Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
Hot-wire arc additive manufacturing of aluminum alloy with reduced porosity and high deposition rate
Wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) technology has attracted considerable interest in large-scale metallic components, but porosity and low deposition rate are the two dominating technical challenges in WAAM of aluminum alloy. In order to effectively solve these problems, a novel method of hot-wire arc additive manufacturing is used to fabricate aluminum alloy. Systematic studies are carried out to investigate the formation mechanism of the pores, the macro/microstructures, as well as the ... Read more
Rui Fu, Shuiyuan Tang, Jiping Lu, Yinan Cui, Zixiang Li, Haoru Zhang, Tianqiu Xu, Zhuo Chen, Changmeng Liu
Porosity and Structure of Hierarchically Porous Ni/Al2O3 Catalysts for CO2 Methanation
Carbon dioxide emissions must be reduced significantly to limit the negative consequences of climate change. For this reason, fossil fuels must be replaced by renewable energy sources. However, wind and solar energy, for example, are sporadic sources and, thus, not inevitably available when needed. This results in periods of energy surplus and shortage, which are not necessarily predictable. Hence, energy storage concepts are required to compensate for these fluctuations, thereby retaining en... Read more
Sebastian Weber, Ken L. Abel, Ronny T. Zimmermann, Xiaohui Huang, Jens Bremer, Liisa K. Rihko-Struckmann, Darren Batey, Silvia Cipiccia, Juliane Titus, David Poppitz, Christian Kübel, Kai Sundmacher, Roger Gläser, Thomas L. Sheppard

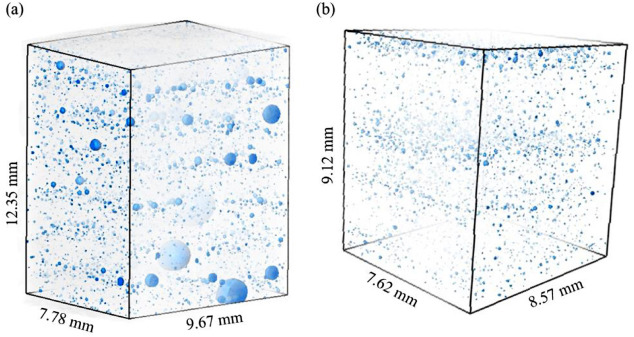
Defect structure process maps for laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing
Accurate detection, characterization, and prediction of defects has great potential for immediate impact in the production of fully-dense and defect free metal additive manufacturing (AM) builds. Accordingly, this paper presents Defect Structure Process Maps (DSPMs) as a means of quantifying the role of porosity as an exemplary defect structure in powder bed printed materials. Synchrotron-based micro-computed tomography (μSXCT) was used to demonstrate that metal AM defects follow predictable... Read more
Jerard V.Gordon, Sneha P.Narra, Ross W.Cunningham, He Liu, Hangman Chen, Robert M.Suter, Jack L.Beuth, Anthony D.Rollett
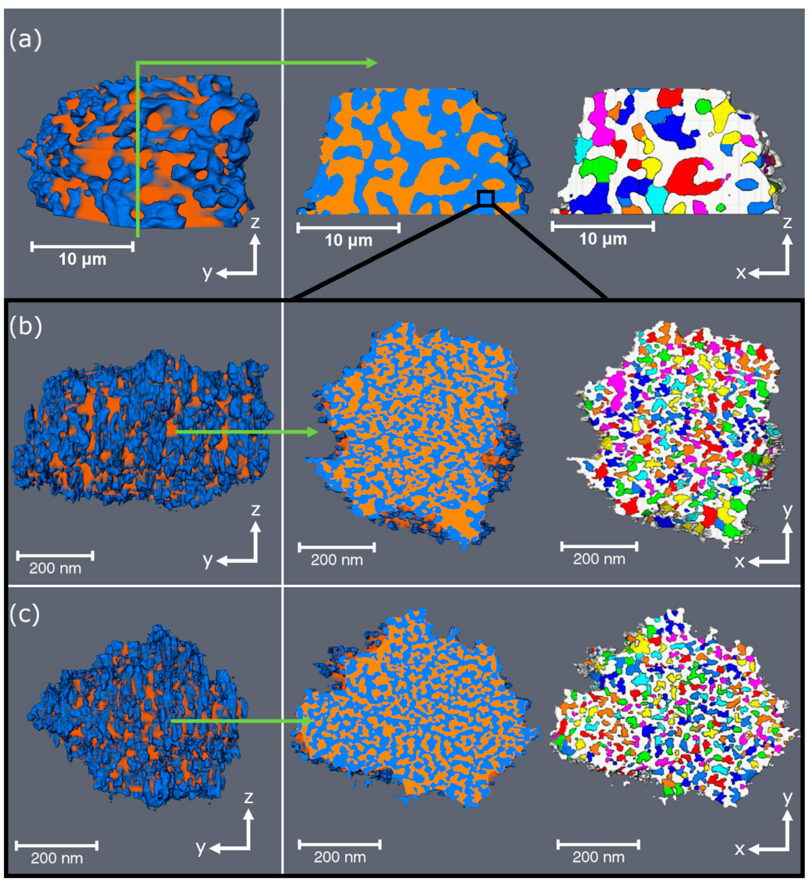
A virtual testing platform for filter materials and textile masks
In order to provide the population with consistent and science-based advice on preferred materials for face masks, we are characterizing the microstructure of different materials using X-ray microfocus computed tomography (microCT), and we use these datasets to simulate the pressure drop (i.e. measure for breathability). We validate our measurements with physically measured filter efficiency and pressure drop, and in this way, we try to develop a “virtual testing platform” for the charac... Read more
The ContrasTTeam of Prof. dr. Greet Kerckhofs, UCLouvain and MTM
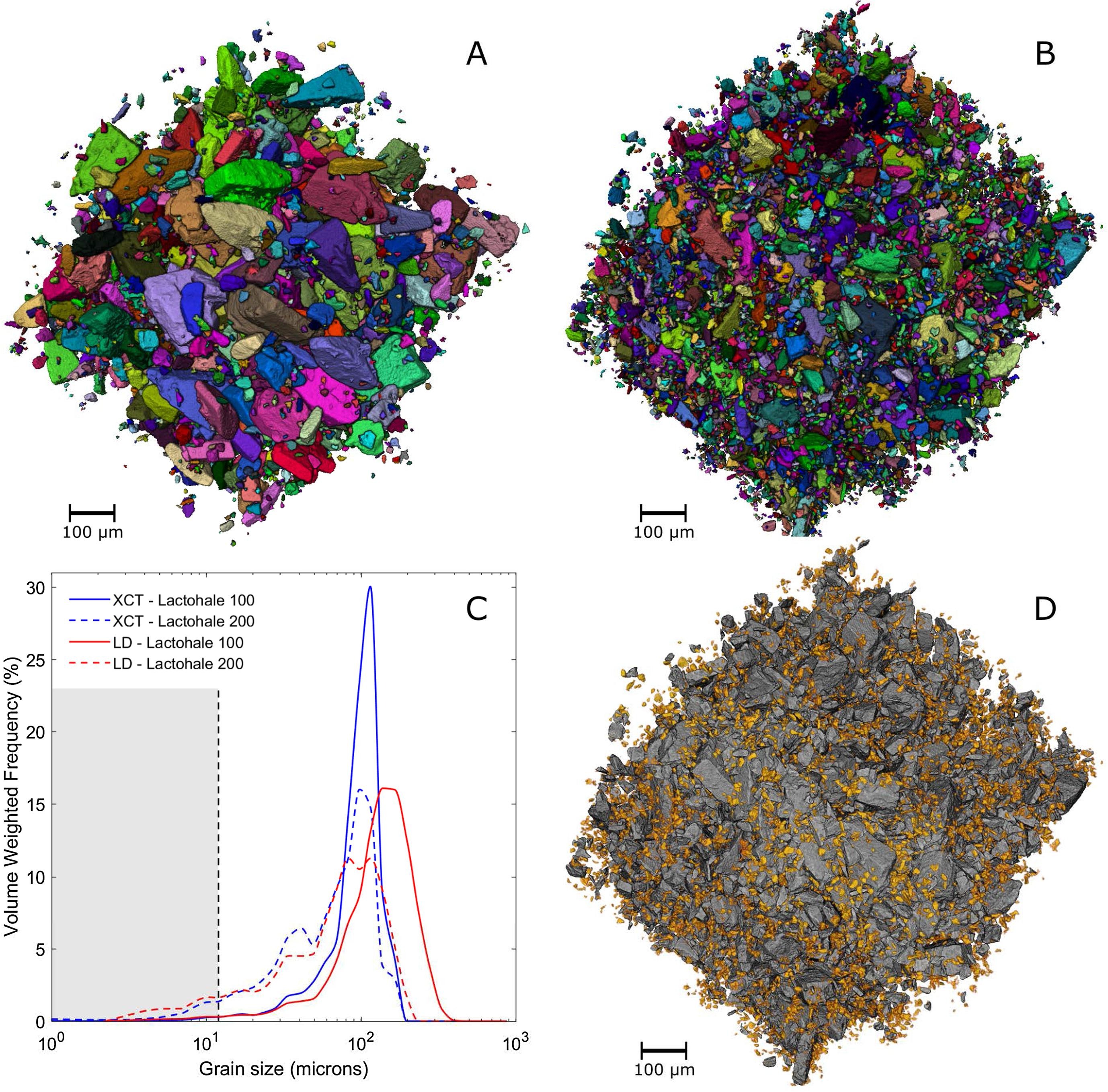
3D characterisation of dry powder inhaler formulations
Carrier-based dry powder inhaler (DPI) formulations need to be accurately characterised for their particle size distributions, surface roughnesses, fines contents and flow properties. Understanding the micro-structure of the powder formulation is crucial, yet current characterisation methods give incomplete information. Commonly used techniques like laser diffraction (LD) and optical microscopy (OM) are limited due to the assumption of sphericity and can give variable results depending on par... Read more
P. Gajjar, I.D. Styliari, T.T.H. Nguyen, J. Carr, X. Chen, J.A. Elliott, R.B. Hammond, T.L. Burnett, K. Roberts, P.J. Withers, D.Murnane
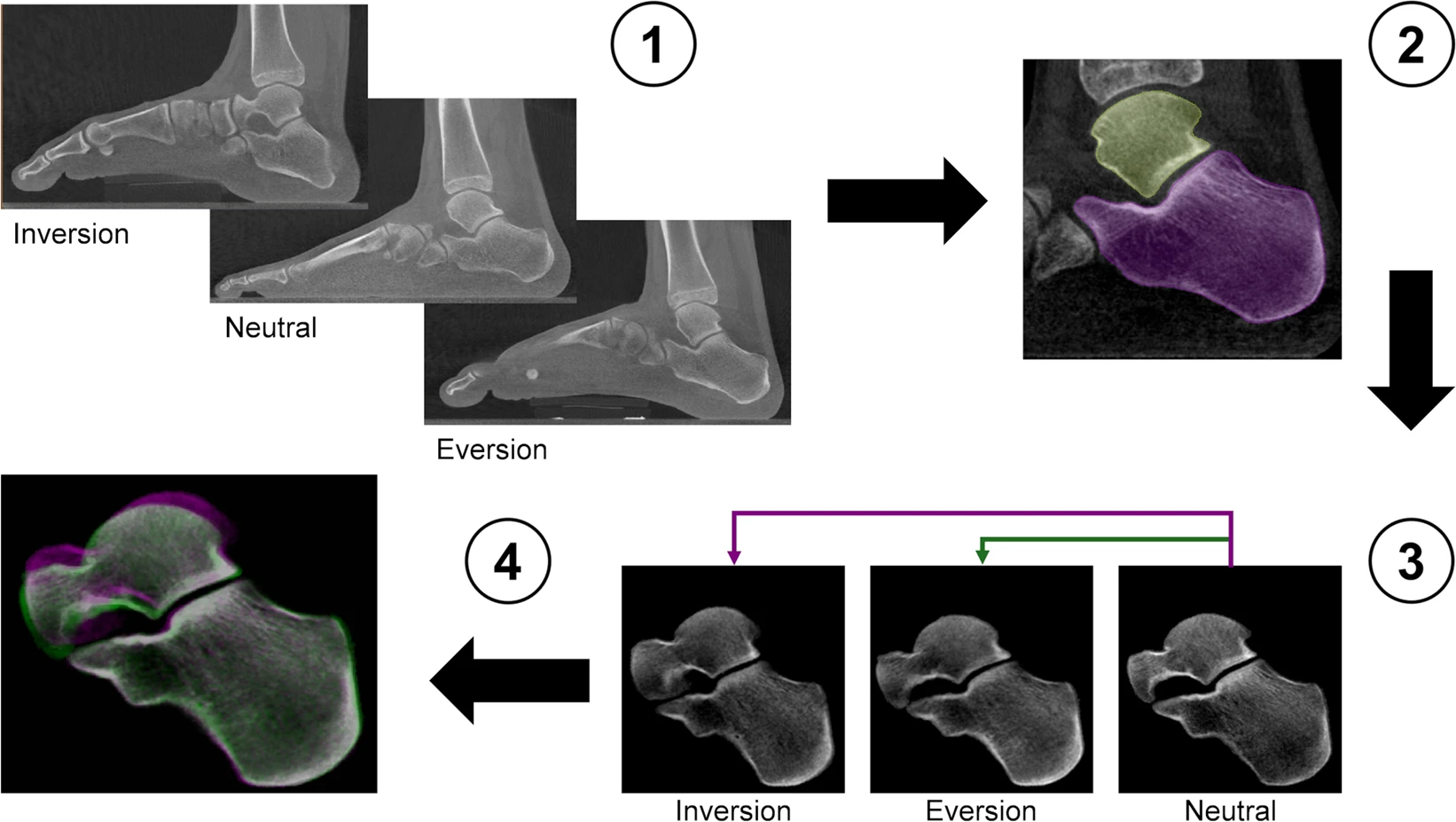
Centre of Rotation of the Human Subtalar Joint Using Weight-Bearing Clinical Computed Tomography
The subtalar joint describes an articulation between talus and calcaneus, forming one of two joints of the hindfoot with the tibiotalar or ankle joint above the talus and the subtalar joint below. The talus comprises of three facets (anterior, middle and posterior) that articulate with the mating facets on the calcaneus at the subtalar joint. The bones are connected by a complex of ligamentous structures that connect the talus to the calcaneus and both structures to the adjacent navicular bon... Read more
Marta Peña Fernández, Dorela Hoxha, Oliver Chan, Simon Mordecai, Gordon W. Blunn, Gianluca Tozzi & Andy Goldberg
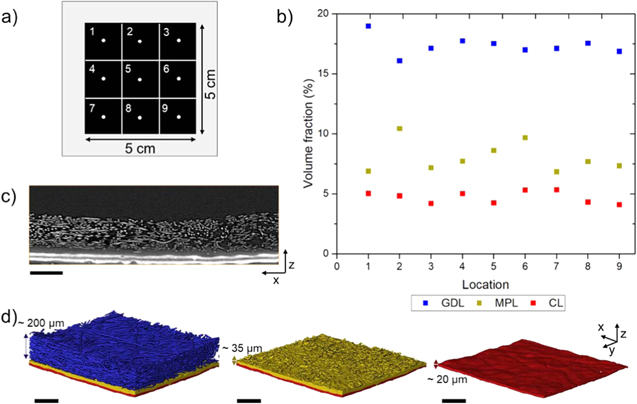
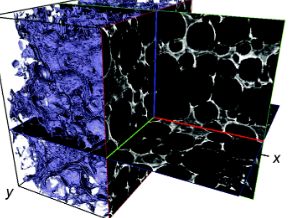
With the growing use of X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) datasets for modelling of transport properties, comes the need to define the representative elementary volume (REV) if considering three dimensions or the representative elementary area (REA) if considering two dimensions. The resolution used for imaging must be suited to the features of interest in the sample and the region-of-interest must be sufficiently large to capture key information. Polymer electrolyte fuel cells have a hier... Read more
Jennifer Hack et al 2020 J. Electrochem.
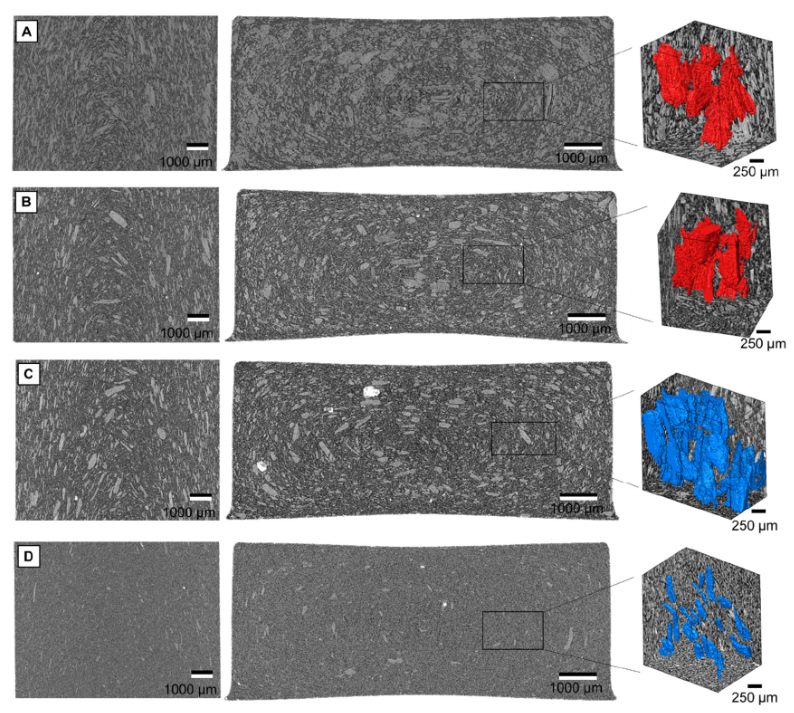
The microstructure morphologies have been characterized by high resolution laboratory X-ray computed tomography in Carbon Fiber Reinforced Carbon and Silicon Carbide (C/C-SiC) ceramic composites fabricated by Gaseous Silicon Infiltration (GSI) from C/C preforms of three different architectures: 3D stitched cloth fabric; 3D orthogonal woven fabric; and needled short-cut felt. Each composites’ microstructure was influenced by the structure of the C/C preform. By incorporating tomography with ... Read more
Fan Wan, Talha, J. Pirzada, Rongjun Liu, Yanfei Wang, Changrui Zhang, Thomas James Marrow
In this study, various wood material sources were used for the manufacture of wood-polymer composites (WPC). The materials were categorised as virgin wood particles (VWP), reprocessed WPC particles (RWP) and recycled thermoset composite particles (RCP) and derived from two virgin wood sources, three-layer particle boards, medium-density fibre boards (MDF) boards,or two different wood/polypropylene composites. All produced wood-polypropylene compounds contained 60% wood material and were manu... Read more
Kim Christian Krause, D, Philipp Sauerbier, Tim Koddenberg and Andreas Krause
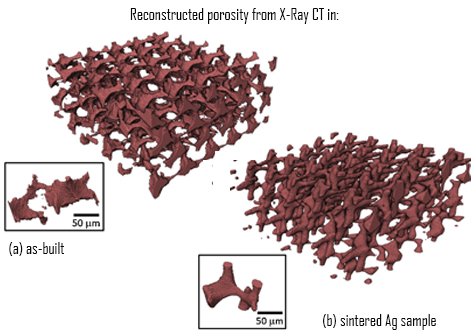
Towards digital metal additive manufacturing via high-temperature drop-on-demand jetting
Drop-on-demand jetting of metals offers a fully digital manufacturing approach to surpass the limitations of the current generation powder-based additive manufacturing technologies. However, research on this topic has been restricted mainly to near-net shaping of relatively low melting temperature metals. Here it is proposed a novel approach to jet molten metals at high-temperatures (>1000 °C) to enable the direct digital additive fabrication of micro- to macro-scale objects. […] ... Read more
Marco Simonelli, Nesma Aboulkhair, Mircea Rasa, Mark East, Chris Tuck, Ricky Wildman, Otto Salomons, Richard Hague
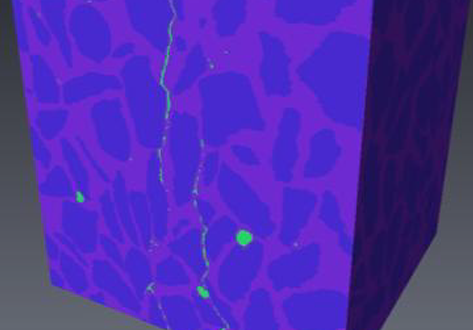
X-ray Computed Tomography (XCT) is a powerful technology that can accurately image the internal structures of composite and heterogeneous materials in three-dimensions (3D). In this study, in-situ micro XCT tests of concrete specimens under progressive compressive loading are carried out. The aim of the observations is to gain a better understanding of 3D fracture and failure mechanisms at the meso-scale. To characterise the fracture evolution as the deformation increases, two methods are use... Read more
College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Zhejiang University | School of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering, the University of Manchester | Manchester X-ray Imaging Facility | Oxford Martin School and Department of Materials
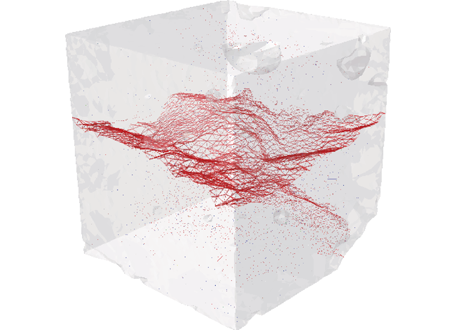
Three-Dimensional In Situ XCT Characterisation and FE Modelling of Cracking in Concrete
An improved understanding of 3D cracking in concrete can be achieved by multiscale experiments and numerical modelling based on realistic microstructures, for the development of materials with higher strength, durability, and fracture resistance.
Three-dimensional (3D) characterisation and modelling of cracking in concrete have been always of great importance and interest in civil engineering. In this study, an in situ microscale X-ray computed tomography (XCT) test was carried out to ... Read more
Wenyuan Ren, Zhenjun Yang, Rajneesh Sharma, Samuel A. McDonald, Paul M. Mummery
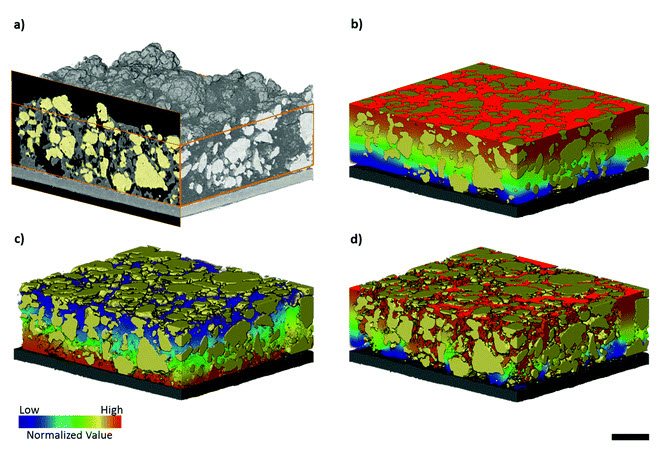
Three-dimensional image based modelling of transport parameters in lithium–sulfur batteries
An elemental sulfur electrode was imaged with X-ray micro and nano computed tomography and segmented into its constituent phases. Morphological parameters including phase fractions and pore and particle size distributions were calculated directly from labelled image data, and flux based simulations were performed to determine the effective molecular diffusivity of the pore phase and electrical conductivity of the conductive carbon and binder phase, D... Read more
Chun Tan, Matthew D. R. Kok , Sohrab R. Daemi , Daniel J. L. Brett and Paul R. Shearing
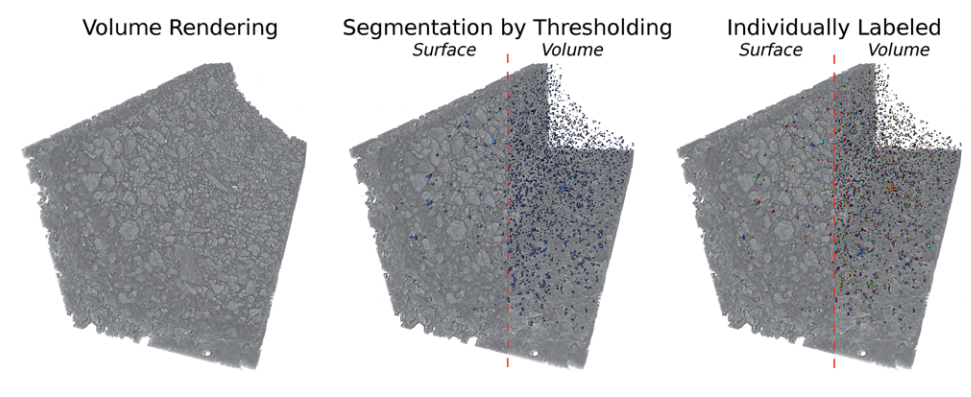
Biodegradable materials, such as collagen scaffolds, are used extensively in clinical medicine for tissue regeneration and/or as an implantable drug delivery vehicle. However, available methods to study biomaterial degradation are typically invasive, destructive, and/or non-volumetric. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate a new method for nondestructive, longitudinal, and volumetric measurement of collagen scaffold degradation. Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) were covalently ... Read more
Tyler A. Finamore, Tyler E. Curtis, James V. Tedesco, Kathryn Grandfield, Ryan K. Roeder
Aging of a Pt/Al2O3 exhaust gas catalyst monitored by quasi in situ X-ray micro computed tomography
Catalyst aging effects were analyzed using X-ray absorption micro-computed tomography in combination with conventional characterization methods on various length scales ranging from nm to μm to gain insight into deactivation mechanisms.
For this purpose, a 4 wt% Pt/Al2O3 model exhaust gas catalyst was coated on a cordierite honeycomb and subjected to sequential thermal aging in static air at 950 °C for 4, 8, 12 and 24 hours. The ag... Read more
Georg Hofmann, Amélie Rochet, Elen Ogel, Maria Casapu, Stephan Ritter, Malte Ogurreck and Jan-Dierk Grunwaldt

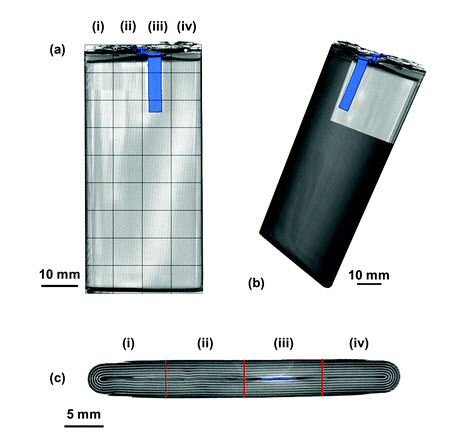
Visualizing the Carbon Binder Phase of Battery Electrodes in Three Dimensions
This study presents a technique to directly characterize the carbon and binder domain (CBD) in lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery electrodes in three dimensions and use it to determine the effective transport properties of a LiNi0.33Mn0.33Co0.33O2 (NMC) electrode. X-ray nanocomputed tomography (nano-CT) is used to image an electrode composed solely of carbon and binder, whereas focused ion beam–scanning electron microscopy is used to analyze cross-sect... Read more
Sohrab R. Daemi, Chun Tan, Tobias Volkenandt, Samuel J. Cooper, Anna Palacios-Padros, James Cookson, Dan J. L. Brett, and Paul R. Shearing
Spatially resolved ultrasound diagnostics of Li-ion battery electrodes
The importance of reliable battery diagnostic systems has grown substantially in recent years as a result of the use of high power Li-ion battery packs in an increasingly diverse range of applications. Here, spatially resolved ultrasound acoustic measurements are used to analyse the condition of Li-ion electrodes. Ultrasonic measurements are performed on a commercial mobile phone battery over the full operating voltage window with the lithiation and delithiation of electrodes o... Read more
James B. Robinson, Maximilian Maier , George Alster , Tomos Compton , Dan J. L. Brett and Paul R. Shearing
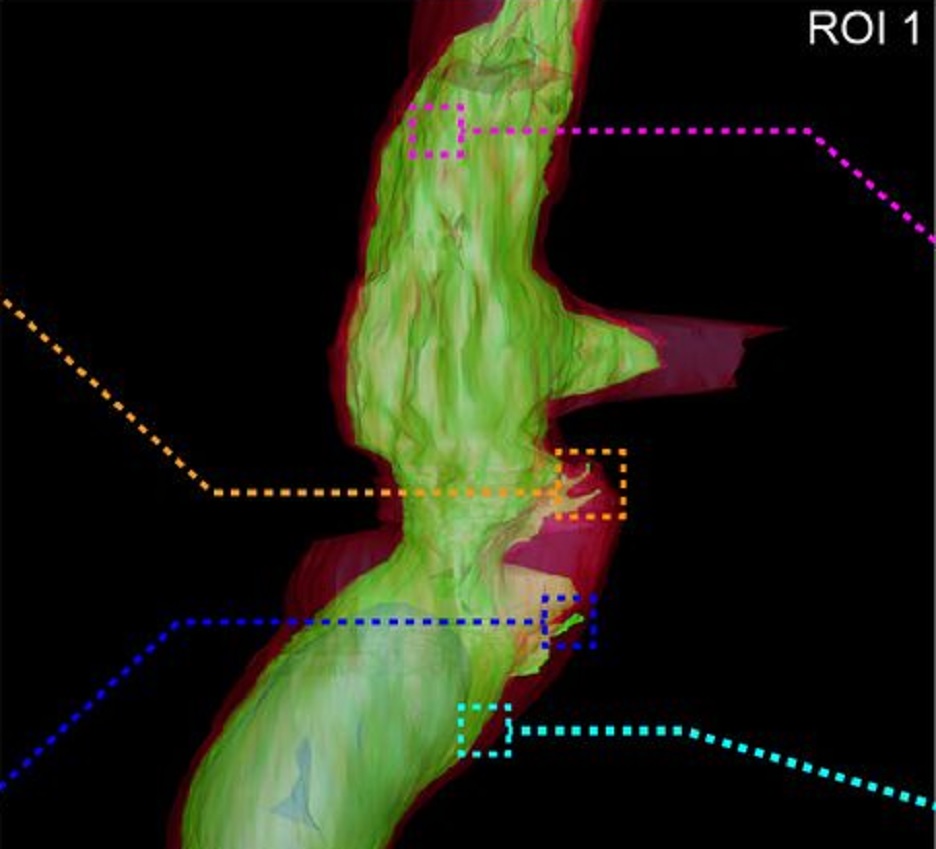
Fast and precise targeting of single tumor cells in vivo by multimodal correlative microscopy
Intravital microscopy provides dynamic understanding of multiple cell biological processes, but its limited resolution has so far precluded structural analysis. Because it is difficult to capture rare and transient events, only a few attempts have been made to observe specific developmental and pathological processes in animal models using electron microscopy. The multimodal correlative approach that we propose here combines intravital microscopy, microscopic X-ray computed tomography and thr... Read more
Matthia A. Karreman, Luc Mercier, Nicole L. Schieber, Gergely Solecki, Guillaume Allio, Frank Winkler, Bernhard Ruthensteiner, Jacky G. Goetz, Yannick Schwab
In biomedical research, a huge variety of different techniques is currently available for the structural examination of small specimens, including conventional light microscopy (LM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), microscopic X-ray computed tomography (microCT), and many others. Since every imaging method is physically limited by certain parameters, a correlative use of complementary methods often yields a significant broader range of inform... Read more
Stephan Handschuh, Natalie Baeumler, Thomas Schwaha and Bernhard Ruthensteiner
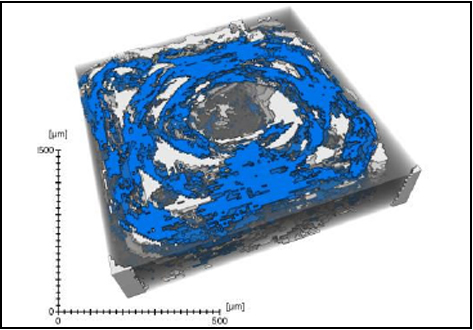
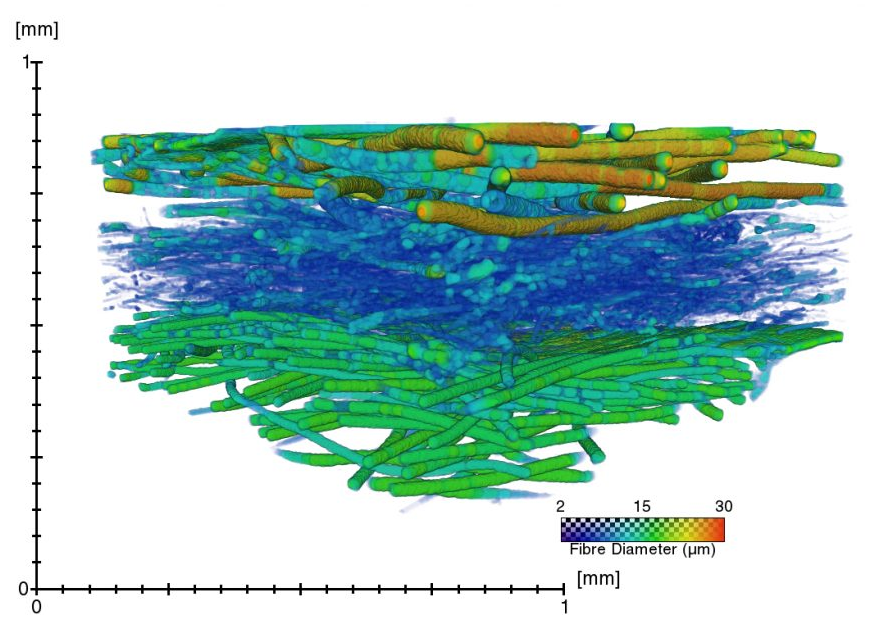
Defect detection in 3D printed carbon fibre composites using X-ray Computed Tomography
X-ray Computed Tomography (X-ray CT) has become a vital tool for product quality inspection. The X-ray CT analysis of 3D printed composites, with a layer-by-layer structure of carbon fibre/polyamide and polyamide plies, demonstrates how the void content increases with an increasing number of consecutive carbon fibre layers. Not only the void content, but also the pore
network complexity increases, as more pore types are introduced into the sample. The PolyAmide (PA) matrix has an averag... Read more
Jeroen Soete1, Brice Badoux, Yentl Swolfs, Larissa Gorbatikh, Martine Wevers
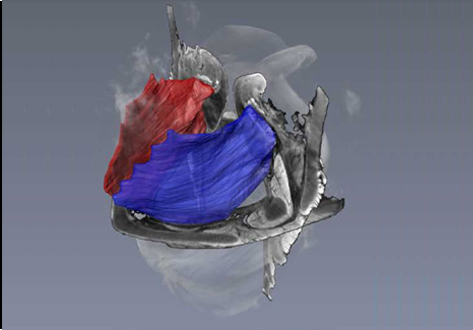
Juvenile Ovine Ex Vivo Larynges: Phonatory, Histologic, and Micro CT Based Anatomic Analyses
It is well known that the phonatory process changes during the life span. However, detailed investigations on potential factors concerned are rare. To deal with this issue, we performed extended biomechanical, macro anatomical, and histological analyses of the contributing laryngeal structures in ex vivo juvenile sheep models. Altogether twelve juvenile sheep larynges were analyzed within the phonatory experiments. Three different elongation levels and 16 different flow levels were applied to... Read more
Michael Döllinger, Olaf Wendler, Claus Gerstenberger, Tanja Grossmann, Marion Semmler, Hossein Sadeghi, and Markus Gugatschka