Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
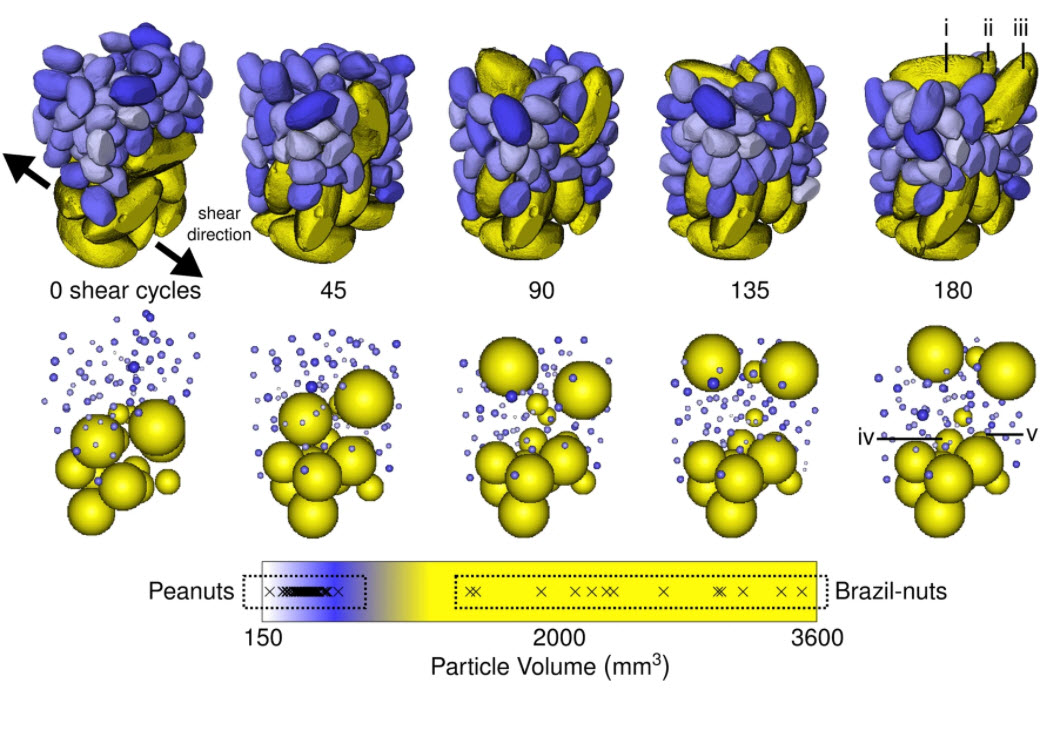
Scientists use Avizo to capture the complex dynamics of particle movement in granular materials
Scientists have for the first time captured the complex dynamics of particle movement in granular materials, helping to explain why mixed nuts often see the larger Brazil nuts gather at the top. This phenomenon, known as the ‘Brazil-nut effect’, has huge implications for industries where uneven mixing can critically degrade product quality. The findings could have vital impact on industries struggling with the phenomenon, such as pharmaceuticals and mining.
For th... Read more
Parmesh Gajjar, Chris G. Johnson, James Carr, Kevin Chrispeels, J. M. N. T. Gray & Philip J. Withers
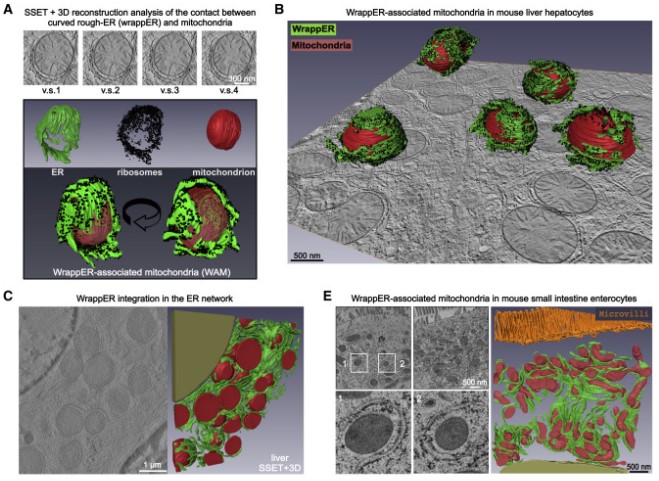
Mitochondria-rough-ER contacts in the liver regulate systemic lipid homeostasis
In this work, we studied mitochondria-rER contacts in vivo by serial section electron tomography (SSET) and 3D reconstruction analysis of cryo-fixed mouse tissue samples. We characterized this inter-organelle association as mitochondria tightly wrapped by sheets of curved rER (wrappER). Further, we used multi-omics and genetic approaches to obtain evidence that the wrappER is a distinct intracellular compartment and demonstrate the importance of wrappER-mitochondria contacts for v... Read more
Irene Anastasia, Nicolò Ilacqua, Andrea Raimondi, Philippe Lemieux, Rana Ghandehari-Alavijeh, Guilhem Faure, Sergei L. Mekhedov, Kevin J. Williams, Federico Caicci, Giorgio Valle, Marta Giacomello, Ariel D. Quiroga, Richard Lehner, Michael J. Miksis, Katalin Toth, Thomas Q. de Aguiar Vallim, Eugene V. Koonin, Luca Scorrano, Luca Pellegrini
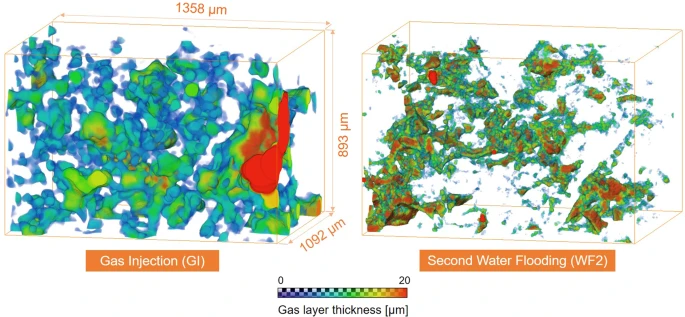
Pore-scale mechanisms of CO2 storage in oilfields
Rapid implementation of global scale carbon capture and storage is required to limit temperature rises to 1.5 °C this century. Depleted oilfields provide an immediate option for storage, since injection infrastructure is in place and there is an economic benefit from enhanced oil recovery. To design secure storage, we need to understand how the fluids are configured in the microscopic pore spaces of the reservoir rock. We use high-resolution X-ray imaging to study the flow of oil, water and ... Read more
Abdulla Alhosani, Alessio Scanziani, Qingyang Lin, Ali Q. Raeini, Branko Bijeljic & Martin J. Blunt
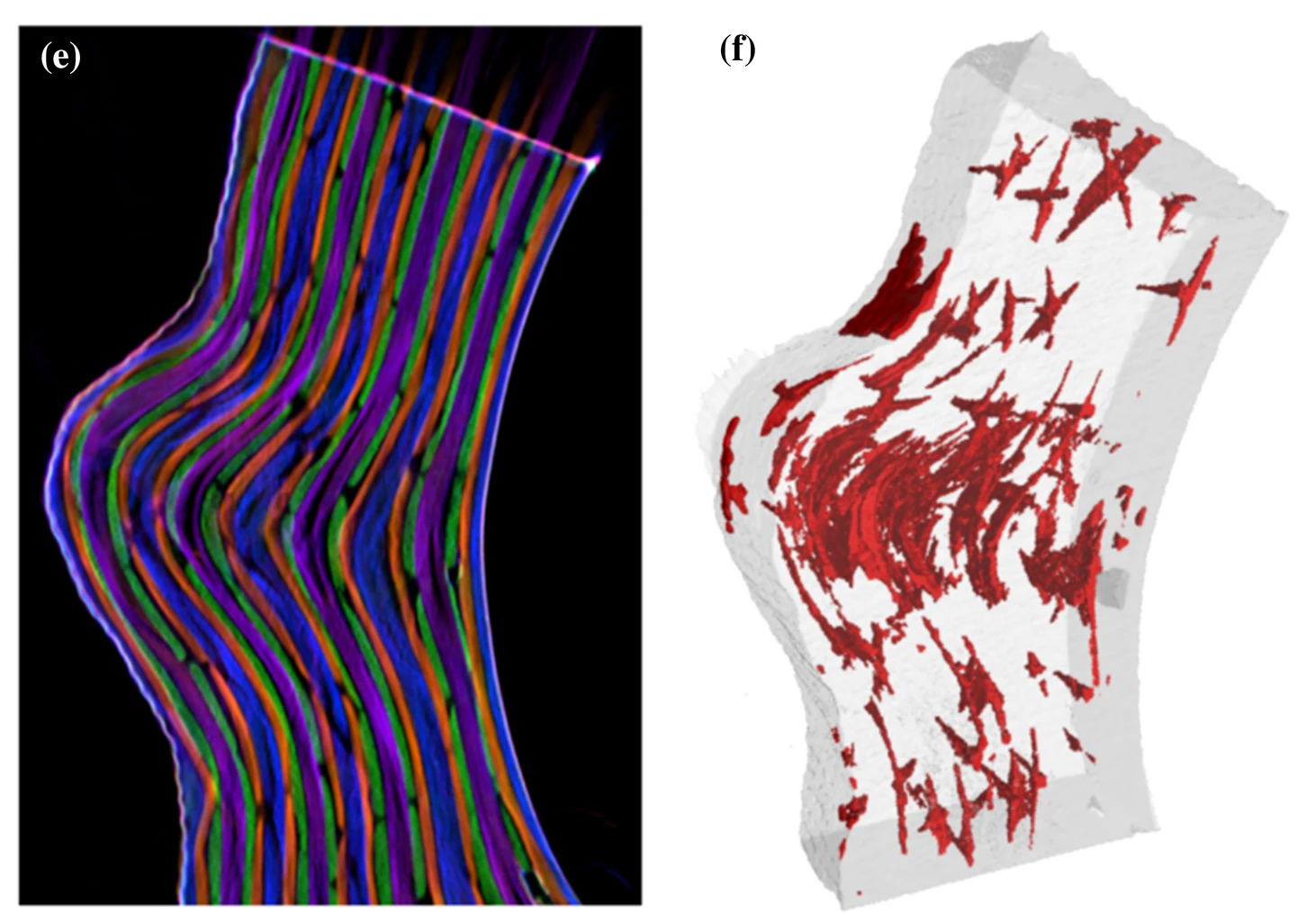
The high strength at moderate weight in combination with superior corrosion and fatigue properties makes carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) an attractive material for lightweight applications in aerospace. Nonetheless, besides several benefits, CFRP components also bear significant risks like a low resistance to impact damage. […] In this work, we present a multimodal approach to three-dimensionally quantify and visualize fiber orientation and resin-rich areas in carbon-fiber-reinf... Read more
Jonathan Glinz, Jan Šleichrt, Daniel Kytýř, Santhosh Ayalur-Karunakaran, Simon Zabler, Johann Kastner & Sascha Senck
Thermal Runaway of a Li-Ion Battery Studied by Combined ARC and Multi-Length Scale X-ray CT
Lithium ion battery failure occurs across multiple length scales. In this work, the properties of thermal failure and its effects on electrode materials were investigated in a commercial battery using a combination of accelerating rate calorimetry (ARC) and multi-length scale X-ray computed tomography (CT). ARC measured the heat dissipated from the cell during thermal runaway and enabled the identification of key thermal failure characteristics such as onset temperature and the rate of heat g... Read more
Drasti Patel, James B. Robinson, Sarah Ball, Daniel J. L. Brett and Paul R. Shearing
High market demands related to material quality and properties strongly influence redesigning of common safety loaded aluminum alloy castings. The quality of aluminum components and associated obtained mechanical properties are strongly dependent on the casting process and parameters, as well as on the chemical composition. Therefore, the redesigning of chemical composition of high-strength aluminum alloys becomes significant for safety critical structural components in automotive industry.Read more
Davor Stanić, Zdenka Zovko Brodarac, Letian Li
Porosity and Structure of Hierarchically Porous Ni/Al2O3 Catalysts for CO2 Methanation
Carbon dioxide emissions must be reduced significantly to limit the negative consequences of climate change. For this reason, fossil fuels must be replaced by renewable energy sources. However, wind and solar energy, for example, are sporadic sources and, thus, not inevitably available when needed. This results in periods of energy surplus and shortage, which are not necessarily predictable. Hence, energy storage concepts are required to compensate for these fluctuations, thereby retaining en... Read more
Sebastian Weber, Ken L. Abel, Ronny T. Zimmermann, Xiaohui Huang, Jens Bremer, Liisa K. Rihko-Struckmann, Darren Batey, Silvia Cipiccia, Juliane Titus, David Poppitz, Christian Kübel, Kai Sundmacher, Roger Gläser, Thomas L. Sheppard
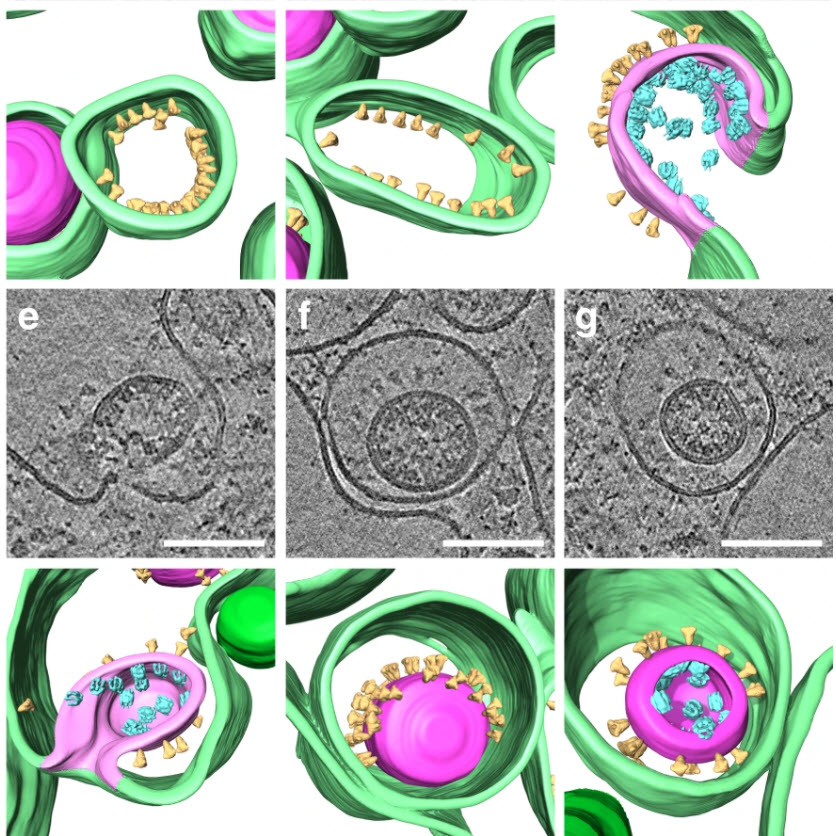
SARS-CoV-2 structure and replication characterized by in situ cryo-electron tomography
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of the COVID19 pandemic, is a highly pathogenic β-coronavirus. As other coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2 is enveloped, replicates in the cytoplasm and assembles at intracellular membranes. Here, we structurally characterize the viral replication compartment and report critical insights into the budding mechanism of the virus, and the structure of extracellular virions close to their native state by in situ cryo-electr... Read more
Steffen Klein, Mirko Cortese, Sophie L. Winter, Moritz Wachsmuth-Melm, Christopher J. Neufeldt, Berati Cerikan, Megan L. Stanifer, Steeve Boulant, Ralf Bartenschlager, Petr Chlanda
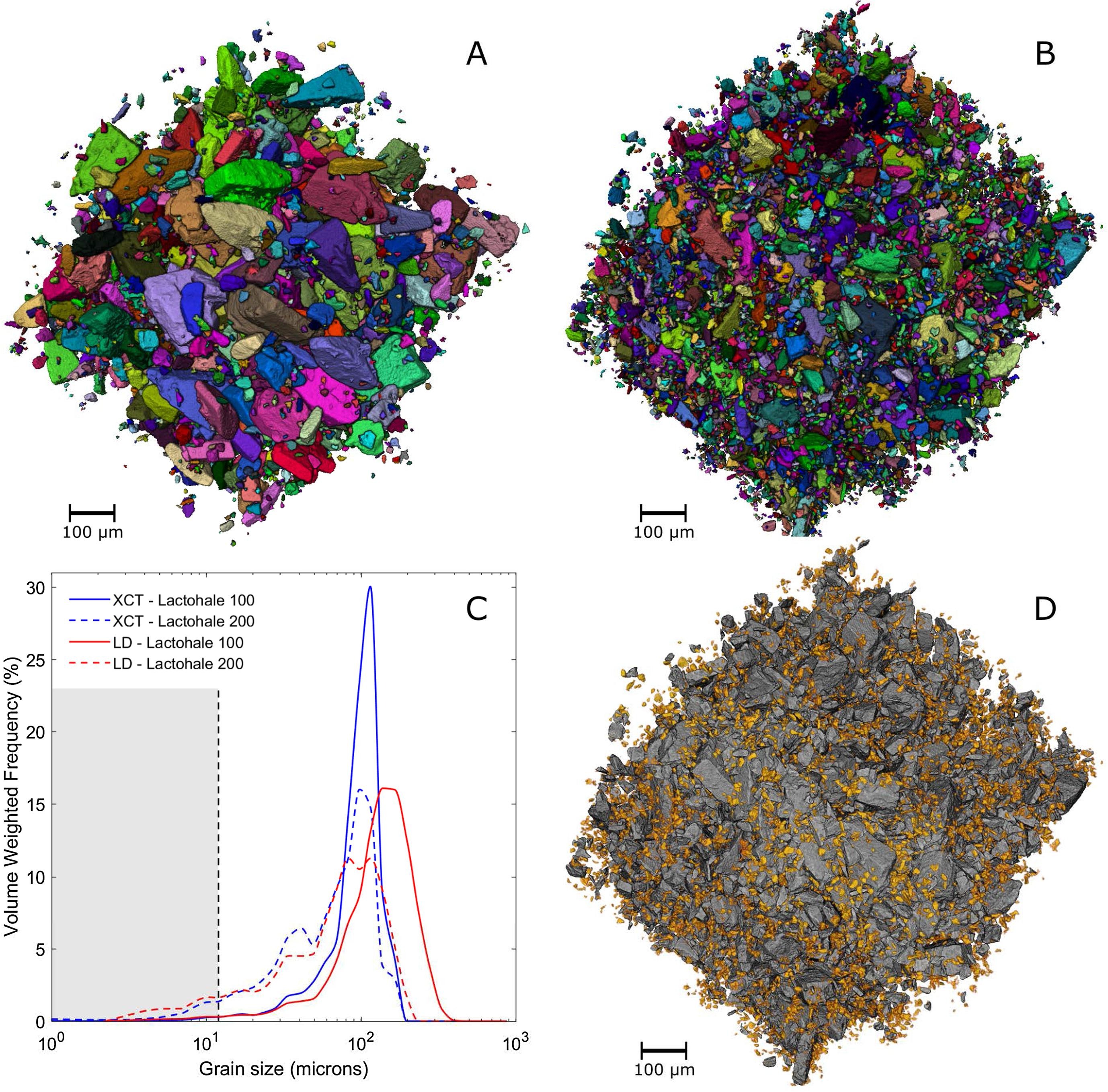
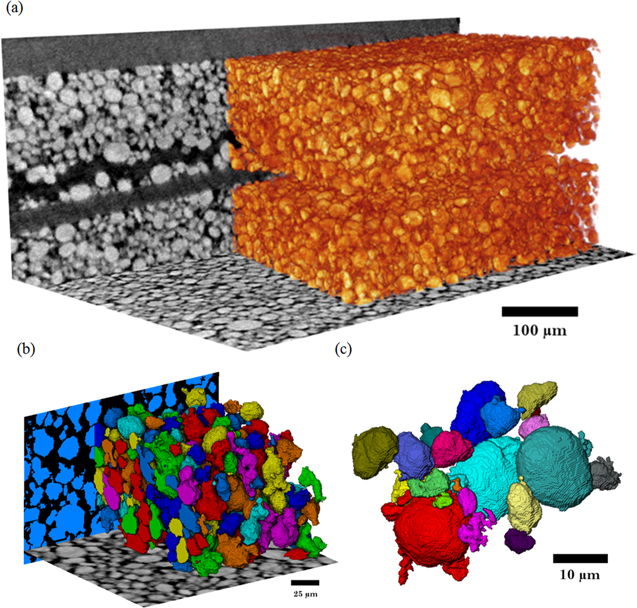
3D characterisation of dry powder inhaler formulations
Carrier-based dry powder inhaler (DPI) formulations need to be accurately characterised for their particle size distributions, surface roughnesses, fines contents and flow properties. Understanding the micro-structure of the powder formulation is crucial, yet current characterisation methods give incomplete information. Commonly used techniques like laser diffraction (LD) and optical microscopy (OM) are limited due to the assumption of sphericity and can give variable results depending on par... Read more
P. Gajjar, I.D. Styliari, T.T.H. Nguyen, J. Carr, X. Chen, J.A. Elliott, R.B. Hammond, T.L. Burnett, K. Roberts, P.J. Withers, D.Murnane
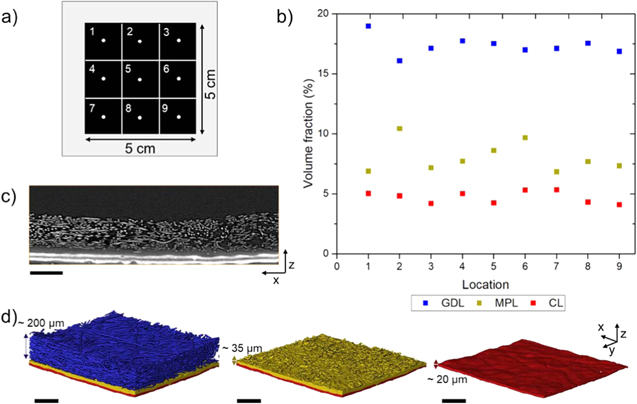
With the growing use of X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) datasets for modelling of transport properties, comes the need to define the representative elementary volume (REV) if considering three dimensions or the representative elementary area (REA) if considering two dimensions. The resolution used for imaging must be suited to the features of interest in the sample and the region-of-interest must be sufficiently large to capture key information. Polymer electrolyte fuel cells have a hier... Read more
Jennifer Hack et al 2020 J. Electrochem.
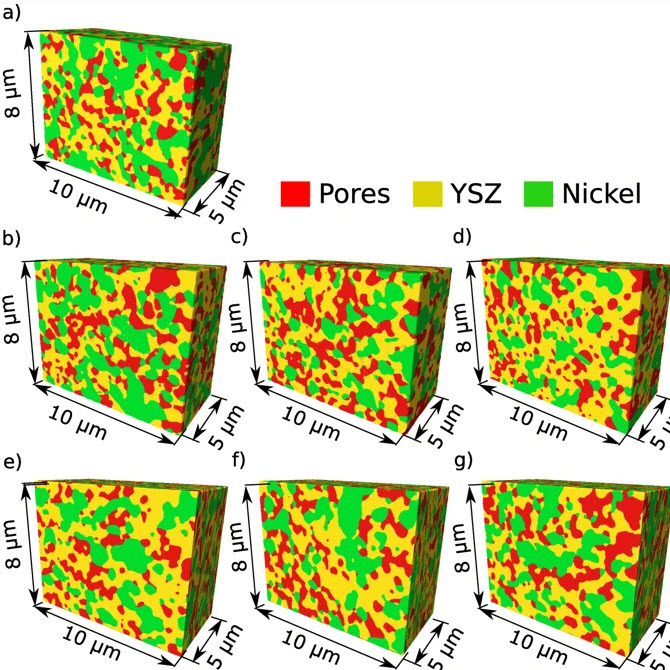
An Anisotropic Microstructure Evolution in a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Anode
A solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) is an electrochemical device that converts the chemical energy of hydrogen directly into electricity. A single cell usually has a form of a flat plate in which an impervious and dense ion-conducting electrolyte is sandwiched between two porous catalytic electrodes: an anode and a cathode. Fuel is fed to the anode side, and the air is supplied to the cathode. The gasses cannot mix to avoid unproductive combustion. Instead, gasses hit catalyst material, lose their... Read more
Grzegorz Brus, Hiroshi Iwai, Janusz S. Szmyd
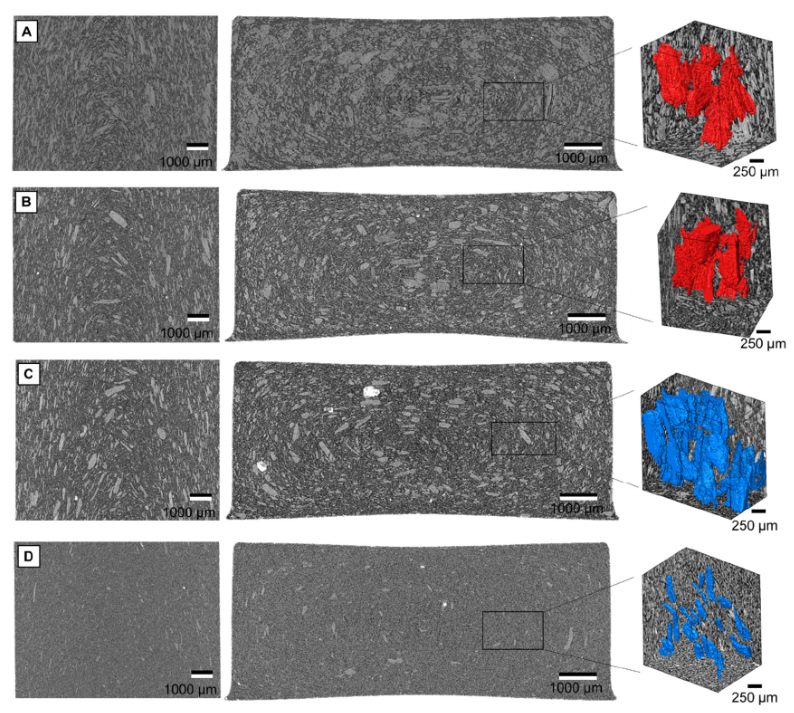
In this study, various wood material sources were used for the manufacture of wood-polymer composites (WPC). The materials were categorised as virgin wood particles (VWP), reprocessed WPC particles (RWP) and recycled thermoset composite particles (RCP) and derived from two virgin wood sources, three-layer particle boards, medium-density fibre boards (MDF) boards,or two different wood/polypropylene composites. All produced wood-polypropylene compounds contained 60% wood material and were manu... Read more
Kim Christian Krause, D, Philipp Sauerbier, Tim Koddenberg and Andreas Krause
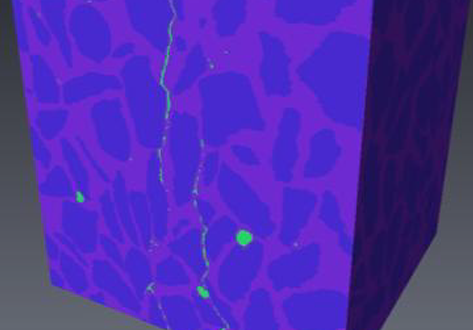
X-ray Computed Tomography (XCT) is a powerful technology that can accurately image the internal structures of composite and heterogeneous materials in three-dimensions (3D). In this study, in-situ micro XCT tests of concrete specimens under progressive compressive loading are carried out. The aim of the observations is to gain a better understanding of 3D fracture and failure mechanisms at the meso-scale. To characterise the fracture evolution as the deformation increases, two methods are use... Read more
College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Zhejiang University | School of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering, the University of Manchester | Manchester X-ray Imaging Facility | Oxford Martin School and Department of Materials
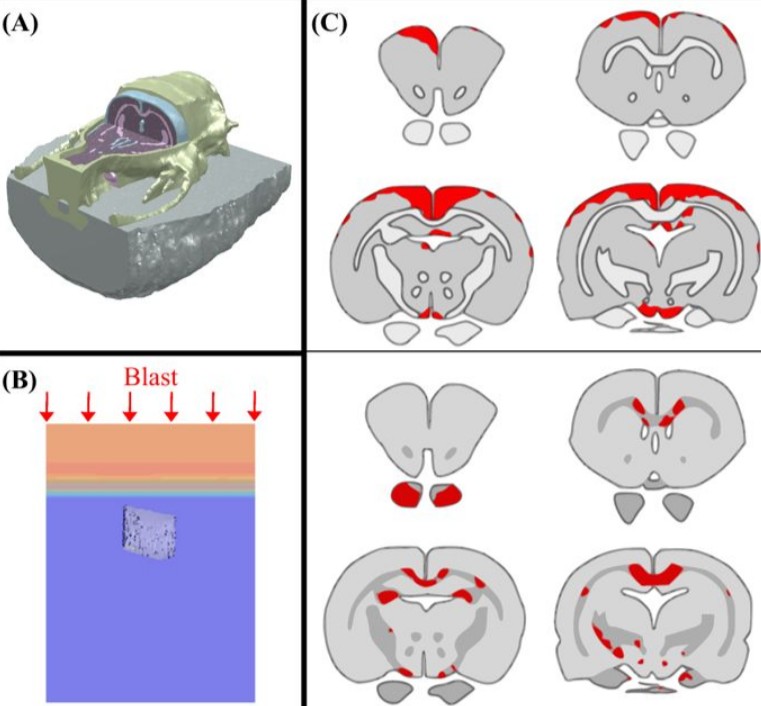
Cognition based bTBI mechanistic criteria; a tool for preventive and therapeutic innovations
Blast-induced traumatic brain injury has been associated with neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders. To date, although damage due to oxidative stress appears to be important, the specific mechanistic causes of such disorders remain elusive. Here, to determine the mechanical variables governing the tissue damage eventually cascading into cognitive deficits, we performed a study on the mechanics of rat brain under blast conditions. To this end, experiments were carried out to analyse... Read more
Daniel Garcia-Gonzalez, Nicholas S. Race, Natalie L. Voets, Damian R. Jenkins, Stamatios N. Sotiropoulos, Glen Acosta, Marcela Cruz-Haces, Jonathan Tang, Riyi Shi & Antoine Jérusalem
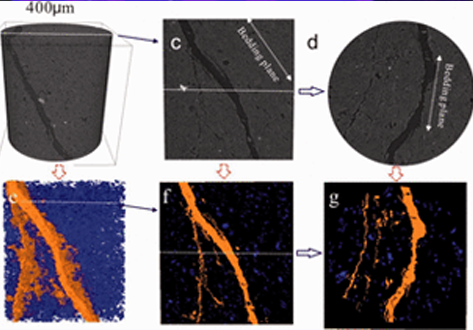
Experimental study on the cracking process of layered shale using X-ray microCT
The cracking process in Longmaxi formation shale was experimentally studied during uniaxial compressive loading. Both the evolution of the three-dimensional fracture network and the micromechanics of failure in the layered shale were examined as a function of the inclination angle of the bedding plane. To visualize the cracking process, the test devices presented here used an industrial X-ray CT scanner that enabled scanning during the uniaxial compressive loading. Scanning electron microscop... Read more
Institue of Geomechanic, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Laboratory of Shale Oil & Gas, Beijing, China
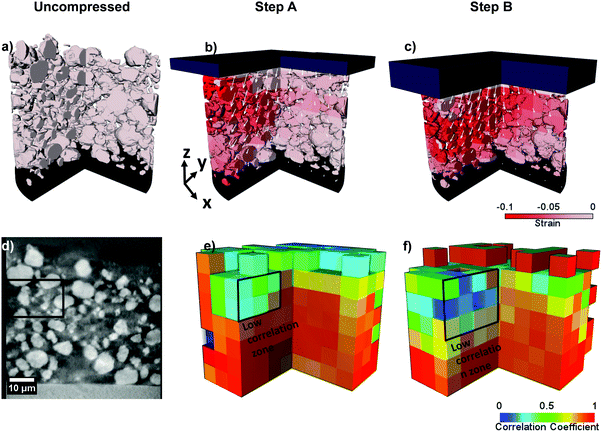
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries operate via electrochemical reactions between positive and negative electrodes, formed by complex porous microstructures. An improved understanding of these materials can lead to a greater insight into the link between microscopic electrode morphology and macroscopic performance. The practice of calendering electrodes after manufacturing has been widely used to increase the volumetric energy density and improve the electrical contact between electrode... Read more
S. R. Daemi,X. Lu, D. Sykes, J. Behnsen, C. Tan, A. Palacios-Padros, J. Cookson, E. Petrucco, P. J. Withers, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
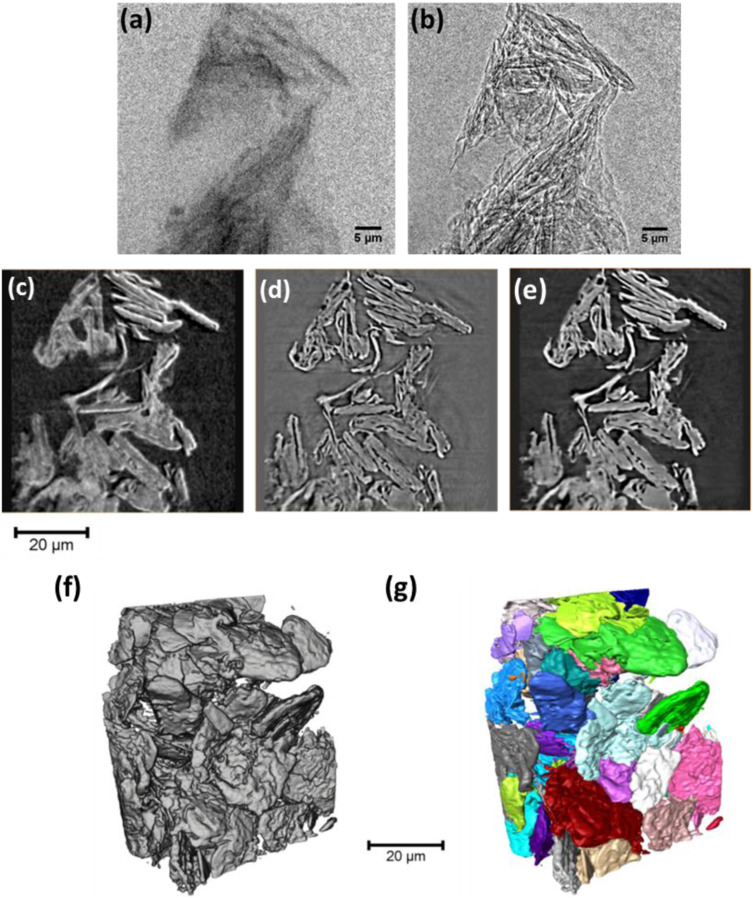
The use of contrast enhancement techniques in X-ray imaging of lithium–ion battery electrodes
Understanding the microstructural morphology of Li–ion battery electrodes is crucial to improving the electrochemical performance of current Li–ion battery systems and in developing next-generation power systems. The use of 3D X-ray imaging techniques, which are continuously evolving, provides a noninvasive platform to study the relationship between electrode microstructure and performance at various time and length scales. In addition to characterizing a weakly (X-ray) absorbing graphite... Read more
Oluwadamilola O. Taiwo , Donal P. Finegan , Jeff Gelb , Christian Holzner , Daniel J.L. Brett , Paul R. Shearing
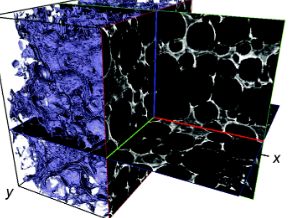
Biodegradable materials, such as collagen scaffolds, are used extensively in clinical medicine for tissue regeneration and/or as an implantable drug delivery vehicle. However, available methods to study biomaterial degradation are typically invasive, destructive, and/or non-volumetric. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate a new method for nondestructive, longitudinal, and volumetric measurement of collagen scaffold degradation. Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) were covalently ... Read more
Tyler A. Finamore, Tyler E. Curtis, James V. Tedesco, Kathryn Grandfield, Ryan K. Roeder
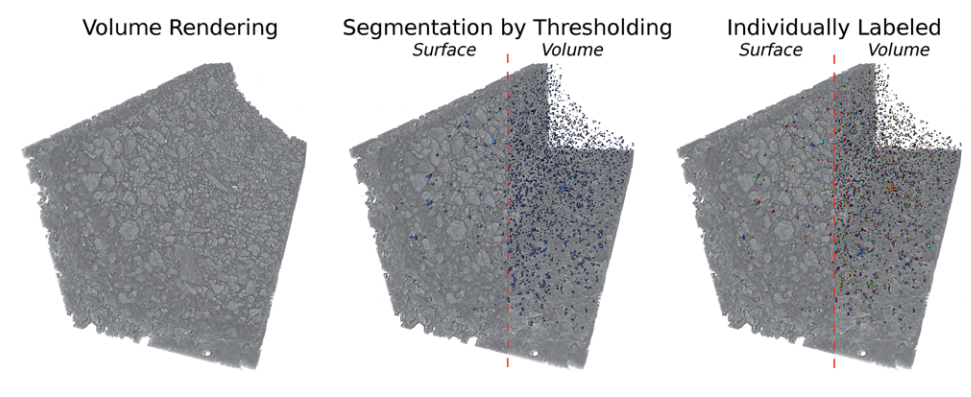
Aging of a Pt/Al2O3 exhaust gas catalyst monitored by quasi in situ X-ray micro computed tomography
Catalyst aging effects were analyzed using X-ray absorption micro-computed tomography in combination with conventional characterization methods on various length scales ranging from nm to μm to gain insight into deactivation mechanisms.
For this purpose, a 4 wt% Pt/Al2O3 model exhaust gas catalyst was coated on a cordierite honeycomb and subjected to sequential thermal aging in static air at 950 °C for 4, 8, 12 and 24 hours. The ag... Read more
Georg Hofmann, Amélie Rochet, Elen Ogel, Maria Casapu, Stephan Ritter, Malte Ogurreck and Jan-Dierk Grunwaldt
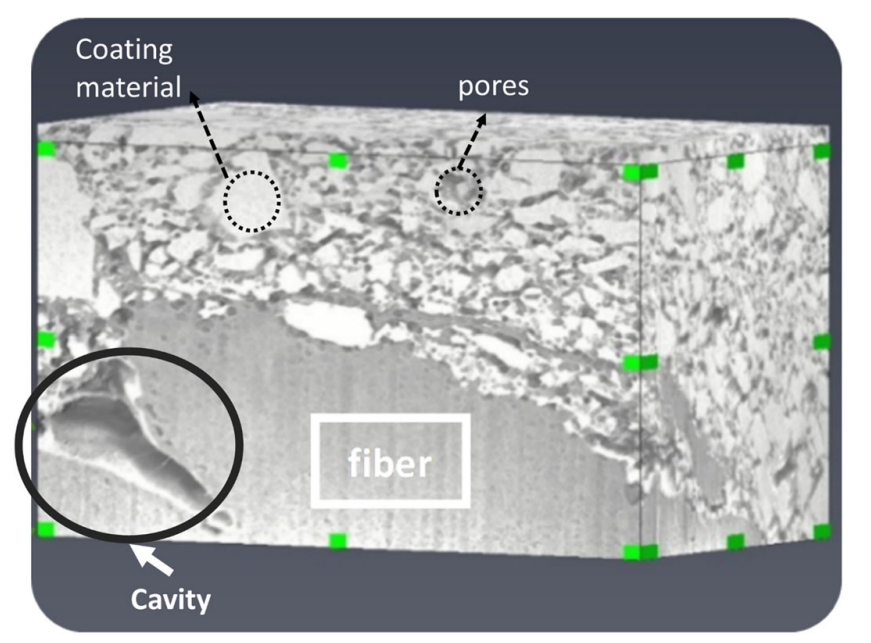
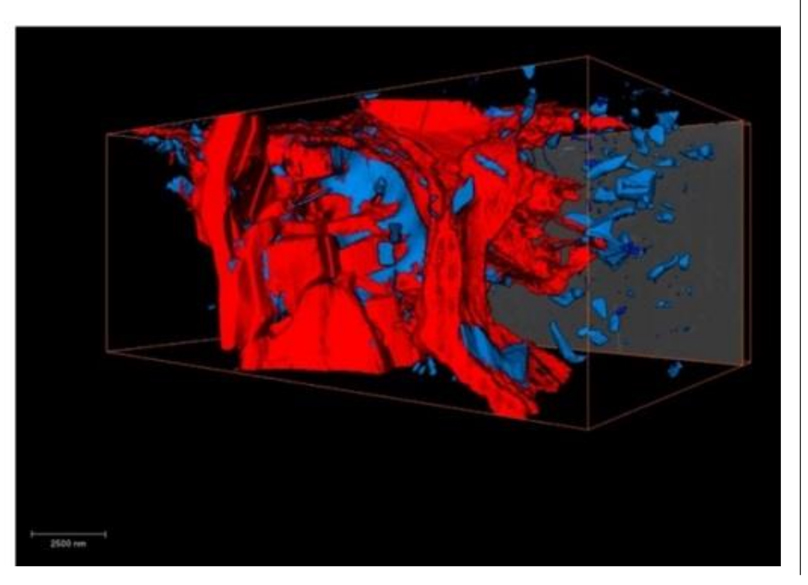
Characterization of the Interface Between Coating and Fibrous Layers of Paper
Coated paper is an example of a multi-layer porous medium, involving a coating layer along the two surfaces of the paper and a fibrous layer in the interior of the paper. The interface between these two media needs to be characterized in order to develop relevant modeling tools. After careful cutting of the paper, a cross section was imaged using focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy. The resulting image was analyzed to characterize the coating layer and its transition to the fibrous ... Read more
H. Aslannejad, S. M. Hassanizadeh, M. A. Celia
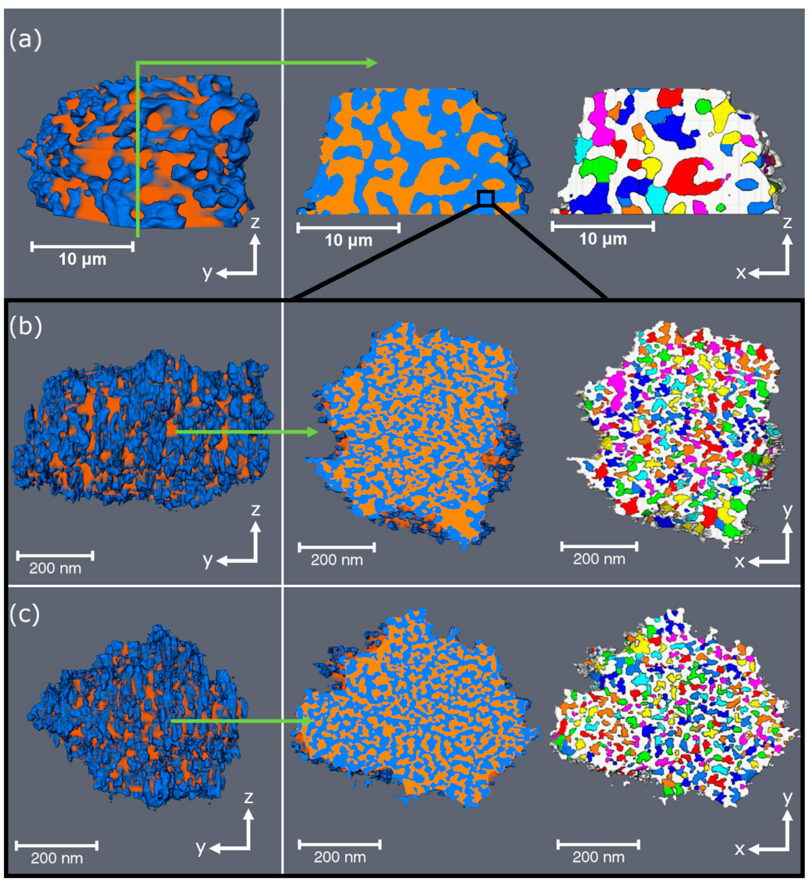
The development of focused ion beam-scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) techniques has allowed high-resolution 3D imaging of nanometre-scale porous materials. These systems are of important interest to the oil and gas sector, as well as for the safe long-term storage of carbon and nuclear waste. This work focuses on validating the accurate representation of sample pore space in FIB-SEM-reconstructed volumes and the predicted permeability of these systems from subsequent single-phase flow s... Read more
Department of Chemical Engineering, Qatar Carbonates and Carbon Storage Research Centre, Imperial College London | Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, Cambridge University