Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
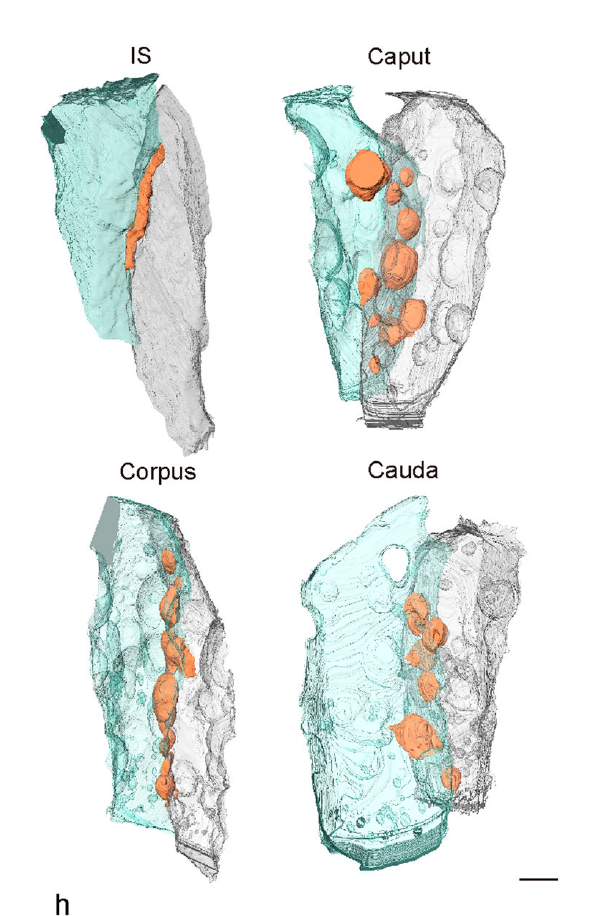
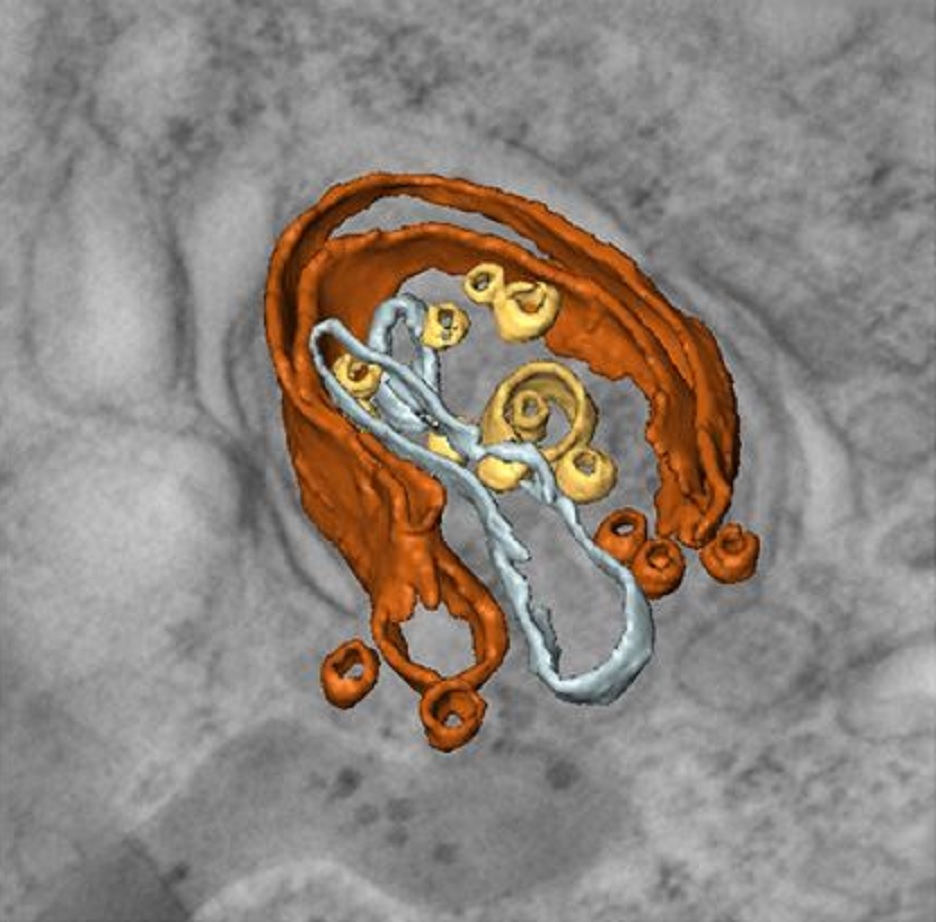
Mammalian epididymal epithelial cells are crucial for sperm maturation. Historically,
vacuole-like ultrastructures in epididymal epithelial cells were
observed via transmission electron microscopy but were undefined. Here, we
utilize volume electron microscopy (vEM) to generate 3D reconstructions of
epididymal epithelial cells and identify these vacuoles as intercellular organelle
reservoirs (IORs) in the lateral intercellular space (LIS), which contains
pr... Read more
Xia Li, Feng Qiao, Jiansheng Guo, Ting Jiang, Huifang Lou, Huixia Li, Gangcai Xie, Hangjun Wu, Weizhen Wang, Ruoyu Pei, Sha Liu, Mei Ye, Jin Li, Shiqin Huang, Mengya Zhang, Chaoye Ma, Yiwen Huang, Shushu Xu, Xiaofeng Li, Xiao Sun, Jun Yu, Kin Lam Fok, Shumin Duan & Hao Chen
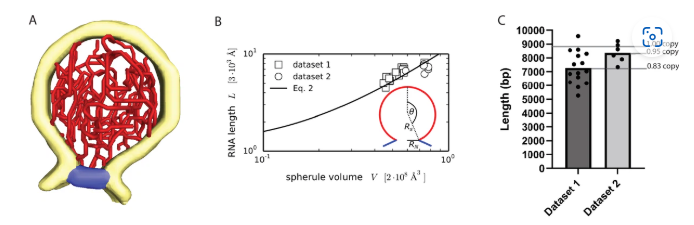
Architecture of the chikungunya virus replication organelle
Alphaviruses are mosquito-borne viruses that cause serious disease in humans and other mammals. Along with its mosquito vector, the Alphavirus chikungunya virus (CHIKV) has spread explosively in the last 20 years, and there is no approved treatment for chikungunya fever. On the plasma membrane of the infected cell, CHIKV generates dedicated organelles for viral RNA replication, so-called spherules. Whereas structures exist for several viral proteins that make up the spherule, ... Read more
Timothée Laurent, Pravin Kumar, Susanne Liese, Farnaz Zare, Mattias Jonasson, Andreas Carlson, Lars-Anders Carlson.
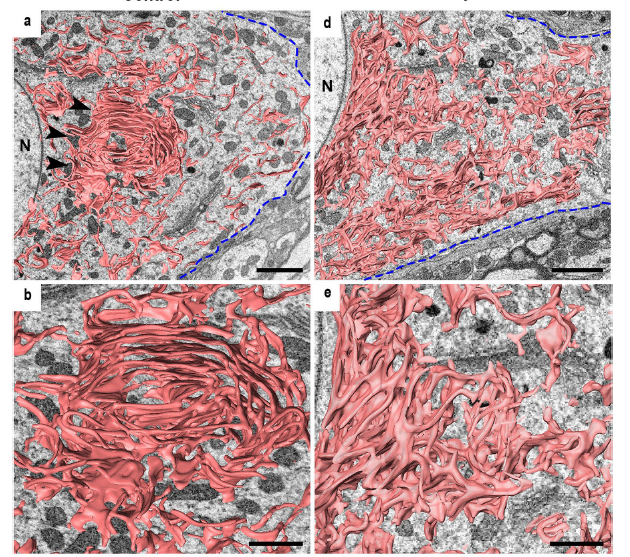
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) extends throughout a cell and plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Changes in ER shape could provide a clue to explore the mechanisms that underlie the fate determination of neurons after
axon injury because the ER drastically changes its morphology under neuronal stress to maintain cellular homeostasis and
recover from damage. Because of their tiny structures and richness in the soma, the detailed morphology of the ER and... Read more
Mahmoud Elgendy,Hiromi Tamada, Takaya Taira, Yuma Iio, Akinobu Kawamura, Ayusa Kunogi, Yuka Mizutani, Hiroshi Kiyama
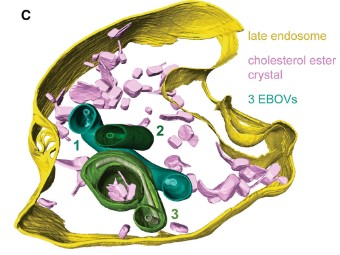
The Ebola virus VP40 matrix layer undergoes endosomal disassembly essential for membrane fusion
Ebola viruses (EBOVs) assemble into filamentous virions, whose shape and stability are determined by the matrix viral protein 40 (VP40). Virus entry into host cells occurs via membrane fusion in late endosomes; however, the mechanism of how the remarkably long virions undergo uncoating, including virion disassembly and nucleocapsid release into the cytosol, remains unknown. Here, we investigate the structural architecture of EBOVs entering host cells and discover that the VP40 matrix disassem... Read more
Sophie L Winter, Gonen Golani, Fabio Lolicato, Melina Vallbracht, Keerthihan Thiyagarajah, Samy Sid Ahmed, Christian Lüchtenborg, Oliver T Fackler, Britta Brügger, Thomas Hoenen, Walter Nickel Ulrich S Schwarz, Petr Chlanda
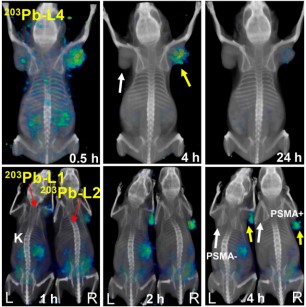
Targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy (TRT) using α-particle radiation is a promising approach for treating both large and micrometastatic lesions. Researchers developed prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–targeted low-molecular-weight agents for 212Pb-based TRT of patients with prostate cancer (PC) by evaluating the matching γ-emitting surrogate.
Targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy using α-particles (α-TRTs), which cause deposition of ionizing radiation of high-linear-ener... Read more
Sangeeta Ray Banerjee, Il Minn, Vivek Kumar, Anders Josefsson, Ala Lisok, Mary Brummet, Jian Chen, Ana P. Kiess, Kwamena Baidoo, Cory Brayton, Ronnie C. Mease, Martin Brechbiel, George Sgouros, Robert F. Hobbs, and Martin G. Pomper

Synergistic role of nucleotides and lipids for the self-assembly of Shs1 septin oligomers
Amira capacities for membranes and filaments segmentation in cryo-TEM images are featured on the front cover of Biochemical Journal, July 2020.
Budding yeast septins are essential for cell division and polarity. (…) [The authors] have dissected, here, for the first time, the behavior of the Shs1 protomer bound to membranes at nanometer resolution, in complex with the other septins. Using electron microscopy, [the authors] have shown that on membranes, Shs1 protomers self-assembl... Read more
Cyntia Taveneau, Rémi Blanc, Gerard Pehau-Arnaudet, Aurélie Cicco, Aurélie Bertin
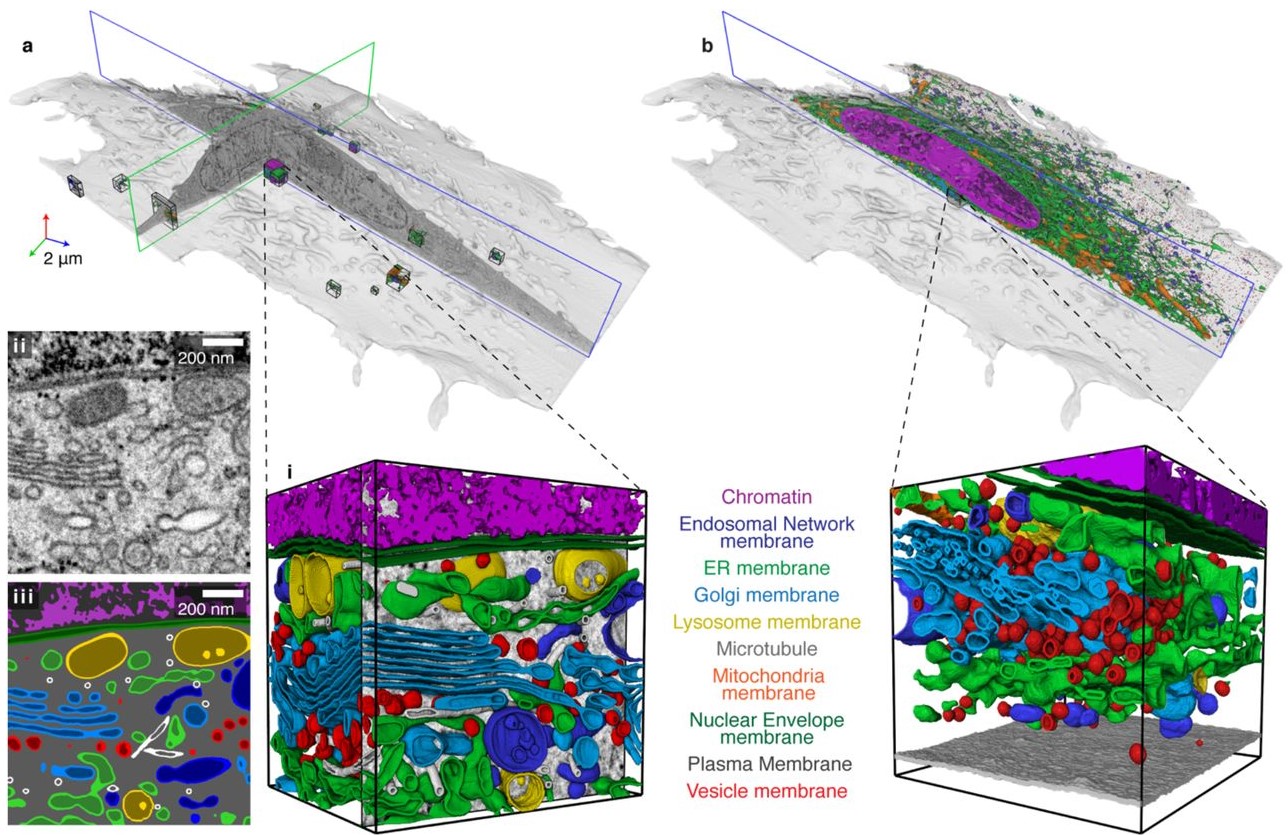
Automatic whole cell organelle segmentation in volumetric electron microscopy
Cells contain hundreds of different organelle and macromolecular assemblies intricately organized relative to each other to meet any cellular demands. Obtaining a complete understanding of their organization is challenging and requires nanometer-level, three-dimensional reconstruction of whole cells. Even then, the immense size of datasets and large number of structures to be characterized requires generalizable, automatic methods.
To meet this challenge, we developed an analy... Read more
Larissa Heinrich, Davis Bennett, David Ackerman, Woohyun Park, John Bogovic, View ORCID ProfileNils Eckstein, Alyson Petruncio, Jody Clements, C. Shan Xu, Jan Funke, Wyatt Korff, Harald F. Hess, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Stephan Saalfeld, Aubrey V. Weigel, COSEM Project Team
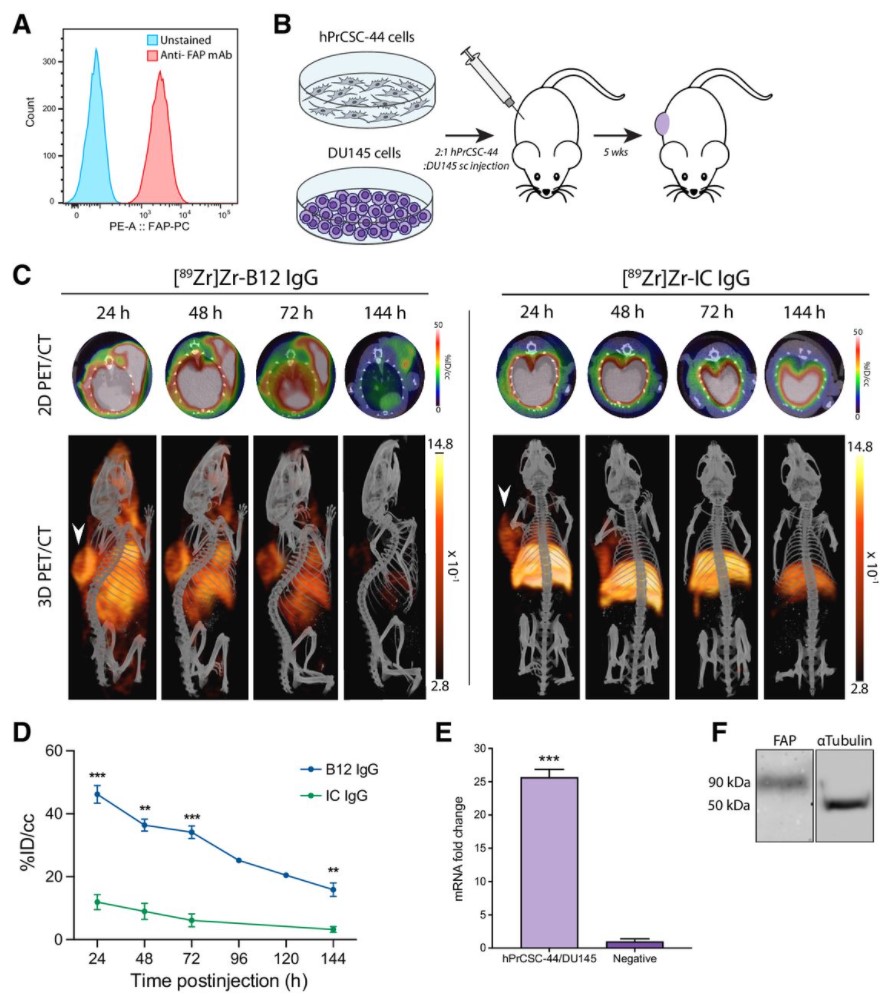
Malignant cells are surrounded by a complex and supportive tumor microenvironment that consists of immune cells, extracellular matrix, vasculature, and fibroblasts. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) are the major cell type in the reactive stroma and are known to promote tumorigenesis and metastasis. Fibroblast activation protein alpha (FAP) is a transmembrane serine protease expressed by CAFs in the microenvironment of epithelial tumors.
Meta-analysis of FAP expression and clinical ... Read more
Hallie M. Hintz, Joseph P. Gallant, Donald J. Vander Griend, Ilsa M. Coleman, Peter S. Nelson and Aaron M. LeBeau
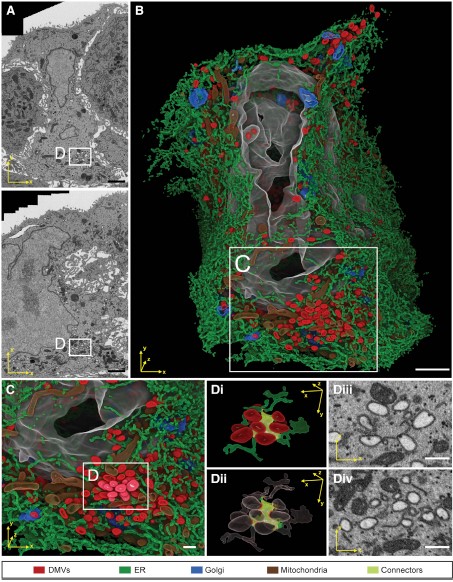
Integrative Imaging Reveals SARS-CoV-2-Induced Reshaping of Subcellular Morphologies
Cortese et al. use integrative imaging techniques to generate a publicly available repository of morphological alterations induced by SARS-CoV-2 in lung cells. Accumulation of ER-derived double-membrane vesicles, the viral replication organelle, occurs concomitantly with cytoskeleton remodeling and Golgi fragmentation. Pharmacological alteration of cytoskeleton dynamics restricts viral replication and spread.
Pathogenesis induced by SARS-CoV-2 is thought to result from both an inflamma... Read more
Mirko Cortese, Ji-Young Lee, Berati Cerikan, ..., Laurent Chatel-Chaix, Yannick Schwab, Ralf Bartenschlager
Macroautophagy is morphologically characterized by autophagosome formation. Autophagosomes are double-membraned vesicles that sequester cytoplasmic components for further degradation in the lysosome. Basal autophagy is paramount for intracellular quality control in post-mitotic cells but, surprisingly, the number of autophagosomes in post-mitotic neurons is very low, suggesting that alternative degradative structures could exist in neurons…
Read more
Maria Rosario Fernandez-Fernandez, Desire Ruiz-Garcia, Eva Martin-Solana, Francisco Javier Chichon, Jose L. Carrascosa, Jose-Jesus Fernandez
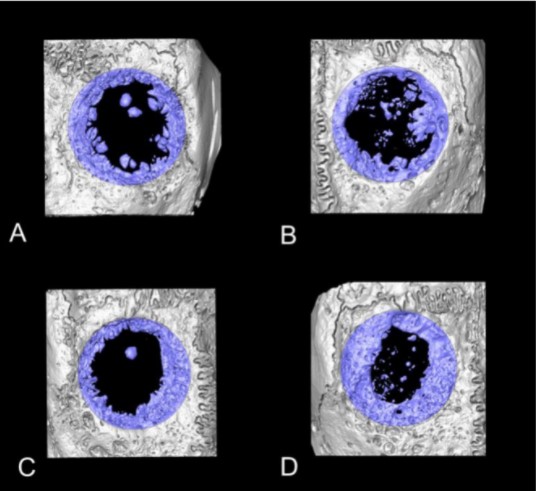
Collagen-Based Matrices for Osteoconduction: A Preclinical In Vivo Study
The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of additional hydroxyapatite (HA) in collagen-based matrices (CM) and membrane placement on bone formation in calvarial defects.
Critical size defects in the calvaria of 16 New Zealand White Rabbits were randomly treated with CM or mineralized collagen-based matrices (mCM). Half of the sites were covered with a collagen membrane. Animals were euthanized after 12 weeks of healing. The samples were studied by micro-CT and histology. New... Read more
Hiroki Katagiri, Yacine El Tawil, Niklaus P. Lang, Jean-Claude Imber, Anton Sculean, Masako Fujioka-Kobayashi and Nikola Saulacic
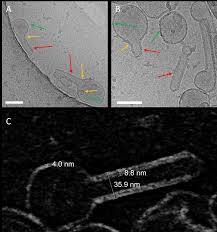
Influenza A matrix protein M1 is sufficient to induce lipid membrane deformation
The matrix protein M1 of the Influenza A virus is considered to mediate viral assembly and budding at the plasma membrane (PM) of infected cells. In order for a new viral particle to form, the PM lipid bilayer has to bend into a vesicle towards the extracellular side. Studies in cellular models have proposed that different viral proteins might be responsible for inducing membrane curvature in this context (including M1), but a clear consensus has not been reached. In this study, we use a comb... Read more
Ismail Dahmani, Kai Ludwig, Salvatore Chiantia
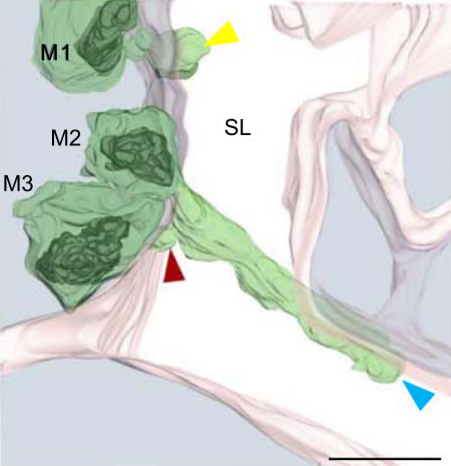
Multiple membrane extrusion sites drive megakaryocyte migration into bone marrow blood vessels
Platelets, cells central to hemostasis and thrombosis, are formed from parent cell megakaryocytes. Although the process is highly efficient in vivo, our ability to generate them in vitro is still remarkably inefficient. We proposed that greater understanding of the process in vivo is needed and used an imaging approach, intravital correlative light electron microscopy, to visualize platelet generation in bone marrow in the living mouse. In contrast to current understanding, we found that most... Read more
Edward Brown, Leo M Carlin, Claus Nerlov, Cristina Lo Celso, Alastair W Poole
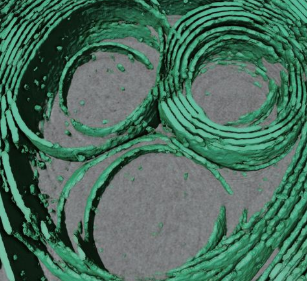
Membrane architecture of pulmonary lamellar bodies revealed by post-correlation on-lamella cryo-CLEM
Lamellar bodies (LBs) are surfactant rich organelles in alveolar type 2 cells. LBs disassemble into a lipid-protein network that reduces surface tension and facilitates gas exchange at the air-water interface in the alveolar cavity. Current knowledge of LB architecture is predominantly based on electron microscopy studies using disruptive sample preparation methods. We established a post-correlation on-lamella cryo-correlative light and electron microscopy approach for cryo-FIB milled lung ce... Read more
Steffen Klein, Benedikt H. Wimmer, Sophie L. Winter, Androniki Kolovou, Vibor Laketa, Petr Chlanda
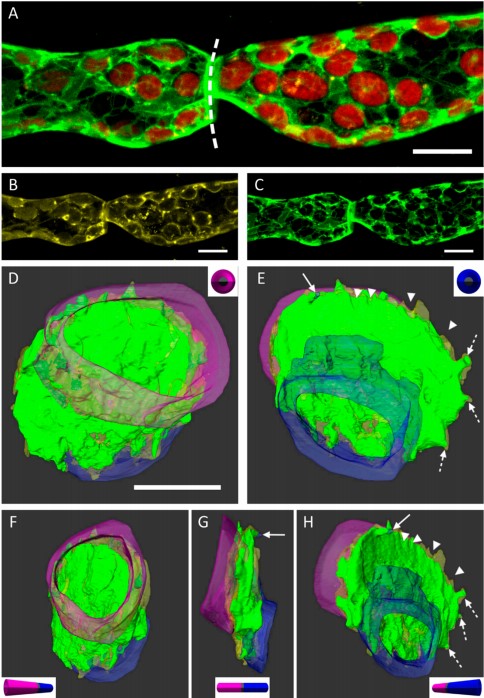
3D Dissection of Structural Membrane-Wall Contacts in Filamentous Moss Protonemata
Cell-to-cell contact is essential for communication and development of multicellular organisms. A prerequisite is the passage through membranes. That way, molecular exchange and information flow is regulated via hormones, membrane proteins and pores.
In plants, the rigid cell walls prevent large membrane contact areas between protoplasts. Only plasmodesmata, minute channels between adjacent cells, form direct connections. Often, molecular data of the proteins involved are manifold but t... Read more
Dominik Harant and Ingeborg Lang
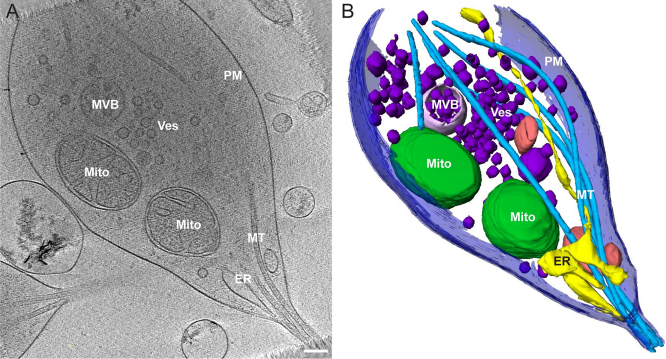
Morphology of mitochondria in spatially restricted axons revealed by cryo-electron tomography
Neurons project axons to local and distal sites and can display heterogeneous morphologies with limited physical dimensions that may influence the structure of large organelles such as mitochondria. Using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET), we characterized native environments within axons and presynaptic varicosities to examine whether spatial restrictions within these compartments influence the morphology of mitochondria. Segmented tomographic reconstructions revealed distinctive morphologi... Read more
Tara D. Fischer, Pramod K. Dash, Jun Liu, M. Neal Waxham
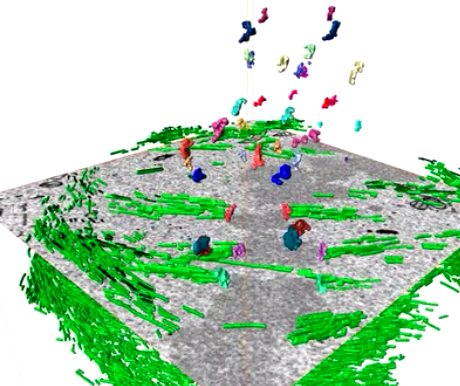
Serial block face scanning electron microscopy (SBF-SEM) is a powerful method to analyze cells in 3D. Here, working at the resolution limit of the method, we describe a correlative light–SBF-SEM workflow to resolve microtubules of the mitotic spindle in human cells. We present four examples of uses for this workflow that are not practical by light microscopy and/or transmission electron microscopy. First, distinguishing closely associated microtubules within K-fibers; second, resolving brid... Read more
Faye M. Nixon, Thomas R. Honnor, Nicholas I. Clarke, Georgina P. Starling, Alison J. Beckett, Adam M. Johansen, Julia A. Brettschneider, Ian A. Prior, Stephen J. Royle
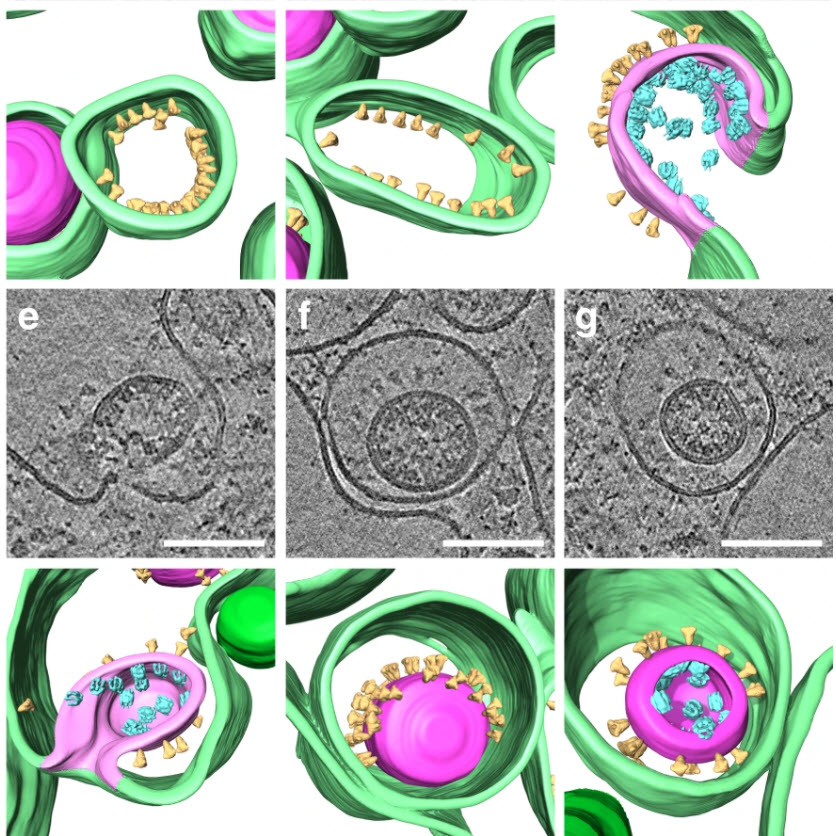
SARS-CoV-2 structure and replication characterized by in situ cryo-electron tomography
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of the COVID19 pandemic, is a highly pathogenic β-coronavirus. As other coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2 is enveloped, replicates in the cytoplasm and assembles at intracellular membranes. Here, we structurally characterize the viral replication compartment and report critical insights into the budding mechanism of the virus, and the structure of extracellular virions close to their native state by in situ cryo-electr... Read more
Steffen Klein, Mirko Cortese, Sophie L. Winter, Moritz Wachsmuth-Melm, Christopher J. Neufeldt, Berati Cerikan, Megan L. Stanifer, Steeve Boulant, Ralf Bartenschlager, Petr Chlanda
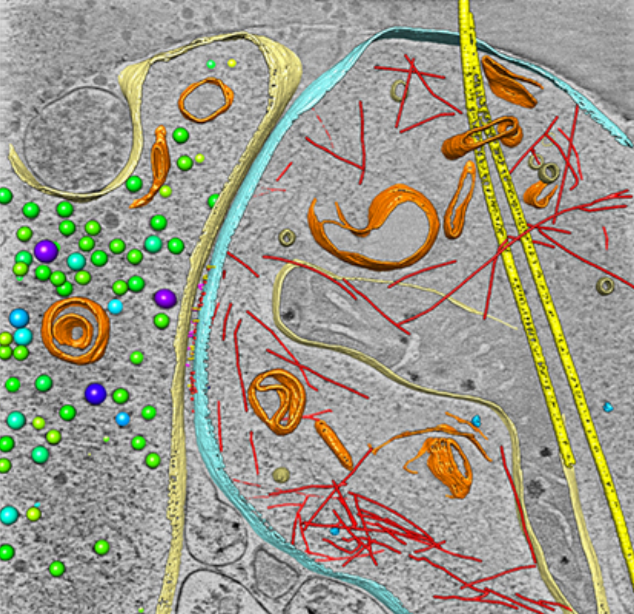
As key functional units in neural circuits, different types of neuronal synapses play distinct roles in brain information processing, learning, and memory. Synaptic abnormalities are believed to underlie various neurological and psychiatric disorders. Here, by combining cryo-electron tomography and cryo-correlative light and electron microscopy, we distinguished intact excitatory and inhibitory synapses of cultured hippocampal neurons, and visualized the in situ 3D organization of ... Read more
Chang-Lu Tao, Yun-Tao Liu, Rong Sun, Bin Zhang, Lei Qi, Sakar Shivakoti, Chong-Li Tian, Peijun Zhang, Pak-Ming Lau, Z. Hong Zhou and Guo-Qiang Bi
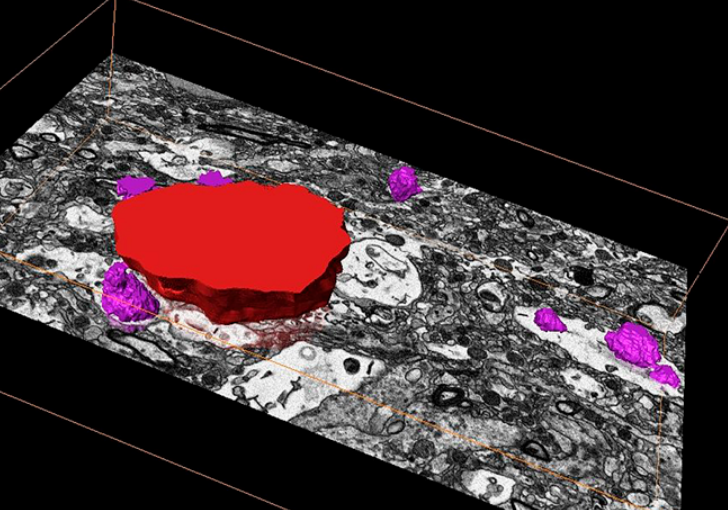
Corpora amylacea are cell-derived structures that appear physiologically in the aged human brain. While their histological identification is straightforward, their ultrastructural composition and microenvironment at the nanoscale have remained unclear so far, as has their relevance to aging and certain disease states that involve the sequestration of toxic cellular metabolites. Here, we apply correlative serial block-face scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron tomograp... Read more
Paula P. Navarro, Christel Genoud, Daniel Castaño-Díez, Alexandra Graff-Meyer, Amanda J. Lewis, Yvonne de Gier, Matthias E. Lauer, Markus Britschgi, Bernd Bohrmann, Stephan Frank, Jürgen Hench, Gabriel Schweighauser, Annemieke J. M. Rozemuller, Wilma D. J. van de Berg, Henning Stahlberg & Sarah H. Shahmoradian
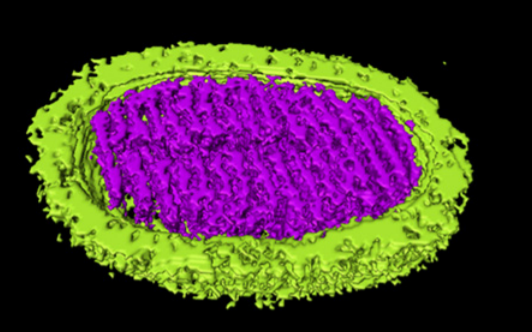
Novel Sulfolobus Virus with an Exceptional Capsid Architecture
A novel archaeal virus, denoted Sulfolobus ellipsoid virus 1 (SEV1), was isolated from an acidic hot spring in Costa Rica. The morphologically unique virion of SEV1 contains a protein capsid with 16 regularly spaced striations and an 11-nm-thick envelope. The capsid exhibits an unusual architecture in which the viral DNA, probably in the form of a nucleoprotein filament, wraps around the longitudinal axis of the virion in... Read more
Haina Wang, Zhenqian Guo, Hongli Feng, Yufei Chen, Xiuqiang Chen, Zhimeng Li, Walter Hernández-Ascencio, Xin Dai, Zhenfeng Zhang, Xiaowei Zheng, Marielos Mora-López, Yu Fu, Chuanlun Zhang, Ping Zhu, Li Huang