Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
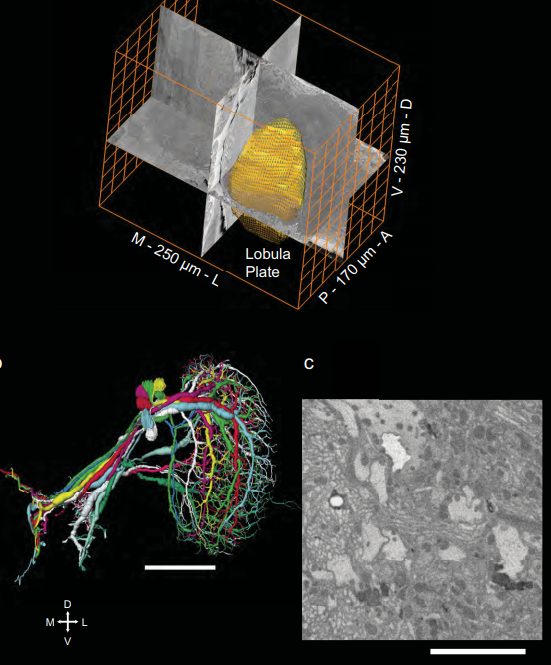
Full reconstruction of large lobula plate tangential cells in Drosophila from a 3D EM dataset
With the advent of neurogenetic methods, the neural basis of behavior is presently being analyzed in more and more detail. This is particularly true for visually driven behavior of Drosophila melanogaster where cell-specific driver lines exist that, depending on the combination with appropriate effector genes, allow for targeted recording, silencing and optogenetic stimulation of individual cell-types. Together with detailed connectomic data of large parts of the fly optic lobe, this has rece... Read more
Kevin M. Boergens , Christoph Kapfer, Moritz Helmstaedter, Winfried Denk, Alexander Borst
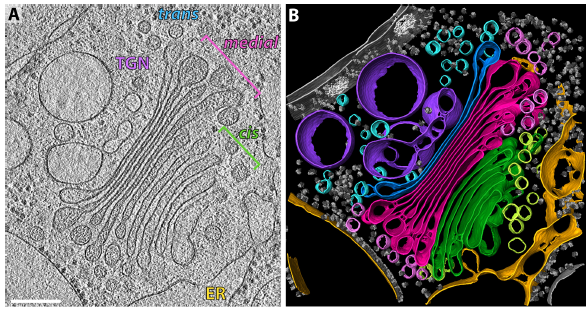
The structure of the COPI coat determined within the cell
COPI-coated vesicles mediate trafficking within the Golgi apparatus and from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum. Here, we applied cryo-focused ion beam milling, cryo-electron tomography and subtomogram averaging to determine the native structure of the COPI coat within vitrified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells. The native algal structure resembles the in vitro mammalian structure, but additionally reveals cargo bound beneath beta’–COP. We find that all coat components disassemble... Read more
Yury S Bykov, Miroslava Schaffer, Svetlana O Dodonova, Sahradha Albert, Jurgen M Plitzko, Wolfgang Baumeister, Benjamin D Engel, John AG Briggs
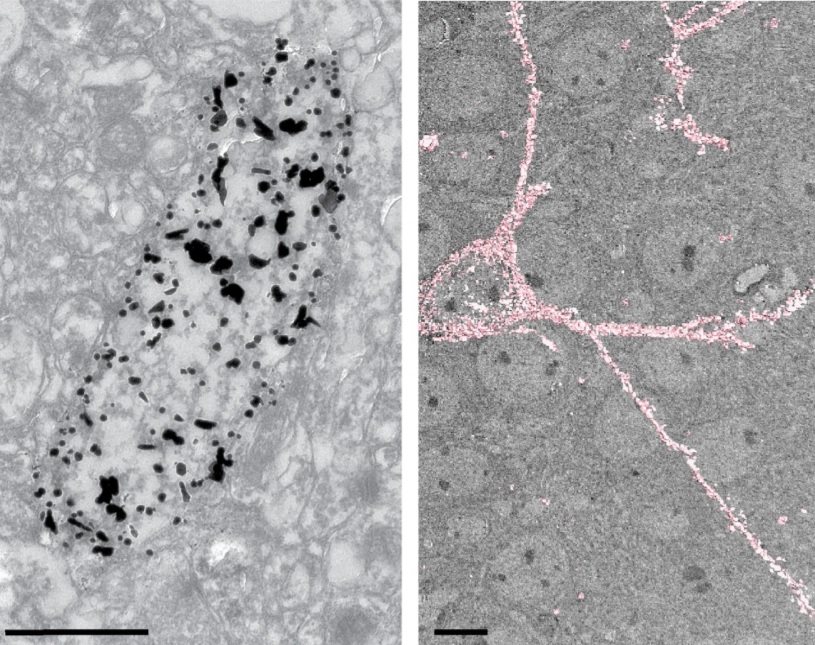
Analysis of neuronal arborization and connections is a powerful tool in fundamental and clinical neuroscience. Changes in neuronal morphology are central to brain development and plasticity and are associated with numerous diseases. Golgi staining is a classical technique based on a deposition of metal precipitate in a random set of neurons. Despite their versatility, Golgi methods have limitations that largely precluded their use in advanced microscopy. We combined Golgi staining with fluore... Read more
Katlijn Vints, Dorien Vandael, Pieter Baatsen, Benjamin Pavie, Frank Vernaillen, Nikky Corthout, Vasily Rybakin, Sebastian Munck & Natalia V. Gounko
In biomedical research, a huge variety of different techniques is currently available for the structural examination of small specimens, including conventional light microscopy (LM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), microscopic X-ray computed tomography (microCT), and many others. Since every imaging method is physically limited by certain parameters, a correlative use of complementary methods often yields a significant broader range of inform... Read more
Stephan Handschuh, Natalie Baeumler, Thomas Schwaha and Bernhard Ruthensteiner
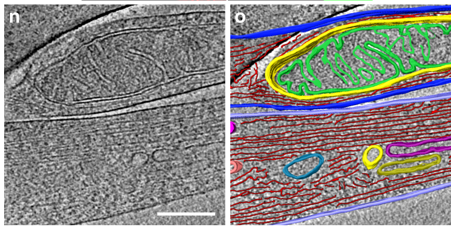
Correlative cryo-electron microscopy reveals the structure of TNTs in neuronal cells
The orchestration of intercellular communication is essential for multicellular organisms. One mechanism by which cells communicate is through long, actin-rich membranous protrusions called tunneling nanotubes (TNTs), which allow the intercellular transport of various cargoes, between the cytoplasm of distant cells in vitro and in vivo. Here, we use correlative FIB-SEM, light- and cryo-electron microscopy approaches to elucidate the structural organization of neuronal TNTs. Our data indicate ... Read more
Anna Sartori-Rupp, Diégo Cordero Cervantes, Anna Pepe, Karine Gousset, Elise Delage, Simon Corroyer-Dulmont, Christine Schmitt, Jacomina Krijnse-Locker & Chiara Zurzolo
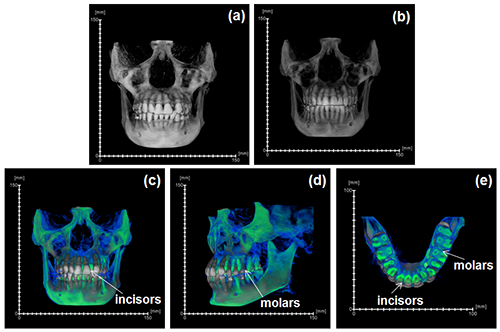
During the acts of biting and chewing, the muscles of the jaw (consisting of the masseter, temporalis, and medial pterygoid in the elevator group, and lateral pterygoid as the main depressor) generate forces that dictate jaw kinematics . The movement of jaws hinges about the temporomandibular joint and are brought together by the muscles attached to respective bones through bone-tendon interfaces known as entheses . Thus, chewing forces affect aspects of craniofacial structure as well as bo... Read more
Kyle H.-Y. Chan, fourth-year undergraduate student in Molecular and Cell Biology, and Public Health at UC Berkeley, FeiFei Yang, Ph.D., postdoctoral scholar in the Laboratory of Multiscale Biomechanics and Biomineralization, School of Dentistry, UCSF, and Sunita P. Ho, Ph.D., Division of Biomaterials and Bioengineering, Department of Preventive and Restorative Dental Sciences, School of Dentistry, University of California San Francisco
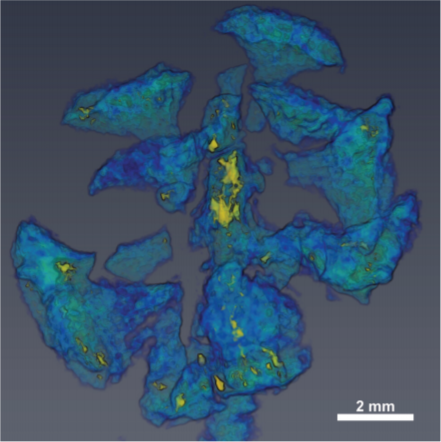
Computed tomography is an increasingly popular technique for the non-destructive study of fossils. Whilst the science of X-ray computed tomography (CT) has greatly matured since its first fossil applications in the early 1980s, the applications and limitations of neutron tomography (NT) remain relatively unexplored in palaeontology. These highest resolution neutron tomographic scans in palaeontology to date were conducted on a specimen of Austrosequoia novae-zeelandiae (Ettingshausen) Mays an... Read more
Chris Mays, Joseph J. Bevitt, and Jeffrey D. Stilwell
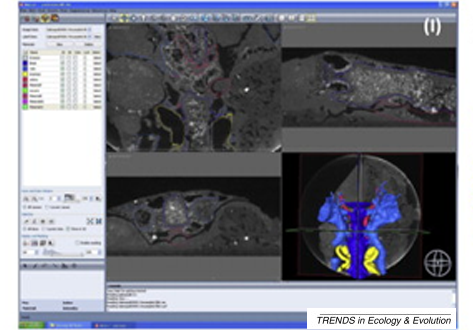
A virtual world of paleontology
Computer-aided visualization and analysis has revolutionized the study of fossils. Fossils can now be characterized in three dimensions and in unprecedented detail. The resulting digital reconstructions can be used in rigorous functional analyses. Hypotheses regarding the function of extinct organisms can therefore be tested.
Read more
Trends in Ecology & Evolution

2 BILLION years old fossils appear to represent a first experiment in megascopic multicellularity
The Paleoproterozoic Era witnessed crucial steps in the evolution of Earth’s surface environments following the first appreciable rise of free atmospheric oxygen concentrations ∼2.3 to 2.1 Ga ago, and concomitant shallow ocean oxygenation. Combined microtomography, geochemistry, and sedimentary analysis suggest a biota fossilized during early diagenesis. The emergence of this biota follows a rise in atmospheric oxygen, which is consistent with the idea that surface oxygenation allowe... Read more
Abderrazak El Albani, Laboratoire HYDRASA, UMR 6269 CNRS-INSU, Université de Poitiers, France
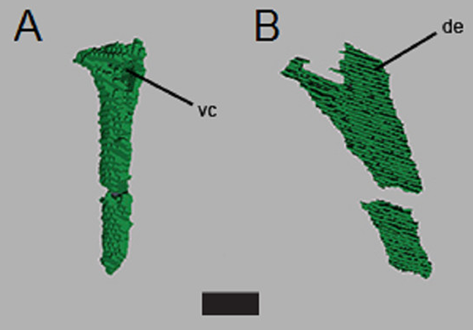
Aetosauria is a clade of heavily armored, quadrupedal omnivorous to herbivorous archosaurs known from the Late Triassic across what was the supercontinent of Pangea. Their abundance in many deposits relative to the paucity of other Triassic herbivores indicates that they were key components of Late Triassic ecosystems. However, their evolutionary relationships remain contentious due, in large part, to their extensive dermal armor, which often obstructs observation of internal skeletal anatomy... Read more
Devin K. Hoffman, Andrew B. Heckert, Lindsay E. Zanno
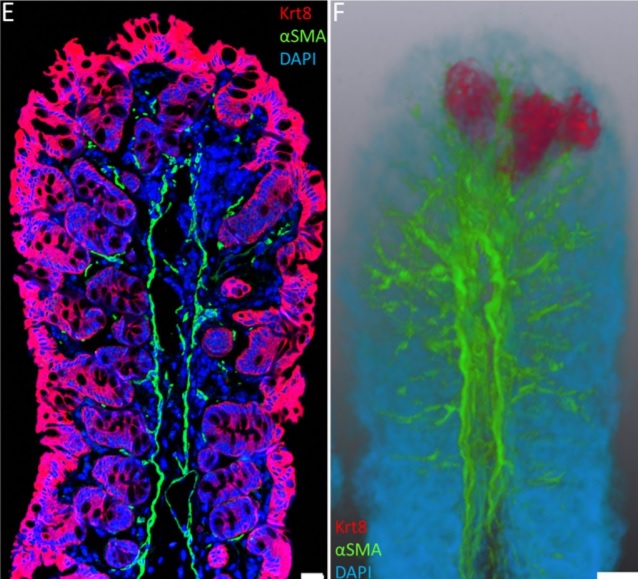
Immunofluorescence tomography is a high-resolution 3-D reconstruction method based on methacrylate embedding and serial-sectioning, where 2-D images of immuno-stained serial-sections are computationally aligned into image stacks, and the 3-D volume rendered. Butyl-Methyl Methacrylate (BMMA) plastic was adopted as it preserves excellent tissue morphology and can be de-plasticized easily using an organic solvent, which enables immuno-staining of serial-sections without antibody penetration issu... Read more
Parfitt, Geraint J
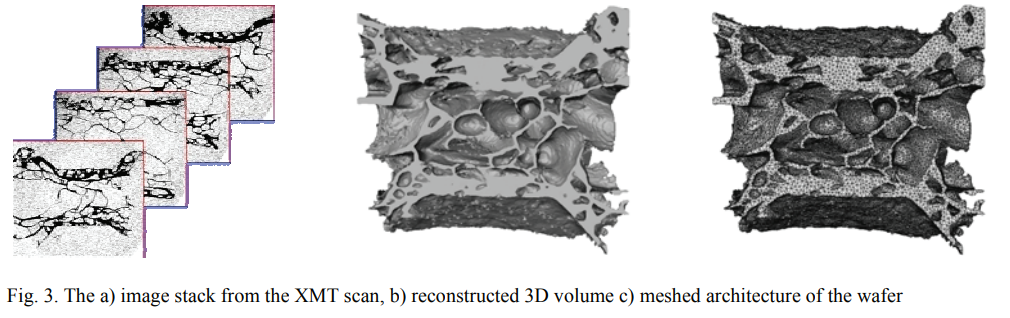
Modelling deformation and fracture in confectionery wafers
The aim of this research is to model the deformation and fracture behaviour of brittle wafers often used in chocolate confectionery products.
Three point bending and compression experiments were performed on beam and circular disc samples respectively to determine the ‘apparent’ stress-strain curves in bending and compression. The deformation of the wafer for both these testing types was observed in-situ within an SEM. The wafer is modelled analytically and numerically as a composi... Read more
Idris K. Mohammeda, Maria N. Charalambides , J. Gordon Williams , John Rasburn
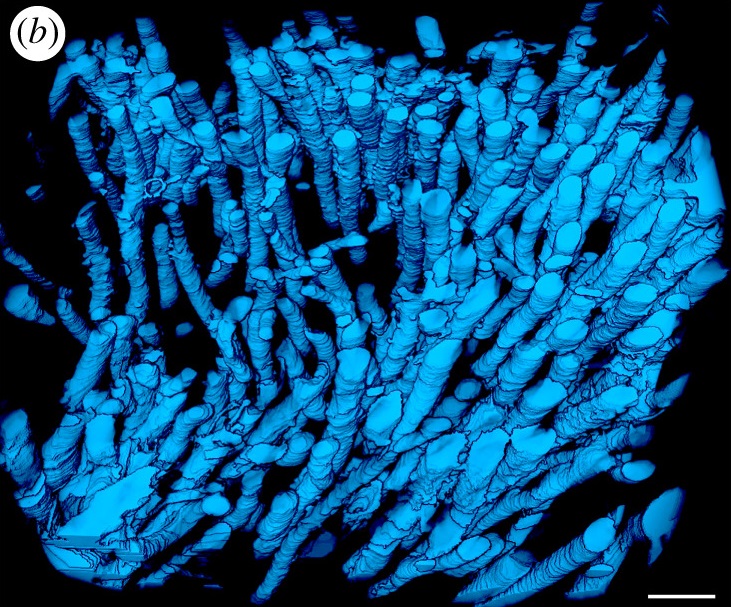
Microbial-tubeworm associations in a 440 million year old hydrothermal vent community
Microorganisms are the chief primary producers within present-day deep-sea hydrothermal vent ecosystems, and play a fundamental role in shaping the ecology of these environments. (…) The oldest known hydrothermal vent community that includes metazoans is preserved within the Ordovician to early Silurian Yaman Kasy massive sulfide deposit, Ural Mountains, Russia. (…) A re-examination of these fossils using a range of microscopy, chemical analysis and nano-tomography techniques re... Read more
Magdalena N. Georgieva , Crispin T. S. Little , Russell J. Bailey , Alexander D. Ball and Adrian G. Glover
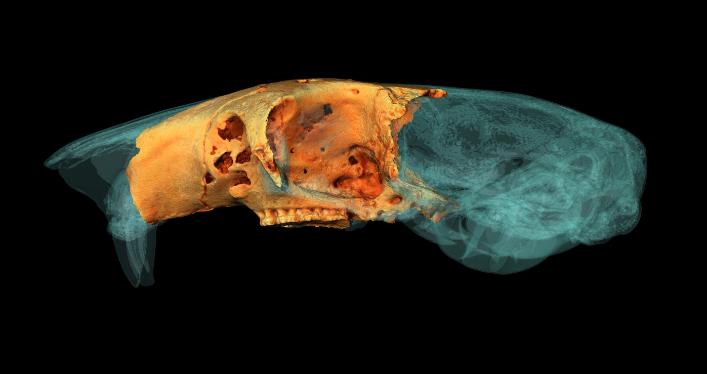
University of York student wins Anatomical Society Best Image Prize using Amira-Avizo Software
PhD student Jesse Hennekam wins for his reconstruction of the skull of a giant dormouse.
A York PhD student has won a prestigious award for his work reconstructing the skull of a giant rodent.
Jesse Hennekam, from the Centre for Anatomical and Human Sciences at the Hull York Medical School, created a digital reconstruction of the skull of a gigantic dormouse (Leithia melitensis), which roamed on the island of Sicily during the Pleistocene, roughly 2 million years ago... Read more
Jesse Hennekam
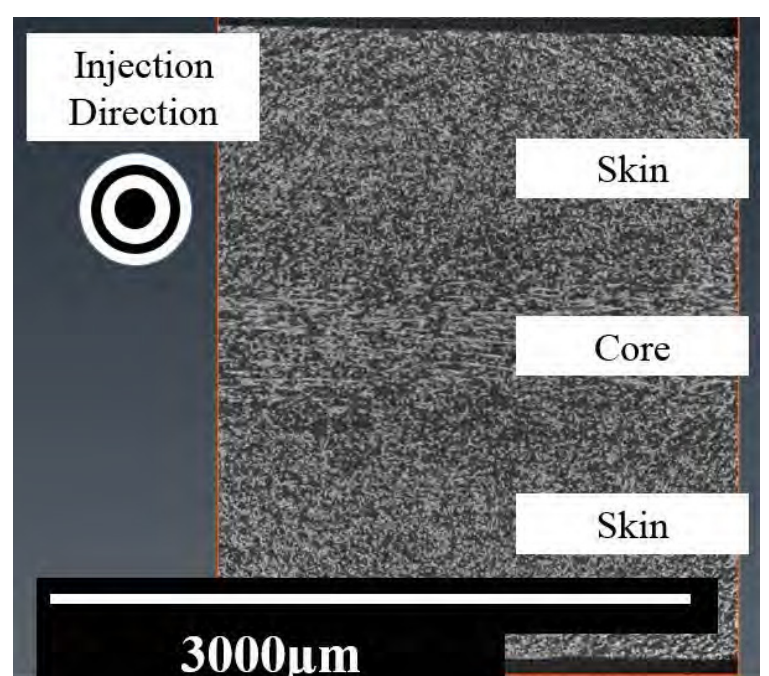
For many years, SFRPs (short fibre reinforced polyamides) have been used in the automotive industry as a means to reduce vehicle weight. However, their complex anisotropic and heterogeneous microstructure requires sophisticated material characterisation and simulation. This study aims at presenting the simulation strategy adopted by an automotive company address these challenges. The manufacturing process is first simulated and correlated with tomography analysis. Then, based on the numerical... Read more
Pablo Wilson, Peter Heyes
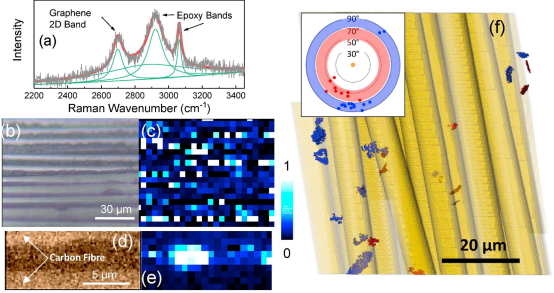
It is shown that approximately 2wt% of graphene in the matrix of a unidirectionally-reinforced carbon fiber epoxy composite leads to a significant enhancement in mechanical properties. Particularly, it is found that the axial stiffness of the composites is increased by 10GPa accompanied by an increase in axial strength of 200MPa.
Read more
Jingwen Chu, Robert J.Young, Thomas J.A.Slater, Timothy L.Burnett, Broderick Coburn, Ludovic Chichignoud, Aurèle Vuilleumier, Zheling Li
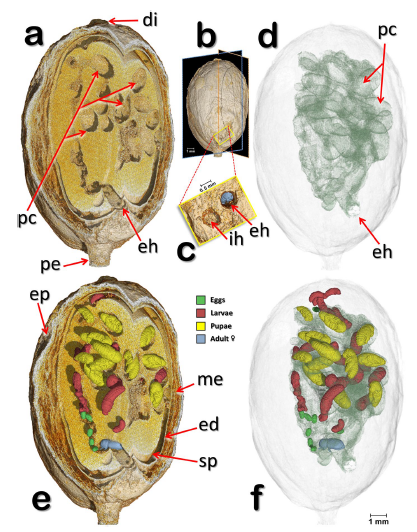
The coffee berry borer is the most devastating insect pest of coffee throughout the world. The insect spends most of its life cycle inside the coffee berry, which makes it quite difficult to observe its behaviour. Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) was used to observe all developmental stages of the coffee berry borer inside coffee berries (Coffea canephora). An interesting oviposition pattern involving a sequential placement of eggs starting in the periphery of the seed and moving inwards ... Read more
Ignacio Alba-Alejandre, Javier Alba-Tercedor, Fernando E. Vega
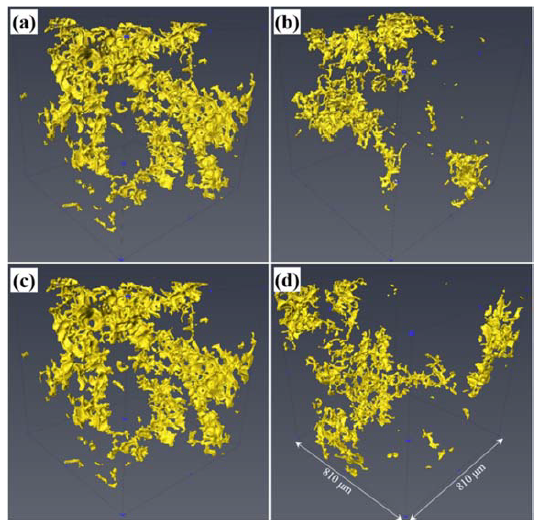
The porous transport layer (PTL) is a vital component of the polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolyser (PEMWE) as it is both a conduit for current distribution and mass transport. This study aims to examine the influence of the microstructure of the PTL on the performance of a PEMWE by the combination of ex-situ and in-situ techniques. Two PTLs with distinctly different mean pore diameter were characterized to determine key properties such as surface morphology, porosity, pore size dist... Read more
Jude O Majasan, Francesco Iacoviello, Paul R Shearing, Dan JL Brett
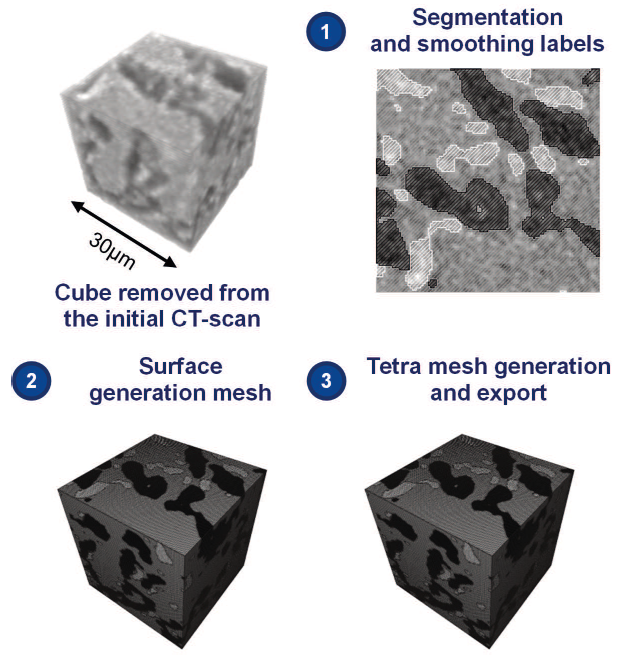
Current materials such nickel based superalloys cannot be used anymore and new materials are thus considered. For the hottest parts of jet engines, eutectic ceramics have potentially interesting features. In order to assess the thermo-mechanical properties of this material, numerical multi-scale analyses may be performed. Thus, a 3D finite element model was generated from a CT scan, representative of the microstructure and with a similar volume fraction. Effective elastic properties were calc... Read more
S. Gourdin, L. Marcin, M. Podgorski, M. Cherif, L. Carroz
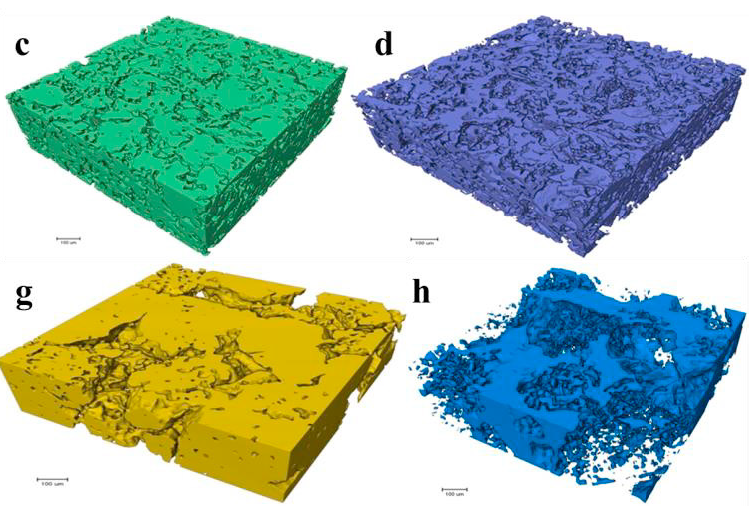
The effect of ultrasonic melting processing on three-dimensional architecture of intermetallic phases and pores in two multicomponent cast Al-5.0Cu 0.6Mn-0.5 Fe alloys is characterized using conventional microscopy and synchrotron X-ray microtomography. (…) The results show that ultrasonic melt processing (USP) significantly reduce the volume fraction, grain size, interconnectivity, and equivalent diameter of the intermetallic phases in both alloys. The volume fraction of pores in both ... Read more
Yuliang Zhao, Dongfu Song, Bo Lin, Chun Zhang, Donghai Zheng, Zhi Wang, Weiwen Zhang
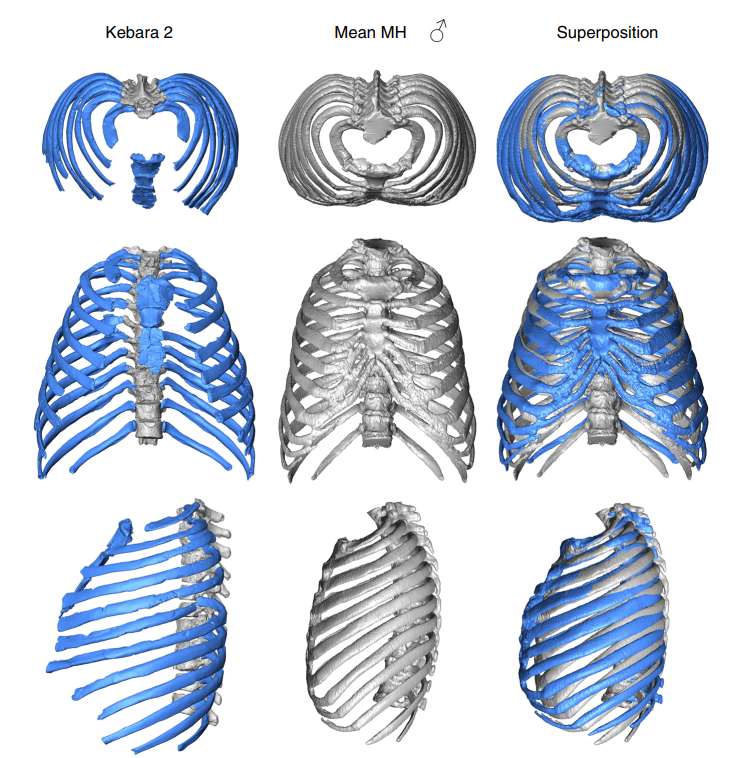
3D virtual reconstruction of the Kebara 2 Neandertal thorax
The size and shape of the Neandertal thorax has been debated since the first discovery of Neandertal ribs more than 150 years ago, with workers proposing different interpretations ranging from a Neandertal thoracic morphology that is indistinguishable from modern humans, to one that was significantly different from them. Here, we provide a virtual 3D reconstruction of the thorax of the adult male Kebara 2 Neandertal. Our analyses reveal that the Kebara 2 thorax is significantly different but ... Read more
Asier Gomez-Olivencia, Alon Barash, Daniel Garcia-Martinez, Mikel Arlegi, Patricia Kramer, Markus Bastir, Ella Been