Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
The behavior of loess is controlled by its microstructure, consisting of silt sized skeleton particles and complex bonding structures formed by clay-sized particles. Achieving a deep understanding and precise modelling of loess behavior necessitates comprehensive knowledge of the realistic 3D microstructure.
- Innovative 3D analysis of loess microstructure using μXCT and FIB-SEM.
- Detailed visualizat... Read more
B. Yu, T.A. Dijkstra, W. Fan, I.J. Smalley, Y.N. Wei, L.S. Deng
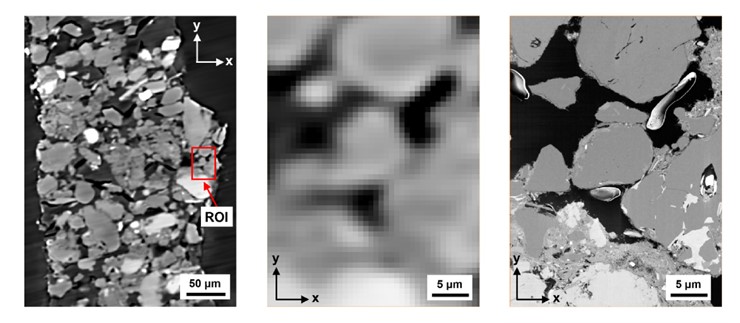
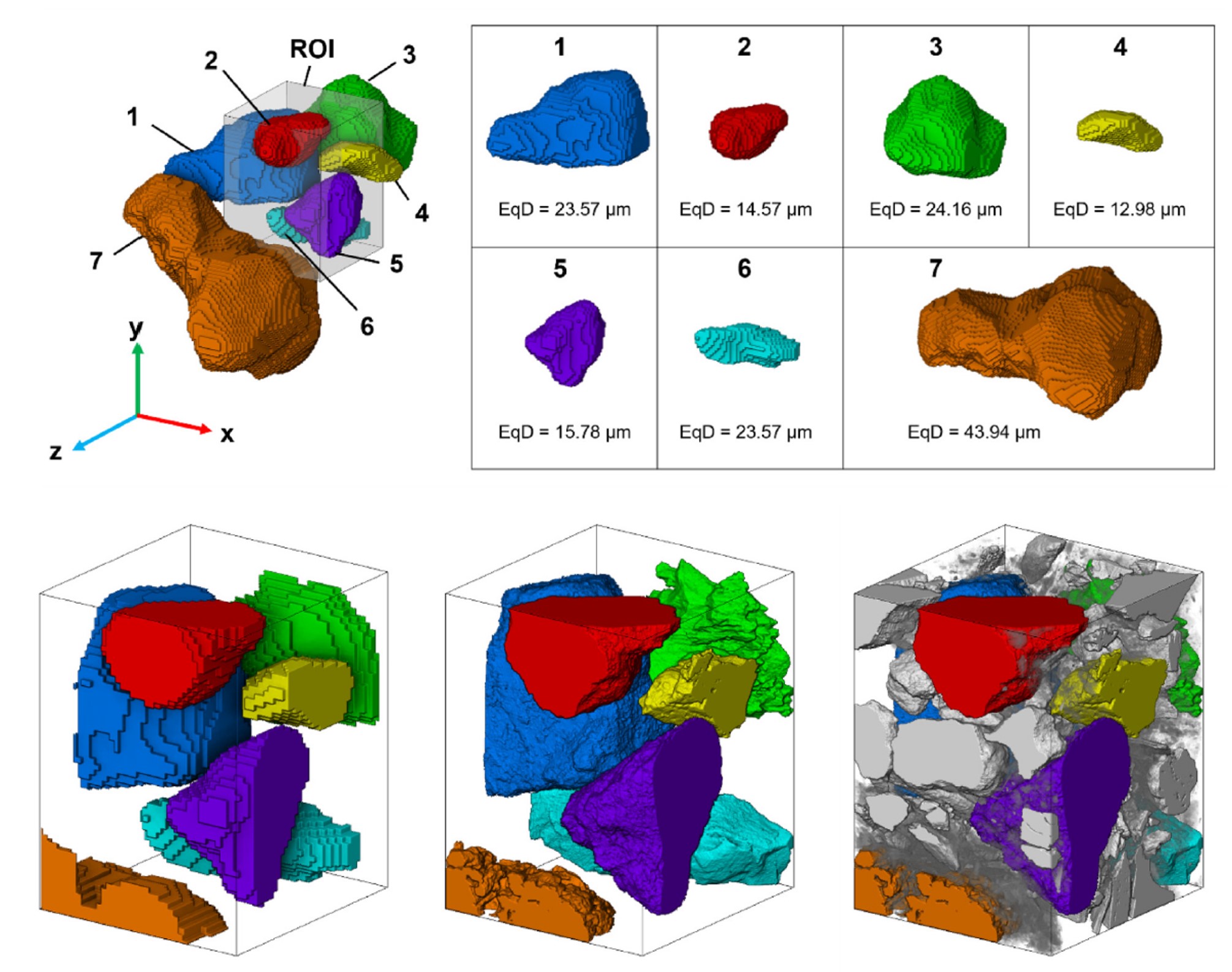
3D loess microstructure of loess, including skeleton particles as well as inter-particle bonding structures, was characterized through a correlative approach using μXCT and FIB-SEM
Loess, a Quaternary wind-blown deposit, is a problem soil that gives rise to frequent geohazards such as landslides and water-induced subsidence. The behavior of loess is controlled by its microstructure, consisting of silt sized
skeleton particles and complex bonding structures formed by clay-sized p... Read more
B. Yu, T.A. Dijkstra, W. Fan, I.J. Smalley, Y.N. Wei, L.S. Deng
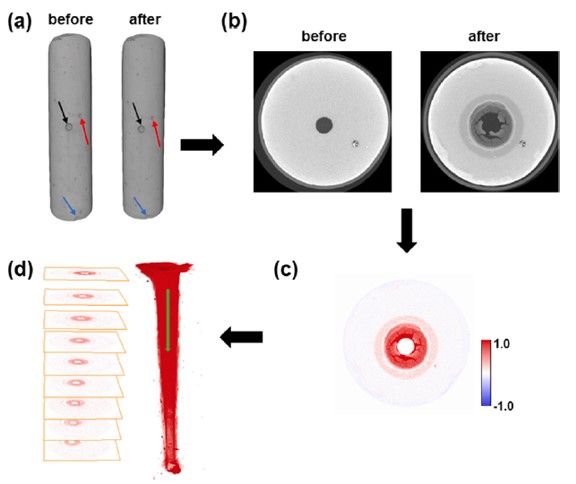
Comparative experimental observations of cement with a flow channel subject to CO2-saturated brine flow by micro-CT scanning and CT image post processing.
Understanding CO2-induced micro-structural changes at the imperfections in wellbore cement is vital for assessing the risk of CO2 leakage through wellbore cement under geologic CO2 storage (GCS) conditions. To investigate the evolution of a flow channel width in cement under GCS conditions and the influence of effective stress and fl... Read more
Manguang Gan, Liwei Zhang, Yan Wang, Kaiyuan Mei, Xiaojuan Fu, Xiaowei Cheng, Mingxing Bai, Hejuan Liu, Xiaochun Li

Paleozoic Nymphal Wing Pads Support Dual Model of Insect Wing Origins
The appearance of wings in insects, early in their evolution [1], has been one of the more critical innovations contributing to their extraordinary diversity. Despite the conspicuousness and importance of wings, the origin of these structures has been difficult to resolve and represented one of the “abominable mysteries” in evolutionary biology [2]. More than a century of debate has boiled the matter down to two competing alternatives—one of wings representing an extension of the thorac... Read more
Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Charles University, Praha, Czech Republic and al.
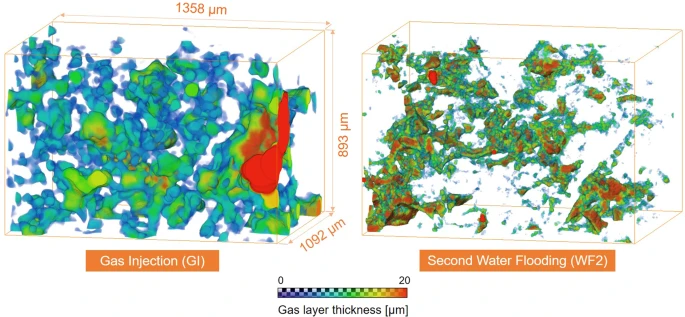
Pore-scale mechanisms of CO2 storage in oilfields
Rapid implementation of global scale carbon capture and storage is required to limit temperature rises to 1.5 °C this century. Depleted oilfields provide an immediate option for storage, since injection infrastructure is in place and there is an economic benefit from enhanced oil recovery. To design secure storage, we need to understand how the fluids are configured in the microscopic pore spaces of the reservoir rock. We use high-resolution X-ray imaging to study the flow of oil, water and ... Read more
Abdulla Alhosani, Alessio Scanziani, Qingyang Lin, Ali Q. Raeini, Branko Bijeljic & Martin J. Blunt
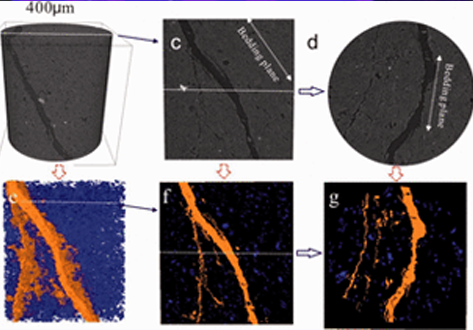
Experimental study on the cracking process of layered shale using X-ray microCT
The cracking process in Longmaxi formation shale was experimentally studied during uniaxial compressive loading. Both the evolution of the three-dimensional fracture network and the micromechanics of failure in the layered shale were examined as a function of the inclination angle of the bedding plane. To visualize the cracking process, the test devices presented here used an industrial X-ray CT scanner that enabled scanning during the uniaxial compressive loading. Scanning electron microscop... Read more
Institue of Geomechanic, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Laboratory of Shale Oil & Gas, Beijing, China
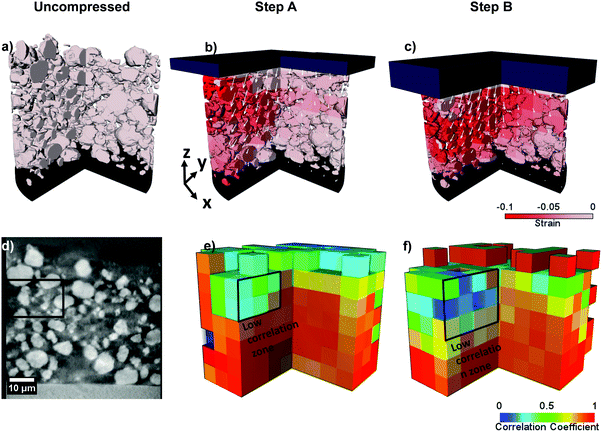
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries operate via electrochemical reactions between positive and negative electrodes, formed by complex porous microstructures. An improved understanding of these materials can lead to a greater insight into the link between microscopic electrode morphology and macroscopic performance. The practice of calendering electrodes after manufacturing has been widely used to increase the volumetric energy density and improve the electrical contact between electrode... Read more
S. R. Daemi,X. Lu, D. Sykes, J. Behnsen, C. Tan, A. Palacios-Padros, J. Cookson, E. Petrucco, P. J. Withers, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
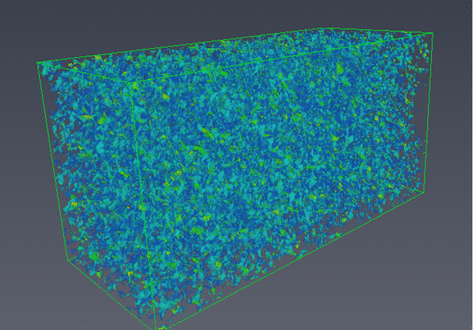
The development of focused ion beam-scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) techniques has allowed high-resolution 3D imaging of nanometre-scale porous materials. These systems are of important interest to the oil and gas sector, as well as for the safe long-term storage of carbon and nuclear waste. This work focuses on validating the accurate representation of sample pore space in FIB-SEM-reconstructed volumes and the predicted permeability of these systems from subsequent single-phase flow s... Read more
Department of Chemical Engineering, Qatar Carbonates and Carbon Storage Research Centre, Imperial College London | Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, Cambridge University
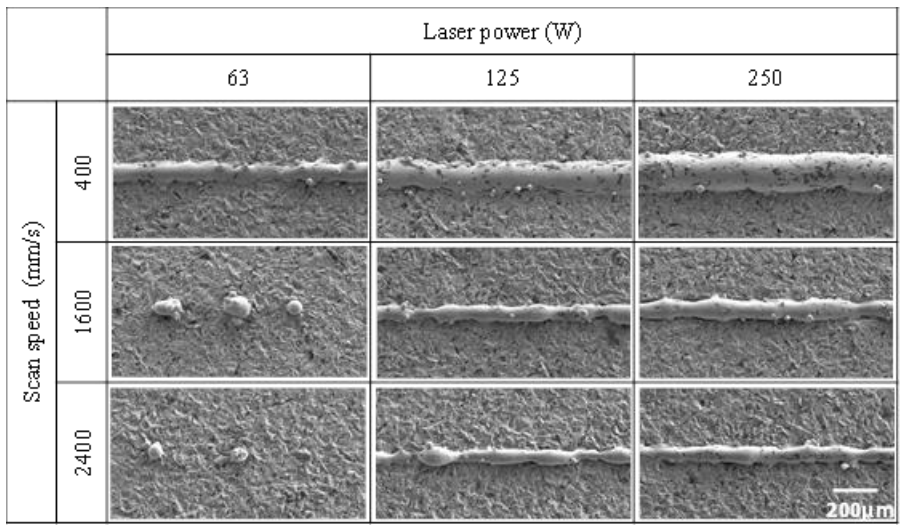
Two-fluid model to simulate metal powder bed fusion additive manufacturing
This paper reports our simulations of the metal powder fusion additive manufacturing process based on a two-fluid model. In simulations of metal behavior in which heat is applied by high-density energy sources (e.g., laser or electron beam), the aspects that need to be correctly modeled include boiling and evaporation, as well as melting and solidification. The potential of the two-fluid model to clarify numerous physical phenomena—deep penetration, plume generation, spatter generation due ... Read more
Noriko WATARI, Yuzuru OGURA, Noriko YAMAZAKI, Yukihiko INOUE, Keisuke KAMITANI, Yasuyuki FUJIYA, Masahiko TOYODA, Saneyuki GOYA, Toshiya WATANABE
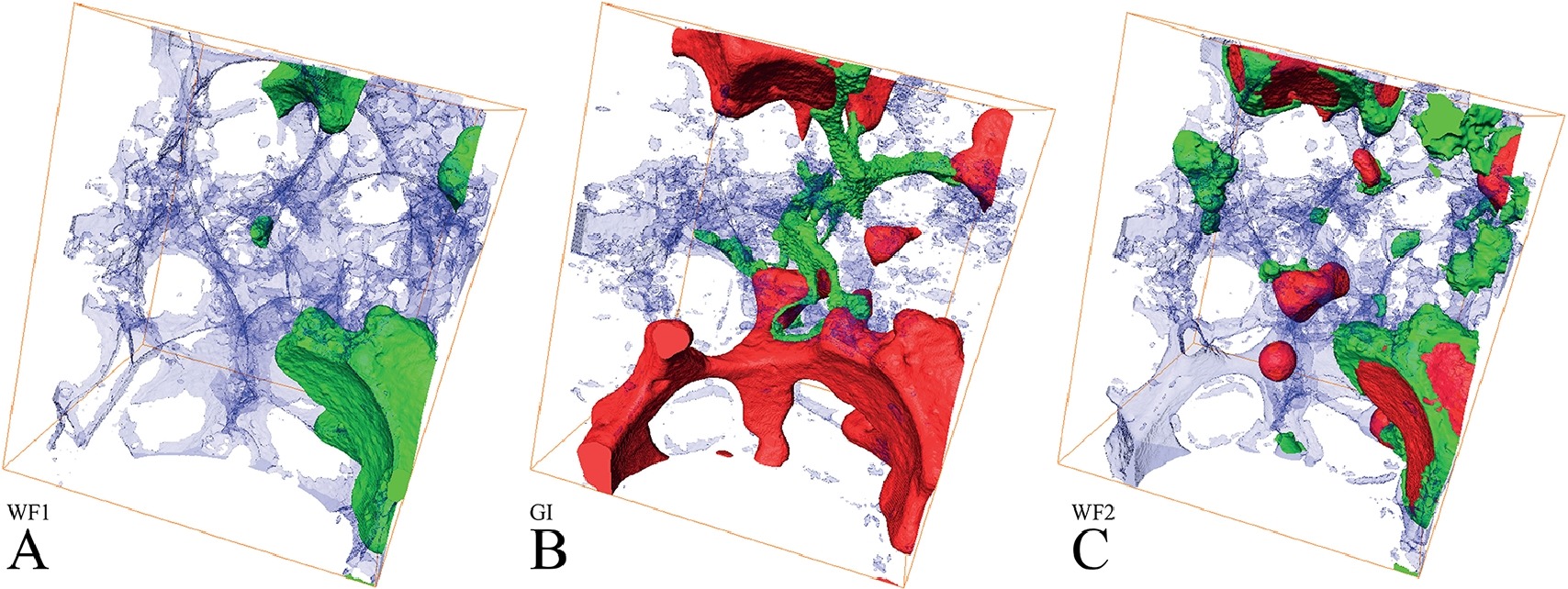
X-ray micro-tomography is used to image the pore-scale configurations of fluid in a rock saturated with three phases – brine, oil and gas – mimicking a subsurface reservoir, at high pressure and temperature. We determine pore occupancy during a displacement sequence that involves waterflooding, gas injection and water re-injection. In the water-wet sample considered, brine occupied the smallest pores, gas the biggest, while oil occupied pores of intermediate size and is displaced ... Read more
Alessio Scanziani, Kamaljit Singh, Tom Bultreys, Branko Bijeljic, Martin J. Blunt
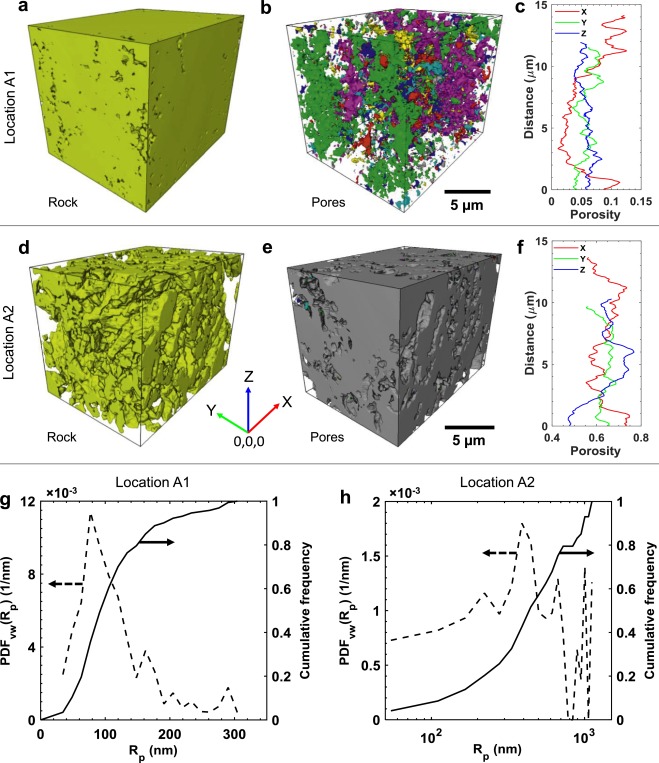
Our novel procedure of injecting oil after reactive transport has revealed previously unidentified (ghost) regions of partially-dissolved grains of carbonate rock. X-ray micro-tomography and FIB-SEM techniques were used to identify and resolve these ghost regions in three-dimensions at the nm- to µm-scale. Considering the solid part of the ghost regions as macro (bulk) pore space can result in the overestimation of porosity and permeability predi... Read more
Kamaljit Singh , Benaiah U. Anabaraonye , Martin J. Blunt , John Crawshaw
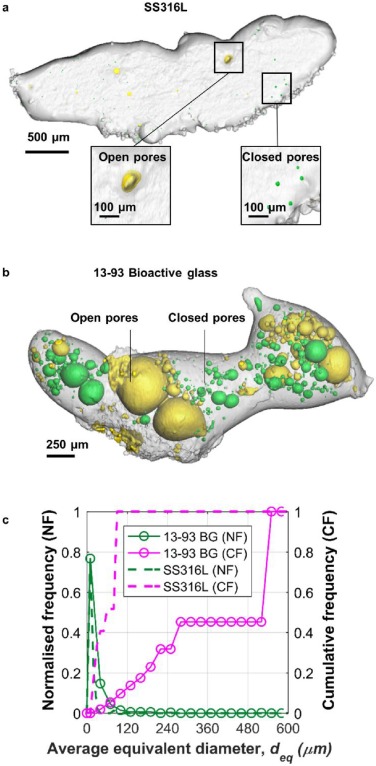
Laser-matter interactions in laser additive manufacturing (LAM) occur on short time scales (10-6 – 10-3 s) and have traditionally proven difficult to characterise. We investigate these interactions during LAM of stainless steel (SS316 L) and 13-93 bioactive glass powders using a custom built LAM process replicator (LAMPR) with in situ and operando synchrotron X-ray radiography. This reveals a range of melt track solidification phenomena as... Read more
Chu Lun Alex Leung, Sebastian Marussi, Michael Towrie, Jesus del Val Garcia, Robert C. Atwood, Andrew J. Bodey, Julian R. Jones, Philip J. Withers, Peter D.Lee
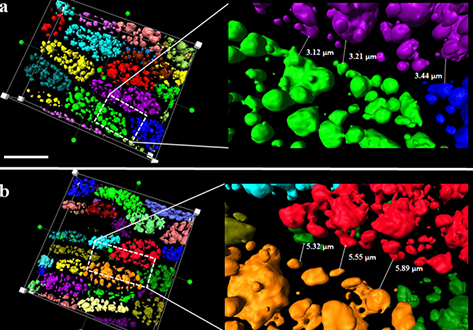
3D Reconstruction of Lipid Droplets in the Seed of Brassica napus
Rapeseed is one of the most important and widely cultured oilseed crops for food and nonfood purposes worldwide. Neutral lipids are stored in lipid droplets (LDs) as fuel for germination and subsequent seedling growth. Most of the LD detection in seeds was still in 2D levels, and some of the details might have been lost in previous studies. In the present work, the configuration of LDs in seeds was obtained by confocal imaging combined with 3D reconstruction technology in Brassica napus<... Read more
Yongtai Yin, Liangxing Guo, Kang Chen, Zhenyi Guo, Hongbo Chao, Baoshan Wang, and Maoteng Licorresponding author
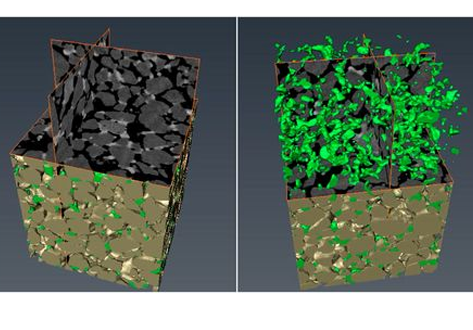
We introduce the application of microbial-induced calcite precipitation via the ureolytic soil bacterium Sporosarcina Pasteurii in freeze-dried form, as a means of enhancing overall MICP efficiency and reproducibility for geotechnical engineering applications. We show that the execution of urea hydrolysis and CaCO3 precipitation persist as a “cell-free” mechanism upon the complete breakdown of rehydrated cell clusters. Further, strength and stiffness parameters of bio-cemented ... Read more
Dimitrios Terzis, Lyesse Laloui
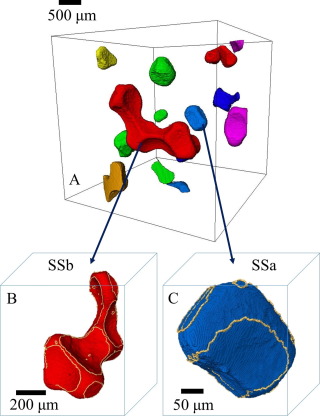
Multiphase flow in porous media is strongly influenced by the wettability of the system, which affects the arrangement of the interfaces of different phases residing in the pores.
We present a method for estimating the effective contact angle, which quantifies the wettability and controls the local capillary pressure within the complex pore space of natural rock samples, based on the physical constraint of constant curvature of the interface between two fluids. This algorithm is ... Read more
Alessio Scanziani, Kamaljit Singh, Martin J. Blunt, Alberto Guadagnini
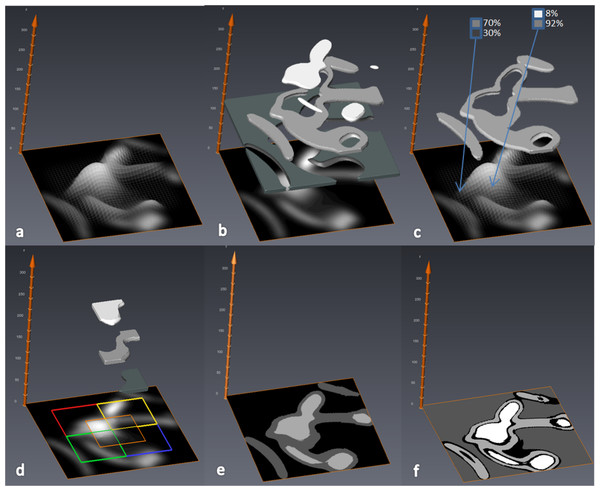
MIA-Clustering: a novel method for segmentation of paleontological material
Paleontological research increasingly uses high-resolution micro-computed tomography (μCT) to study the inner architecture of modern and fossil bone material to answer important questions regarding vertebrate evolution. This non-destructive method allows for the measurement of otherwise inaccessible morphology. Digital measurement is predicated on the accurate segmentation of modern or fossilized bone from other structures imaged in μCT scans, as errors in segmentation can result in inaccur... Read more
Christopher J. Dunmore, Gert Wollny, Matthew M. Skinner