Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
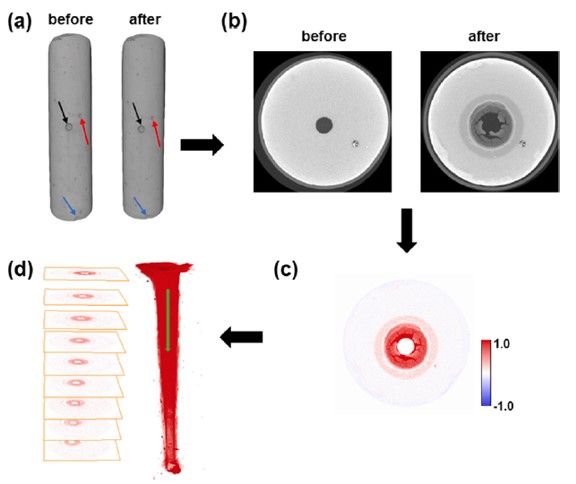
Comparative experimental observations of cement with a flow channel subject to CO2-saturated brine flow by micro-CT scanning and CT image post processing.
Understanding CO2-induced micro-structural changes at the imperfections in wellbore cement is vital for assessing the risk of CO2 leakage through wellbore cement under geologic CO2 storage (GCS) conditions. To investigate the evolution of a flow channel width in cement under GCS conditions and the influence of effective stress and fl... Read more
Manguang Gan, Liwei Zhang, Yan Wang, Kaiyuan Mei, Xiaojuan Fu, Xiaowei Cheng, Mingxing Bai, Hejuan Liu, Xiaochun Li
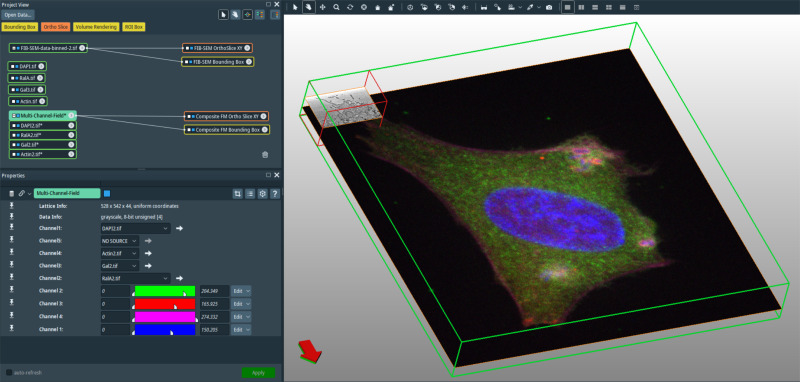
In recent years new methodologies and workflow pipelines for acquiring correlated fluorescence microscopy and volume electron microscopy datasets have been extensively described and made accessible to users of different levels. Post-acquisition image processing, and particularly correlation of the optical and electron data in a single integrated three-dimensional framework can be key for extracting valuable information, especially when imaging large sample volumes such as whole cells or tissu... Read more
Allon Weiner
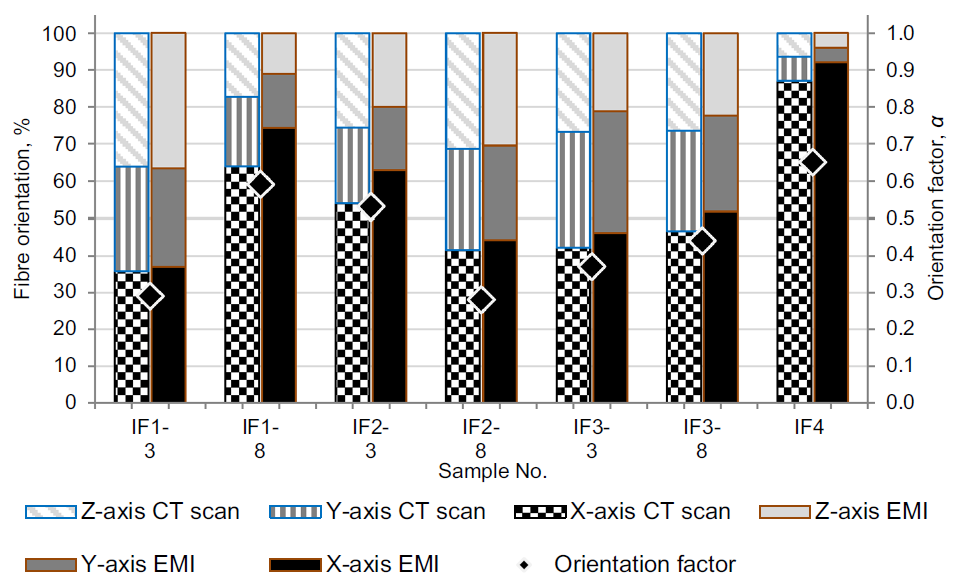
The interest in potential applications produced with self-compacting fibre reinforced concrete continues to grow, but in practice, problems associated with an uneven distribution and orientation of fibres in the concrete structure occur. It is not clear what exactly influences uneven distribution of fibres in selfcompacting concrete (SCC) mixtures, especially during the casting and how different factors influence fibre orientation. The objective of this work was to investigate how rheological... Read more
Elena Jasiuniene, Vaidotas Cicenas, Paulius Grigaliunas, Zymantas Rudzionis, Arunas Aleksandras Navickas
Microstructural analysis of TRISO particles using multi-scale X-ray computed tomography
TRISO particles, a composite nuclear fuel built up by ceramic and graphitic layers, have outstanding high temperature resistance. TRISO fuel is the key technology for High Temperature Reactors (HTRs) and the Generation IV Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR) variant.
TRISO offers unparalleled containment of fission products and is extremely robust during accident conditions. An understanding of the thermal performance and mechanical properties of TRISO fuel requires a detailed knowledg... Read more
T. Lowe, R.S. Bradley, S. Yue, K. Barii, J. Gelb, N. Rohbeck, J. Turner, P.J. Withers

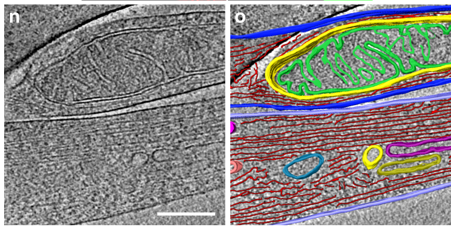
The molecular basis for sarcomere organization in vertebrate skeletal muscle
Sarcomeres are force-generating and load-bearing devices of muscles. A precise molecular picture of how sarcomeres are built underpins understanding their role in health and disease. Here, we determine the molecular architecture of native vertebrate skeletal sarcomeres by electron cryo-tomography.
Our reconstruction reveals molecular details of the three-dimensional organization and interaction of actin and myosin in the A-band, I-band, and Z-disc and demonstrates that α-actinin cros... Read more
Zhexin Wang, Michael Grange, Thorsten Wagner, Ay Lin Kho, Mathias Gautel, Stefan Raunser
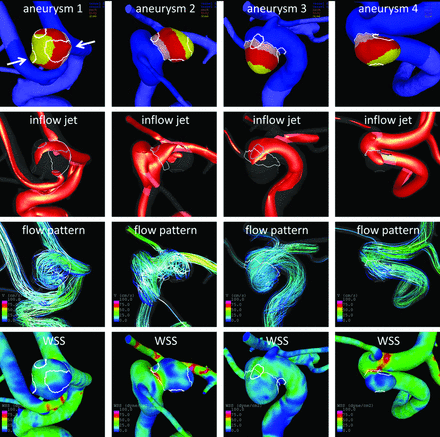
Regional Aneurysm Wall Enhancement is Affected by Local Hemodynamics: A 7T MRI Study
Aneurysm wall enhancement has been proposed as a biomarker for inflammation and instability. However, the mechanisms of aneurysm wall enhancement remain unclear. We used 7T MR imaging to determine the effect of flow in different regions of the wall.
Twenty-three intracranial aneurysms imaged with 7T MR imaging and 3D angiography were studied with computational fluid dynamics. Local flow conditions were compared between aneurysm wall enhancement and nonenhanced regions. Aneurysm wall en... Read more
S. Hadad, F. Mut, B.J. Chung, J.A. Roa, A.M. Robertson, D.M. Hasan, E.A. Samaniego and J.R. Cebral
The Architecture of Traveling Actin Waves Revealed by Cryo-Electron Tomography
Actin waves are dynamic supramolecular structures involved in cell migration, cytokinesis, adhesion, and neurogenesis. Although wave-like propagation of actin networks is a widespread phenomenon, the actin architecture underlying wave propagation remained unknown. In situ cryo-electron tomography of Dictyostelium cells unveils the wave architecture and provides evidence for wave progression by de novo actin nucleation. Subtomogram averaging reveals the structu... Read more
Marion Jasnin, Florian Beck, Mary Ecke, Yoshiyuki Fukuda, Antonio Martinez-Sanchez, Wolfgang Baumeister, Günther Gerisch
The Spontaneous Emulsification of Entrained Inclusions During Casting of High Aluminum Steels
The cleanliness of liquid steel is defined by the amounts of dissolved unwanted impurities and precipitated unwanted non-metallic phases.[…] Improving the cleanliness of the steel would mean a lower fraction of impurities in the final product. […] A novel approach, utilizing controlled synthetic inclusion/metal samples, has been developed to study the reactions between free inclusion-slag droplets and steel. The technique combines High-Temperature Confocal Scanning Laser Microscop... Read more
Akalya Raviraj, Nadia Kourra, Mark A. Williams, Gert Abbel, Claire Davis, Wouter Tiekink, Seetharaman Sridhar & Stephen Spooner
Correlative cryo-electron microscopy reveals the structure of TNTs in neuronal cells
The orchestration of intercellular communication is essential for multicellular organisms. One mechanism by which cells communicate is through long, actin-rich membranous protrusions called tunneling nanotubes (TNTs), which allow the intercellular transport of various cargoes, between the cytoplasm of distant cells in vitro and in vivo. Here, we use correlative FIB-SEM, light- and cryo-electron microscopy approaches to elucidate the structural organization of neuronal TNTs. Our data indicate ... Read more
Anna Sartori-Rupp, Diégo Cordero Cervantes, Anna Pepe, Karine Gousset, Elise Delage, Simon Corroyer-Dulmont, Christine Schmitt, Jacomina Krijnse-Locker & Chiara Zurzolo
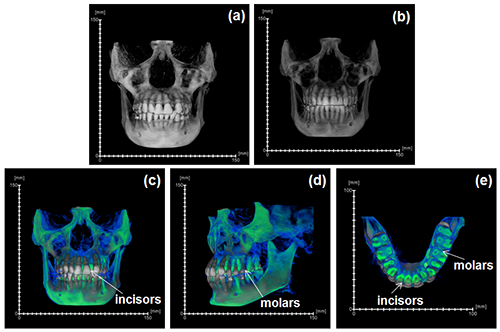
During the acts of biting and chewing, the muscles of the jaw (consisting of the masseter, temporalis, and medial pterygoid in the elevator group, and lateral pterygoid as the main depressor) generate forces that dictate jaw kinematics . The movement of jaws hinges about the temporomandibular joint and are brought together by the muscles attached to respective bones through bone-tendon interfaces known as entheses . Thus, chewing forces affect aspects of craniofacial structure as well as bo... Read more
Kyle H.-Y. Chan, fourth-year undergraduate student in Molecular and Cell Biology, and Public Health at UC Berkeley, FeiFei Yang, Ph.D., postdoctoral scholar in the Laboratory of Multiscale Biomechanics and Biomineralization, School of Dentistry, UCSF, and Sunita P. Ho, Ph.D., Division of Biomaterials and Bioengineering, Department of Preventive and Restorative Dental Sciences, School of Dentistry, University of California San Francisco
In this paper a study concerning an automatic determination of distribution of steel fibres in self-compacting concrete (SCC) is presented. The determination of fibre distribution is required to assess any relationship between those features and casting methods of concrete elements. Concrete beams with steel fibres of various types and casting methods were examined. Involved methods were computed tomography imaging followed by image analysis. After image analysis a label map consisting of all... Read more
T. Ponikiewski, J. Golaszewski, M. Rudzki, M. Bugdol
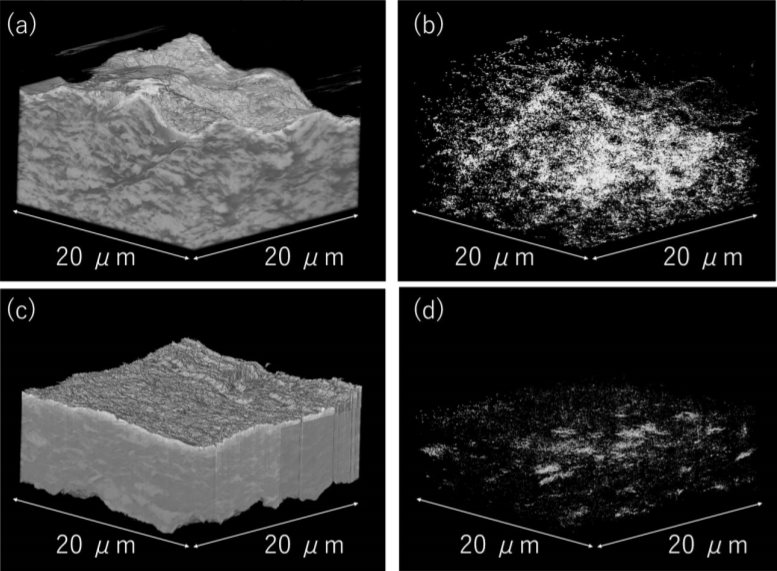
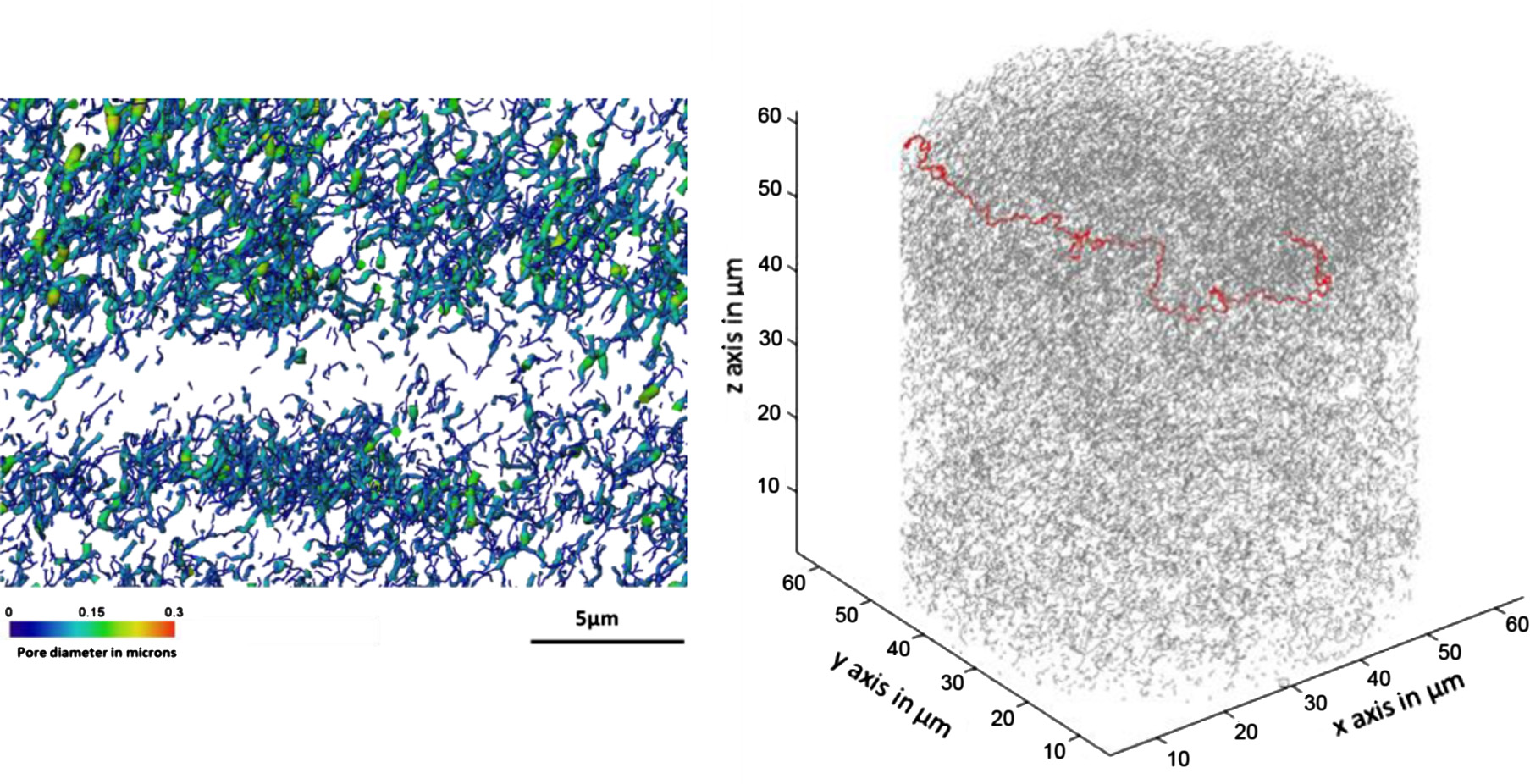
We had proposed an image-processing scheme using union operation suitable for extracting target features with hierarchical dimensions from the original data, and applied it to void analysis in a composite electrode of an all-solid-state lithium ion battery (LIB). Void analysis is very important in developing better composite electrodes for all-solid-state LIBs because internal voids should increase the interfacial resistance. Film formation of electrode-solid electrolyte composites by the aer... Read more
Yuta Yamamoto , Yasutoshi Iriyama, and Shunsuke Muto
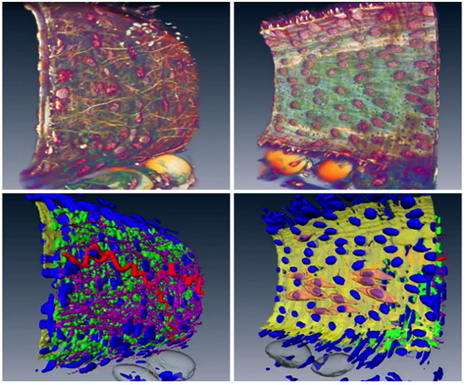
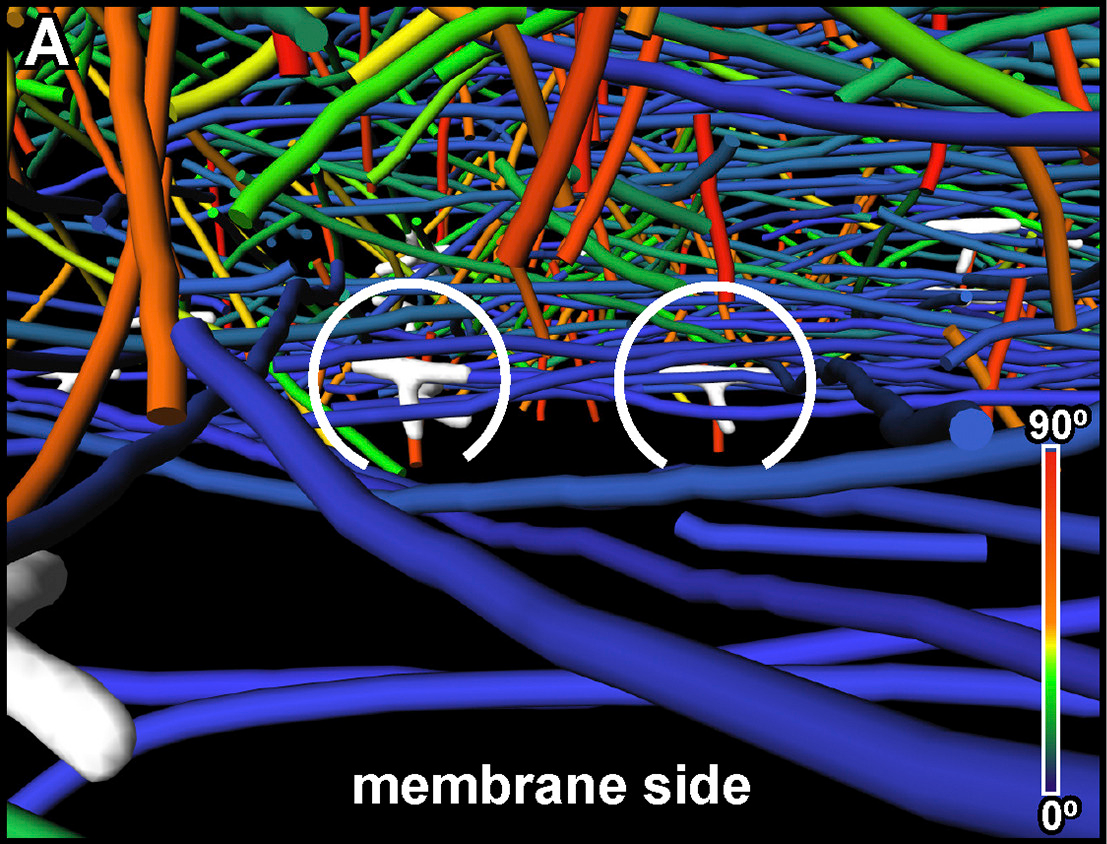
University of Glasgow uses Amira software to analyze vascular structures
The vascular (arterial or venous) wall is a fascinating structure. At the simplest level, we can think of the wall as being composed of three distinct, but interacting, layers . The vascular wall changes its structure in conditions such as hypertension which can cause a thickening of the wall. Unfortunately, the details of this ‘remodeling’ process are poorly understood.
Therefore, studying the 3D architecture may provide vital clues for future therapeutic targets.
R... Read more
Dr. Craig J Daly, School of Life Sciences, College of Medical Veterinary & Life Sciences, University of Glasgow