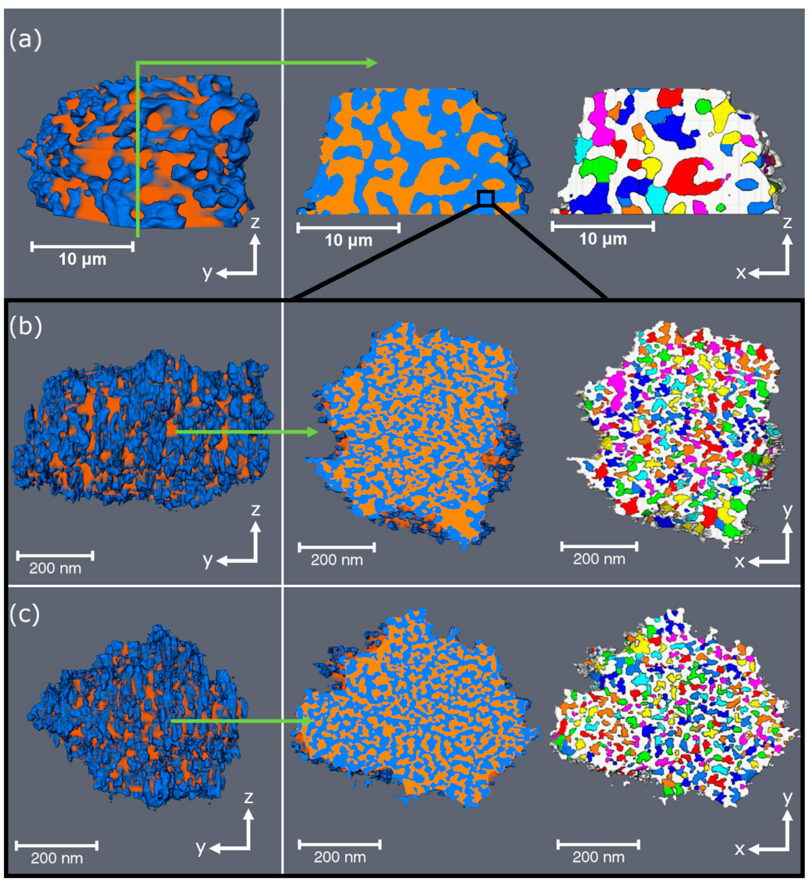
Alternative battery technologies are required to meet growing energy demands and address the limitations of present technologies. As such, it is necessary to look beyond lithium-ion batteries. Zinc batteries enable high power density while being sourced from ubiquitous and cost-effective materials. This paper presents, for the first time known to the authors, multi-length scale tomography studies of failure mechanisms in zinc batteries with and without commercial microporous separators. In bo... Read more
Vladimir Yufit, Farid Tariq David S. Eastwood Moshiel Biton Billy Wu Peter D. Lee Nigel P. Brandon
Porous Metal–Organic Frameworks for Enhanced Performance Silicon Anodes in Lithium-Ion Batteries
Maintaining the physical integrity of electrode microstructures in Li-ion batteries is critical to significantly extend their cycle life. This is especially important for high-capacity anode materials such as silicon, whose operational volume expansion exerts huge internal stress within the anode, resulting in electrode destruction and capacity fade. In this study, we demonstrate that by incorporating metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) with carboxylate organic linkers into Si-based anodes, a s... Read more
Romeo Malik, Melanie. J. Loveridge, Luke J. Williams, Qianye Huang, Geoff West, Paul R. Shearing, Rohit Bhagat, Richard I. Walton
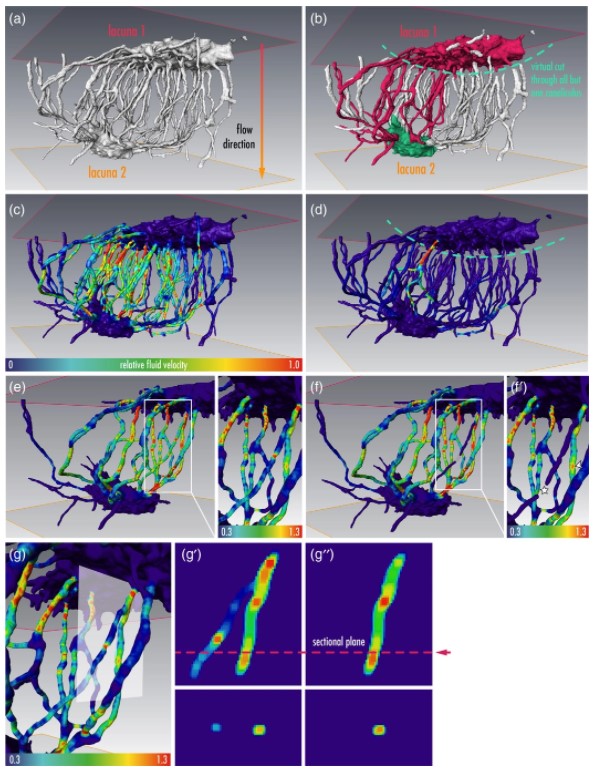
Osteocytes are the most frequent bone cells connected with each other through cell processes within tiny tubular-shaped canaliculi. The so-called osteocyte lacunar-canalicular network (LCN) plays a crucial role in bone remodeling and mineral homeostasis. Given the critical nature of these functions, it is herein hypothesized that the LCN must be structurally “overengineered” to provide network resilience.
This hypothesis is tested by characterizing canalicular networks in human bon... Read more
Emely Bortel, Liam M Grover, Neil Eisenstein, Christian Seim, Heikki Suhonen, Alexandra Pacureanu, Peter Westenberger, Kay Raum, Max Langer, Francoise Peyrin, Owen Addison, Bernhard Hesse
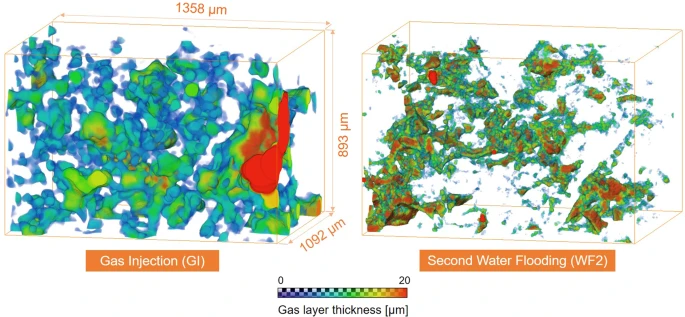
Pore-scale mechanisms of CO2 storage in oilfields
Rapid implementation of global scale carbon capture and storage is required to limit temperature rises to 1.5 °C this century. Depleted oilfields provide an immediate option for storage, since injection infrastructure is in place and there is an economic benefit from enhanced oil recovery. To design secure storage, we need to understand how the fluids are configured in the microscopic pore spaces of the reservoir rock. We use high-resolution X-ray imaging to study the flow of oil, water and ... Read more
Abdulla Alhosani, Alessio Scanziani, Qingyang Lin, Ali Q. Raeini, Branko Bijeljic & Martin J. Blunt
Thermal Runaway of a Li-Ion Battery Studied by Combined ARC and Multi-Length Scale X-ray CT
Lithium ion battery failure occurs across multiple length scales. In this work, the properties of thermal failure and its effects on electrode materials were investigated in a commercial battery using a combination of accelerating rate calorimetry (ARC) and multi-length scale X-ray computed tomography (CT). ARC measured the heat dissipated from the cell during thermal runaway and enabled the identification of key thermal failure characteristics such as onset temperature and the rate of heat g... Read more
Drasti Patel, James B. Robinson, Sarah Ball, Daniel J. L. Brett and Paul R. Shearing
Porosity and Structure of Hierarchically Porous Ni/Al2O3 Catalysts for CO2 Methanation
Carbon dioxide emissions must be reduced significantly to limit the negative consequences of climate change. For this reason, fossil fuels must be replaced by renewable energy sources. However, wind and solar energy, for example, are sporadic sources and, thus, not inevitably available when needed. This results in periods of energy surplus and shortage, which are not necessarily predictable. Hence, energy storage concepts are required to compensate for these fluctuations, thereby retaining en... Read more
Sebastian Weber, Ken L. Abel, Ronny T. Zimmermann, Xiaohui Huang, Jens Bremer, Liisa K. Rihko-Struckmann, Darren Batey, Silvia Cipiccia, Juliane Titus, David Poppitz, Christian Kübel, Kai Sundmacher, Roger Gläser, Thomas L. Sheppard
Material synthesis techniques have been historically used to engineer the mechanical and biological properties of biomaterials. Despite the overall success of this approach in different fronts […] there are still major unaddressed challenges due to the limited range of material properties that can be obtained through such synthesis techniques […]. Recent advances in additive manufacturing (AM) have initiated a new paradigm, which could facilitate better control of mechanical and b... Read more
Maryam Tilton, Alireza Borjali, Aaron Isaacson, Kartik Mangudi Varadarajan, Guha P.Manogharan
Nowadays, industrial processes demand materials with specific properties and localized microstructures to improve material performance. To satisfy particular needs, the development of materials with changing mechanical properties and/or microstructures along a preferential direction has been developed. These are called Functional Graded Materials (FGMs). Among these materials, a variation on the porosity along the part is very useful for different industrial applications, such as microfiltrat... Read more
Jorge Sergio Téllez-Martínez, Luis Olmos, Víctor Manuel Solorio-García, Héctor Javier Vergara-Hernández, Jorge Chávez, Dante Arteaga
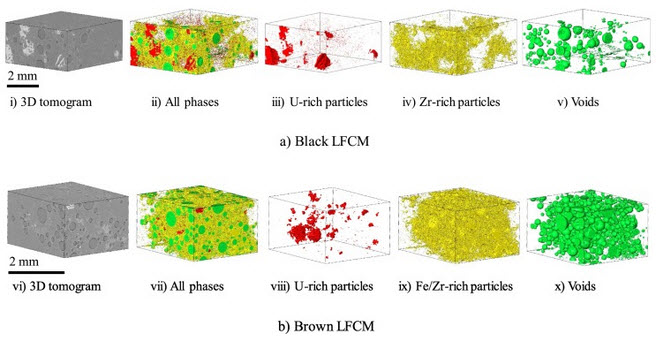
Decommissioning of the damaged Chernobyl nuclear reactor Unit 4 is a top priority for the global community. Before such operations begin, it is crucial to understand the behaviour of the hazardous materials formed during the accident. Since those materials formed under extreme and mostly unquantified conditions, modelling alone is insufficient to accurately predict their physical, chemical and, predominantly, mechanical behaviour. Meanwhile, knowledge of the mechanical characteristics of thos... Read more
C.Paraskevoulakos, J.P.Forna-Kreutzer, K.R.Hallam, C.P.Jones, T.B.Scott, C.Gausse, D.J.Bailey, C.A.Simpson, D.Liu, C.Reinhard, C.L.Corkhill, M.Mostafavi
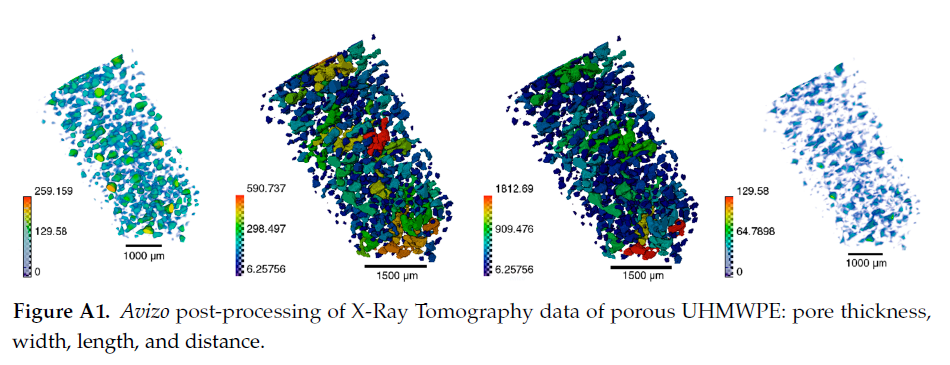
Since its invention and commercialization in the 1950s, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) has been known as a high-performance polymer successfully applied in diverse engineering systems ranging from strong ropes for naval demands and wear-resistant liners in bearings, transportation belts and heavy trucks in mines and quarries, through the lining of chemical vessels and disposable bags in bioreactors, to sophisticated products such as orthopaedic implants and replacements of ... Read more
Eugene S. Statnik, Codrutza Dragu, Cyril Besnard, Alexander J.G. Lunt, Alexey I. Salimon, Aleksey Maksimkin and Alexander M. Korsunsky
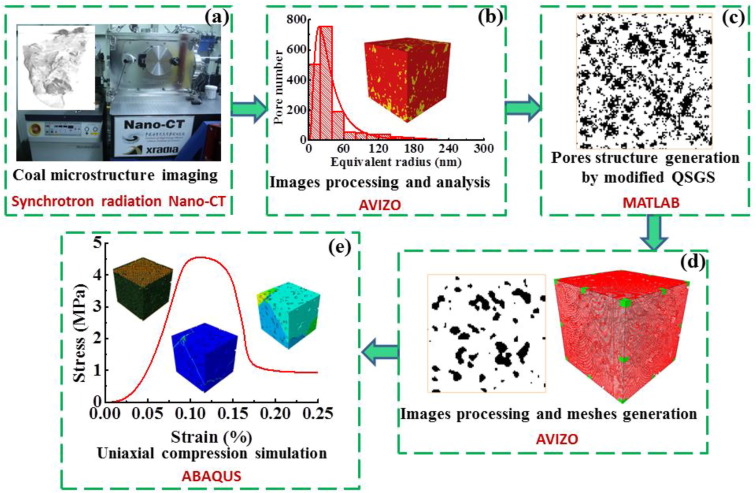
Impact of nanopore structure on coal strength
In China’s energy consumption structure, coal is the main energy source, accounting for about 60% of primary energy consumption. Coal is a porous medium with complex pore structures. Nanopore structure in coal particle is the basic underlying factor driving coal particle strength. A better knowledge of nanopore structure – coal particle strength correlation is of great significance for coal mining and other fields of engineering problems.
Read more
Yixin Zhao - Liang Yuan - QuanXue
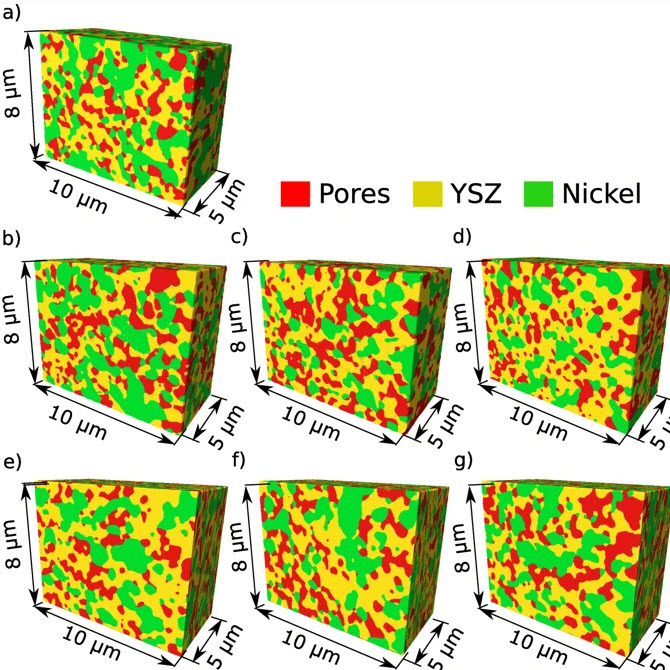
An Anisotropic Microstructure Evolution in a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Anode
A solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) is an electrochemical device that converts the chemical energy of hydrogen directly into electricity. A single cell usually has a form of a flat plate in which an impervious and dense ion-conducting electrolyte is sandwiched between two porous catalytic electrodes: an anode and a cathode. Fuel is fed to the anode side, and the air is supplied to the cathode. The gasses cannot mix to avoid unproductive combustion. Instead, gasses hit catalyst material, lose their... Read more
Grzegorz Brus, Hiroshi Iwai, Janusz S. Szmyd
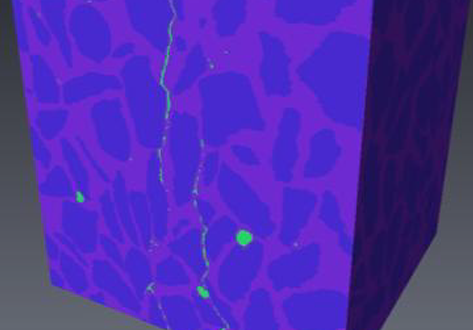
X-ray Computed Tomography (XCT) is a powerful technology that can accurately image the internal structures of composite and heterogeneous materials in three-dimensions (3D). In this study, in-situ micro XCT tests of concrete specimens under progressive compressive loading are carried out. The aim of the observations is to gain a better understanding of 3D fracture and failure mechanisms at the meso-scale. To characterise the fracture evolution as the deformation increases, two methods are use... Read more
College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Zhejiang University | School of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering, the University of Manchester | Manchester X-ray Imaging Facility | Oxford Martin School and Department of Materials
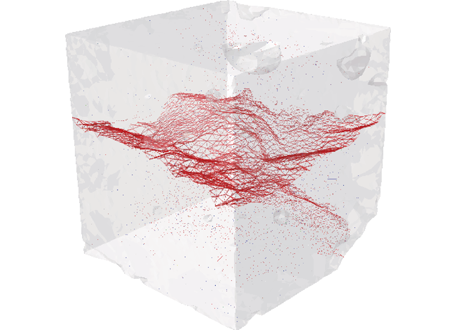
Three-Dimensional In Situ XCT Characterisation and FE Modelling of Cracking in Concrete
An improved understanding of 3D cracking in concrete can be achieved by multiscale experiments and numerical modelling based on realistic microstructures, for the development of materials with higher strength, durability, and fracture resistance.
Three-dimensional (3D) characterisation and modelling of cracking in concrete have been always of great importance and interest in civil engineering. In this study, an in situ microscale X-ray computed tomography (XCT) test was carried out to ... Read more
Wenyuan Ren, Zhenjun Yang, Rajneesh Sharma, Samuel A. McDonald, Paul M. Mummery
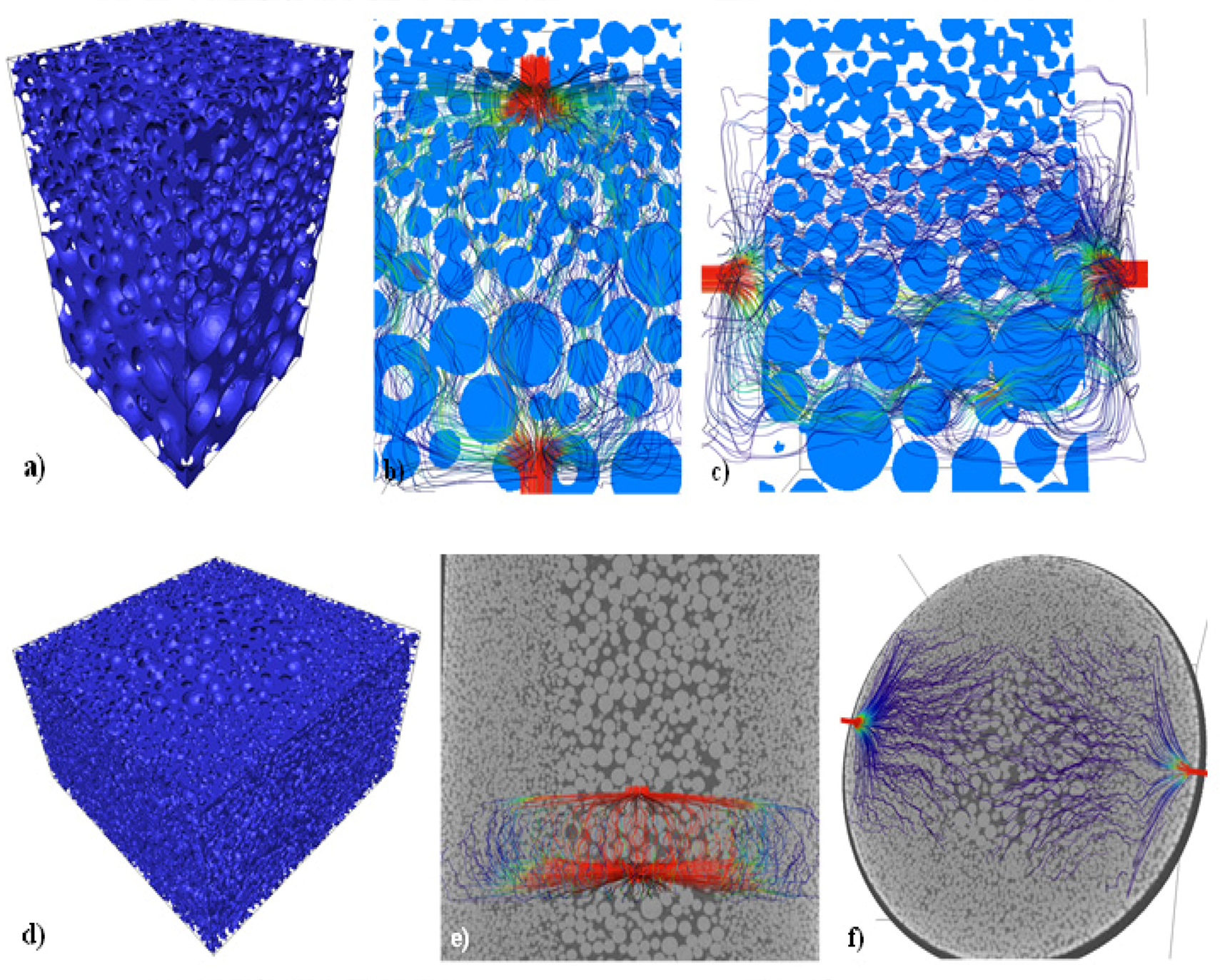
Three-dimensional image based modelling of transport parameters in lithium–sulfur batteries
An elemental sulfur electrode was imaged with X-ray micro and nano computed tomography and segmented into its constituent phases. Morphological parameters including phase fractions and pore and particle size distributions were calculated directly from labelled image data, and flux based simulations were performed to determine the effective molecular diffusivity of the pore phase and electrical conductivity of the conductive carbon and binder phase, D... Read more
Chun Tan, Matthew D. R. Kok , Sohrab R. Daemi , Daniel J. L. Brett and Paul R. Shearing
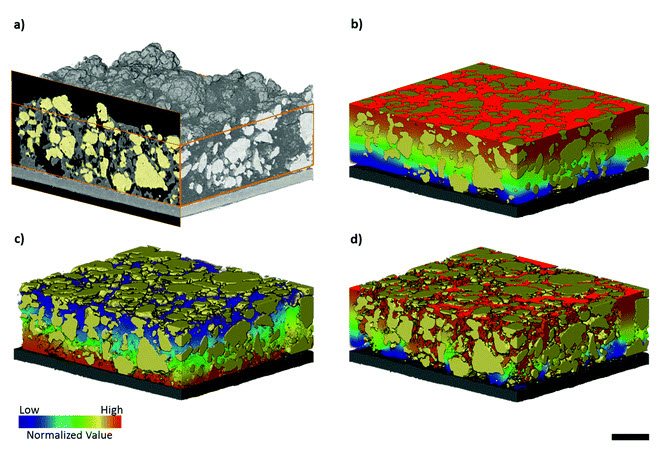
Evaluating microstructure evolution in an SOFC electrode using digital volume correlation
Degradation mechanisms within solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) during thermal cycling limit operational start-up times and cell lifetime, and must therefore be better understood and mitigated. This work explores such mechanisms using digital volume correlation (DVC) techniques applied to lab-based X-ray tomograms where the microstructural evolution is evaluated during the operational cycling of a Ni–YSZ/YSZ cell. To emulate reduced start-up times, five tomograms were collected over four operat... Read more
T. M. M. Heenan, X. Lu,, D. P. Finegan,, J. Robinson, F. Iacoviello, J. J. Bailey, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
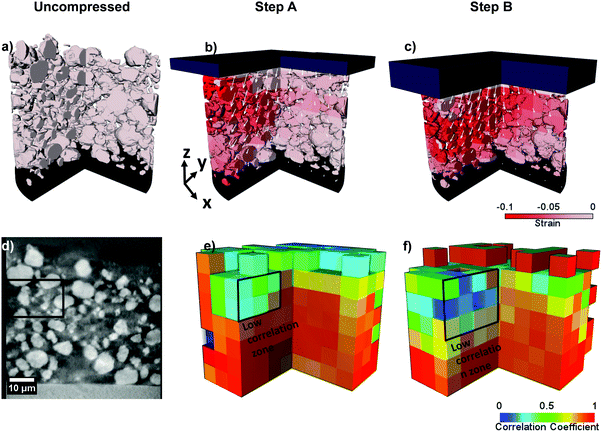
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries operate via electrochemical reactions between positive and negative electrodes, formed by complex porous microstructures. An improved understanding of these materials can lead to a greater insight into the link between microscopic electrode morphology and macroscopic performance. The practice of calendering electrodes after manufacturing has been widely used to increase the volumetric energy density and improve the electrical contact between electrode... Read more
S. R. Daemi,X. Lu, D. Sykes, J. Behnsen, C. Tan, A. Palacios-Padros, J. Cookson, E. Petrucco, P. J. Withers, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
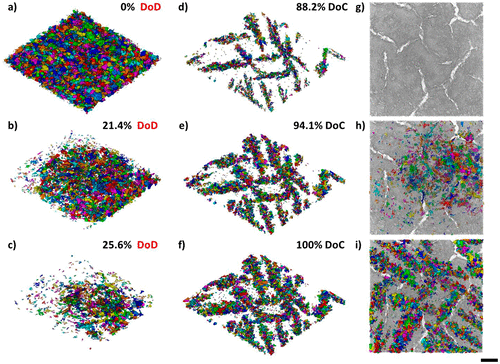
Four-Dimensional Studies of Morphology Evolution in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
Lithium sulfur (Li–S) batteries have great potential as a successor to Li-ion batteries, but their commercialization has been complicated by a multitude of issues stemming from their complex multiphase chemistry. In situ X-ray tomography investigations enable direct observations to be made about a battery, providing unprecedented insight into the microstructural evolution of the sulfur cathode and shedding light on the reaction kinetics of the sulfur phase. Here, for the first time, the mor... Read more
Chun Tan, Thomas M. M. Heenan, Ralf F. Ziesche, Sohrab R. Daemi, Jennifer Hack, Maximilian Maier, Shashidhara Marathe, Christoph Rau, Daniel J. L. Brett, Paul R. Shearing
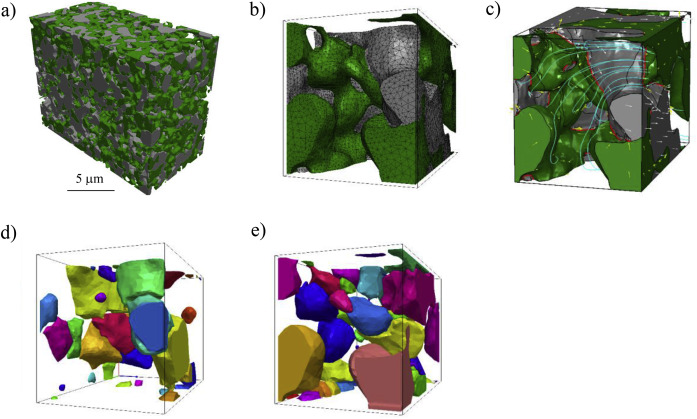
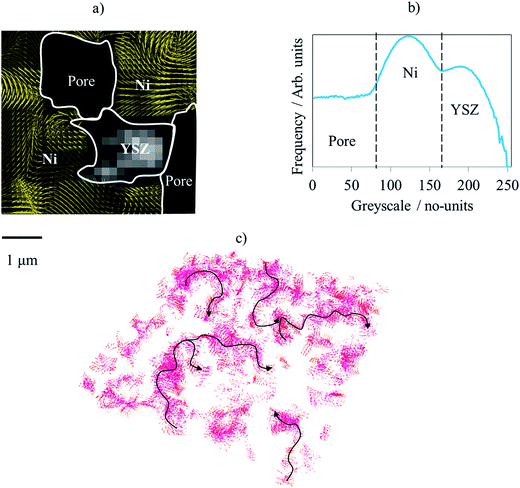
The electrode microstructural properties significantly influence the efficiency and durability of many electrochemical devices including solid oxide fuel cells. Despite the possibility of simulating the electrochemical phenomena within real three-dimensional microstructures, the potential of such 3D microstructural information has not yet been fully exploited. We introduce here a completely new methodology for the advanced characterization of inhomogeneous current distribution base... Read more
A.Bertei, V.Yufit, F.Tariq, N.P.Brandon
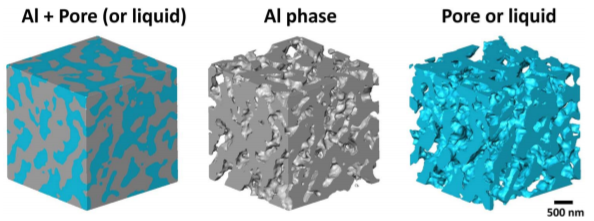
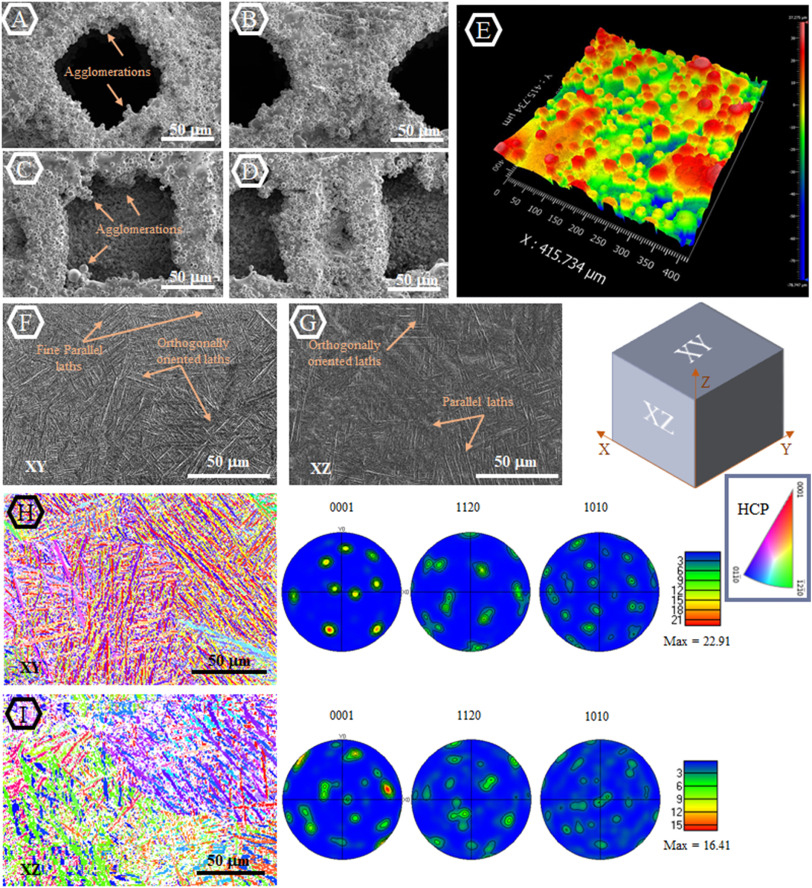
Nanoporous Aluminum by Galvanic Replacement: Dealloying and Inward-Growth Plating
In aqueous solutions, electro/chemically deposited metals usually grow outward into electrolyte. Here we report that the reduced Al grows inward into the sample, surprisingly, while Mg (in pure Mg and Al2Mg3 alloy) is galvanically replaced with Al in an ionic liquid. The galvanic replacement reaction (GRR) of Al2Mg3 involves a dealloying process that generates a nanoporous Al skeleton, and simultaneously the inward-growth plating of Al that thicke... Read more
Wei Yang, Xian-Gui Zheng, Shao-Gang Wang, Hai-Jun Jin