Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
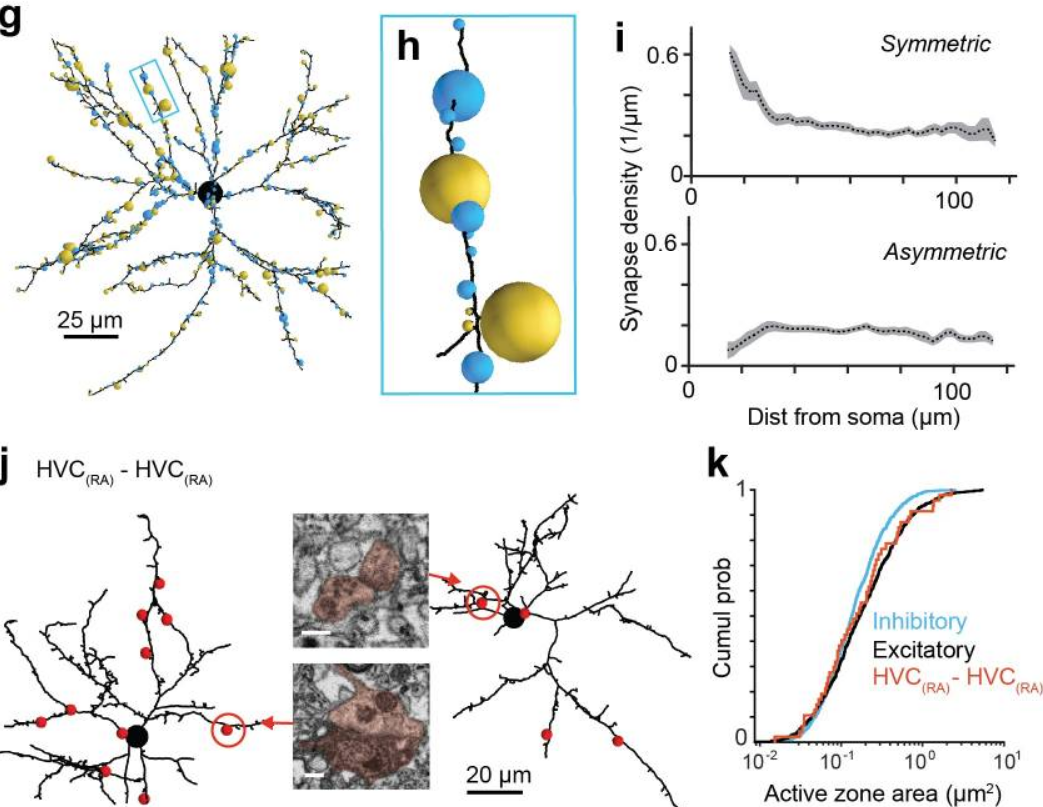
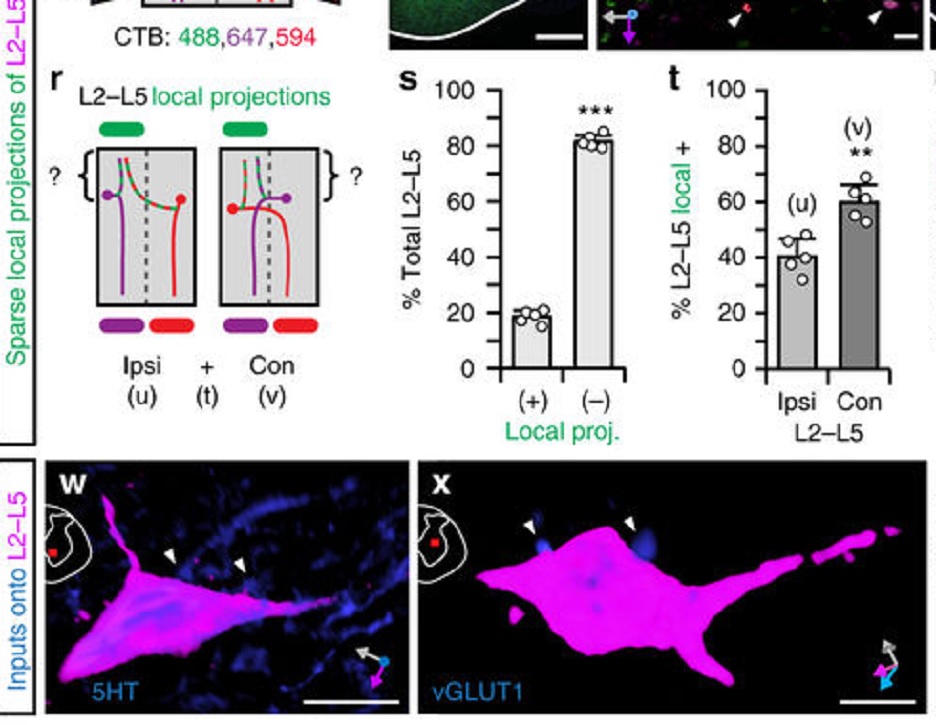
EM connectomics reveals axonal target variation in a sequence-generating network
The sequential activation of neurons has been observed in various areas of the brain, but in no case is the underlying network structure well understood. Here we examined the circuit anatomy of zebra finch HVC, a cortical region that generates sequences underlying the temporal progression of the song. We combined serial block-face electron microscopy with light microscopy to determine the cell types targeted by HVC(RA) neurons, which control song timing. Close to their soma, axons... Read more
Jörgen Kornfeld, Sam E Benezra, Rajeevan T Narayanan, Fabian Svara, Robert Egger, Marcel Oberlaender, Winfried Denk, Michael A Long
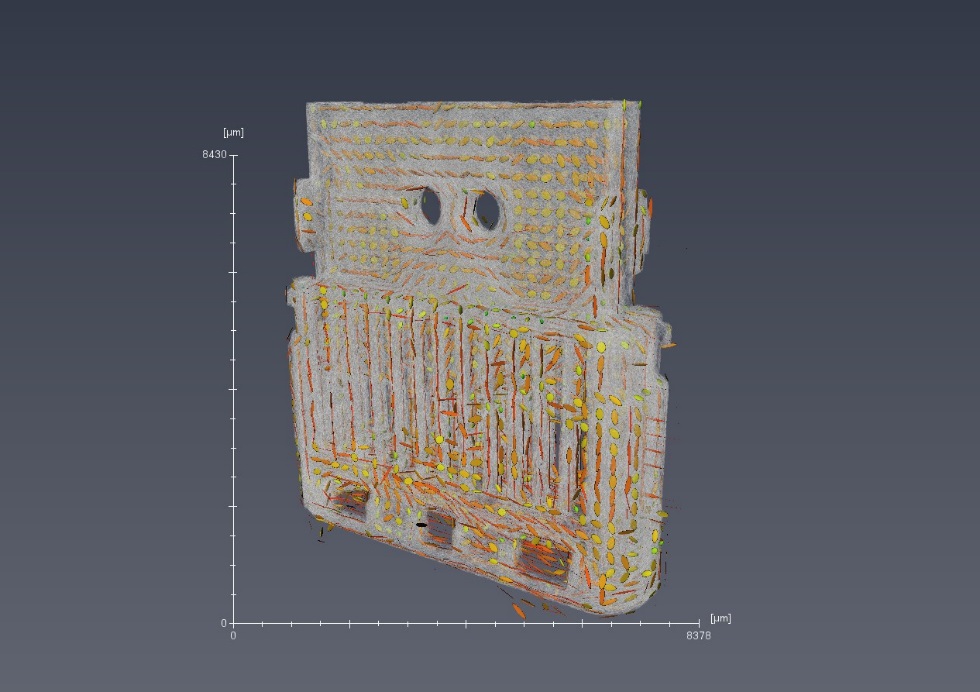
Glass fiber length and orientation analysis of reinforced polymers (GFRP)
Royal DSM is a global science-based company active in health, nutrition and
materials. Within DSM’s Materials Cluster DSM Engineering Plastics is a global player in specialty plastics. These materials are used in components for the electrical and electronics, automotive, flexible food packaging and consumer goods industries.
A typical product made of DSM Engineering Plastics’ polymer portfolio are USB-C connectors. Key performance indicators for this application are dimension... Read more
Jennifer Schillings, Arno Wilbers and Joachim Loos, DSM Materials Science Center, Geleen, The Netherlands
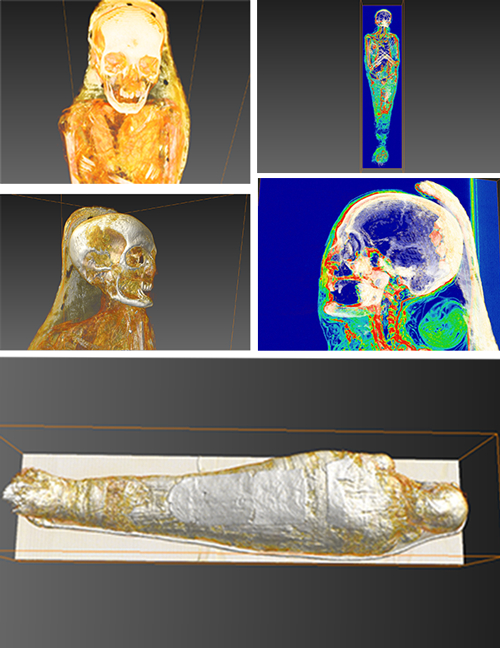
AMSC Research, LLC uses Amira software to understand processes and rituals of Egyptian mummification
“Scanning is important, but it is really just the first step in an immersive exploration of artifacts” says Elias. Raw data from scans taken of mummies (or other archaeological subject matter) is delivered to AMSC Research as files in a language known as DICOM. Next, these are converted into a visually readable form for analytical purposes and to launch the creative modeling process.
Elias uses Amira software to analyze scan data. Mummies are biological entities, so apart f... Read more
Dr. Jonathan Elias, AMSC Research, LLC
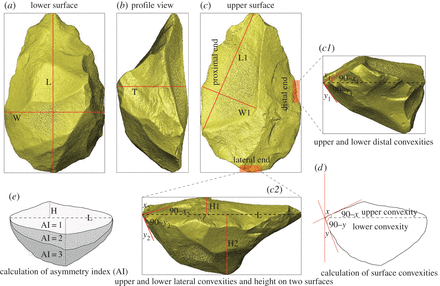
Prepared core technology illustrates in-depth planning and the presence of a mental template during the core reduction process. This technology is, therefore, a significant indicator in studying the evolution of abstract thought and the cognitive abilities of hominids. Here, we report on Victoria West cores excavated from the Canteen Kopje site in central South Africa, with a preliminary age estimate of approximately 1 Ma (million years ago) for these cores. Technological analysis shows tha... Read more
Hao Li, Kathleen Kuman, Matt G. Lotter, George M. Leader, Ryan J. Gibbon
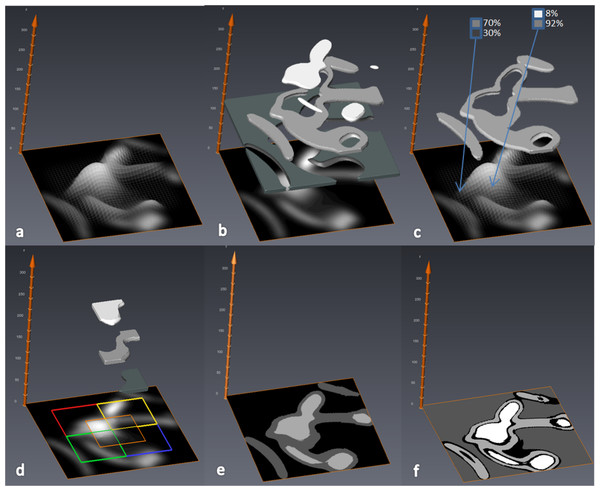
MIA-Clustering: a novel method for segmentation of paleontological material
Paleontological research increasingly uses high-resolution micro-computed tomography (μCT) to study the inner architecture of modern and fossil bone material to answer important questions regarding vertebrate evolution. This non-destructive method allows for the measurement of otherwise inaccessible morphology. Digital measurement is predicated on the accurate segmentation of modern or fossilized bone from other structures imaged in μCT scans, as errors in segmentation can result in inaccur... Read more
Christopher J. Dunmore, Gert Wollny, Matthew M. Skinner
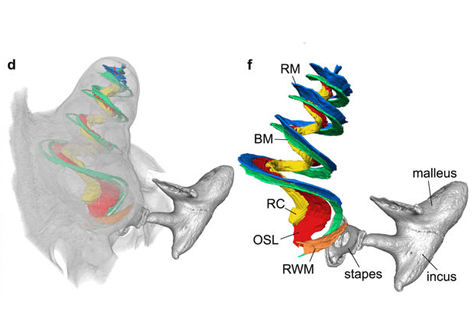
Propagation-based phase-contrast x-ray tomography of cochlea using a compact synchrotron source
We demonstrate that phase retrieval and tomographic imaging at the organ level of small animals can be advantageously carried out using the monochromatic radiation emitted by a compact x-ray light source, without further optical elements apart from source and detector. This approach allows to carry out microtomography experiments which – due to the large performance gap with respect to conventional laboratory instruments – so far were usually limited to synchrotron sources. We dem... Read more
Mareike Töpperwien, Regine Gradl, Daniel Keppeler, Malte Vassholz, Alexander Meyer, Roland Hessler, Klaus Achterhold, Bernhard Gleich, Martin Dierolf, Franz Pfeiffer, Tobias Moser & Tim Salditt
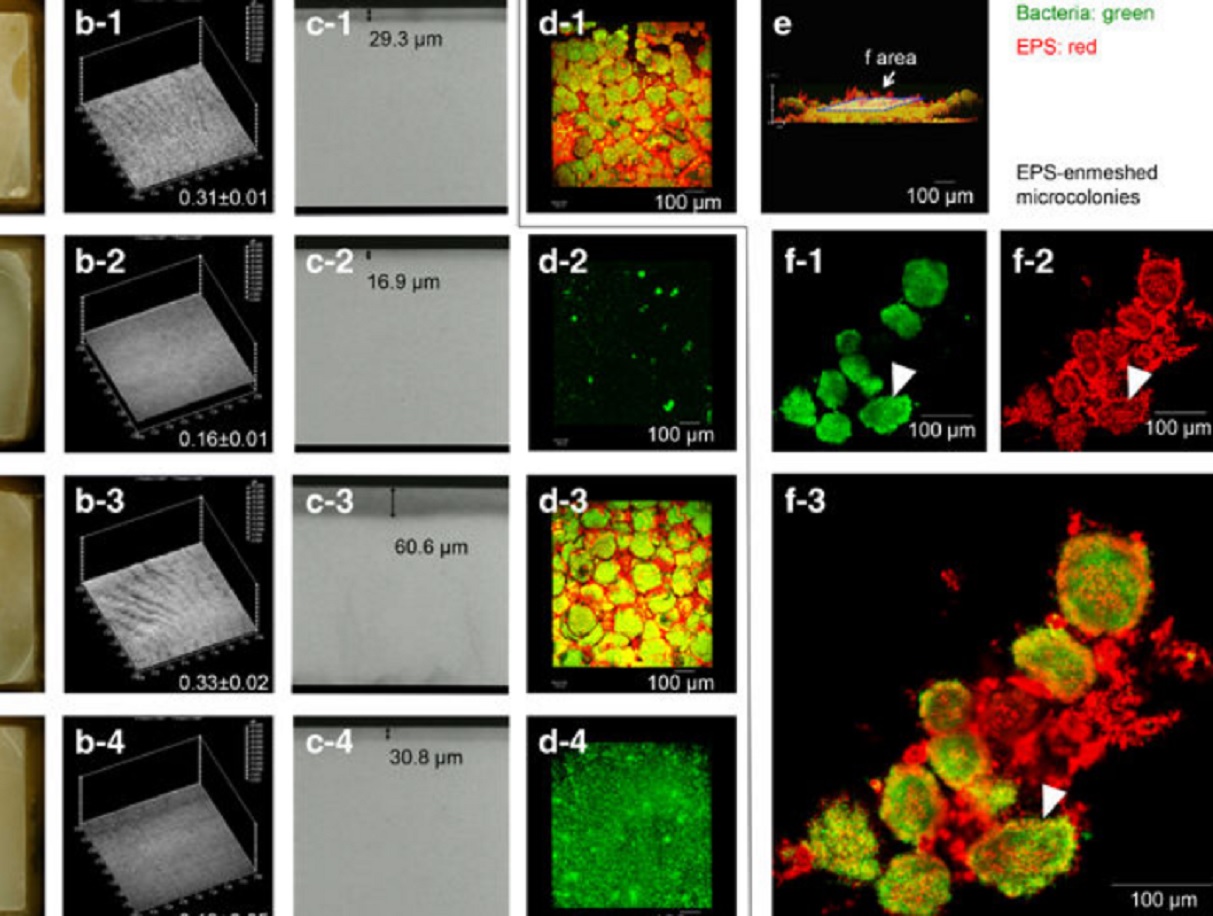
Acidic microenvironments created by bacterial clusters thriving in a polysaccharide matrix could be behind localized tooth decay. Jin Xiao of the University of Rochester Medical Center and Geelsu Hwang of the University of Pennsylvania with colleagues in the US mapped acidity changes across tooth enamel caused by the microstructure of dental plaque: a film of bacteria and the polysaccharide matrix they secrete. Using fluorescence microscopy, they studied the 3D architecture of plaque that for... Read more
Jin Xiao, Anderson T Hara, Dongyeop Kim, Domenick T Zero, Hyun Koo et al.
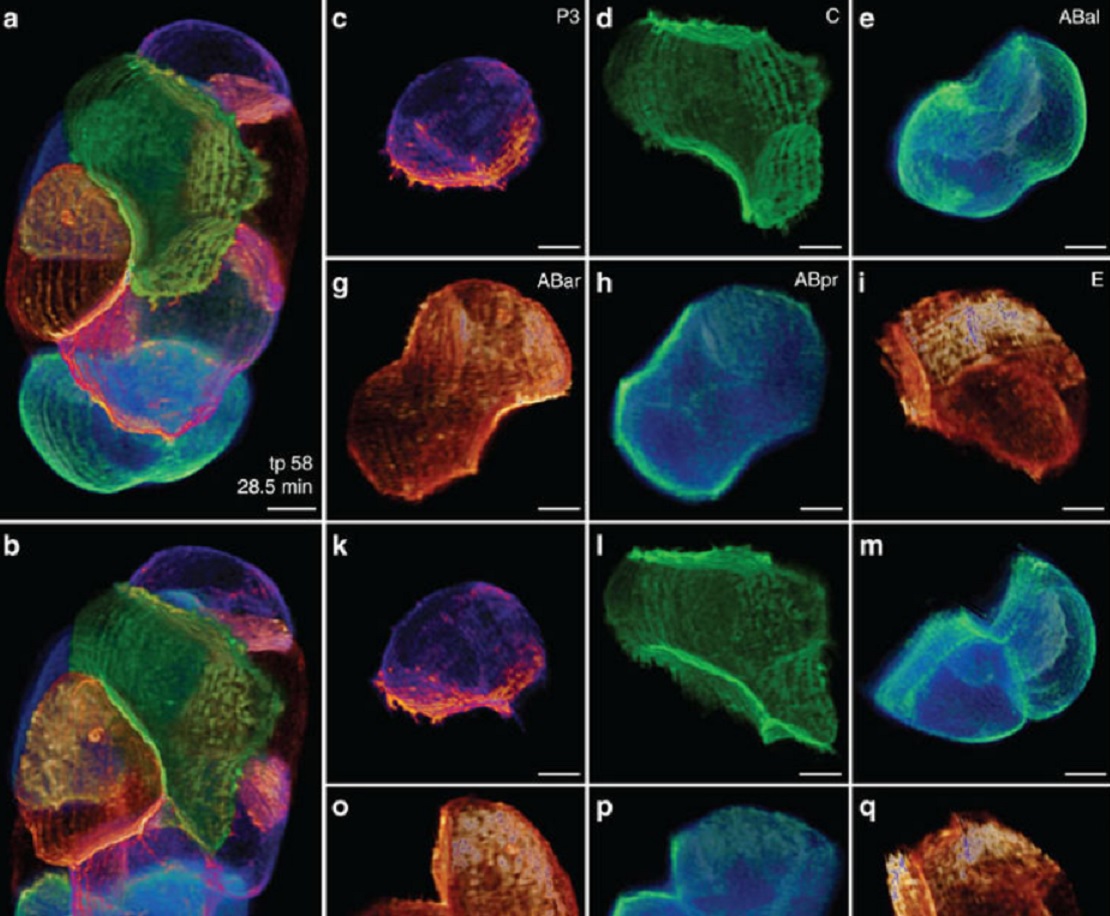
Despite the progress made in selective plane illumination microscopy, high-resolution 3D live imaging of multicellular specimens remains challenging. Tiling light-sheet selective plane illumination microscopy (TLS-SPIM) with real-time light-sheet optimization was developed to respond to the challenge…
Read more
Qinyi Fu, Benjamin L. Martin, David Q. Matus, Liang Gao
Neural circuitry in the lumbar spinal cord governs two principal features of locomotion, rhythm and pattern, which reflect intra- and interlimb movement. These features are functionally organized into a hierarchy that precisely controls stepping in a stereotypic, speed-dependent fashion. Here, we show that a specific component of the locomotor pattern can be independently manipulated…
Read more
Amanda M. Pocratsky, Darlene A. Burke, Johnny R. Morehouse, Jason E. Beare, Amberly S. Riegler, Pantelis Tsoulfas, Gregory J. R. States, Scott R. Whittemore & David S. K. Magnuson
Noise induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a disease that affects millions of Americans. Identifying genetic pathways that influence recovery from noise exposure is an important step forward in understanding NIHL. The transcription factor Foxo3 integrates the cellular response to oxidative stress and plays a role in extending lifespan in many organisms, including humans. Here we show that Foxo3 is required for auditory function after noise exposure in a mouse model system, measured by ABR…Read more
Felicia Gilels, Stephen T. Paquette, Holly J. Beaulac, Anwen Bullen & Patricia M. White
This paper demonstrates for the first time down-regulation of the endogenous nuclear retained mutant DMPK mRNAs targeted with lentivirus-delivered short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs). This nuclear RNAi(-like) phenomenon was not observed when synthetic siRNAs were delivered by cationic lipids, suggesting either a link between processing of the shRNA and nuclear import or a separate pathway for processing shRNAs in the nuclei.
Read more
Marc-André Langlois, Christelle Boniface, Gang Wang, Jessica Alluin, Paul M. Salvaterra, Jack Puymirat, John J. Rossi, Nan Sook Lee
Couinaud based his well-known subdivision of the liver into (surgical) segments on the branching order of portal veins and the location of hepatic veins. However, both segment boundaries and number remain controversial due to an incomplete understanding of the role of liver lobes and vascular physiology on hepatic venous development. Human embryonic livers (5–10 weeks of development) were visualized with Amira 3D-reconstruction and Cinema 4D-remodeling software.
Read more
Jill P. J. M. Hikspoors, Mathijs M. J. P. Peeters, Nutmethee Kruepunga, Hayelom K. Mekonen, Greet M. C. Mommen, S. Eleonore Köhler & Wouter H. Lamers
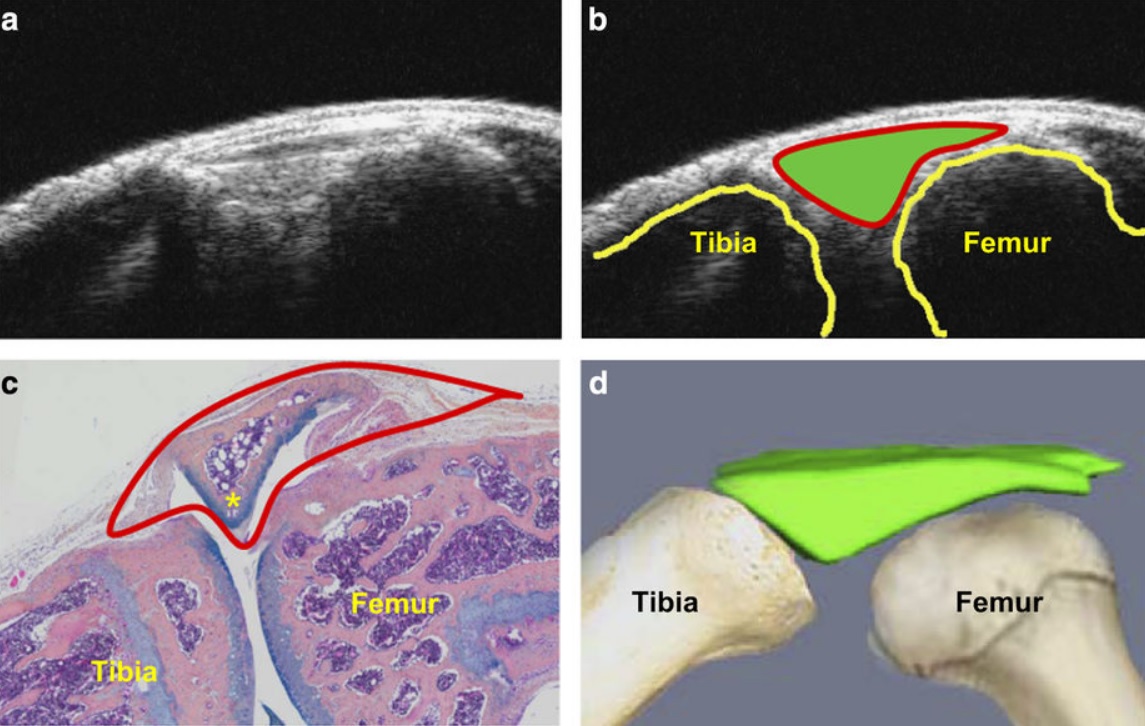
Ultrasound could be a fast and cost-effective means of assessing joint changes in mouse models of posttraumatic osteoarthritis (PTOA). Such models are essential for understanding the biology of this degenerative joint disease and developing new treatments, but noninvasive methods of evaluating disease activity are lacking. Because ultrasound can visualize both joint space volumes and blood flow in the joints, it could provide an alternative to microscopic examination of tissue, assuming it ac... Read more
Hao Xu, Echoe M Bouta, Ronald W Wood, Edward M Schwarz, Yongjun Wang & Lianping Xing
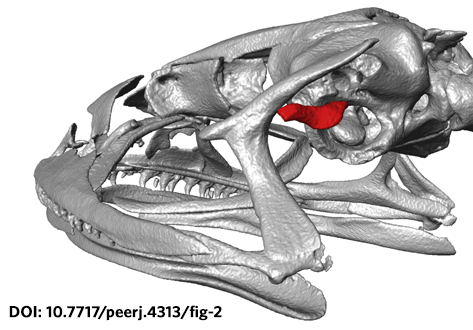
The loss of hearing structures and loss of advertisement calls in many terrestrial breeding frogs (Strabomantidae) living at high elevations in South America are common and intriguing phenomena. The Andean frog genus Phrynopus Peters, 1873 has undergone an evolutionary radiation in which most species lack the tympanic membrane and tympanic annulus, yet the phylogenetic relationships among species in this group remain largely unknown. Here, we present an expanded molecular phylogeny o... Read more
May R, Lehr E, Rabosky DL. PeerJ 6:e4313
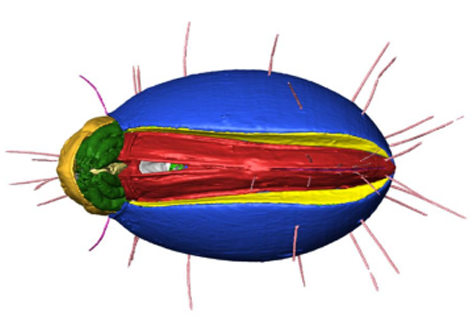
The NOVA project: maximizing beam time efficiency through synergistic analyses of SRµCT data
Beamtime and resulting SRμCT data are a valuable resource for researchers of a broad scientific community in life sciences. Most research groups, however, are only interested in a specific organ and use only a fraction of their data. The rest of the data usually remains untapped. By using a new collaborative approach, the NOVA project (Network for Online Visualization and synergistic Analysis of tomographic data) aims to demonstrate, that more efficient use of the valuable beam time is possi... Read more
The international society for optics and photonics (SPIE)
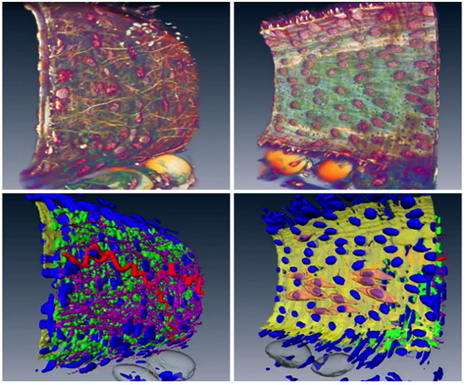
University of Glasgow uses Amira software to analyze vascular structures
The vascular (arterial or venous) wall is a fascinating structure. At the simplest level, we can think of the wall as being composed of three distinct, but interacting, layers . The vascular wall changes its structure in conditions such as hypertension which can cause a thickening of the wall. Unfortunately, the details of this ‘remodeling’ process are poorly understood.
Therefore, studying the 3D architecture may provide vital clues for future therapeutic targets.
R... Read more
Dr. Craig J Daly, School of Life Sciences, College of Medical Veterinary & Life Sciences, University of Glasgow
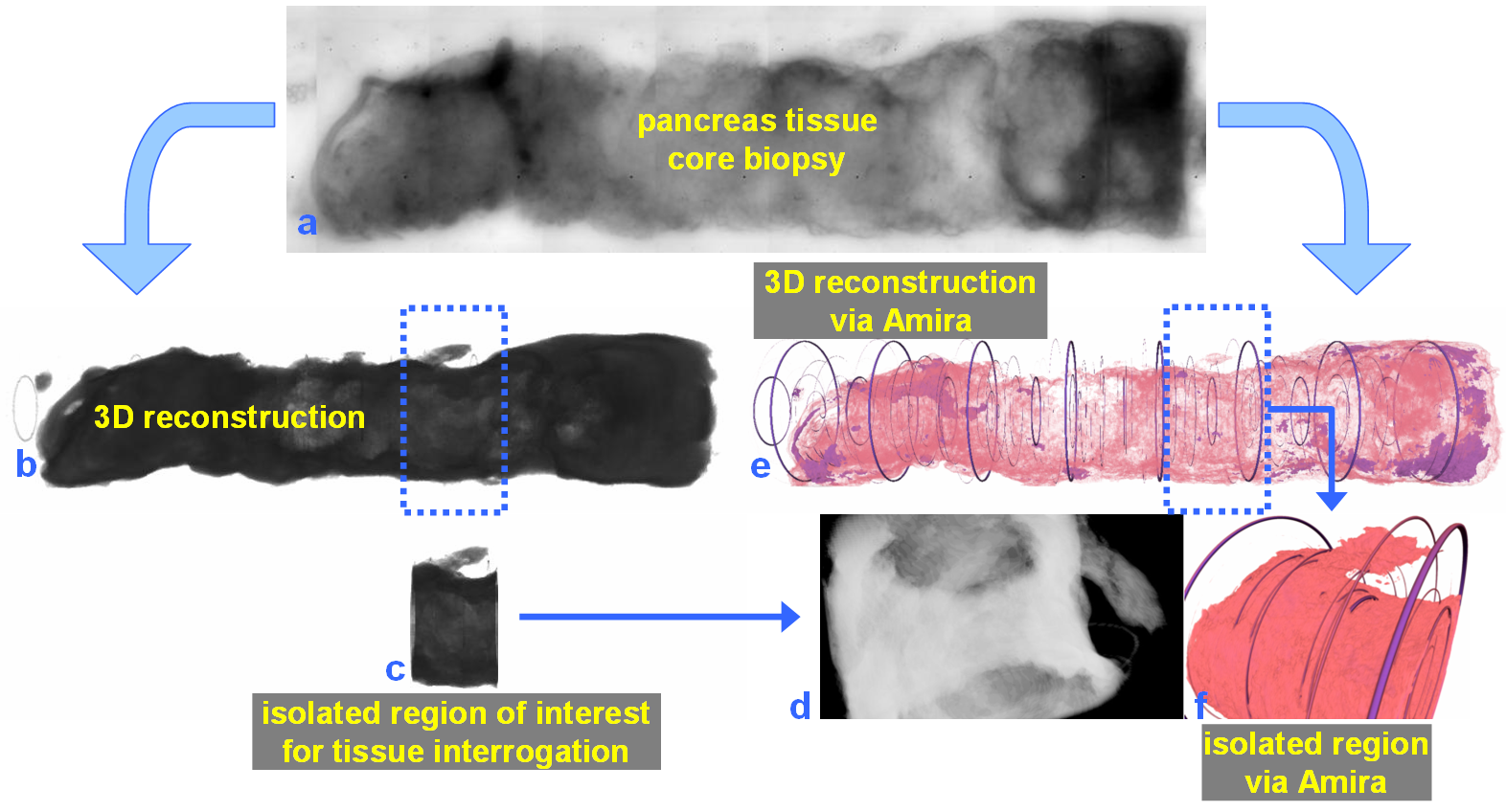
For nearly 100 years, pathology for cancer diagnosis has involved a standard, but complex series of steps to process tissue biopsies procured from a patient in the clinic. Many procedures are a direct result of the fact that observation and evaluation of specimens by pathologists occur using a standard microscope (in 2D).
In 2014, the Human Photonics Laboratory at the University of Washington demonstrated that the rudimentary operations of a pathology laboratory may be replicated on wh... Read more
Ronnie Das, PhD and Eric J. Seibel, PhD
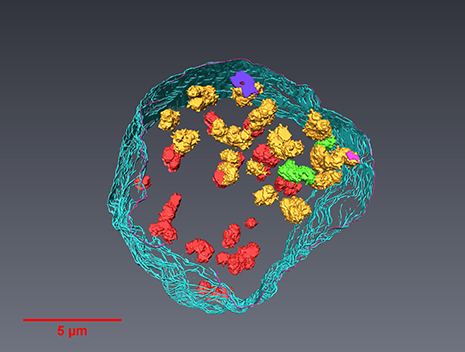
A team led by London Centre for Nanotechnology researchers, Prof. Ian Robinson and Dr. Bo Chen (now a professor at the Tongji University, Shanghai) used newly-developed serial block-face scanning electron microscopy (SBFSEM) and Thermo Scientific™ Avizo® Software, one dominant tool in 3D reconstructed image processing, to reveal the spatial structure of human chromosomes and nucleus quantitatively at high resolution of approximately 50 nm in three dimensions.
Read more
Prof. Ian Robinson, Dr. Bo Chen, London Centre for Nechnology, UCL and Tongji University
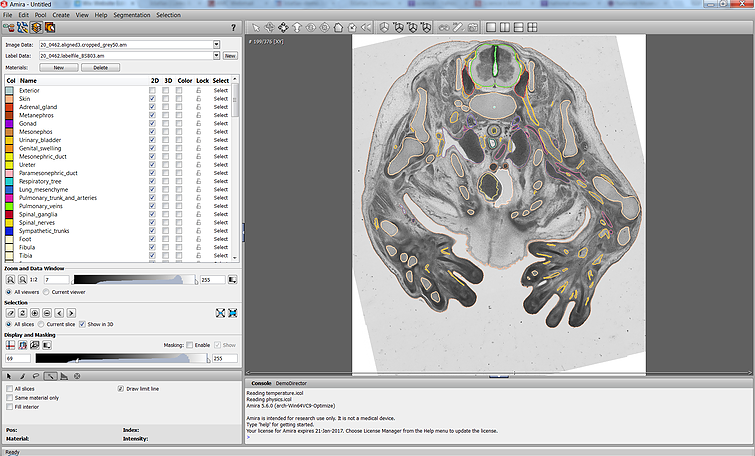
The Academic Medical Center (AMC) uses Amira to build a 3D Atlas for Human Embryology
The 3D Atlas of Human Embryology project was funded by the Academic Medical Center (AMC) in Amsterdam, the Netherlands, in 2009. Since then, over 75 students, under the supervision of embryologists of the Department of Anatomy, Embryology & Physiology, have contributed to this labor-int... Read more
Academic Medical Center
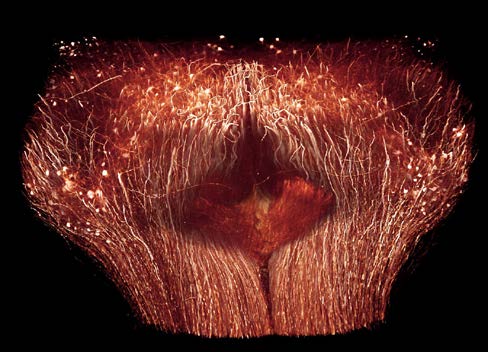
The Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology uses Amira software for axon tracing from head to toe
Ali Ertürk and his collaborators described a novel histo-chemical technique to clear spinal cord tissue of adult mice for fluorescence microscopy imaging of the intact spinal cord.
Previously, the high lipid content of the spinal cord tissue in adult mice allowed imaging of the spinal cord only through destructive histological methods, making the tracing of complete axons impossible. As applied in this study, the improved histo-chemistry enabled Ertürk and his colleagues to show that... Read more
Ali Ertürk, Christoph P Mauch, Farida Hellal, Friedrich Förstner, Tara Keck, Klaus Becker, Nina Jährling, Heinz Steffens, Melanie Richter, Mark Hübener, Edgar Kramer, Frank Kirchhoff, Hans Ulrich Dodt & Frank Bradke