Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
The behavior of loess is controlled by its microstructure, consisting of silt sized skeleton particles and complex bonding structures formed by clay-sized particles. Achieving a deep understanding and precise modelling of loess behavior necessitates comprehensive knowledge of the realistic 3D microstructure.
- Innovative 3D analysis of loess microstructure using μXCT and FIB-SEM.
- Detailed visualizat... Read more
B. Yu, T.A. Dijkstra, W. Fan, I.J. Smalley, Y.N. Wei, L.S. Deng
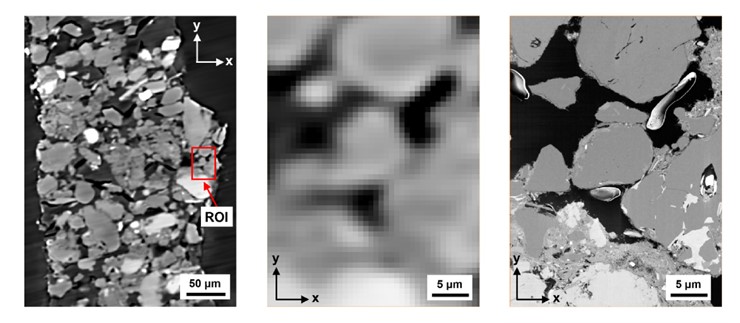
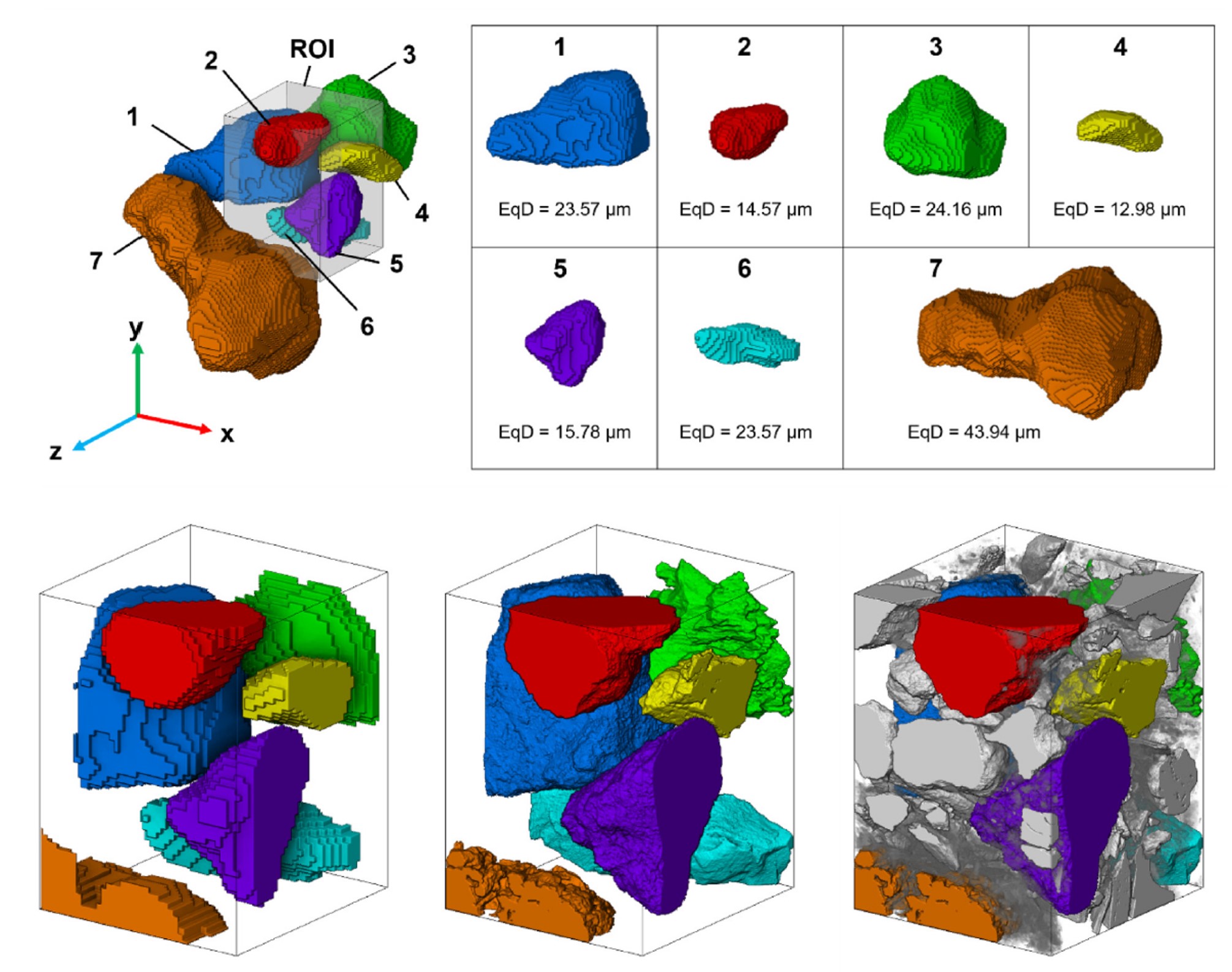
3D loess microstructure of loess, including skeleton particles as well as inter-particle bonding structures, was characterized through a correlative approach using μXCT and FIB-SEM
Loess, a Quaternary wind-blown deposit, is a problem soil that gives rise to frequent geohazards such as landslides and water-induced subsidence. The behavior of loess is controlled by its microstructure, consisting of silt sized
skeleton particles and complex bonding structures formed by clay-sized p... Read more
B. Yu, T.A. Dijkstra, W. Fan, I.J. Smalley, Y.N. Wei, L.S. Deng
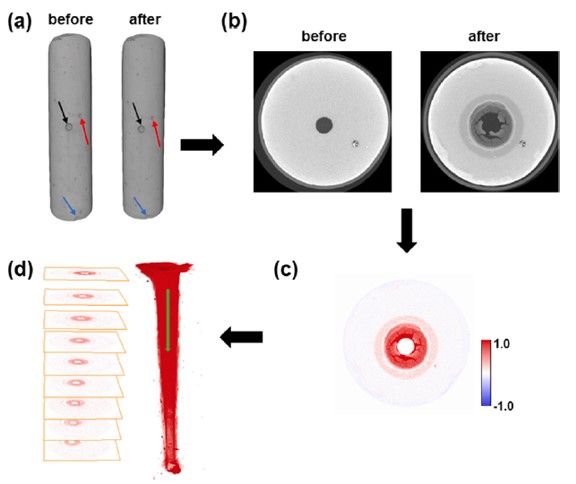
Comparative experimental observations of cement with a flow channel subject to CO2-saturated brine flow by micro-CT scanning and CT image post processing.
Understanding CO2-induced micro-structural changes at the imperfections in wellbore cement is vital for assessing the risk of CO2 leakage through wellbore cement under geologic CO2 storage (GCS) conditions. To investigate the evolution of a flow channel width in cement under GCS conditions and the influence of effective stress and fl... Read more
Manguang Gan, Liwei Zhang, Yan Wang, Kaiyuan Mei, Xiaojuan Fu, Xiaowei Cheng, Mingxing Bai, Hejuan Liu, Xiaochun Li
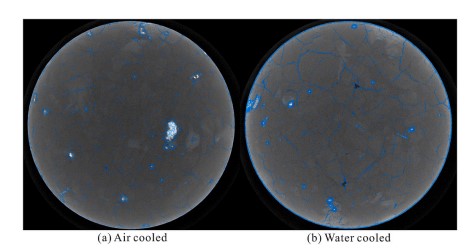
Deep geothermal resources have been widely acknowledged as an alternative energy so... Read more
Zhennan Zhu, Shengqi Yang, Ren Wang, Jingyu Xie, Nuocheng Tian, Hong Tian, Jun Zheng, Guosheng Jiang, Bin Dou
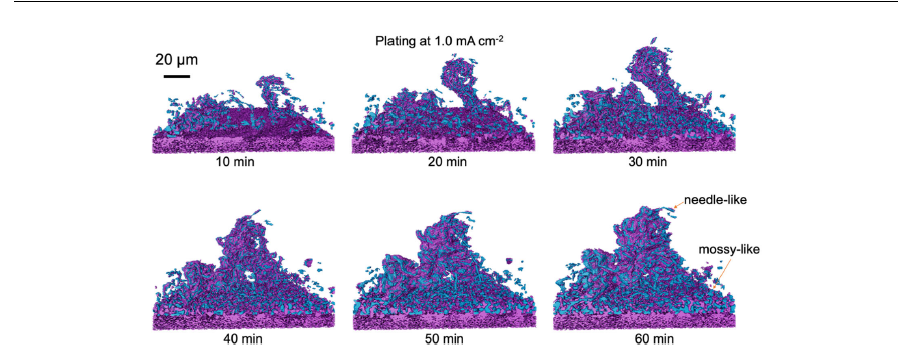
Li metal is considered as the most important negative electrode active material for Li-based batteries because of its high theoretical specific capacity of 3860mAh g-1, which is an order of magnitude higher than the currently used graphite, and by being the most electropositive metal. When coupled with high-capacity cathodes, either Li insertion materials or conversion chemistries, or applied in a solid-sate configuration, a leap in energy density can be obtained. The main challenge in the di... Read more
Matthew Sadd, Shizhao Xiong, Jacob R. Bowen, Federica Marone, Aleksandar Matic
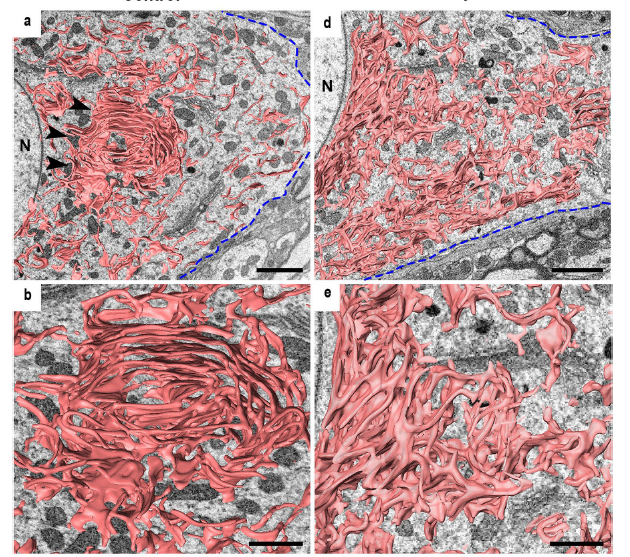
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) extends throughout a cell and plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Changes in ER shape could provide a clue to explore the mechanisms that underlie the fate determination of neurons after
axon injury because the ER drastically changes its morphology under neuronal stress to maintain cellular homeostasis and
recover from damage. Because of their tiny structures and richness in the soma, the detailed morphology of the ER and... Read more
Mahmoud Elgendy,Hiromi Tamada, Takaya Taira, Yuma Iio, Akinobu Kawamura, Ayusa Kunogi, Yuka Mizutani, Hiroshi Kiyama
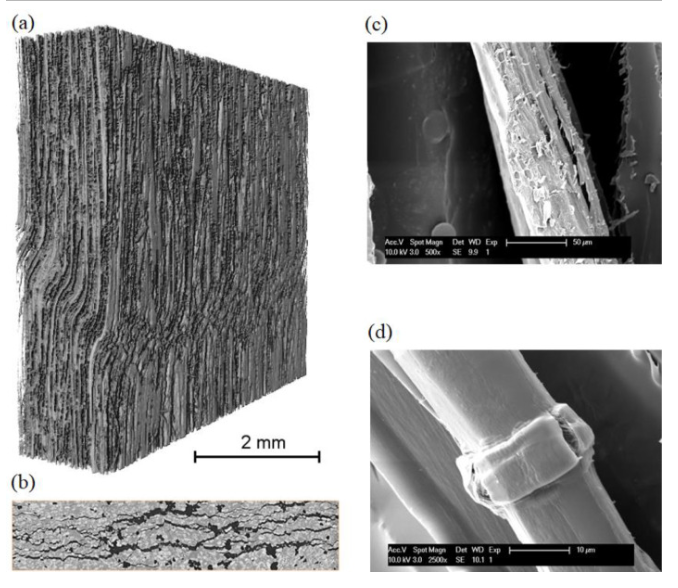
In this study, the researchers investigated the compressive failure mechanisms in flax fiber composites, a promising eco-friendly alternative to synthetic composite materials, through both numerical simulations and experimental analysis. They examined the reasons behind the low compressive strength in comparison to tensile strength, focusing on the compressive-to-tensile strength ratio. A novel thermodynamically consistent continuum damage micromechanics model was introduced to capture the ev... Read more
Vedad Tojaga, Alexandros Prapavesis, Jonas Faleskog, T. Christian Gasser, Aart W. van Vuure, Sören Östlund
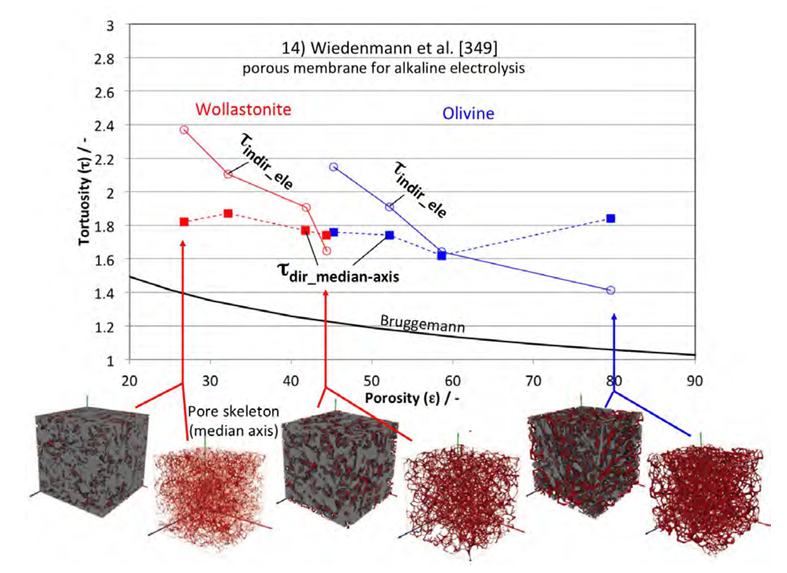
This study provides a comprehensive review of tortuosity and its impact on the transport properties of porous media. It discusses the classical theories and equations related to tortuosity for flow, conduction, and diffusion. The study also highlights the evolution of these theories and their connection to methodologies such as tomography and 3D image analysis. In order to clarify the topic, a new classification scheme and nomenclature for different types of tortuosity are proposed. The study... Read more
Holzer, L. *1, Marmet, P. 1, Fingerle, M. 2, Wiegmann, A. 2, Neumann, M. 3, Schmidt, V. 3
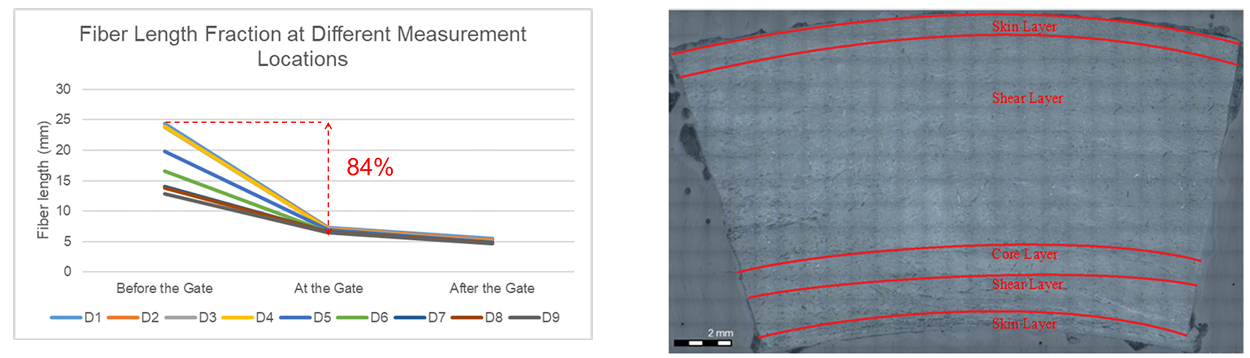
The research focuses on the fiber behavior following injection molding on a spiral-flow mold, particularly its fiber orientation behavior. The behavior of the glass fiber will be examined by altering key experiment settings, the screw speed and the back pressure, and employing different melt paths. The results show that the application of high back pressure and high screw speed decreased the fiber length but successfully increased the fiber orientation average to the flow direction. The desig... Read more
Ahmad Hafizh Ridho, Feng-Jung Cheng, Sheng-Jye Hwang
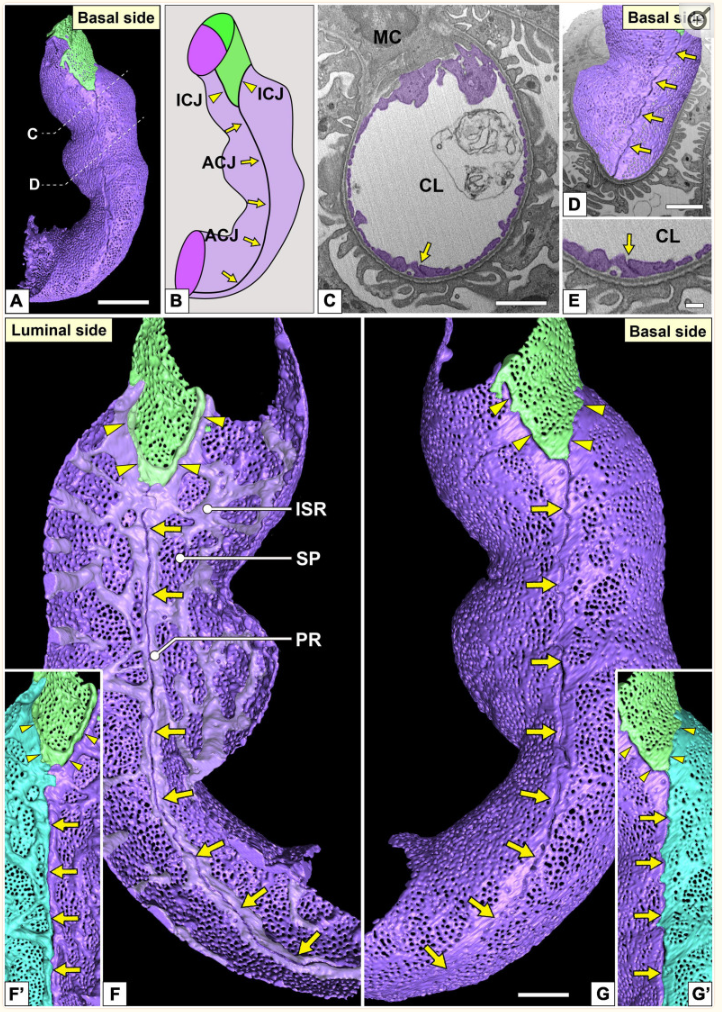
Three-Dimensional Architecture of Glomerular Endothelial Cells Revealed by FIB-SEM Tomography
Focused-ion beam-scanning electron microscopic (FIB-SEM) tomography enables easier acquisition of a series of ultrastructural, sectional images directly from resin-embedded biological samples. In this study, to clarify the three-dimensional (3D) architecture of glomerular endothelial cells (GEnCs) in adult rats, we manually extracted GEnCs from serial FIB-SEM images and reconstructed them on an Amira reconstruction software. The luminal and basal surface structures were clearly visualized in ... Read more
Yuto Kawasaki, Yasue Hosoyamada, Takayuki Miyaki, Junji Yamaguchi, Soichiro Kakuta, Tatsuo Sakai, and Koichiro Ichimura
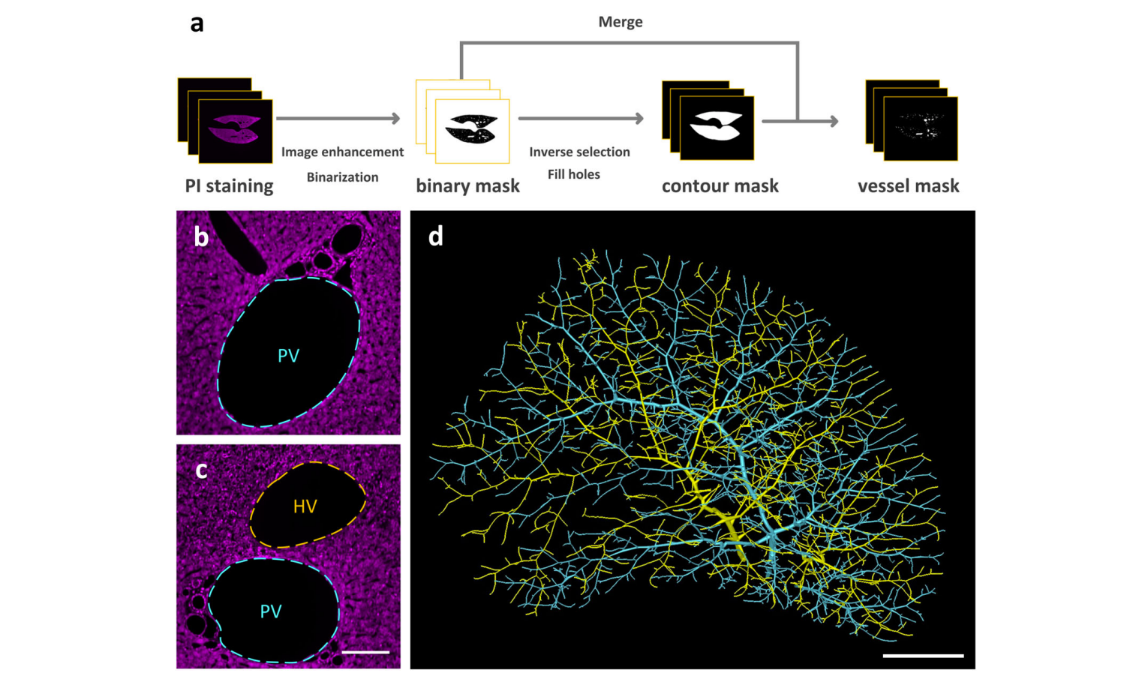
Multiscale reconstruction of various vessels in the intact murine liver lobe
The liver contains a variety of vessels and participates in miscellaneous physiological functions. While past studies generally focused on certain hepatic vessels, we simultaneously obtained all the vessels and cytoarchitectural information of the intact mouse liver lobe at single-cell resolution. […] providing a technology roadmap for studying the fine hepatic vascular structures and their spatial relationship, which will help research into liver diseases and evaluation of medical effi... Read more
Qi Zhang, Anan Li, Siqi Chen, Jing Yuan, Tao Jiang, Xiangning Li, Qingming Luo,Zhao Feng & Hui Gon
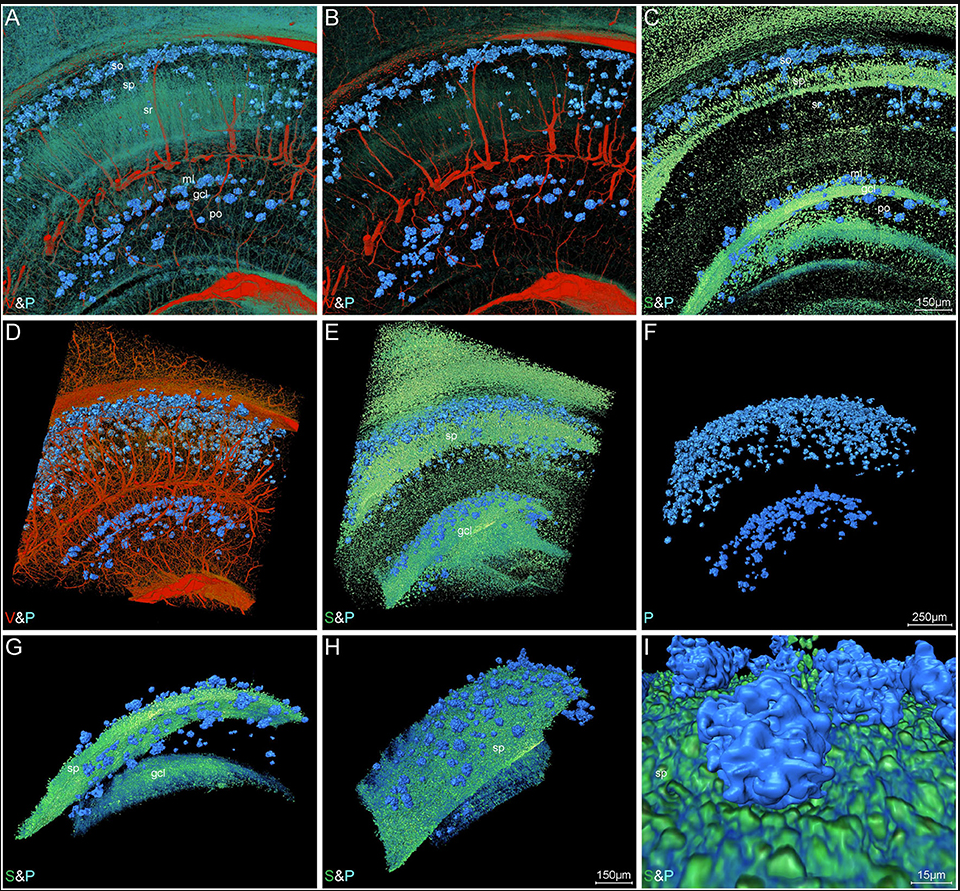
High-Resolution Digital Panorama of Multiple Structures in Whole Brain of Alzheimer's Disease Mice
Our study placed emphasis on solving problems in processing high-throughput bright field images and made attempt in developing a method for the extraction and reconstruction of multiple structures. This will facilitate a better understanding of the cerebral anatomical features under the pathological state of AD and shows extensive application prospect in drug efficacy assessment from brain-wide level.
Simultaneously visualizing Amyloid-β (Aβ) plaque with its surrounding brain structu... Read more
Xianzhen Yin, Xiaochuan Zhang, Jingjing Zhang, Weicheng Yang, Xian Sun, Haiyan Zhang, Zhaobing Gao, Hualiang Jiang
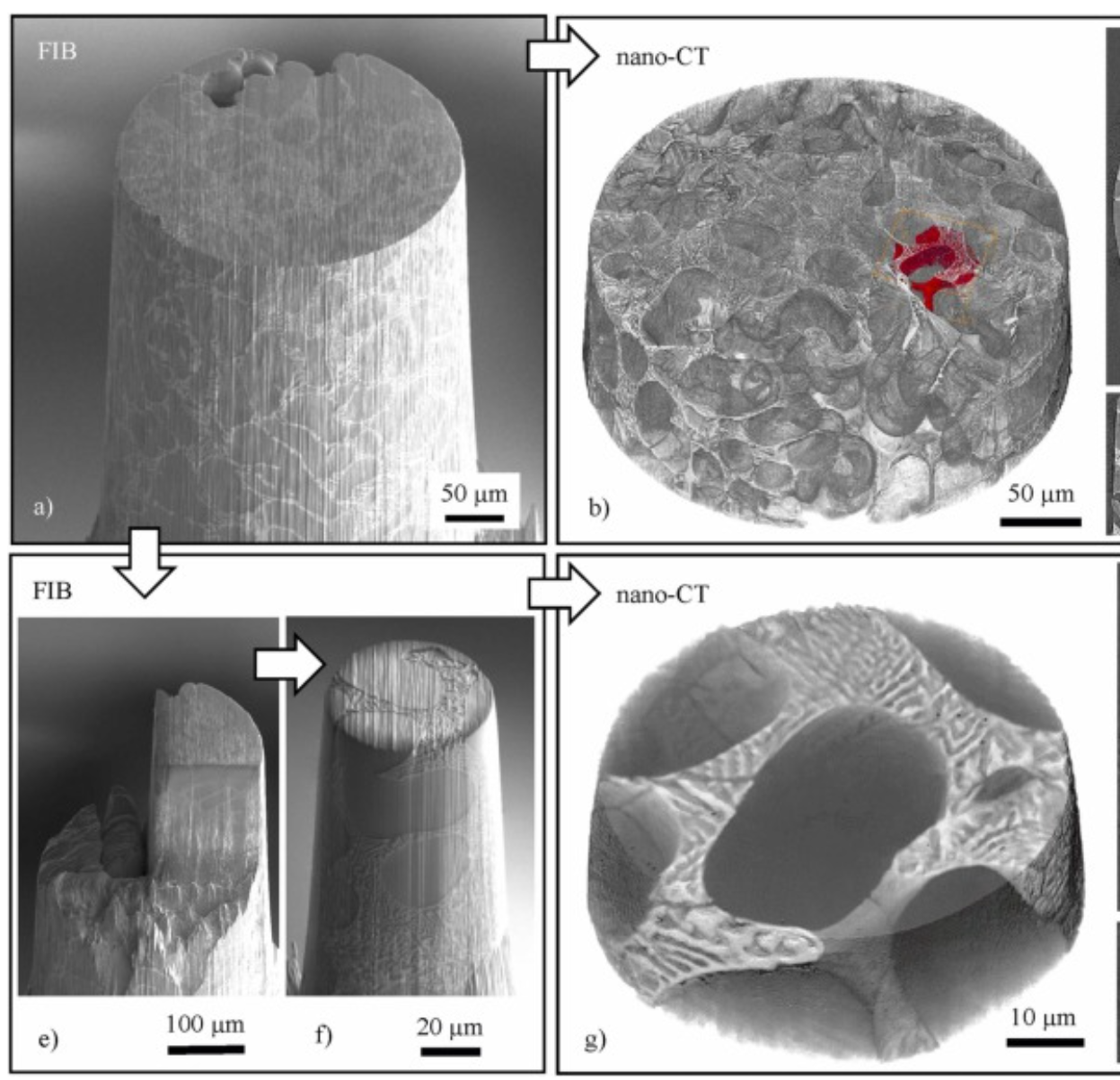

Three-dimensional imaging of microstructural evolution in SEM-based nano-CT
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is a powerful and versatile technique for materials characterization and present in many laboratories. The integration of an X-ray target holder and detector allows expanding the modalities of SEM by X-ray imaging. These little hardware adaptations enable radiography ... Read more
Jonas Fell, Christoph Pauly, Michael Maisl, Simon Zabler, Frank Mücklich, Hans-Georg Herrmann
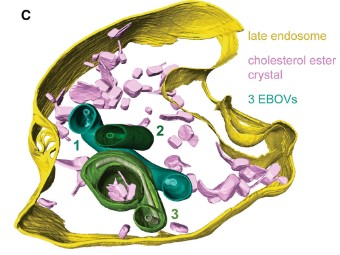
The Ebola virus VP40 matrix layer undergoes endosomal disassembly essential for membrane fusion
Ebola viruses (EBOVs) assemble into filamentous virions, whose shape and stability are determined by the matrix viral protein 40 (VP40). Virus entry into host cells occurs via membrane fusion in late endosomes; however, the mechanism of how the remarkably long virions undergo uncoating, including virion disassembly and nucleocapsid release into the cytosol, remains unknown. Here, we investigate the structural architecture of EBOVs entering host cells and discover that the VP40 matrix disassem... Read more
Sophie L Winter, Gonen Golani, Fabio Lolicato, Melina Vallbracht, Keerthihan Thiyagarajah, Samy Sid Ahmed, Christian Lüchtenborg, Oliver T Fackler, Britta Brügger, Thomas Hoenen, Walter Nickel Ulrich S Schwarz, Petr Chlanda
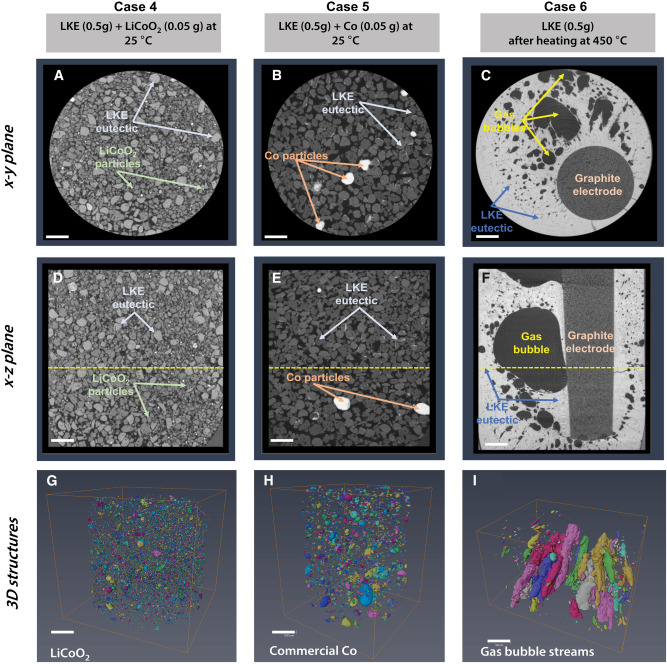
Recycling spent lithium-ion batteries (LiBs) guarantees the conservation of important metal resources by reducing demands on raw supply and offsetting the energy and environmental costs associated with its manufacture. Employing a molten salt as a solvent for extraction affords a much greener and simpler route to metal recovery by electrochemical means. The current mechanistic understanding of the electrochemical recovery of metals in molten salts needs to be improved for the process to be op... Read more
Mateen Mirza, Wenjia Du, Lara Rasha, Steven Wilcock, Arfon H. Jones, Paul R. Shearing, Dan J.L. Brett
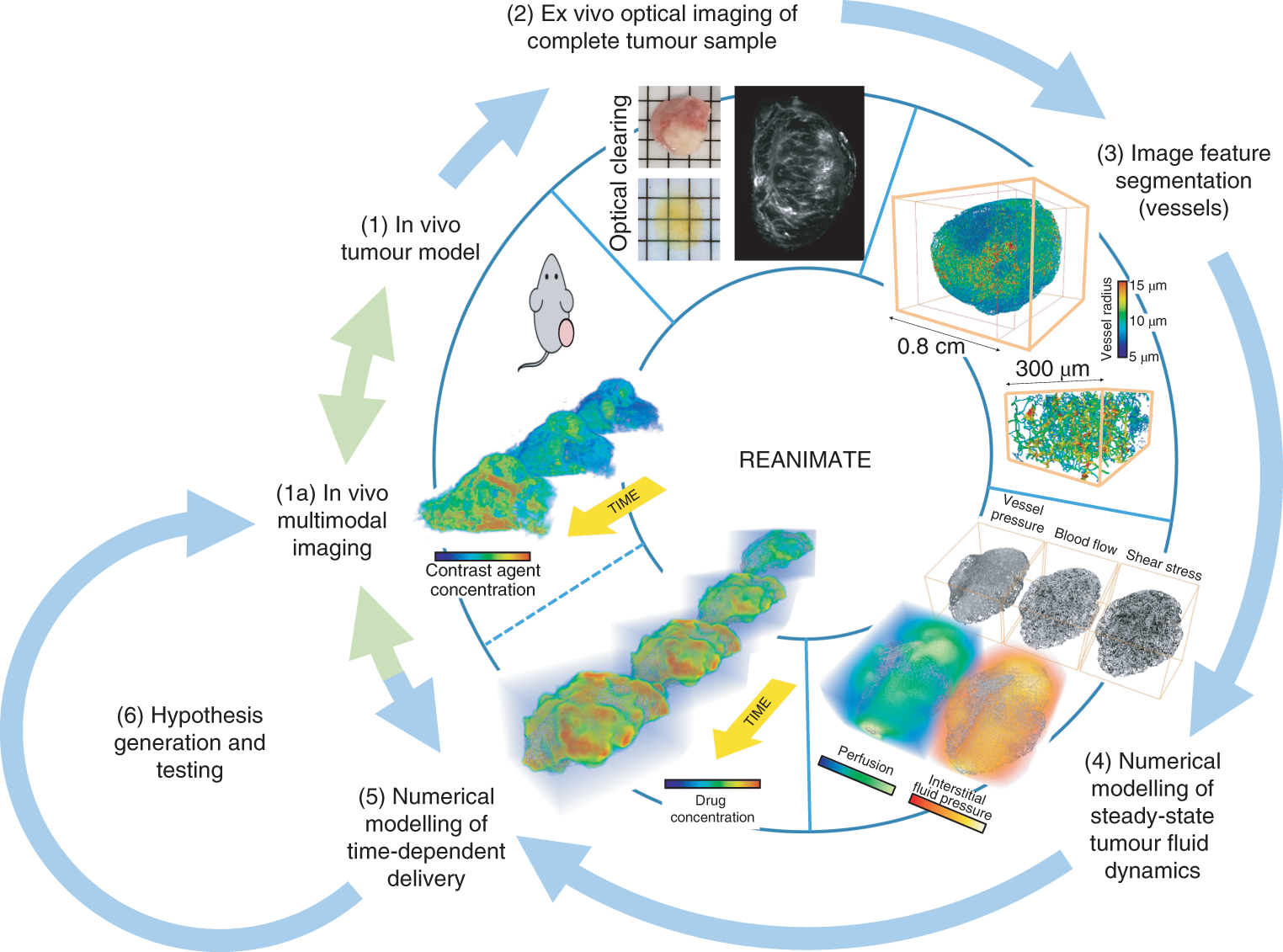
Understanding the uptake of a drug by diseased tissue, and the drug’s subsequent spatiotemporal distribution, are central factors in the development of effective targeted therapies. However, the interaction between the pathophysiology of diseased tissue and individual therapeutic agents can be complex, and can vary across tissue types and across subjects. Here, we show that the combination of mathematical modelling, high-resolution optical imaging of intact and optically cleared tumour tiss... Read more
Angela d’Esposito, Paul W. Sweeney, Morium Ali, Magdy Saleh, Rajiv Ramasawmy, Thomas A. Roberts, Giulia Agliardi, Adrien Desjardins, Mark F. Lythgoe, R. Barbara Pedley, Rebecca Shipley and Simon Walker-Samuel
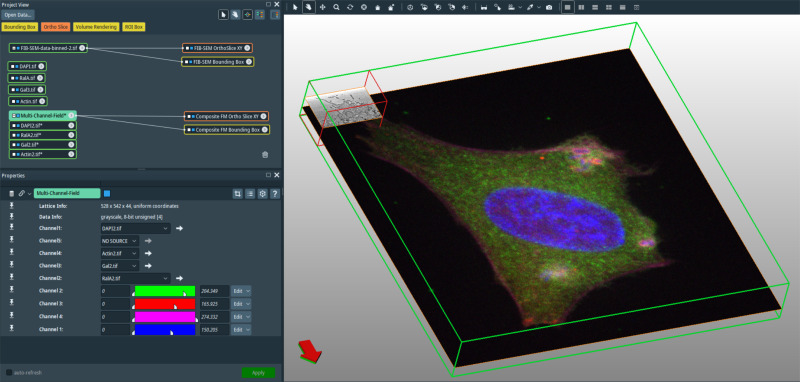
In recent years new methodologies and workflow pipelines for acquiring correlated fluorescence microscopy and volume electron microscopy datasets have been extensively described and made accessible to users of different levels. Post-acquisition image processing, and particularly correlation of the optical and electron data in a single integrated three-dimensional framework can be key for extracting valuable information, especially when imaging large sample volumes such as whole cells or tissu... Read more
Allon Weiner
The internal skeleton of the nasal cavity is sporadically and often incompletely described for many marsupial species and mammals in general. Here, I provide an anatomical survey of the ethmoid in the skulls of adult marsupials based on examination of computed tomography (CT) imagery of 29 taxa representing all the major extant groups of marsupials. (…) I compared ecological data with the number of ecto- and endoturbinals as a preliminary test to determine whether some of the interspec... Read more
Thomas E. Macrini
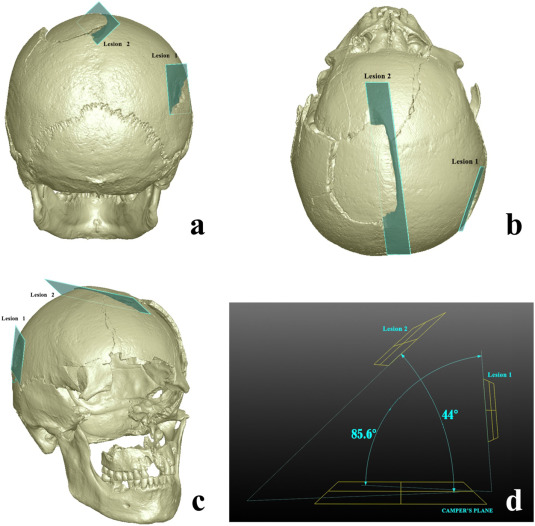
Human skeletal remains from archaeological contexts occasionally present signs of traumatic injuries from weapons, revealing, for example, the degree of interpersonal violence, the type of weapon and the sequence of events of a specific historical context.
Traumatic lesions are generally analyzed using macroscopic and microscopic methods, which are not necessarily integrated in the same study. In this study, we employed a multi-analytical approach to determine i... Read more
Antonino Vazzana, Lucia Martina Scalise, Mirko Traversari, Carla Figus, Salvatore Andrea Apicella, Laura Buti, Gregorio Oxilia, Rita Sorrentino, Silvia Pellegrini, Chiara Matteucci, Lucio Calcagnile, Raffaele Savigni, Robin N.M.Feeney, Giorgio Gruppioni, Stefano Benazziah
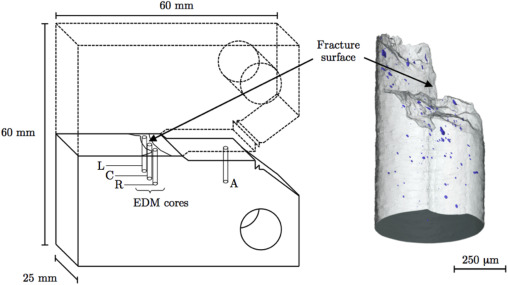
X-ray computed tomography (XCT) has been shown to reveal the true extent of ductile damage below the fracture surface of failed test specimens, which is often significantly underestimated when probed using 2D serial sectioning techniques and a microscope, since a single plane of material may only exhibit only a handful of resolvable voids.
In contrast XCT offers the capability to generate large datasets consisting of hundreds, if not thousands, of individually resolvable voids, where e... Read more
A. J. Cooper ; O. C. G. Tuck ; T. L. Burnett ; A. H. Sherry
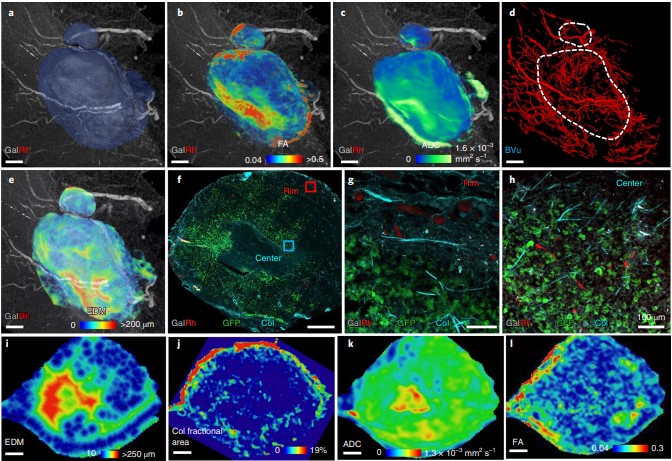
Despite advances in imaging, image-based vascular systems biology has remained challenging because blood vessel data are often available only from a single modality or at a given spatial scale, and cross-modality data are difficult to integrate.
Therefore, there is an exigent need for a multimodality pipeline that enables ex vivo vascular imaging with magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography and optical microscopy of the same sample, while permitting imaging with complementary c... Read more
Akanksha Bhargava, Benjamin Monteagudo, Priyanka Kushwaha, Janaka Senarathna, Yunke Ren, Ryan C. Riddle , Manisha Aggarwal and Arvind P. Pathak