Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
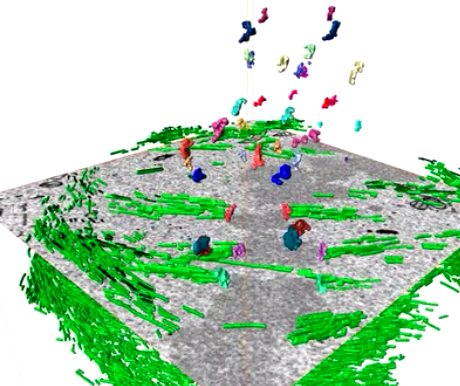
Serial block face scanning electron microscopy (SBF-SEM) is a powerful method to analyze cells in 3D. Here, working at the resolution limit of the method, we describe a correlative light–SBF-SEM workflow to resolve microtubules of the mitotic spindle in human cells. We present four examples of uses for this workflow that are not practical by light microscopy and/or transmission electron microscopy. First, distinguishing closely associated microtubules within K-fibers; second, resolving brid... Read more
Faye M. Nixon, Thomas R. Honnor, Nicholas I. Clarke, Georgina P. Starling, Alison J. Beckett, Adam M. Johansen, Julia A. Brettschneider, Ian A. Prior, Stephen J. Royle
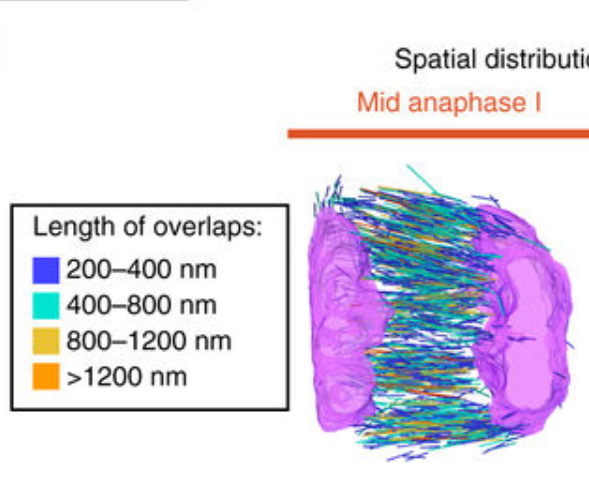
Chromosome segregation occurs by microtubule pushing in oocytes
During cell division, spindle microtubules ensure an equal repartition of chromosomes between the two daughter cells. While the kinetochore-dependent mechanisms that drive mitotic chromosome segregation are well understood, in oocytes of most species atypical spindles assembled in absence of centrosomes entail poorly understood mechanisms of chromosome segregation. In particular, the structure(s) responsible for force generation during meiotic chromosome separation in oocytes is unclear. Usin... Read more
Kimberley Laband, Rémi Le Borgne, Frances Edwards, Marine Stefanutti, Julie C. Canman, Jean-Marc Verbavatz, Julien Dumont
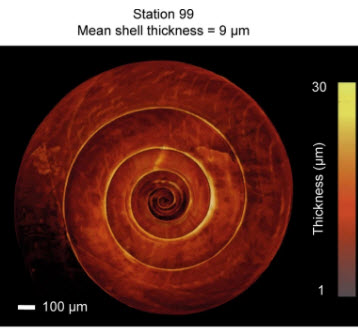
Pteropods make thinner shells in the upwelling region of the California Current Ecosystem
Shelled pteropods are widely regarded as bioindicators for ocean acidification, because their fragile aragonite shells are susceptible to increasing ocean acidity. While short-term incubations have demonstrated that pteropod calcification is negatively impacted by ocean acidification, we know little about net calcification in response to varying ocean conditions in natural populations. Here, we examine in situ calcification of Limacina helicina pteropods collected from the California... Read more
Lisette Mekkes, Willem Renema, Nina Bednaršek, Simone R. Alin, Richard A. Feely, Jef Huisman, Peter Roessingh & Katja T. C. A. Peijnenburg
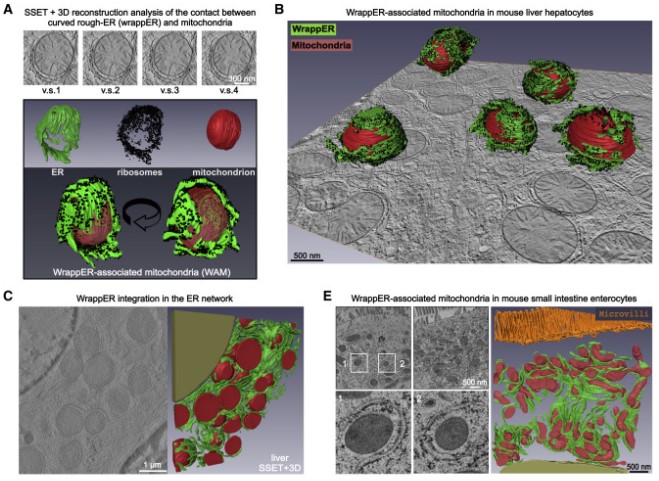
Mitochondria-rough-ER contacts in the liver regulate systemic lipid homeostasis
In this work, we studied mitochondria-rER contacts in vivo by serial section electron tomography (SSET) and 3D reconstruction analysis of cryo-fixed mouse tissue samples. We characterized this inter-organelle association as mitochondria tightly wrapped by sheets of curved rER (wrappER). Further, we used multi-omics and genetic approaches to obtain evidence that the wrappER is a distinct intracellular compartment and demonstrate the importance of wrappER-mitochondria contacts for v... Read more
Irene Anastasia, Nicolò Ilacqua, Andrea Raimondi, Philippe Lemieux, Rana Ghandehari-Alavijeh, Guilhem Faure, Sergei L. Mekhedov, Kevin J. Williams, Federico Caicci, Giorgio Valle, Marta Giacomello, Ariel D. Quiroga, Richard Lehner, Michael J. Miksis, Katalin Toth, Thomas Q. de Aguiar Vallim, Eugene V. Koonin, Luca Scorrano, Luca Pellegrini
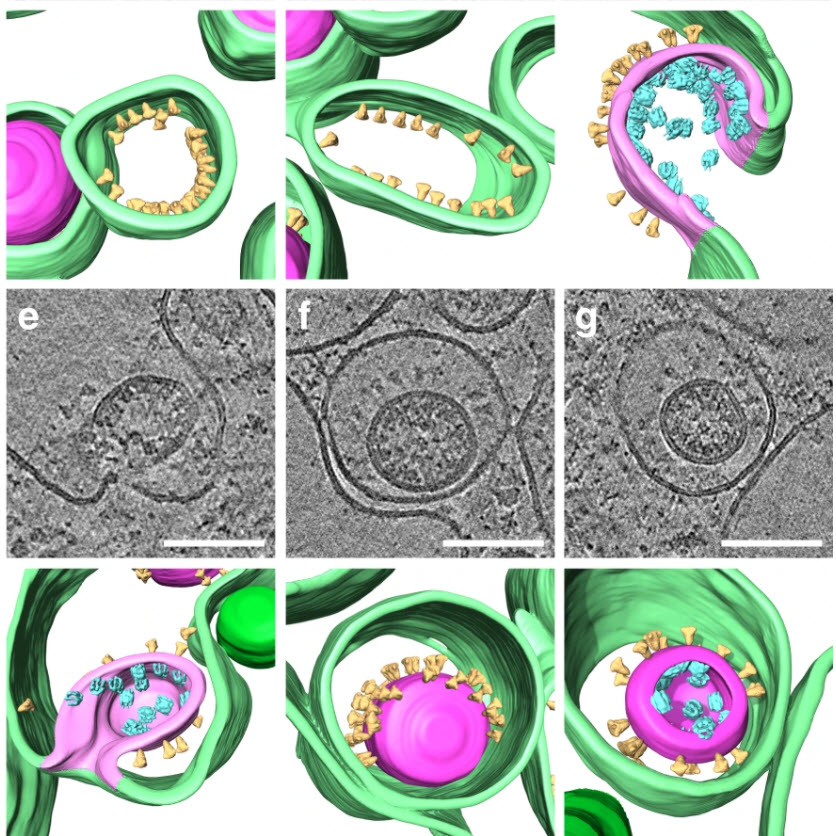
SARS-CoV-2 structure and replication characterized by in situ cryo-electron tomography
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of the COVID19 pandemic, is a highly pathogenic β-coronavirus. As other coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2 is enveloped, replicates in the cytoplasm and assembles at intracellular membranes. Here, we structurally characterize the viral replication compartment and report critical insights into the budding mechanism of the virus, and the structure of extracellular virions close to their native state by in situ cryo-electr... Read more
Steffen Klein, Mirko Cortese, Sophie L. Winter, Moritz Wachsmuth-Melm, Christopher J. Neufeldt, Berati Cerikan, Megan L. Stanifer, Steeve Boulant, Ralf Bartenschlager, Petr Chlanda
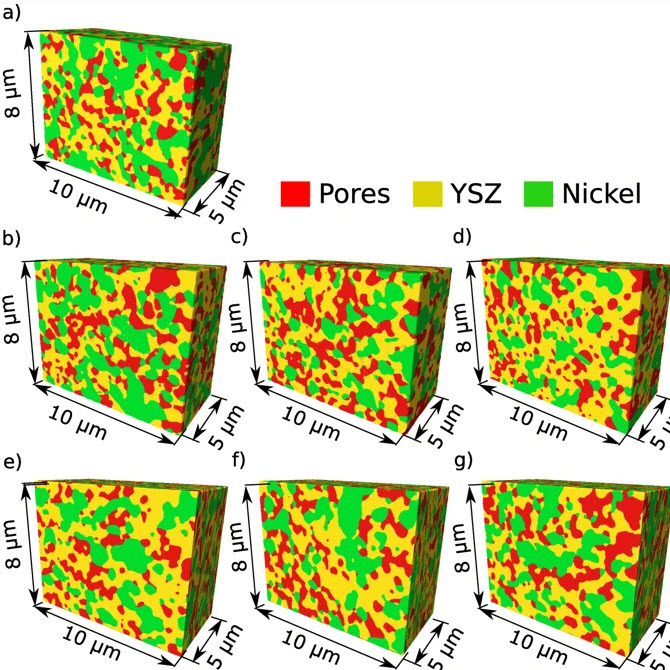
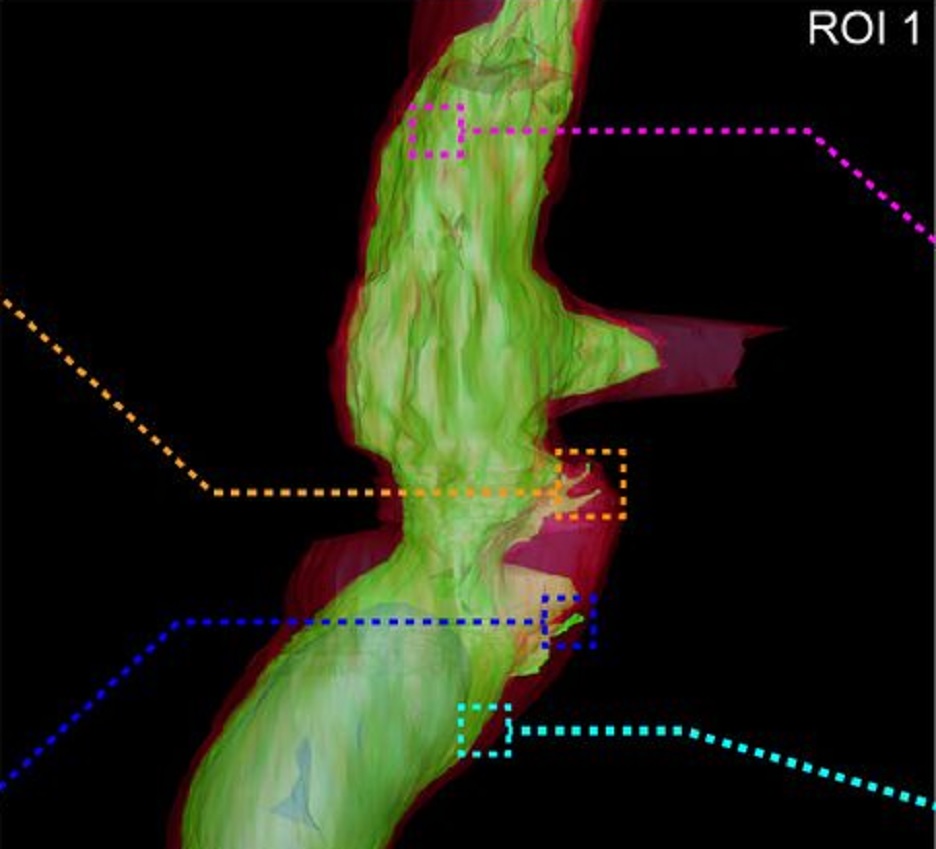
An Anisotropic Microstructure Evolution in a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Anode
A solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) is an electrochemical device that converts the chemical energy of hydrogen directly into electricity. A single cell usually has a form of a flat plate in which an impervious and dense ion-conducting electrolyte is sandwiched between two porous catalytic electrodes: an anode and a cathode. Fuel is fed to the anode side, and the air is supplied to the cathode. The gasses cannot mix to avoid unproductive combustion. Instead, gasses hit catalyst material, lose their... Read more
Grzegorz Brus, Hiroshi Iwai, Janusz S. Szmyd
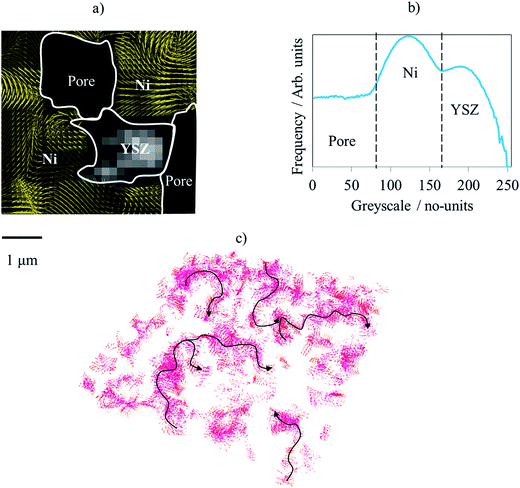
Evaluating microstructure evolution in an SOFC electrode using digital volume correlation
Degradation mechanisms within solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) during thermal cycling limit operational start-up times and cell lifetime, and must therefore be better understood and mitigated. This work explores such mechanisms using digital volume correlation (DVC) techniques applied to lab-based X-ray tomograms where the microstructural evolution is evaluated during the operational cycling of a Ni–YSZ/YSZ cell. To emulate reduced start-up times, five tomograms were collected over four operat... Read more
T. M. M. Heenan, X. Lu,, D. P. Finegan,, J. Robinson, F. Iacoviello, J. J. Bailey, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
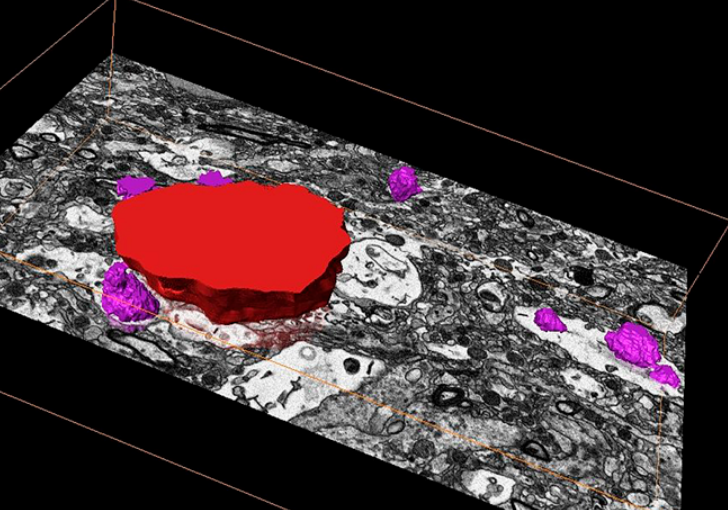
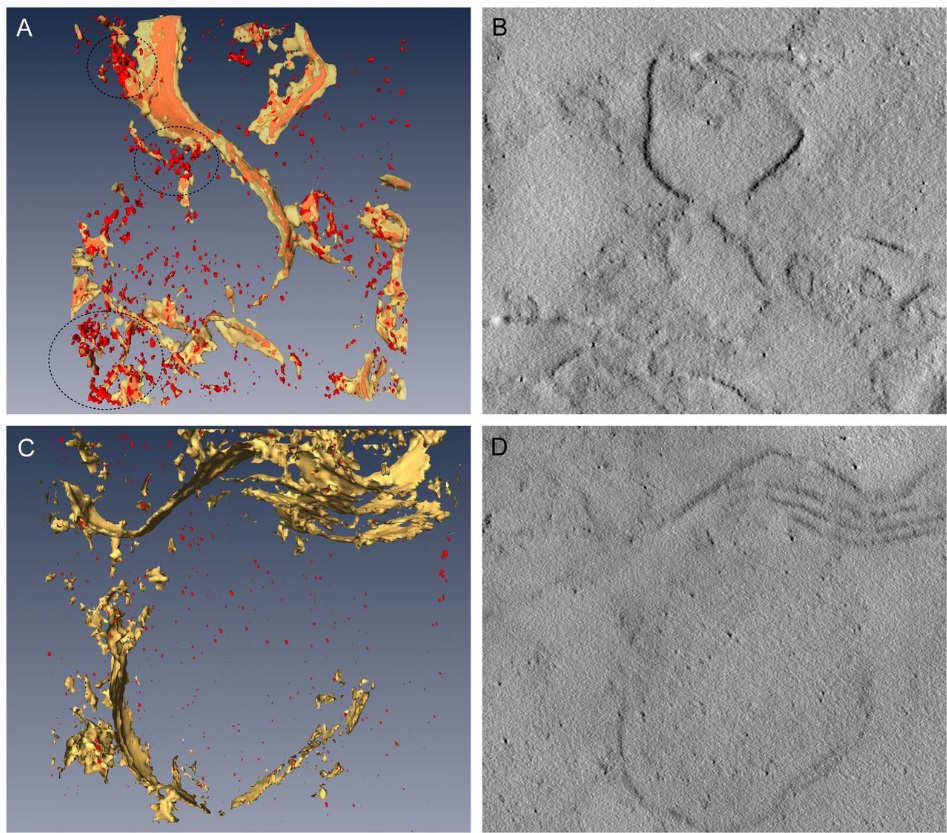
Corpora amylacea are cell-derived structures that appear physiologically in the aged human brain. While their histological identification is straightforward, their ultrastructural composition and microenvironment at the nanoscale have remained unclear so far, as has their relevance to aging and certain disease states that involve the sequestration of toxic cellular metabolites. Here, we apply correlative serial block-face scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron tomograp... Read more
Paula P. Navarro, Christel Genoud, Daniel Castaño-Díez, Alexandra Graff-Meyer, Amanda J. Lewis, Yvonne de Gier, Matthias E. Lauer, Markus Britschgi, Bernd Bohrmann, Stephan Frank, Jürgen Hench, Gabriel Schweighauser, Annemieke J. M. Rozemuller, Wilma D. J. van de Berg, Henning Stahlberg & Sarah H. Shahmoradian
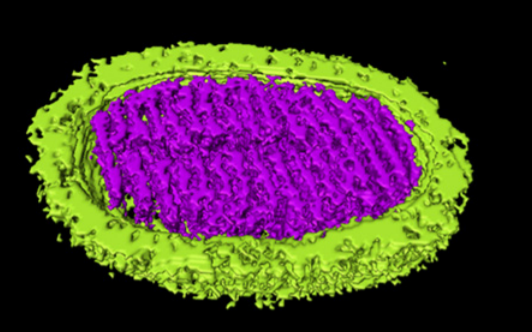
Novel Sulfolobus Virus with an Exceptional Capsid Architecture
A novel archaeal virus, denoted Sulfolobus ellipsoid virus 1 (SEV1), was isolated from an acidic hot spring in Costa Rica. The morphologically unique virion of SEV1 contains a protein capsid with 16 regularly spaced striations and an 11-nm-thick envelope. The capsid exhibits an unusual architecture in which the viral DNA, probably in the form of a nucleoprotein filament, wraps around the longitudinal axis of the virion in... Read more
Haina Wang, Zhenqian Guo, Hongli Feng, Yufei Chen, Xiuqiang Chen, Zhimeng Li, Walter Hernández-Ascencio, Xin Dai, Zhenfeng Zhang, Xiaowei Zheng, Marielos Mora-López, Yu Fu, Chuanlun Zhang, Ping Zhu, Li Huang
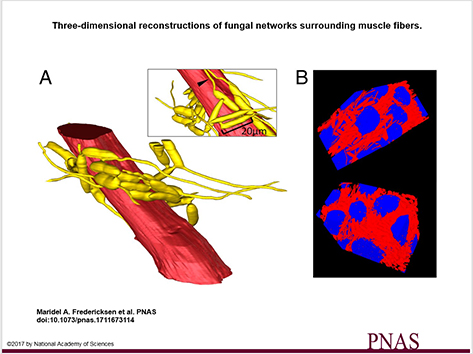
3D visualization and deep-learning reveal complex parasite networks in behaviorally manipulated ants
Microbial parasites may behave collectively to manipulate their host’s behavior. We examine adaptations of a microbial parasite in its natural environment: the body of its coevolved and manipulated host.
Electron microscopy and 3D reconstructions of host and parasite tissues reveal that this fungus invades muscle fibers throughout the ant’s body but leaves the brain intact, and that the fungal cells connect to form extensive networks.
Read more
Maridel A. Fredericksena, Yizhe Zhangb, Missy L. Hazenc, Raquel G. Loretoa,d, Colleen A. Mangoldd,e, Danny Z. Chenb, and David P. Hughes, Department of Entomology, Pennsylvania State University
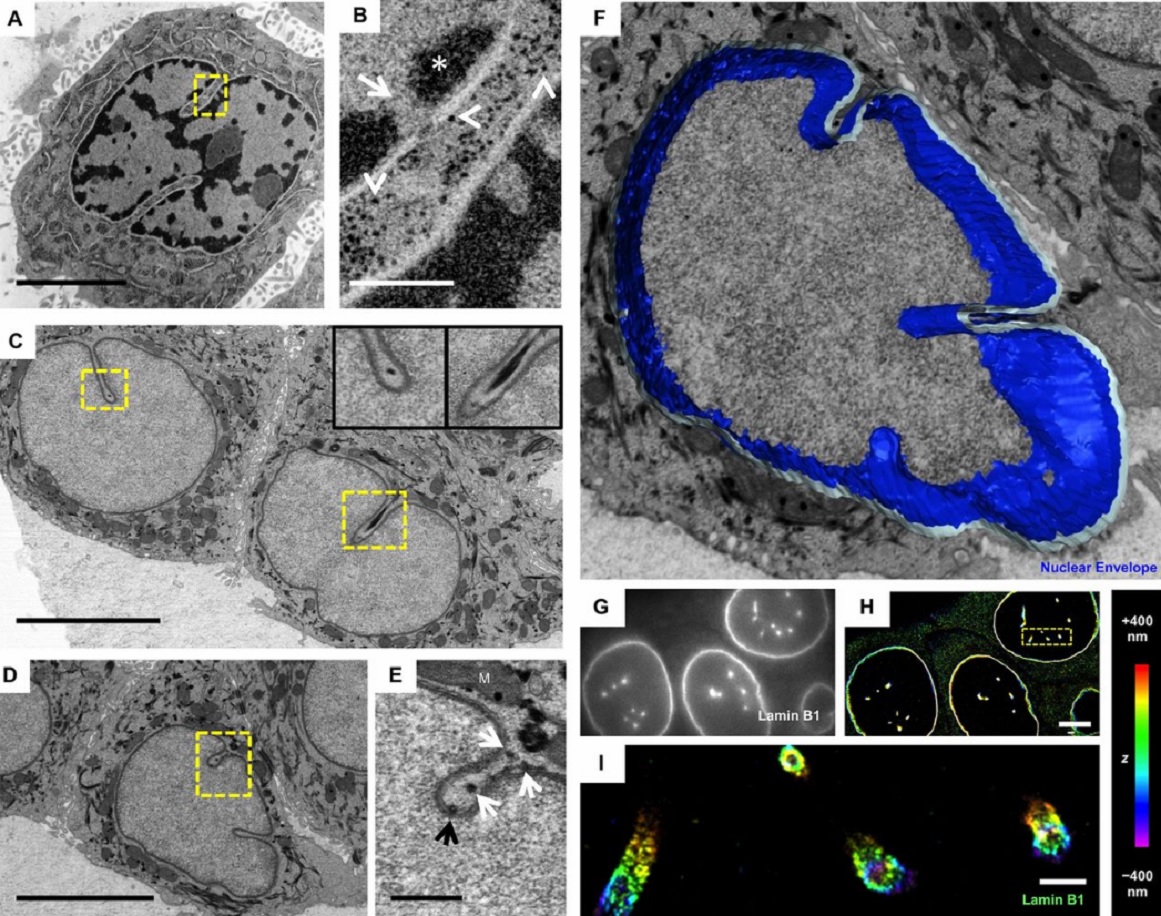
The importance of context in regulation of gene expression is now an accepted principle; yet the mechanism by which the microenvironment communicates with the nucleus and chromatin in healthy tissues is poorly understood. A functional role for nuclear and cytoskeletal architecture is suggested by the phenotypic differences observed between epithelial and mesenchymal cells…
Read more
Danielle M. Jorgens, Jamie L. Inman, Michal Wojcik, Claire Robertson, Hildur Palsdottir, Wen-Ting Tsai, Haina Huang, Alexandre Bruni-Cardoso, Claudia S. López, Mina J. Bissell, Ke Xu, Manfred Auer
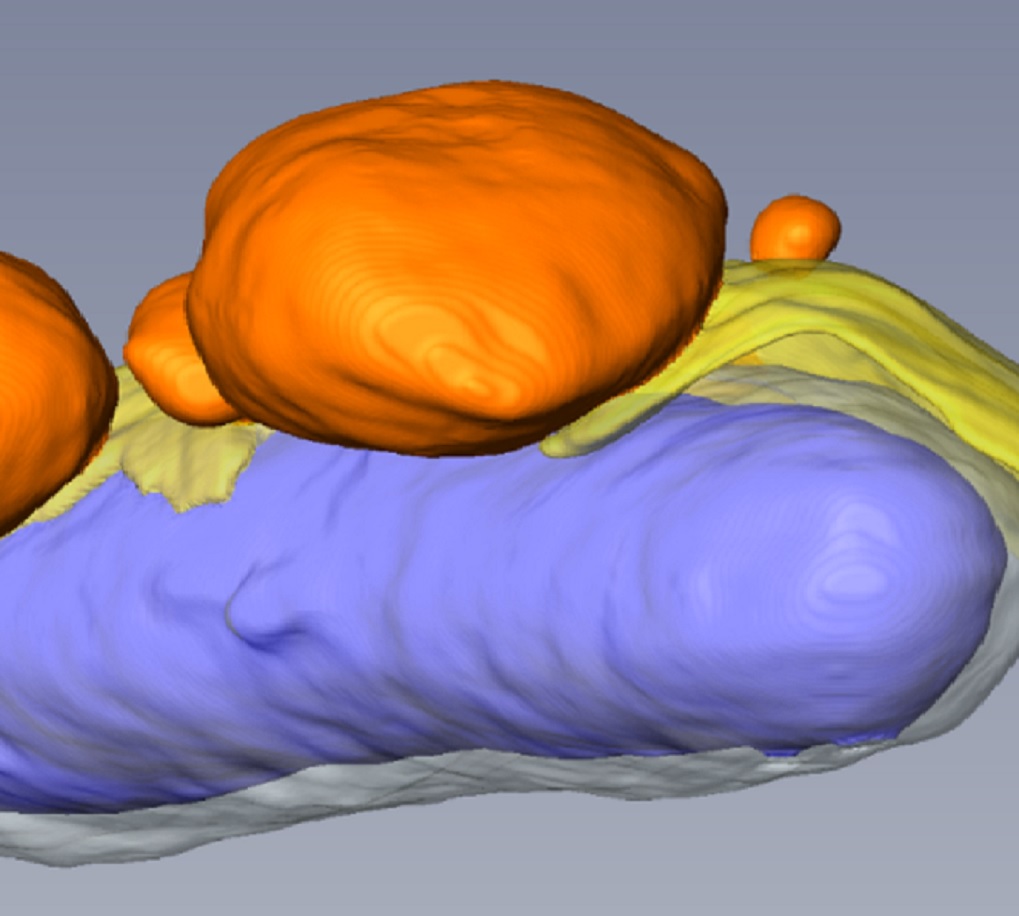
Macropinosomes are key players in early shigella invasion and vacuolar escape in epithelial cells
Intracellular pathogens include all viruses, many bacteria and parasites capable of invading and surviving within host cells. Key to survival is the subversion of host cell pathways by the pathogen for the purpose of propagation and evading the immune system. The intracellular bacterium Shigella flexneri, the causative agent of bacillary dysentery, invades host cells in a vacuole that is subsequently ruptured to allow growth of the pathogen within the host cytoplasm…
Read more
Allon Weiner , Nora Mellouk , Noelia Lopez-Montero , Yuen-Yan Chang, Célia Souque, Christine Schmitt, Jost Enninga
Determining the bacterial cell biology of planctomycetes
Bacteria of the phylum Planctomycetes have been previously reported to possess several features that are typical of eukaryotes, such as cytosolic compartmentalization and endocytosis-like macromolecule uptake. However, recent evidence points towards a Gram-negative cell plan for Planctomycetes, although in-depth experimental analysis has been hampered by insufficient genetic tools…
Read more
Christian Boedeker, Margarete Schüler, Greta Reintjes, Olga Jeske, Muriel C. F. van Teeseling et al.
Three-dimensional imaging of the intracellular assembly of a functional viral RNA replicase complex
Positive-strand RNA viruses, which can be devastating pathogens in humans, animals and plants, replicate their genomes on intracellular membranes. Here, we describe the three-dimensional ultrastructural organization of a tombusvirus replicase in yeast, a valuable model for exploring virus–host interactions…
Read more
Isabel Fernández de Castro, José J. Fernández, Daniel Barajas, Peter D. Nagy, Cristina Risco
Fast and precise targeting of single tumor cells in vivo by multimodal correlative microscopy
Intravital microscopy provides dynamic understanding of multiple cell biological processes, but its limited resolution has so far precluded structural analysis. Because it is difficult to capture rare and transient events, only a few attempts have been made to observe specific developmental and pathological processes in animal models using electron microscopy. The multimodal correlative approach that we propose here combines intravital microscopy, microscopic X-ray computed tomography and thr... Read more
Matthia A. Karreman, Luc Mercier, Nicole L. Schieber, Gergely Solecki, Guillaume Allio, Frank Winkler, Bernhard Ruthensteiner, Jacky G. Goetz, Yannick Schwab
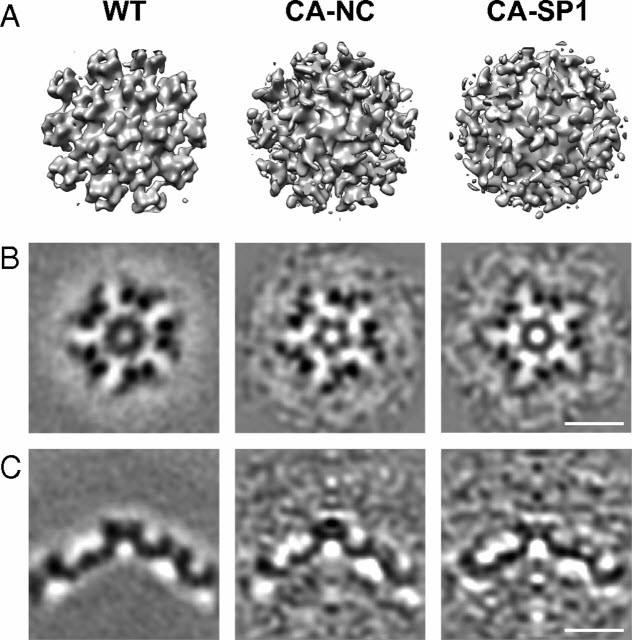
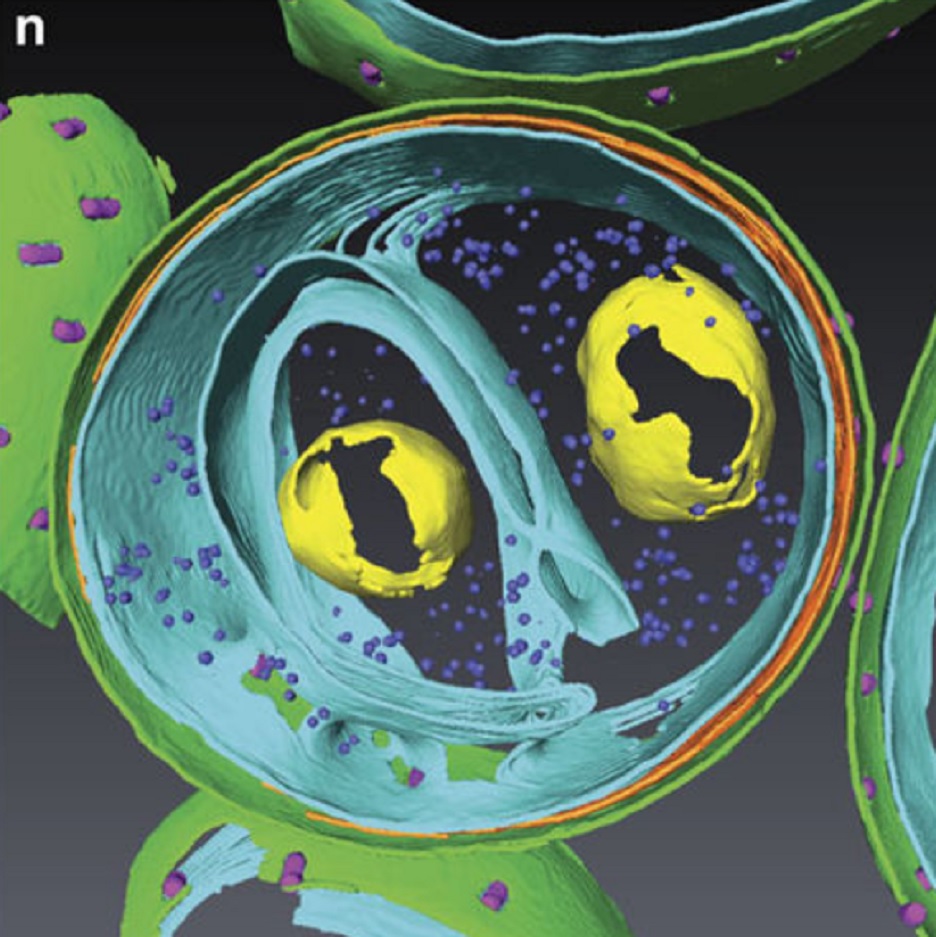
HIV-1 maturation occurs via multiple proteolytic cleavages of the Gag polyprotein, causing rearrangement of the virus particle required for infectivity. (…) How individual cleavages contribute to changes in protein structure and interactions, and how the mature, conical capsid forms, are poorly understood. Here, we employed cryoelectron tomography to determine morphology and high-resolution CA lattice structures for HIV1 derivatives in which Gag cleavage sites are mutated. These analyse... Read more
Simone Mattei, Aaron Tan, Barbel Glass, Barbara Muller, Hans-Georg Krausslich, and John A. G. Briggs
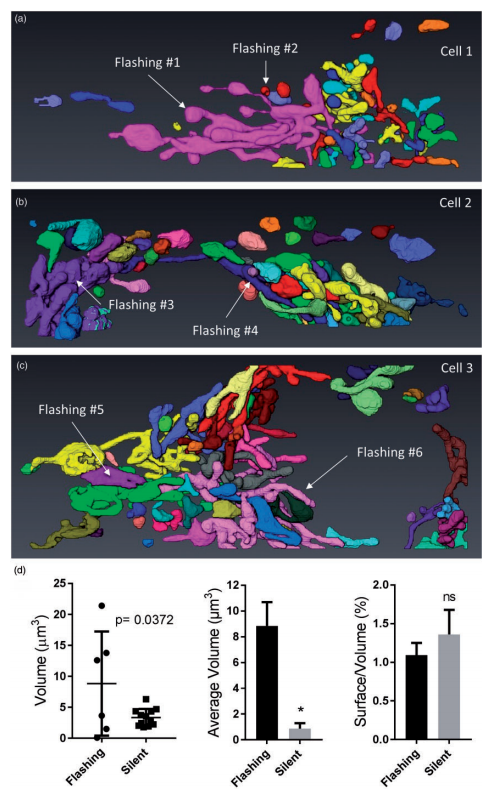
Ultrastructural Characterization of Flashing Mitochondria
Mitochondria undergo spontaneous transient elevations in matrix pH associated with drops in mitochondrial membrane potential. These mitopHlashes require a functional respiratory chain and the profusion protein optic atrophy 1, but their mechanistic basis is unclear. To gain insight on the origin of these dynamic events, we resolved the ultrastructure of flashing mitochondria by correlative light and electron microscopy. HeLa cells expressing the matrix-targeted pH probe mitoSypHer were screen... Read more
Manon Rosselin, Paula Nunes-Hasler, and Nicolas Demaurex
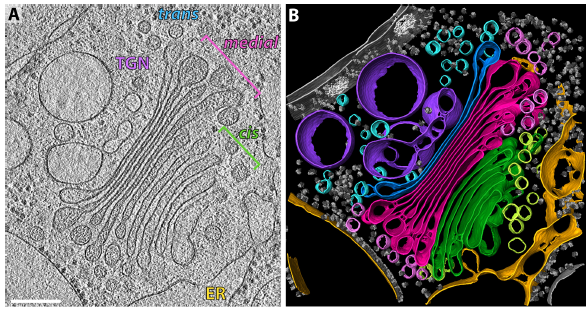
The structure of the COPI coat determined within the cell
COPI-coated vesicles mediate trafficking within the Golgi apparatus and from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum. Here, we applied cryo-focused ion beam milling, cryo-electron tomography and subtomogram averaging to determine the native structure of the COPI coat within vitrified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells. The native algal structure resembles the in vitro mammalian structure, but additionally reveals cargo bound beneath beta’–COP. We find that all coat components disassemble... Read more
Yury S Bykov, Miroslava Schaffer, Svetlana O Dodonova, Sahradha Albert, Jurgen M Plitzko, Wolfgang Baumeister, Benjamin D Engel, John AG Briggs
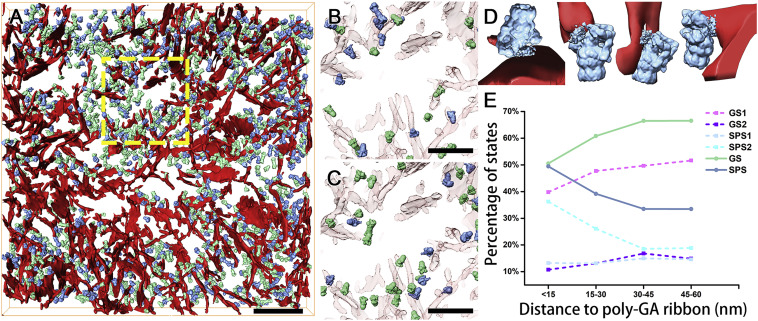
In Situ Structure of Neuronal C9orf72 Poly-GA Aggregates Reveals Proteasome Recruitment
Protein aggregation and dysfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system are hallmarks of many neurodegenerative diseases. Here, we address the elusive link between these phenomena by employing cryo-electron tomography to dissect the molecular architecture of protein aggregates within intact neurons at high resolution. We focus on the poly-Gly-Ala (poly-GA) aggregates resulting from aberrant translation of an expanded GGGGCC repeat in C9orf72, the most common genetic cause of amyotrophic latera... Read more
Qiang Guo, Carina Lehmer, Antonio Martinez-Sanchez, Till Rudack, Florian Beck, Hannelore Hartmann, Manuela Perez-Berlanga, Frederic Frottin, Mark S.Hipp, F. Ulrich Hartl, Dieter Edbauer, Wolfgang Baumeister, Ruben Fernandez-Busnadiego
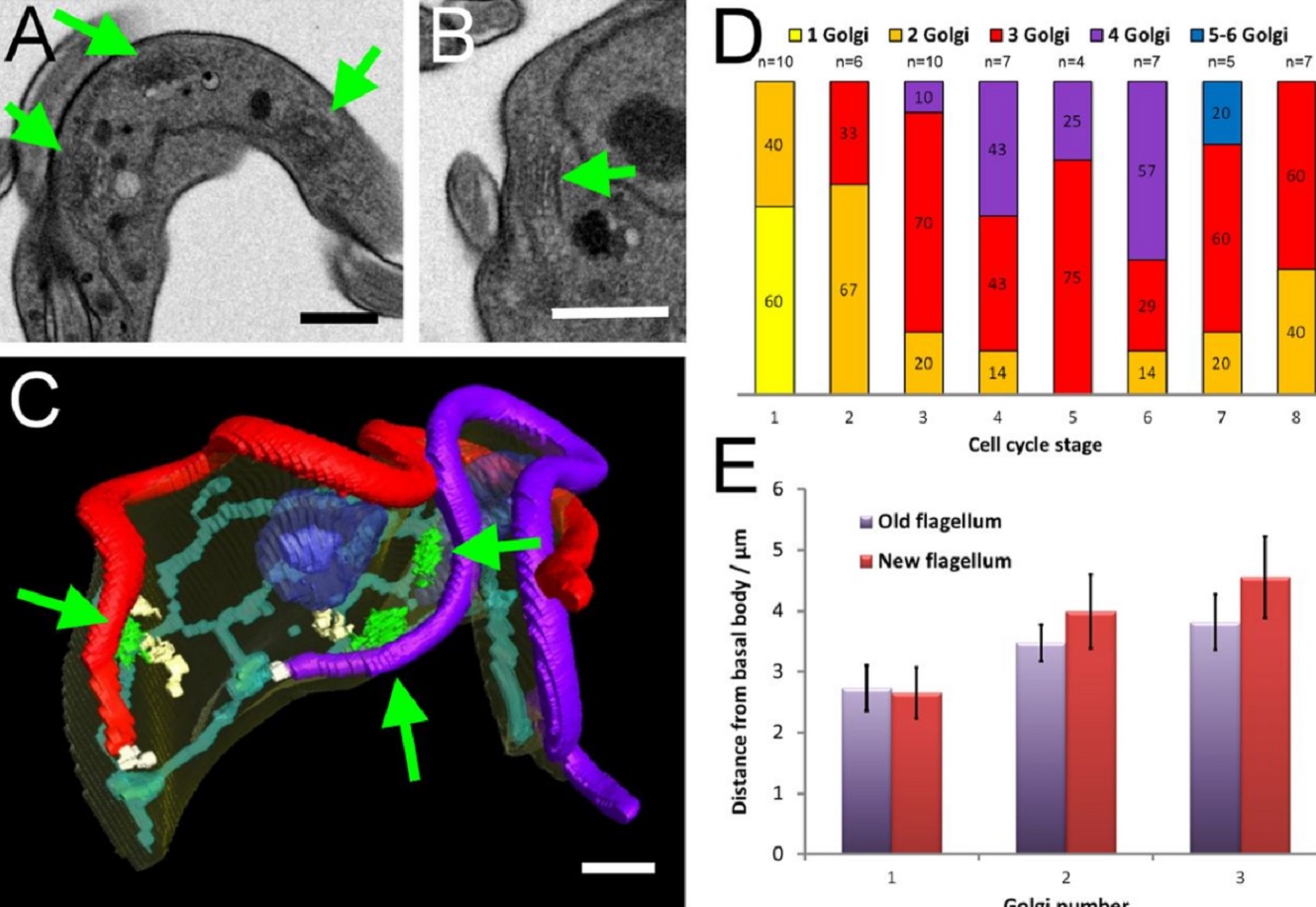
The major mammalian bloodstream form of the African sleeping sickness parasite Trypanosoma bruceimultiplies rapidly, and it is important to understand how these cells divide. Organelle inheritance involves complex spatiotemporal re-arrangements to ensure correct distribution to daughter cells…
Read more
Louise Hughes, Samantha Borrett, Katie Towers, Tobias Starborg, Sue Vaughan
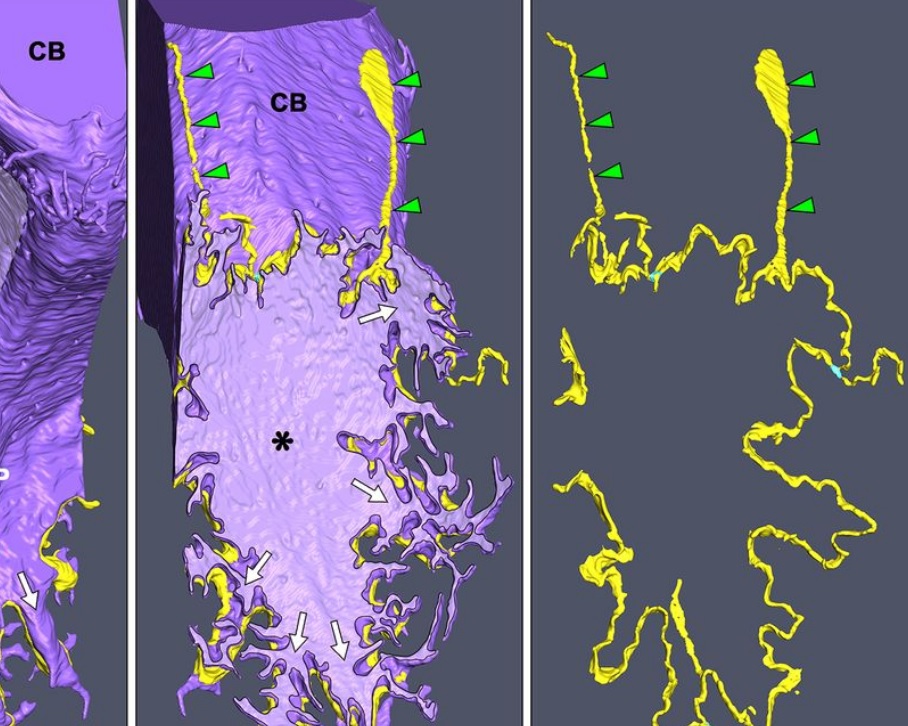
Morphological process of podocyte development revealed by block-face scanning electron microscopy
Podocytes present a unique 3D architecture specialized for glomerular filtration. However, several 3D morphological aspects on podocyte development remain partially understood because they are difficult to reveal using conventional scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Here, we adopted serial block-face SEM imaging…
Read more
Koichiro Ichimura, Soichiro Kakuta, Yuto Kawasaki, Takayuki Miyaki, Takahiro Nonami, Naoyuki Miyazaki, Tomoyo Nakao, Sakiko Enomoto, Shigeo Arai, Masato Koike, Kazuyoshi Murata, Tatsuo Sakai