Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
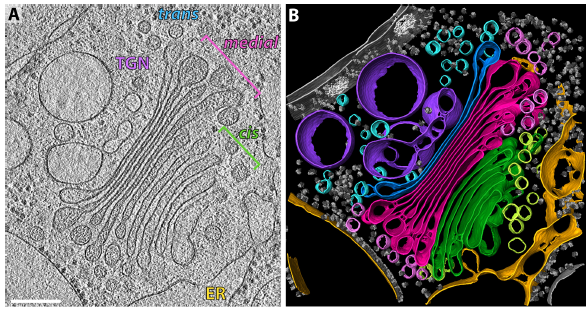
The structure of the COPI coat determined within the cell
COPI-coated vesicles mediate trafficking within the Golgi apparatus and from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum. Here, we applied cryo-focused ion beam milling, cryo-electron tomography and subtomogram averaging to determine the native structure of the COPI coat within vitrified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells. The native algal structure resembles the in vitro mammalian structure, but additionally reveals cargo bound beneath beta’–COP. We find that all coat components disassemble... Read more
Yury S Bykov, Miroslava Schaffer, Svetlana O Dodonova, Sahradha Albert, Jurgen M Plitzko, Wolfgang Baumeister, Benjamin D Engel, John AG Briggs
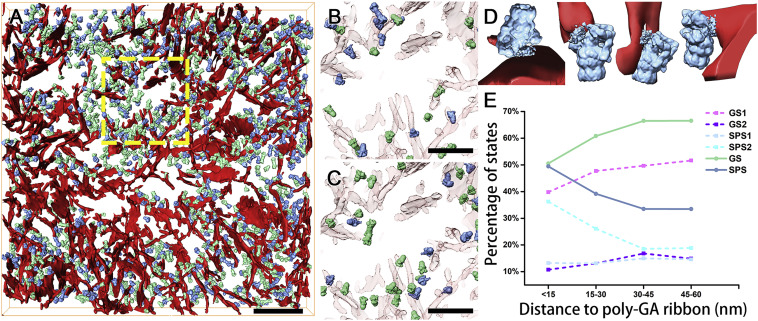
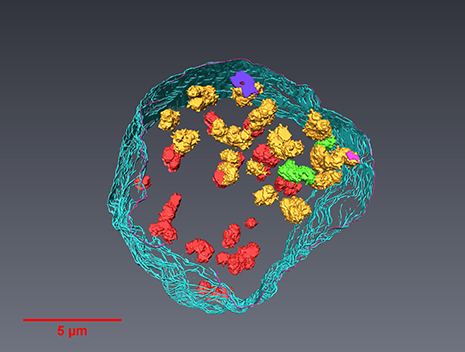
In Situ Structure of Neuronal C9orf72 Poly-GA Aggregates Reveals Proteasome Recruitment
Protein aggregation and dysfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system are hallmarks of many neurodegenerative diseases. Here, we address the elusive link between these phenomena by employing cryo-electron tomography to dissect the molecular architecture of protein aggregates within intact neurons at high resolution. We focus on the poly-Gly-Ala (poly-GA) aggregates resulting from aberrant translation of an expanded GGGGCC repeat in C9orf72, the most common genetic cause of amyotrophic latera... Read more
Qiang Guo, Carina Lehmer, Antonio Martinez-Sanchez, Till Rudack, Florian Beck, Hannelore Hartmann, Manuela Perez-Berlanga, Frederic Frottin, Mark S.Hipp, F. Ulrich Hartl, Dieter Edbauer, Wolfgang Baumeister, Ruben Fernandez-Busnadiego
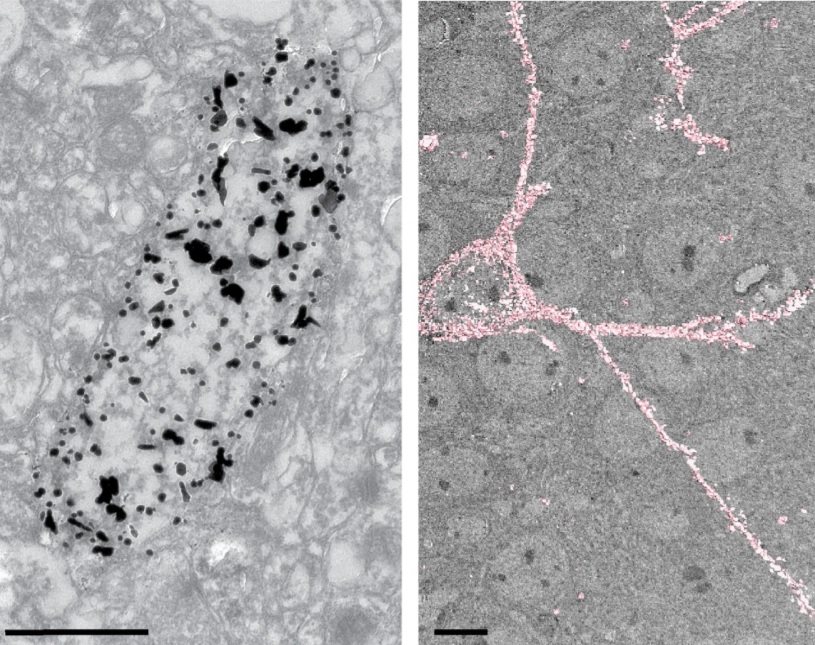
Analysis of neuronal arborization and connections is a powerful tool in fundamental and clinical neuroscience. Changes in neuronal morphology are central to brain development and plasticity and are associated with numerous diseases. Golgi staining is a classical technique based on a deposition of metal precipitate in a random set of neurons. Despite their versatility, Golgi methods have limitations that largely precluded their use in advanced microscopy. We combined Golgi staining with fluore... Read more
Katlijn Vints, Dorien Vandael, Pieter Baatsen, Benjamin Pavie, Frank Vernaillen, Nikky Corthout, Vasily Rybakin, Sebastian Munck & Natalia V. Gounko

Cell-type specific innervation of cortical pyramidal cells at their apical tufts
We investigated the synaptic innervation of apical tufts of cortical pyramidal cells in a region between layers 1 and 2 using 3-D electron microscopy (3D-EM) applied to four cortical regions in mouse. Across all cortices, we found the relative inhibitory input at the apical dendrite’s main bifurcation to be more than 3-fold stronger for layer 2 pyramidal cells than for all other pyramidal cells. Towards the distal tuft dendrites in upper layer 1, however, the relative inhibitory input was a... Read more
Ali Karimi, Jan Odenthal, Florian Drawitsch, Kevin M. Boergens, Moritz Helmstaedter
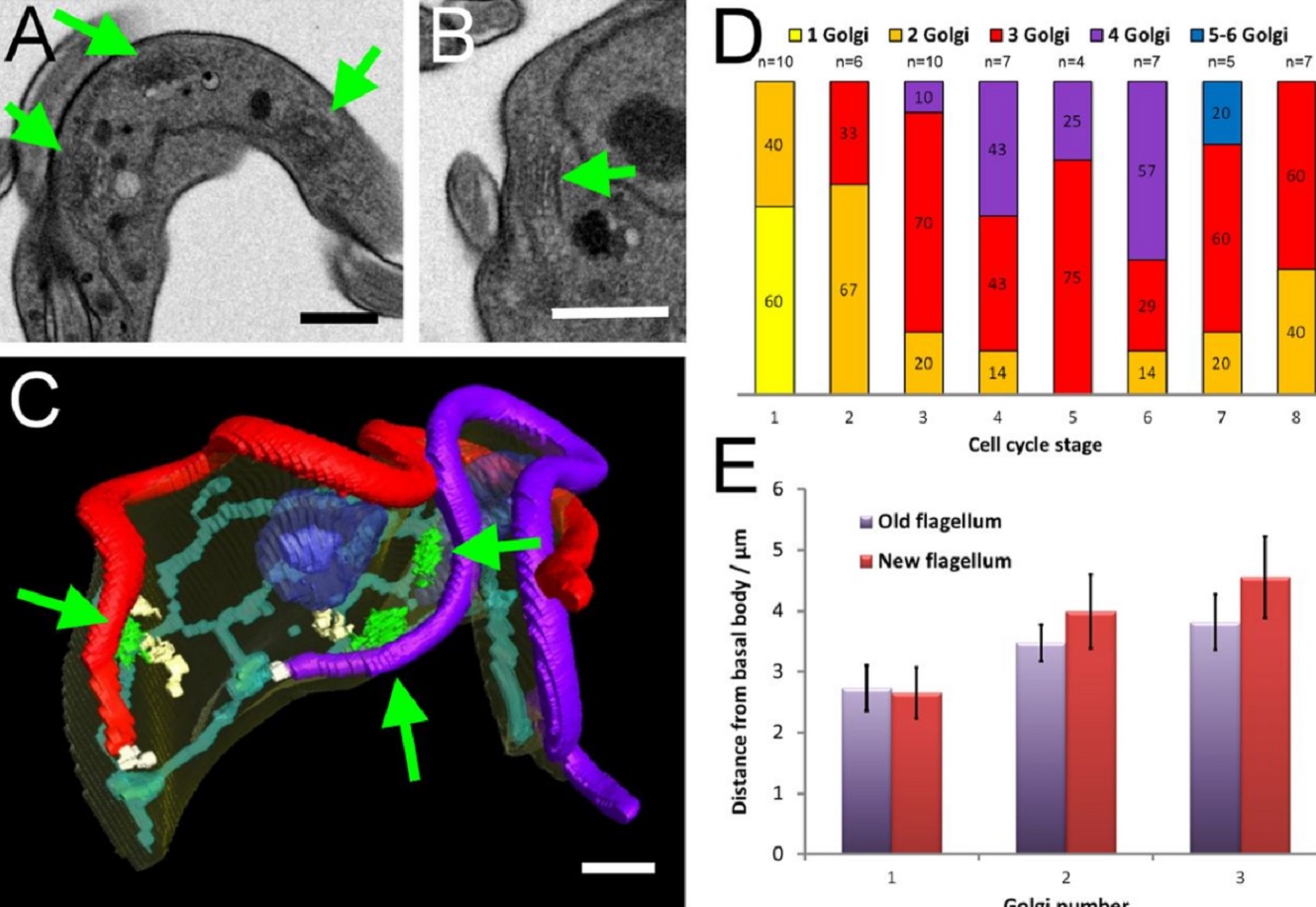
The major mammalian bloodstream form of the African sleeping sickness parasite Trypanosoma bruceimultiplies rapidly, and it is important to understand how these cells divide. Organelle inheritance involves complex spatiotemporal re-arrangements to ensure correct distribution to daughter cells…
Read more
Louise Hughes, Samantha Borrett, Katie Towers, Tobias Starborg, Sue Vaughan
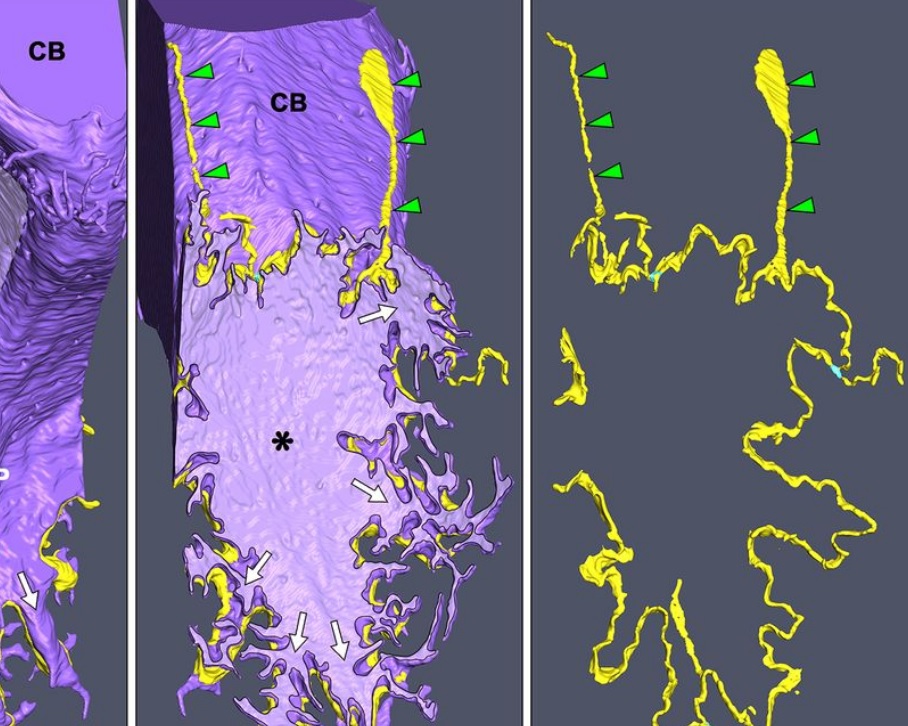
Morphological process of podocyte development revealed by block-face scanning electron microscopy
Podocytes present a unique 3D architecture specialized for glomerular filtration. However, several 3D morphological aspects on podocyte development remain partially understood because they are difficult to reveal using conventional scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Here, we adopted serial block-face SEM imaging…
Read more
Koichiro Ichimura, Soichiro Kakuta, Yuto Kawasaki, Takayuki Miyaki, Takahiro Nonami, Naoyuki Miyazaki, Tomoyo Nakao, Sakiko Enomoto, Shigeo Arai, Masato Koike, Kazuyoshi Murata, Tatsuo Sakai
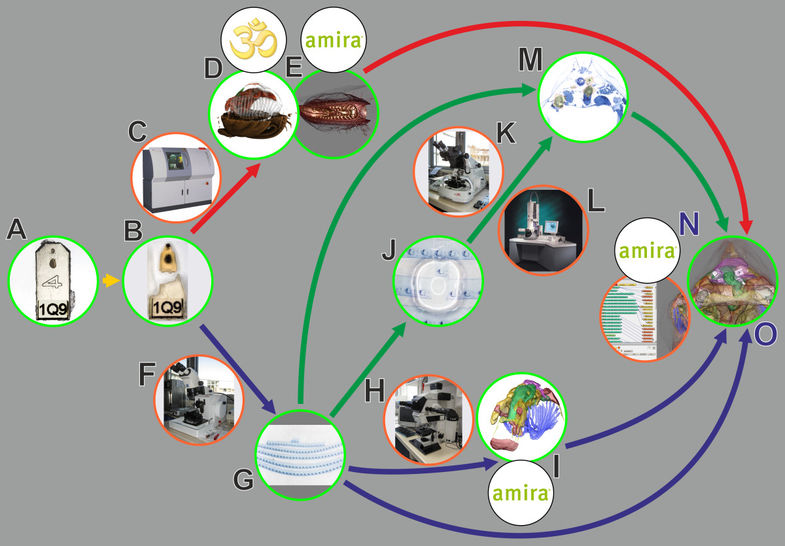
In biomedical research, a huge variety of different techniques is currently available for the structural examination of small specimens, including conventional light microscopy (LM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), microscopic X-ray computed tomography (microCT), and many others. Since every imaging method is physically limited by certain parameters, a correlative use of complementary methods often yields a significant broader range of inform... Read more
Stephan Handschuh, Natalie Baeumler, Thomas Schwaha and Bernhard Ruthensteiner
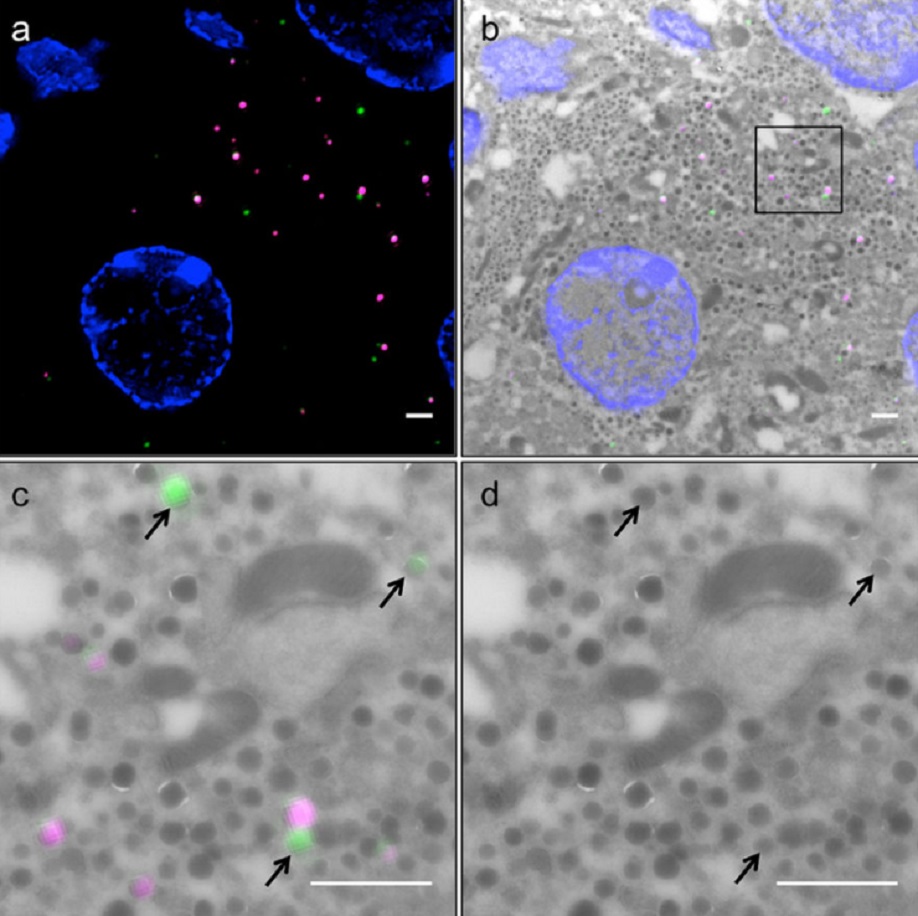
Correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM) is a powerful approach to investigate the molecular ultrastructure of labeled cell compartments. However, quantitative CLEM studies are rare, mainly due to small sample sizes and the sensitivity of fluorescent proteins to strong fixatives and contrasting reagents for EM. Here, we show that fusion of…
Read more
Andreas Müller, Martin Neukam, Anna Ivanova, Anke Sönmez, Carla Münster, Susanne Kretschmar, Yannis Kalaidzidis, Thomas Kurth, Jean-Marc Verbavatz & Michele Solimena
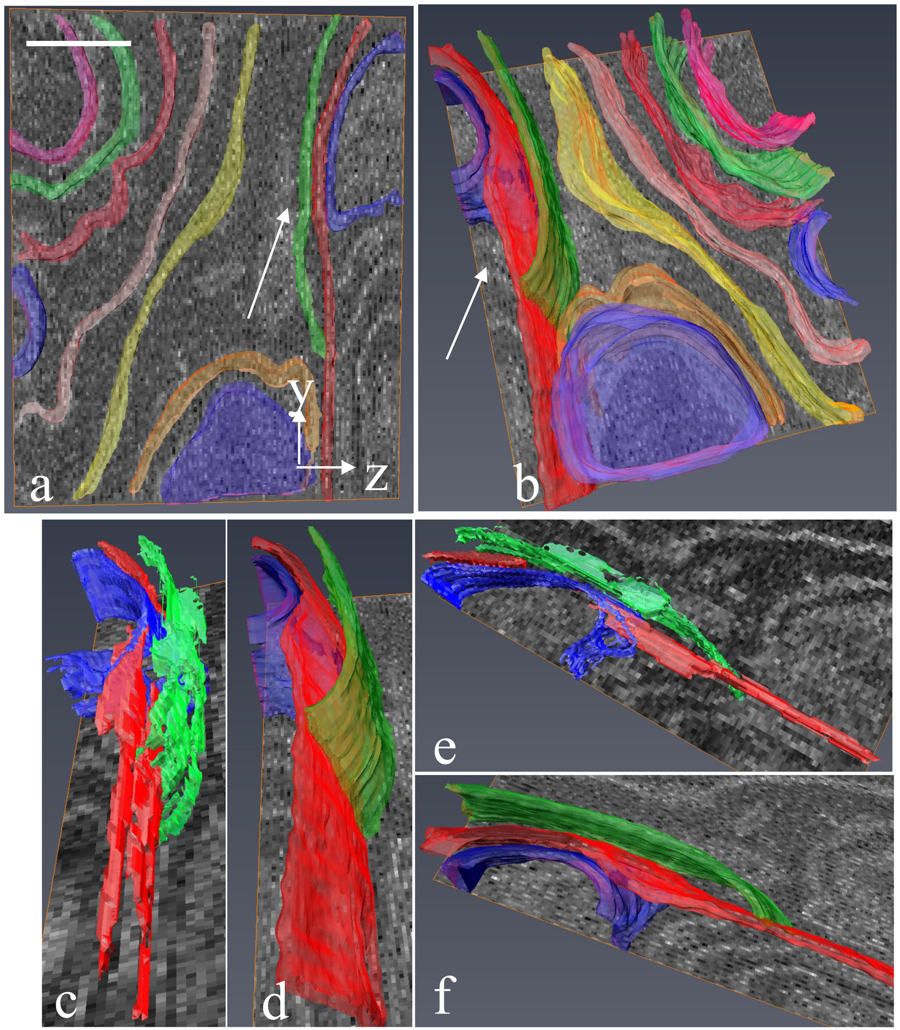
Serial block-face electron microscopy (SBEM) provides nanoscale 3D ultrastructure of embedded and stained cells and tissues in volumes of up to 107 µm3. In SBEM, electrons with 1–3 keV energies are incident on a specimen block, from which backscattered electron (BSE) images are collected with x, y resolution of 5–10 nm in the block-face plane, and successive layers are removed by an in situ ultramicrotome. Sp... Read more
Q. He, M. Hsueh, G. Zhang, D. C. Joy & R. D. Leapman
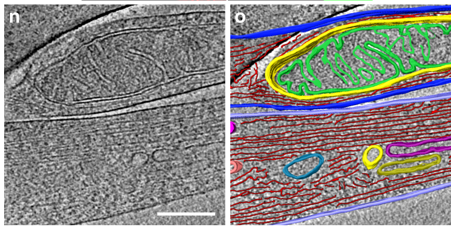
Correlative cryo-electron microscopy reveals the structure of TNTs in neuronal cells
The orchestration of intercellular communication is essential for multicellular organisms. One mechanism by which cells communicate is through long, actin-rich membranous protrusions called tunneling nanotubes (TNTs), which allow the intercellular transport of various cargoes, between the cytoplasm of distant cells in vitro and in vivo. Here, we use correlative FIB-SEM, light- and cryo-electron microscopy approaches to elucidate the structural organization of neuronal TNTs. Our data indicate ... Read more
Anna Sartori-Rupp, Diégo Cordero Cervantes, Anna Pepe, Karine Gousset, Elise Delage, Simon Corroyer-Dulmont, Christine Schmitt, Jacomina Krijnse-Locker & Chiara Zurzolo
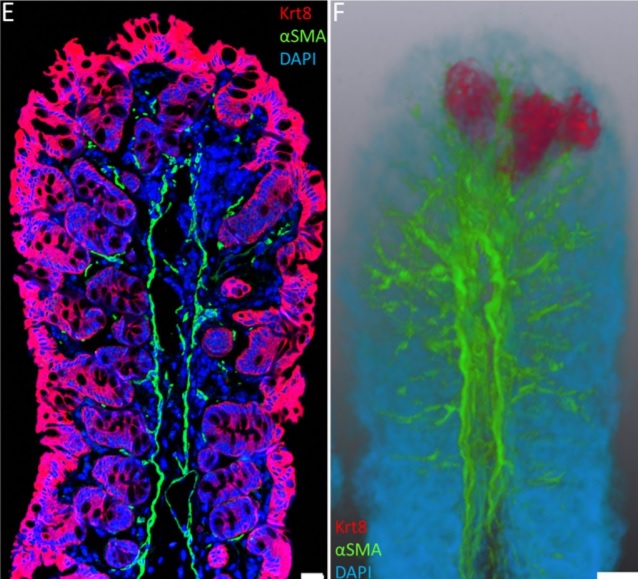
Immunofluorescence tomography is a high-resolution 3-D reconstruction method based on methacrylate embedding and serial-sectioning, where 2-D images of immuno-stained serial-sections are computationally aligned into image stacks, and the 3-D volume rendered. Butyl-Methyl Methacrylate (BMMA) plastic was adopted as it preserves excellent tissue morphology and can be de-plasticized easily using an organic solvent, which enables immuno-staining of serial-sections without antibody penetration issu... Read more
Parfitt, Geraint J
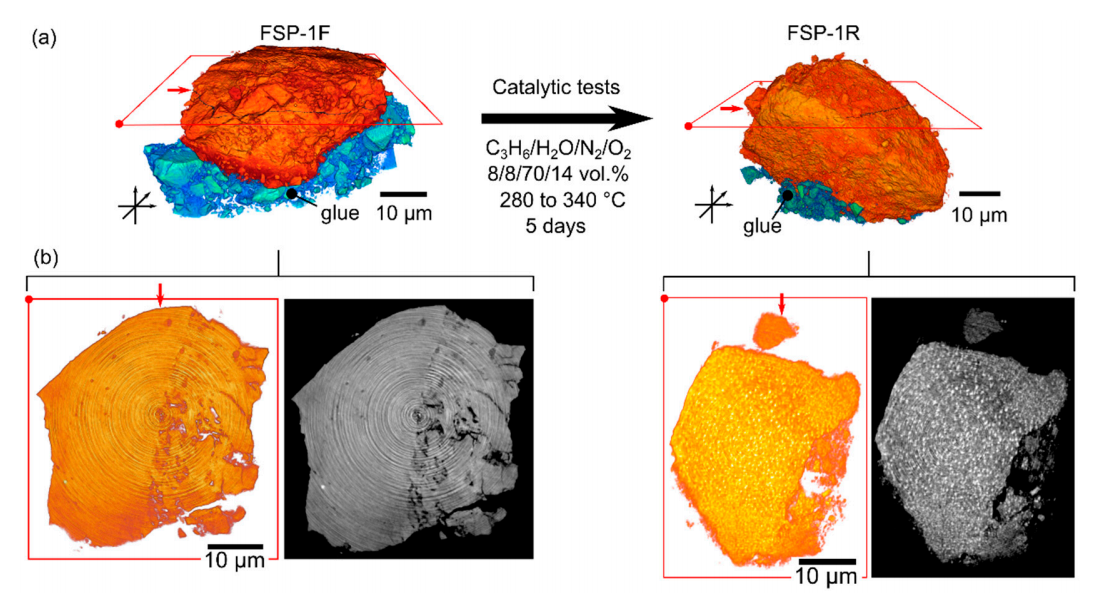
Structural Evolution of Highly Active Multicomponent Catalysts for Selective Propylene Oxidation
Multicomponent Bi-Mo-Fe-Co oxide catalysts prepared via flame spray pyrolysis were tested for selective propylene oxidation, showing high conversion (>70%) and selectivity (>85%) for acrolein and acrylic acid at temperatures of 330 ◦C. During extended time-on-stream tests (5–7 days), the catalysts retained high activity while undergoing diverse structural changes. This was evident on: (a) the atomic scale, using powder X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray absorption spectros... Read more
Paul Sprenger, Thomas L Sheppard, Jussi-Petteri Suuronen, Abhijeet Gaur, Federico Benzi and Jan-Dierk Grunwaldt
Combined expansion and lattice light sheet microscopy enables high
speed, nanoscale molecular imaging of neural circuits over large volumes.
Optical and electron microscopy have made tremendous inroads in understanding the complexity of the brain, but the former offers insufficient resolution to reveal subcellular details and the latter lacks the throughput and molecular contrast to visualize specific molecular constituents over mm-scale or larger dimensions. We combined expansio... Read more
Ruixuan Gao, Shoh M Asano, Srigokul Upadhyayula, Igor Pisarev, Daniel E Milkie, Tsung-Li Liu, Ved Singh, Austin Graves, Grace H Huynh, Yongxin Zhao, John Bogovic, Jennifer Colonell, Carolyn M Ott, Christopher Zugates, Susan Tappan, Alfredo Rodriguez, Kishore R Mosaliganti, Sean G Megason, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Adam Hantman, Gerald M Rubin, Tom Kirchhausen, Stephan Saalfeld, Yoshinori Aso, Edward S Boyden, Eric Betzig
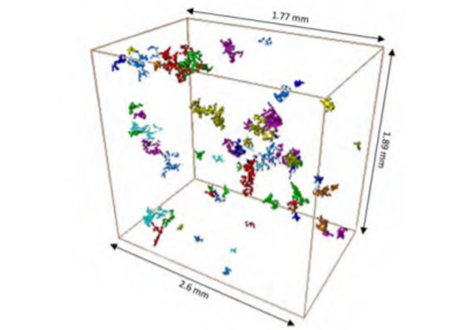
3D characterization of the fracture mechanisms of a Fe-rich Al-Si-Cu alloy
The effect of the defect size and morphology on the fatigue damage evolution was analysed in a recycled Al-Si-Cu alloy by micro-computed tomography and scanning electron microscopy. Fatigue tests were performed and the different crack initiation scenarios were characterized and classified. The interaction between shrinkage and gas pores was the key crack initiation mechanism and the ß-Al5FeSi particles did not play any role in the crack initiation phase. However, crack path analysis indicate... Read more
Angelika Brueckner-Foit, Inigo Bacaicoa, Martin Luetje, Marcel Wicke, Andreas Geisert, Martin Fehlbier
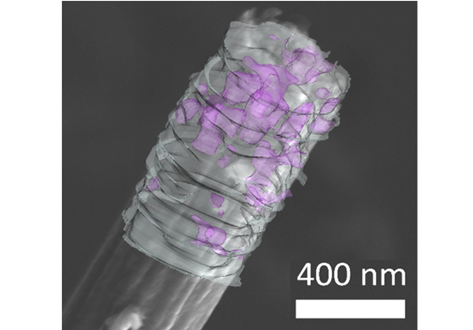
Flexible all-fiber electrospun supercapacitor
Electrospun all-fiber flexible supercapacitor with nanofiber electrodes/separator.
- Increased graphitic degree with the addition of MnACAC and thermal decomposition.
- Enhanced capacitive performance with the addition of MnO.
- Quantified nanofiber alignment and increased bias with MnO over undoped fibers.
- FIBSEM tomography of nanofibers showing MnO disitribution in carbon nanofibers.
We present an all-fiber flexible supercapacitor with compo... Read more
Xinhua Liu, Max Naylor Marlow, Samuel J. Cooper, Bowen Song, Xiaolong Chen, Nigel P. Brandon, Billy Wu
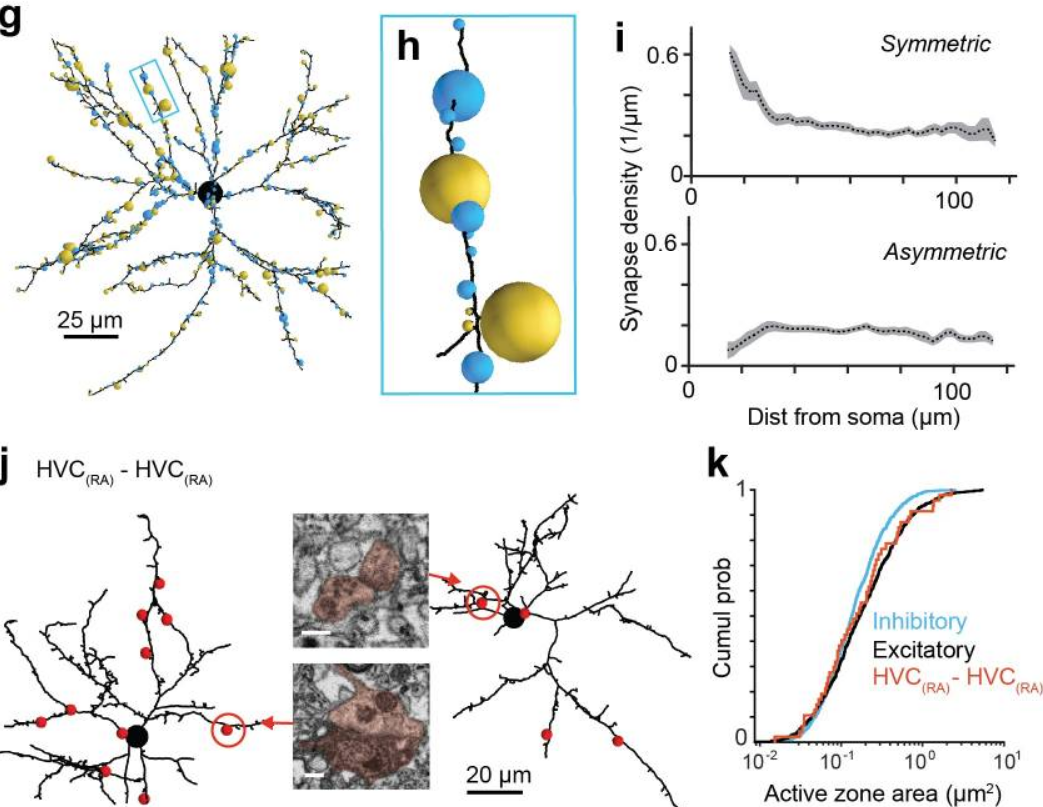
EM connectomics reveals axonal target variation in a sequence-generating network
The sequential activation of neurons has been observed in various areas of the brain, but in no case is the underlying network structure well understood. Here we examined the circuit anatomy of zebra finch HVC, a cortical region that generates sequences underlying the temporal progression of the song. We combined serial block-face electron microscopy with light microscopy to determine the cell types targeted by HVC(RA) neurons, which control song timing. Close to their soma, axons... Read more
Jörgen Kornfeld, Sam E Benezra, Rajeevan T Narayanan, Fabian Svara, Robert Egger, Marcel Oberlaender, Winfried Denk, Michael A Long
Unilever uses Avizo software to visualize and understand food and detergent structures
Food and detergent products are composed of complex micro structures. With modern microscopic techniques we can make them visible. The microstructure greatly affects macroscopic properties such as appearance, taste, mouth feel and solubility. Making these structures visible and quantifying them is essential to the development of products with optimal product properties. A broad range of imaging techniques is used to visualize microstructure elements at different length scales. For example, X-... Read more
Gerard van Dalen, Unilever R&D Vlaardingen (The Netherlands)
A team led by London Centre for Nanotechnology researchers, Prof. Ian Robinson and Dr. Bo Chen (now a professor at the Tongji University, Shanghai) used newly-developed serial block-face scanning electron microscopy (SBFSEM) and Thermo Scientific™ Avizo® Software, one dominant tool in 3D reconstructed image processing, to reveal the spatial structure of human chromosomes and nucleus quantitatively at high resolution of approximately 50 nm in three dimensions.
Read more
Prof. Ian Robinson, Dr. Bo Chen, London Centre for Nechnology, UCL and Tongji University