Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
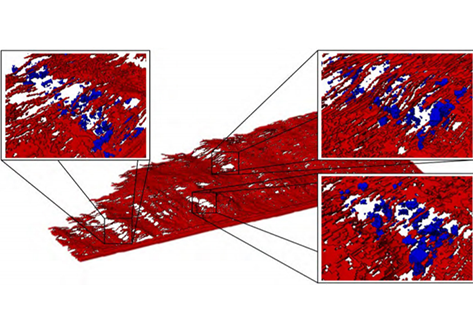
Understanding the near-threshold crack growth behavior in an aluminum alloy by x-ray tomography
The near-threshold behavior of long cracks is evaluated using pre-cracked flat dogbone specimens of a commercial aluminum alloy in two heat treatment states. Once the threshold was known, the crack initially introduced by cyclic compression was propagated under load control with approximately
constant range of the stress intensity factor at values close to the threshold values. The 3D morphology of the crack and the spatial distribution of the primary precipitates obtained by µ-CT were... Read more
Marcel Wicke, Angelika Brueckner-Foit, Tina Kirsten, Martina Zimmermann, Fatih Buelbuel, Hans-Juergen Christ
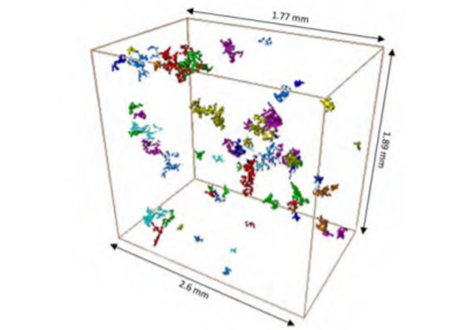
3D characterization of the fracture mechanisms of a Fe-rich Al-Si-Cu alloy
The effect of the defect size and morphology on the fatigue damage evolution was analysed in a recycled Al-Si-Cu alloy by micro-computed tomography and scanning electron microscopy. Fatigue tests were performed and the different crack initiation scenarios were characterized and classified. The interaction between shrinkage and gas pores was the key crack initiation mechanism and the ß-Al5FeSi particles did not play any role in the crack initiation phase. However, crack path analysis indicate... Read more
Angelika Brueckner-Foit, Inigo Bacaicoa, Martin Luetje, Marcel Wicke, Andreas Geisert, Martin Fehlbier
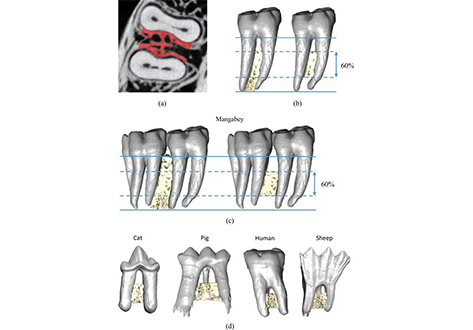
Mechanical adaptation of trabecular bone morphology in the mammalian mandible
Alveolar bone, together with the underlying trabecular bone, fulfils an important role in providing structural support against masticatory forces. Diseases such as osteoporosis or periodontitis cause alveolar bone resorption which weakens this structural support and is a major cause of tooth loss. However, the functional relationship between alveolar bone remodelling within the molar region and masticatory forces is not well understood. This study investigated this relationship by comparing m... Read more
Peter J. Watson, Laura C. Fitton, Carlo Meloro, Michael J. Fagan, Flora Gröning
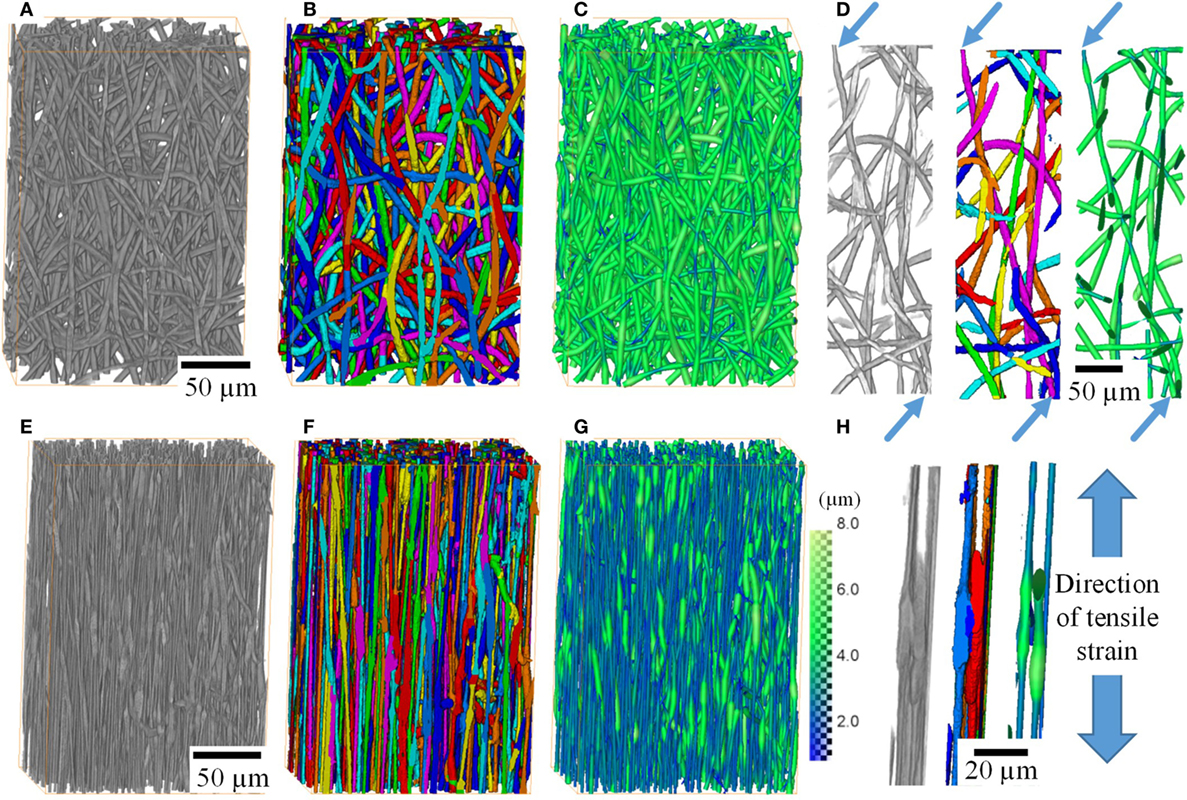
X-ray Tomographic Imaging of Tensile Deformation Modes of Electrospun Biodegradable Polyester Fibers
Electrospun constructs for the repair of load-bearing tissues are required to have adequate mechanical properties. However, the failure mechanisms of electrospun fibrous materials are not well understood. Existing literature focuses on failure modes of individual fibers and/or on bulk mechanical properties of whole fiber mats.
Electrospinning allows the production of fibrous networks for tissue engineering, drug delivery, and wound healing in health care. It enables the production of c... Read more
Jekaterina Maksimcuka; Akiko Obata ; William W. Sampson ; Remi Blanc ; Chunxia Gao ; Philip J. Withers ; Olga Tsigkou ; Toshihiro Kasuga ; Peter D. Lee ; Gowsihan Poologasundarampillai
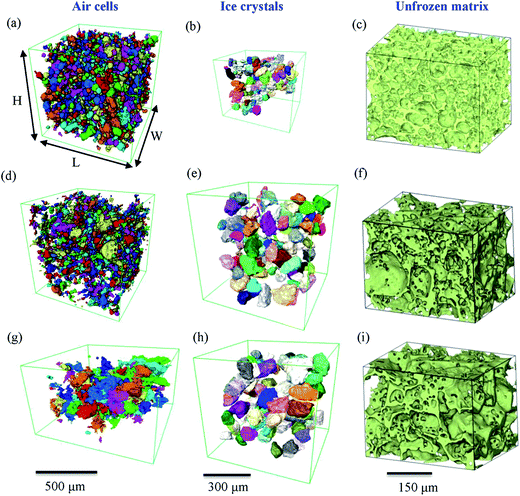
The microstructure of food affects our sensorial perception, its attractiveness, and the manufactured product’s shelf-life.
Microstructural evolution in soft matter directly influences not only the material’s mechanical and functional properties, but also our perception of that material’s taste. Using synchrotron X-ray tomography and cryo-SEM we investigated the time–temperature evolution of ice cream’s microstructure. This was enabled via three adv... Read more
Enyu Guo, Guang Zeng, Daniil Kazantsev, Peter Rockett, Julian Bent, Mark Kirkland, Gerard Van Dalen, David S. Eastwood, David StJohn and Peter D. Lee
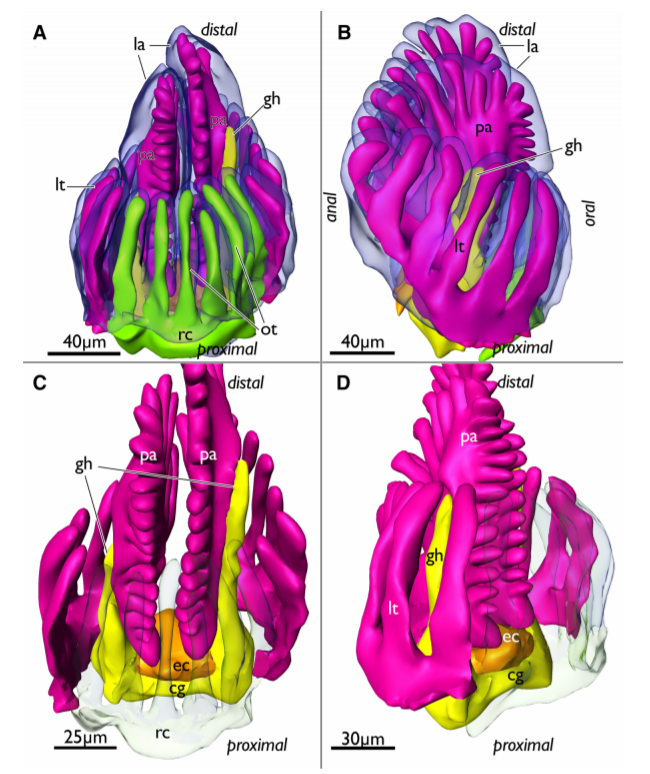
Phylactolaemate bryozoans are the sister-group to all remaining bryozoan taxa. Consequently, their study is essential to reveal and analyze ancestral traits of Phylactolaemata and Bryozoa in general.
They are the only bryozoans to possess an epistome which traditionally has been regarded as shared with phoronids and brachiopods. Contrary to older observations, an epistome was recently reported to be missing in the early branching phylactolaemate Lophopus crystallinus. In this... Read more
Thomas Schwaha
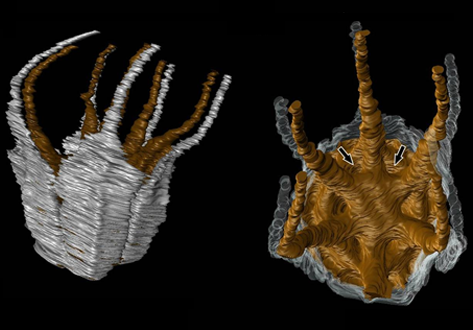
Angiosperm-dominated floras of the Late Cretaceous are essential for understanding the evolutionary, ecological, and geographic radiation of flowering plants.
The Late Cretaceous–early Paleogene Deccan Intertrappean Beds of India contain angiosperm-dominated plant fossil assemblages known from multiple localities in central India. Numerous monocots have been documented from these assemblages, providing a window into an important but poorly understood time in their diversification. On... Read more
Kelly K.S. Matsunaga, Selena Y. Smith, Steven R. Manchester, Dashrath Kapgate, Deepak Ramteke, Amin Garbout, and Herminso Villarraga-Gómez
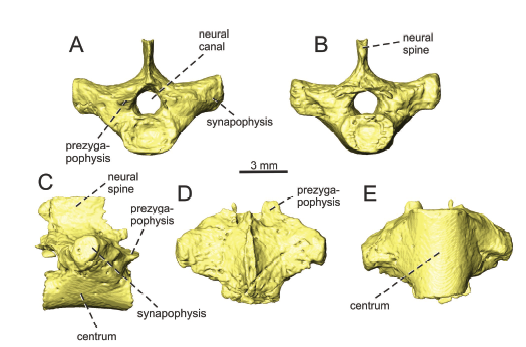
An eosauropterygian skeleton found in the Middle Triassic (upper Anisian) Gutenstein Formation of the Fatric Unit (Demänovská dolina Valley, Low Tatra Mountains, Slovakia) represents the earliest known occurrence of marine tetrapods in the Western Carpathians. The specimen represents a partly articulated portion of the postcranial skeleton (nine dorsal vertebrae, coracoid, ribs, gastral ribs, pelvic girdle, femur and one zeugopodial element). It is assigned to the Pachypleurosauria, more pr... Read more
ANDREJ ČERŇANSKÝ, NICOLE KLEIN, JÁN SOTÁK, MÁRIO OLŠAVSKÝ, JURAJ ŠURKA, and PAVEL HERICH
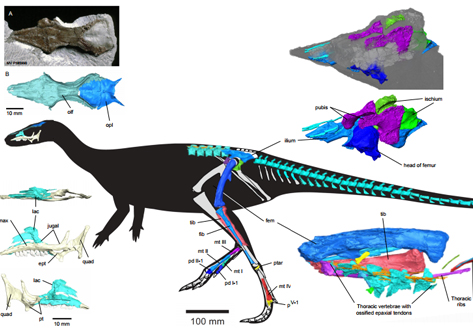
Revealing the skeleton of polar dinosaur using synchrotron computed tomography
Leaellynasaura amicagraphica was a small, bipedal, herbivorous dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous (~106 million years ago) of Australia within the Antarctic Circle of that time.
Synchrotron scans, and the resulting 3D reconstruction of the skull and post-cranial skeleton, provide a unique view of the morphology of Leaellynasaura, and allows this material to be 3D printed for display.
Read more
1University College London, UK; Monash University, Melbourne, Australia; Museum Victoria, Melbourne, Australia
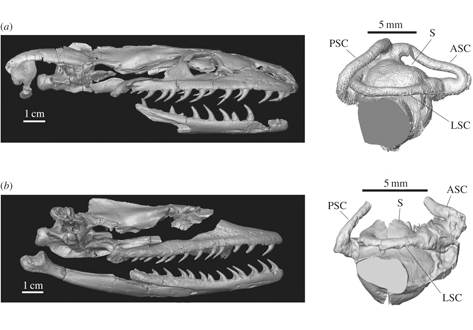
Madtsoiids are among the most basal snakes, with a fossil record dating back to the Upper Cretaceous (Cenomanian). Most representatives went extinct by the end of the Eocene, but some survived in Australia until the Late Cenozoic. Yurlunggur and Wonambi are two of these late forms, and also the best-known madtsoiids to date. A better understanding of the anatomy and palaeoecology of these taxa may shed light on the evolution and extinction of this poorly known group of s... Read more
Alessandro Palci, Mark N. Hutchinson, Michael W. Caldwell, John D. Scanlon, Michael S. Y. Lee
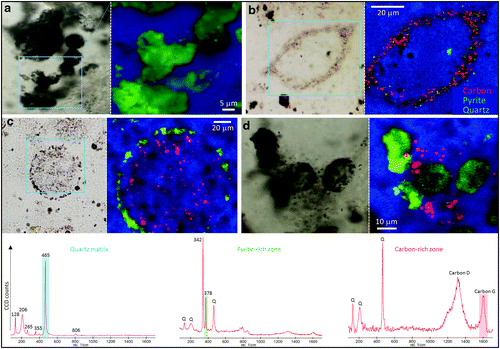
Volcanogenic Pseudo-Fossils from the ∼3.48 Ga
The ∼3.48 billion-year-old Dresser Formation, Pilbara Craton, Western Australia, is a key geological unit for the study of Earth’s earliest life and the habitats it occupied. Here, we describe a new suite of spheroidal to lenticular microstructures that morphologically resemble some previously reported Archean microfossils. Correlative microscopy shows that these objects have a size distribution, wall ultrastructure, and chemistry that are incompatible with a microfossil origin and in... Read more
Wacey David , Noffke Nora , Saunders Martin , Guagliardo Paul , and Pyle David M
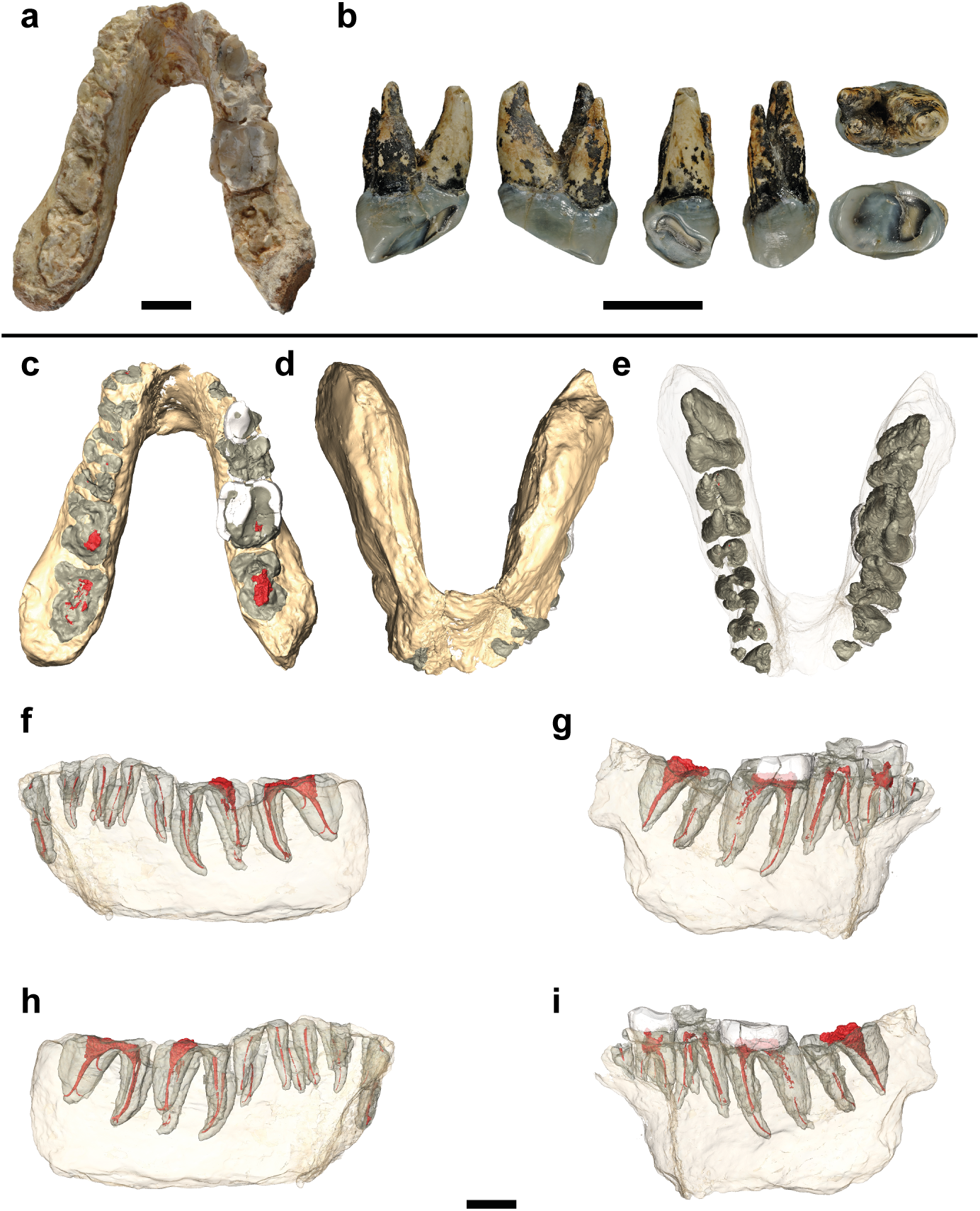
Potential hominin affinities of Graecopithecus from the Late Miocene of Europe
The split of our own clade from the Panini is undocumented in the fossil record. To fill this gap we investigated the dentognathic morphology of Graecopithecus freybergi from Pyrgos Vassilissis (Greece) and cf. Graecopithecus sp. from Azmaka (Bulgaria), using new μCT and 3D reconstructions of the two known specimens. Pyrgos Vassilissis and Azmaka are currently dated to the early Messinian at 7.175 Ma and 7.24 Ma. Mainly based on its external preservation and the previou... Read more
Jochen Fuss, Nikolai Spassov, David R. Begun, Madelaine Böhme
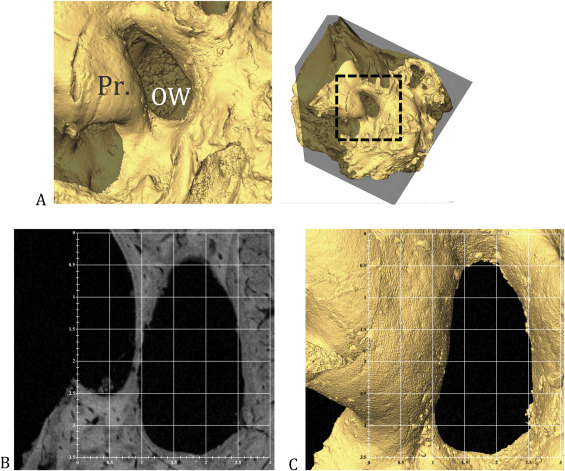
Echoes from the past: New insights into the early hominin cochlea from a phylo-morphometric approach
Investigation on cochlear variation, an indirect evidence of auditory capacities among early hominins and extant catarrhine species, in order to assess (i) the phylogenetic signal of relative external cochlear length (RECL) and oval window area (OWA), the evolutionary model with the highest probability of explaining our observed data, some hominin ancestral nodes for RECL and OWA. RECL has a high phylogenetic signal under a Brownian motion model, and is closely correlated with body mass. Our... Read more
José Braga, Priscille Bouvier, Jordan Romeyer Dherbey, Patricia Balaresque, Laurent Risser , Jean-Michel Loubes , Jean Dumoncel , Benjamin Duployer , Christophe Tenailleau
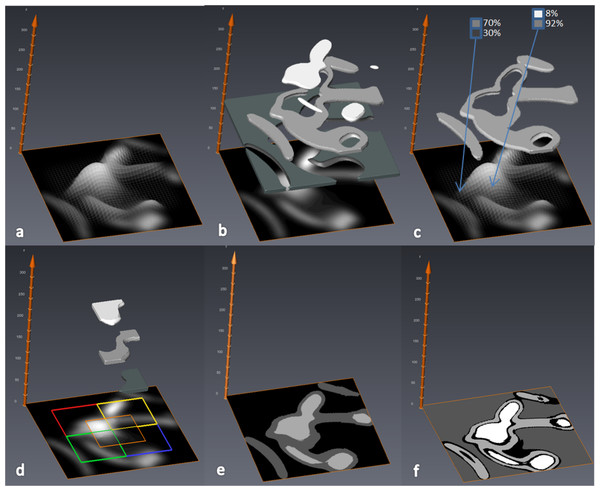
MIA-Clustering: a novel method for segmentation of paleontological material
Paleontological research increasingly uses high-resolution micro-computed tomography (μCT) to study the inner architecture of modern and fossil bone material to answer important questions regarding vertebrate evolution. This non-destructive method allows for the measurement of otherwise inaccessible morphology. Digital measurement is predicated on the accurate segmentation of modern or fossilized bone from other structures imaged in μCT scans, as errors in segmentation can result in inaccur... Read more
Christopher J. Dunmore, Gert Wollny, Matthew M. Skinner