Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
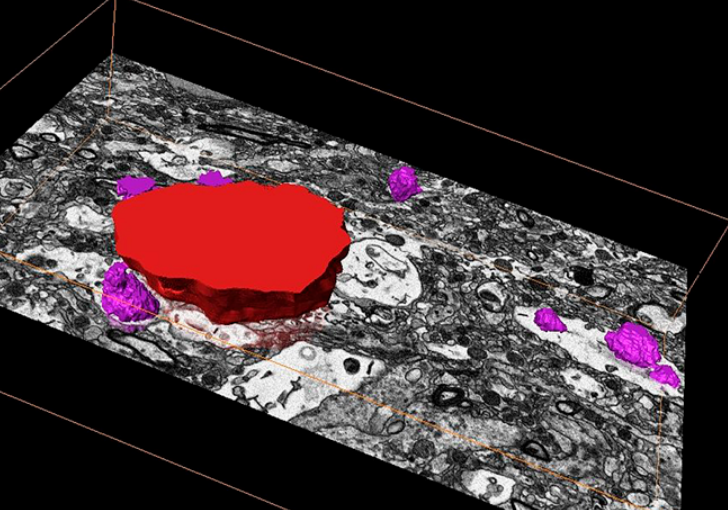
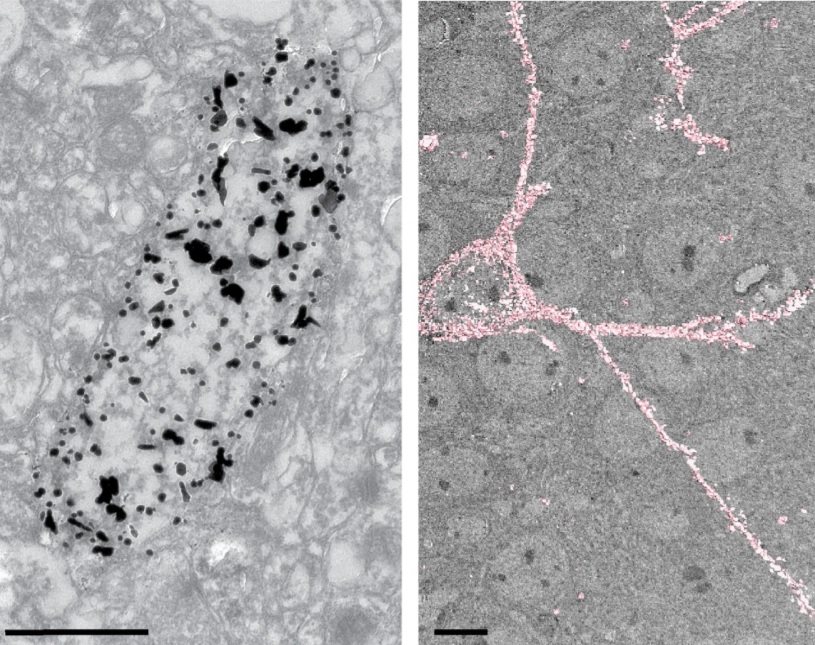
Corpora amylacea are cell-derived structures that appear physiologically in the aged human brain. While their histological identification is straightforward, their ultrastructural composition and microenvironment at the nanoscale have remained unclear so far, as has their relevance to aging and certain disease states that involve the sequestration of toxic cellular metabolites. Here, we apply correlative serial block-face scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron tomograp... Read more
Paula P. Navarro, Christel Genoud, Daniel Castaño-Díez, Alexandra Graff-Meyer, Amanda J. Lewis, Yvonne de Gier, Matthias E. Lauer, Markus Britschgi, Bernd Bohrmann, Stephan Frank, Jürgen Hench, Gabriel Schweighauser, Annemieke J. M. Rozemuller, Wilma D. J. van de Berg, Henning Stahlberg & Sarah H. Shahmoradian
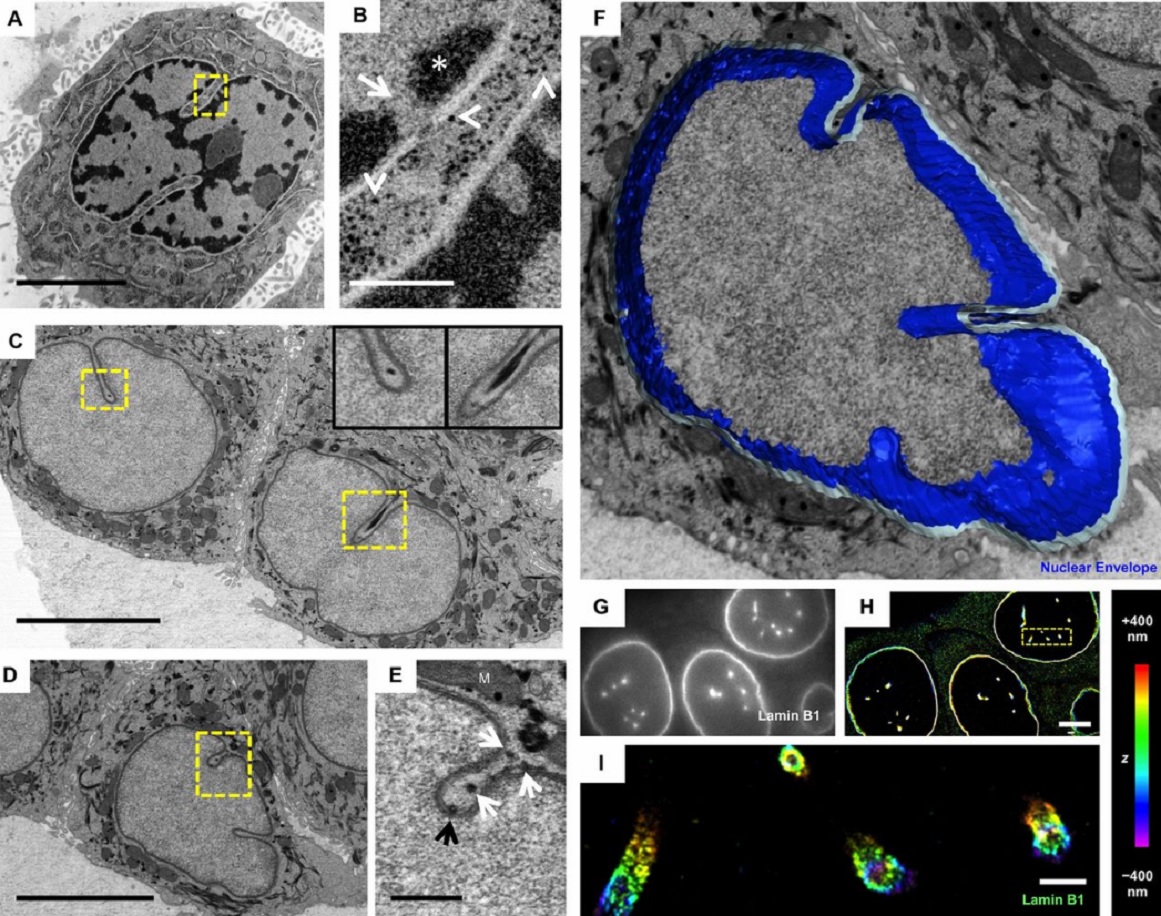
The importance of context in regulation of gene expression is now an accepted principle; yet the mechanism by which the microenvironment communicates with the nucleus and chromatin in healthy tissues is poorly understood. A functional role for nuclear and cytoskeletal architecture is suggested by the phenotypic differences observed between epithelial and mesenchymal cells…
Read more
Danielle M. Jorgens, Jamie L. Inman, Michal Wojcik, Claire Robertson, Hildur Palsdottir, Wen-Ting Tsai, Haina Huang, Alexandre Bruni-Cardoso, Claudia S. López, Mina J. Bissell, Ke Xu, Manfred Auer
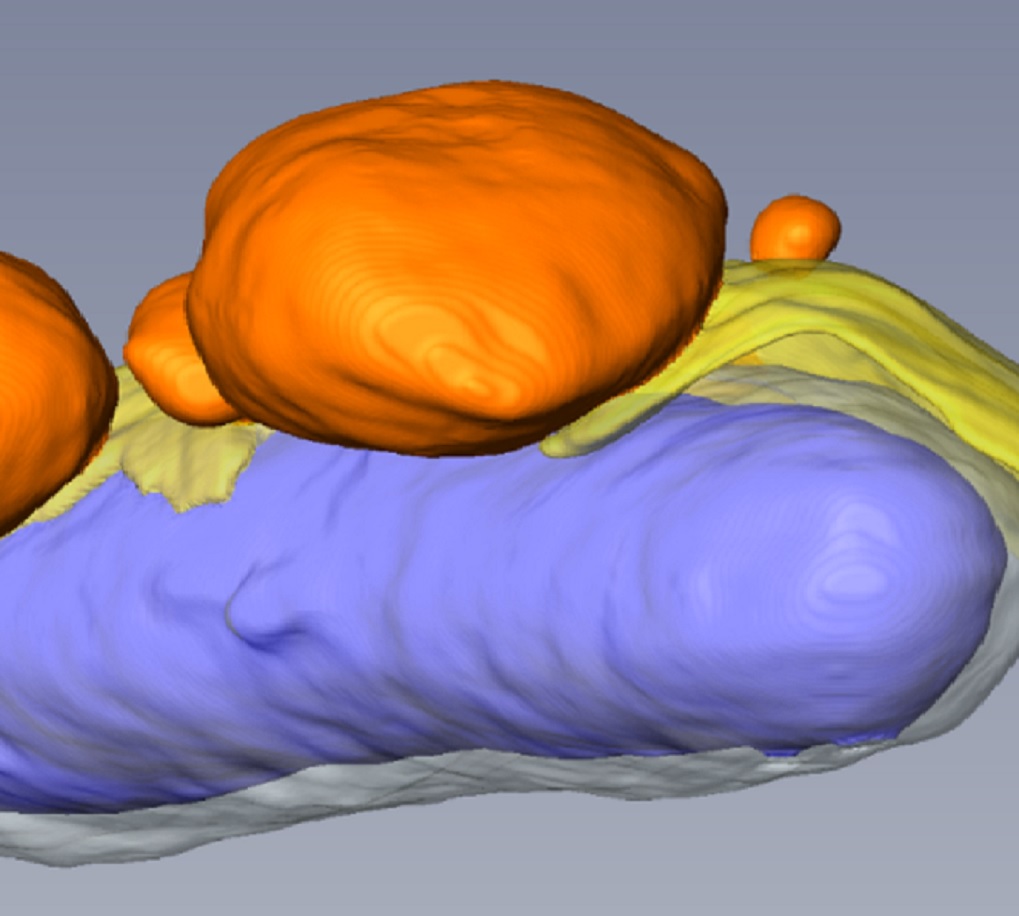
Macropinosomes are key players in early shigella invasion and vacuolar escape in epithelial cells
Intracellular pathogens include all viruses, many bacteria and parasites capable of invading and surviving within host cells. Key to survival is the subversion of host cell pathways by the pathogen for the purpose of propagation and evading the immune system. The intracellular bacterium Shigella flexneri, the causative agent of bacillary dysentery, invades host cells in a vacuole that is subsequently ruptured to allow growth of the pathogen within the host cytoplasm…
Read more
Allon Weiner , Nora Mellouk , Noelia Lopez-Montero , Yuen-Yan Chang, Célia Souque, Christine Schmitt, Jost Enninga
Three-dimensional imaging of the intracellular assembly of a functional viral RNA replicase complex
Positive-strand RNA viruses, which can be devastating pathogens in humans, animals and plants, replicate their genomes on intracellular membranes. Here, we describe the three-dimensional ultrastructural organization of a tombusvirus replicase in yeast, a valuable model for exploring virus–host interactions…
Read more
Isabel Fernández de Castro, José J. Fernández, Daniel Barajas, Peter D. Nagy, Cristina Risco
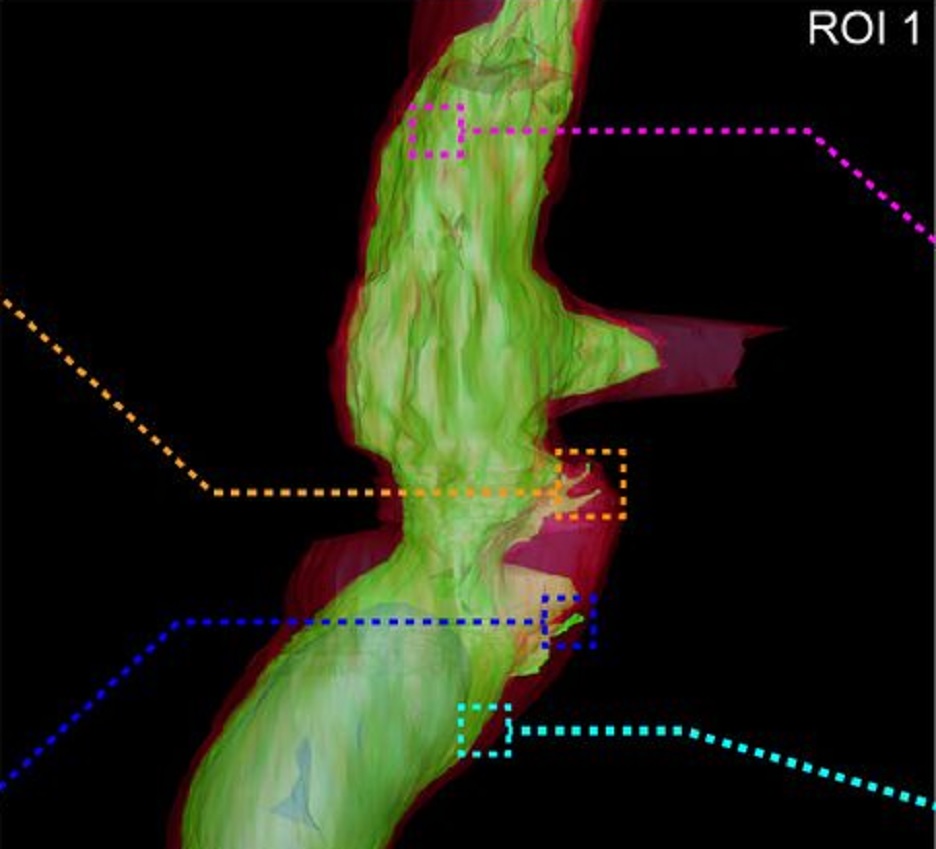
Fast and precise targeting of single tumor cells in vivo by multimodal correlative microscopy
Intravital microscopy provides dynamic understanding of multiple cell biological processes, but its limited resolution has so far precluded structural analysis. Because it is difficult to capture rare and transient events, only a few attempts have been made to observe specific developmental and pathological processes in animal models using electron microscopy. The multimodal correlative approach that we propose here combines intravital microscopy, microscopic X-ray computed tomography and thr... Read more
Matthia A. Karreman, Luc Mercier, Nicole L. Schieber, Gergely Solecki, Guillaume Allio, Frank Winkler, Bernhard Ruthensteiner, Jacky G. Goetz, Yannick Schwab
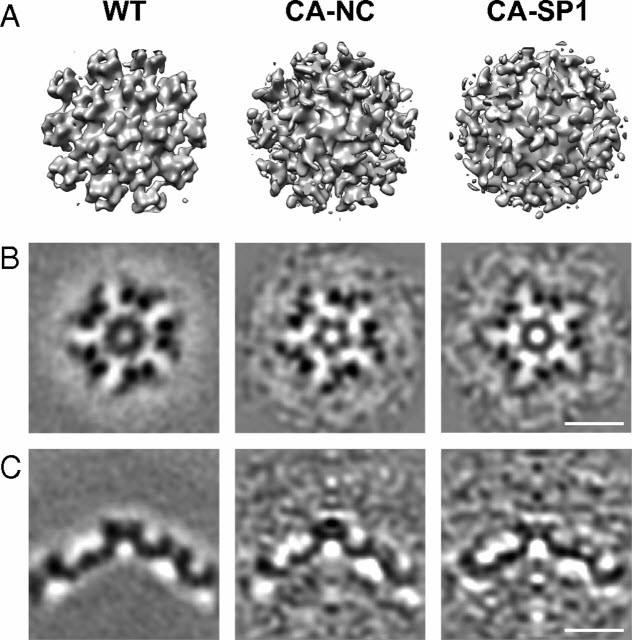
HIV-1 maturation occurs via multiple proteolytic cleavages of the Gag polyprotein, causing rearrangement of the virus particle required for infectivity. (…) How individual cleavages contribute to changes in protein structure and interactions, and how the mature, conical capsid forms, are poorly understood. Here, we employed cryoelectron tomography to determine morphology and high-resolution CA lattice structures for HIV1 derivatives in which Gag cleavage sites are mutated. These analyse... Read more
Simone Mattei, Aaron Tan, Barbel Glass, Barbara Muller, Hans-Georg Krausslich, and John A. G. Briggs
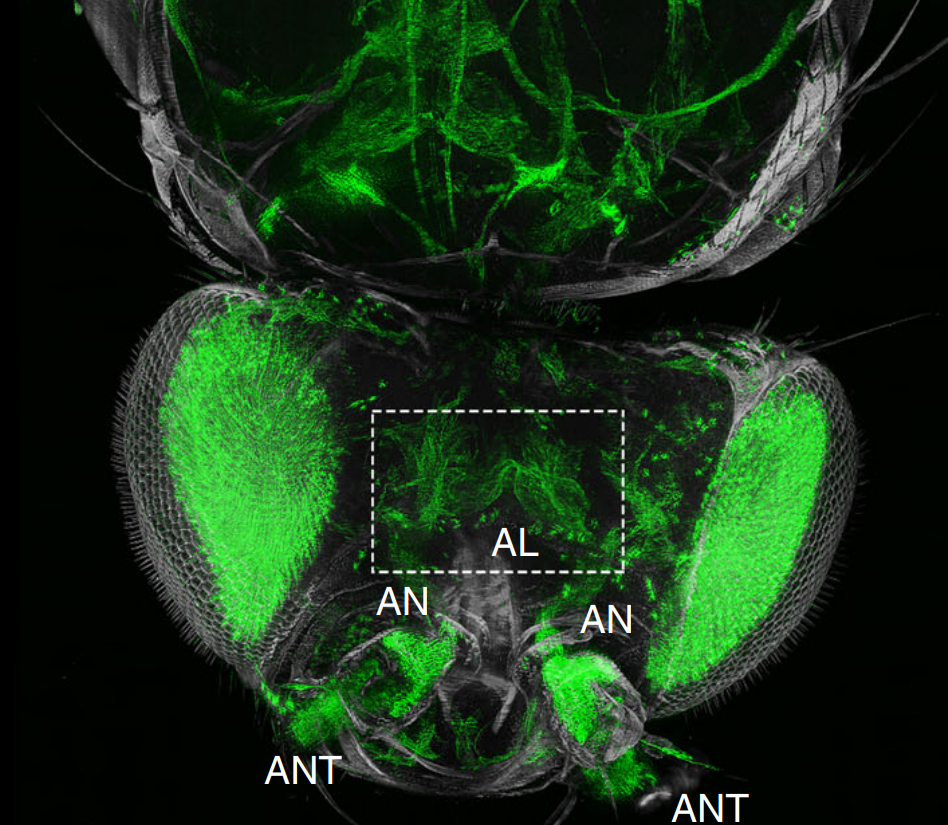
The fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, is an important experimental model to address central questions in neuroscience at an organismic level. However, imaging of neural circuits in intact fruit flies is limited due to structural properties of the cuticle. Here we present a novel approach combining tissue clearing, ultramicroscopy, and data analysis that enables the visualisation of neuronal networks with single-cell resolution from the larval stage up to the adult Drosophila. (…) This... Read more
Marko Pende, Klaus Becker, Martina Wanis, Saiedeh Saghafi, Rashmit Kaur, Christian Hahn, Nika Pende, Massih Foroughipour, Thomas Hummel & Hans-Ulrich Dodt
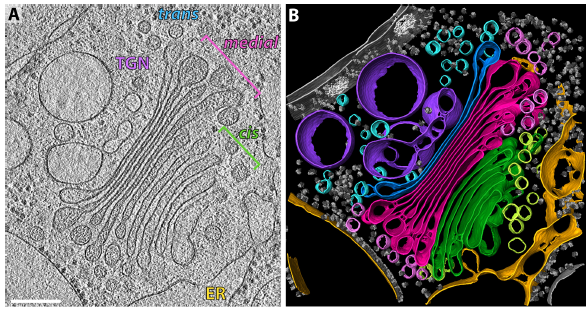
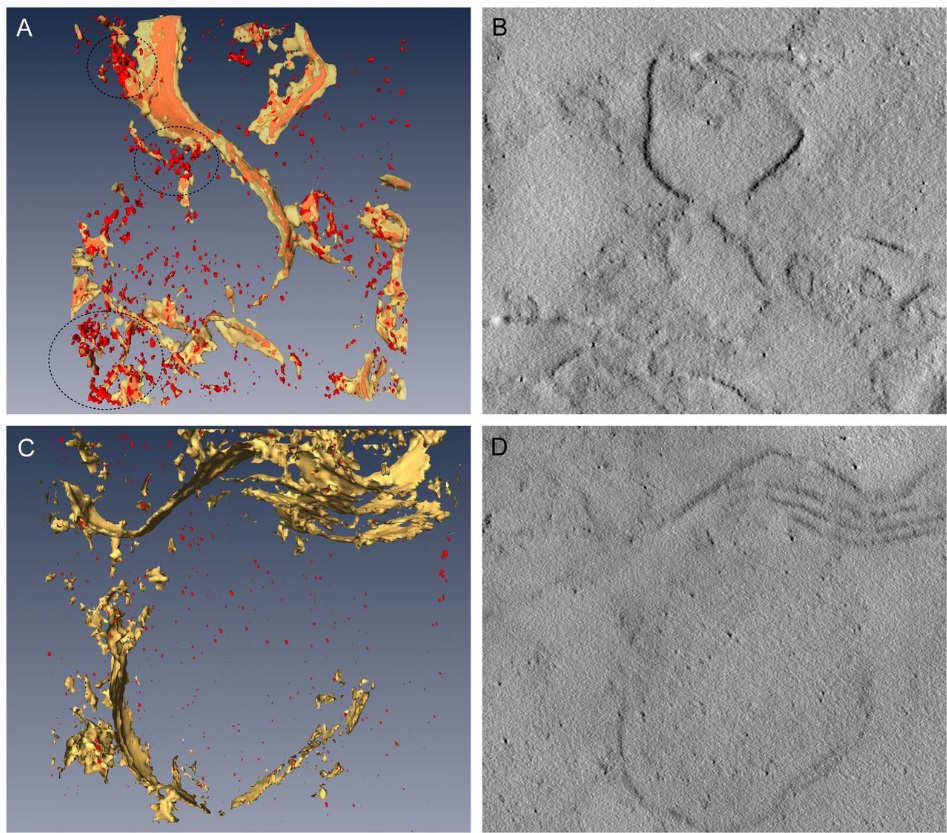
The structure of the COPI coat determined within the cell
COPI-coated vesicles mediate trafficking within the Golgi apparatus and from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum. Here, we applied cryo-focused ion beam milling, cryo-electron tomography and subtomogram averaging to determine the native structure of the COPI coat within vitrified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells. The native algal structure resembles the in vitro mammalian structure, but additionally reveals cargo bound beneath beta’–COP. We find that all coat components disassemble... Read more
Yury S Bykov, Miroslava Schaffer, Svetlana O Dodonova, Sahradha Albert, Jurgen M Plitzko, Wolfgang Baumeister, Benjamin D Engel, John AG Briggs
Analysis of neuronal arborization and connections is a powerful tool in fundamental and clinical neuroscience. Changes in neuronal morphology are central to brain development and plasticity and are associated with numerous diseases. Golgi staining is a classical technique based on a deposition of metal precipitate in a random set of neurons. Despite their versatility, Golgi methods have limitations that largely precluded their use in advanced microscopy. We combined Golgi staining with fluore... Read more
Katlijn Vints, Dorien Vandael, Pieter Baatsen, Benjamin Pavie, Frank Vernaillen, Nikky Corthout, Vasily Rybakin, Sebastian Munck & Natalia V. Gounko
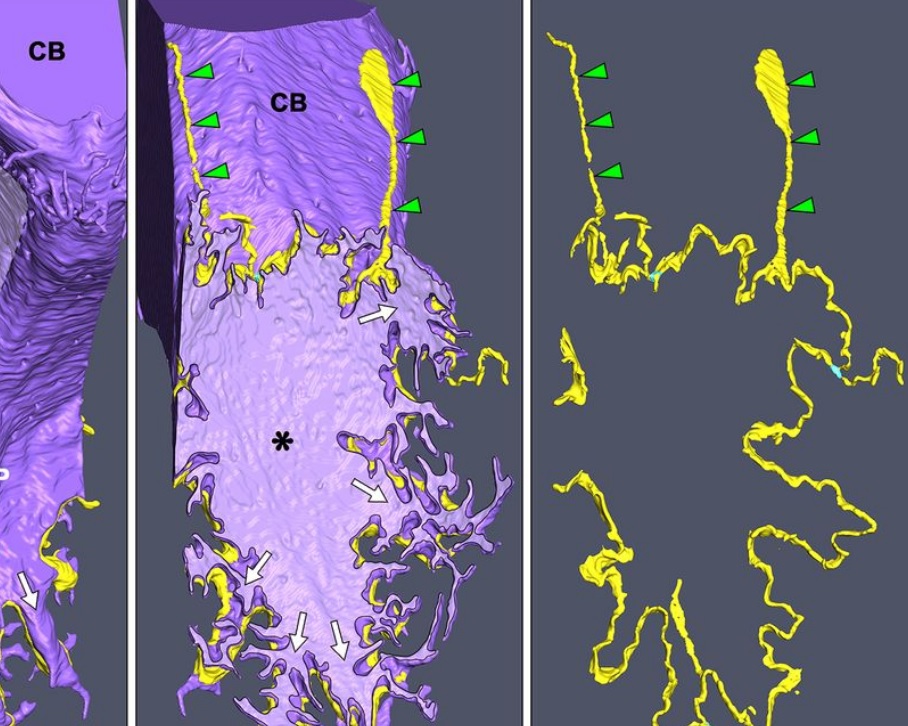
Morphological process of podocyte development revealed by block-face scanning electron microscopy
Podocytes present a unique 3D architecture specialized for glomerular filtration. However, several 3D morphological aspects on podocyte development remain partially understood because they are difficult to reveal using conventional scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Here, we adopted serial block-face SEM imaging…
Read more
Koichiro Ichimura, Soichiro Kakuta, Yuto Kawasaki, Takayuki Miyaki, Takahiro Nonami, Naoyuki Miyazaki, Tomoyo Nakao, Sakiko Enomoto, Shigeo Arai, Masato Koike, Kazuyoshi Murata, Tatsuo Sakai
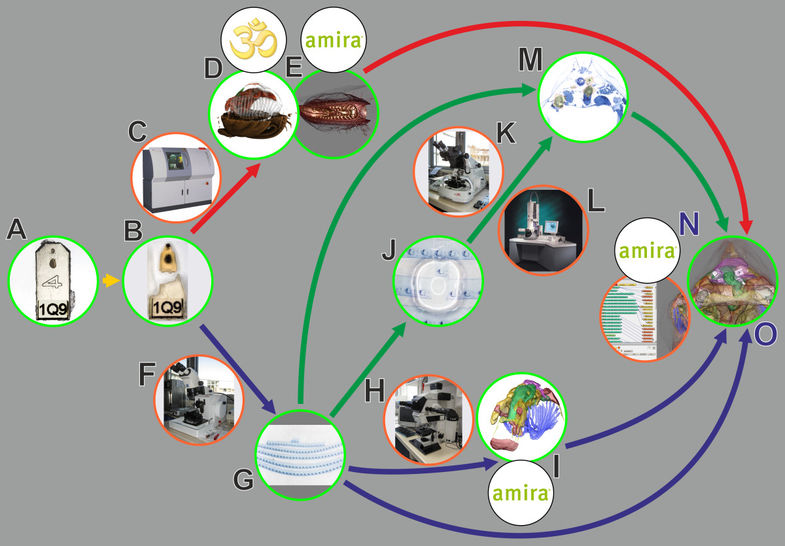
In biomedical research, a huge variety of different techniques is currently available for the structural examination of small specimens, including conventional light microscopy (LM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), microscopic X-ray computed tomography (microCT), and many others. Since every imaging method is physically limited by certain parameters, a correlative use of complementary methods often yields a significant broader range of inform... Read more
Stephan Handschuh, Natalie Baeumler, Thomas Schwaha and Bernhard Ruthensteiner
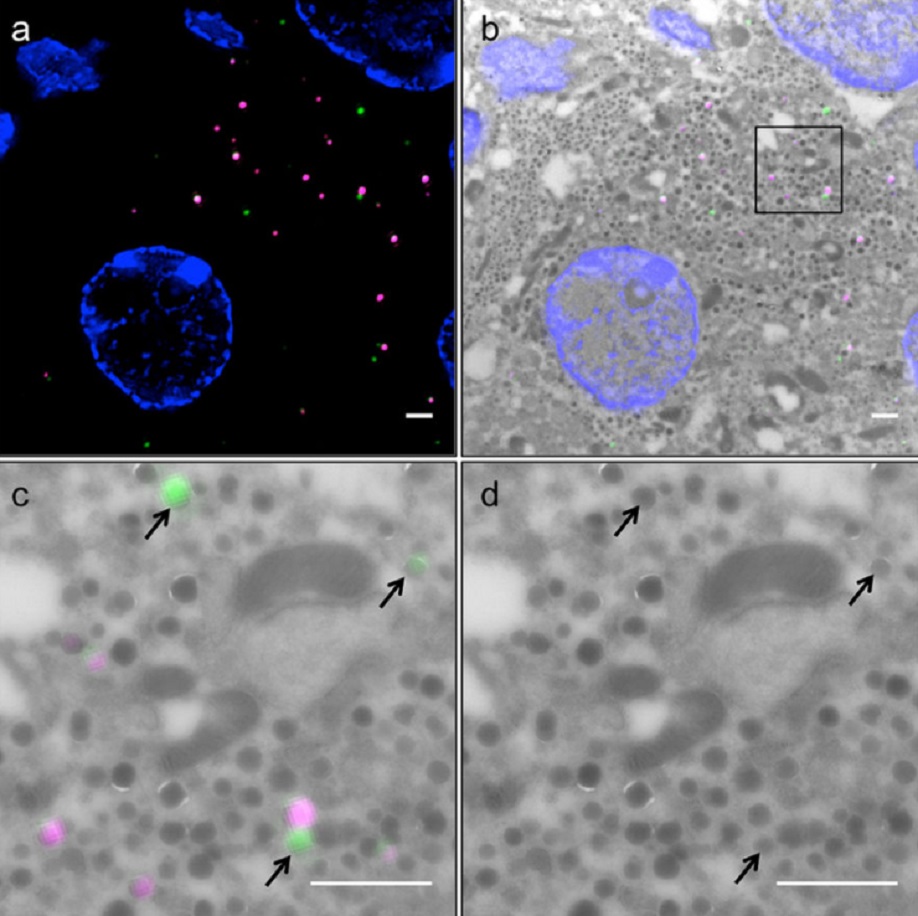
Correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM) is a powerful approach to investigate the molecular ultrastructure of labeled cell compartments. However, quantitative CLEM studies are rare, mainly due to small sample sizes and the sensitivity of fluorescent proteins to strong fixatives and contrasting reagents for EM. Here, we show that fusion of…
Read more
Andreas Müller, Martin Neukam, Anna Ivanova, Anke Sönmez, Carla Münster, Susanne Kretschmar, Yannis Kalaidzidis, Thomas Kurth, Jean-Marc Verbavatz & Michele Solimena
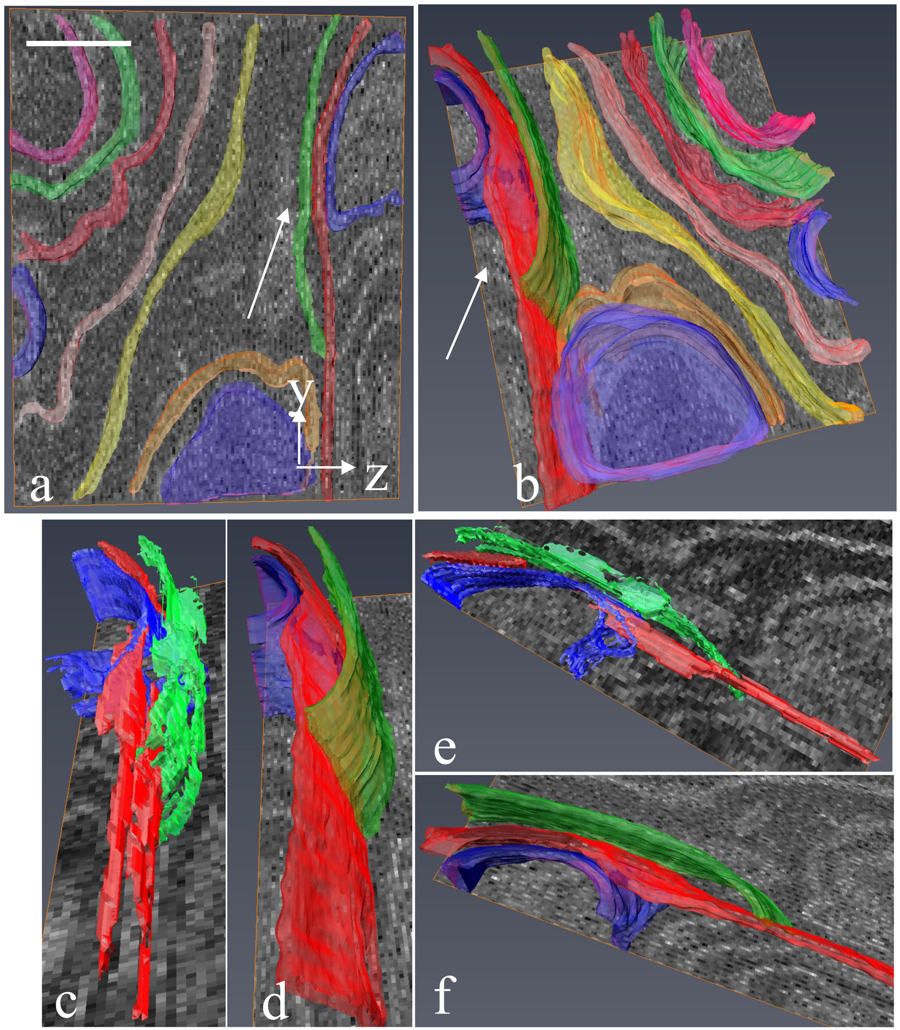
Serial block-face electron microscopy (SBEM) provides nanoscale 3D ultrastructure of embedded and stained cells and tissues in volumes of up to 107 µm3. In SBEM, electrons with 1–3 keV energies are incident on a specimen block, from which backscattered electron (BSE) images are collected with x, y resolution of 5–10 nm in the block-face plane, and successive layers are removed by an in situ ultramicrotome. Sp... Read more
Q. He, M. Hsueh, G. Zhang, D. C. Joy & R. D. Leapman
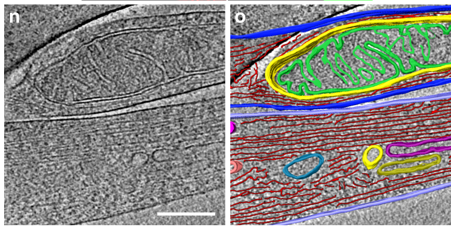
Correlative cryo-electron microscopy reveals the structure of TNTs in neuronal cells
The orchestration of intercellular communication is essential for multicellular organisms. One mechanism by which cells communicate is through long, actin-rich membranous protrusions called tunneling nanotubes (TNTs), which allow the intercellular transport of various cargoes, between the cytoplasm of distant cells in vitro and in vivo. Here, we use correlative FIB-SEM, light- and cryo-electron microscopy approaches to elucidate the structural organization of neuronal TNTs. Our data indicate ... Read more
Anna Sartori-Rupp, Diégo Cordero Cervantes, Anna Pepe, Karine Gousset, Elise Delage, Simon Corroyer-Dulmont, Christine Schmitt, Jacomina Krijnse-Locker & Chiara Zurzolo
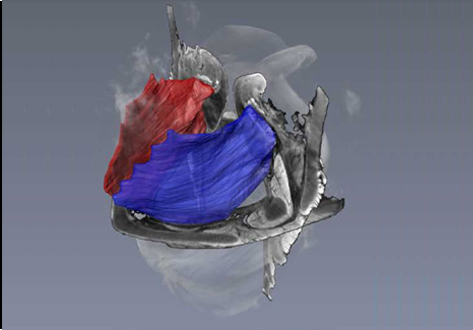
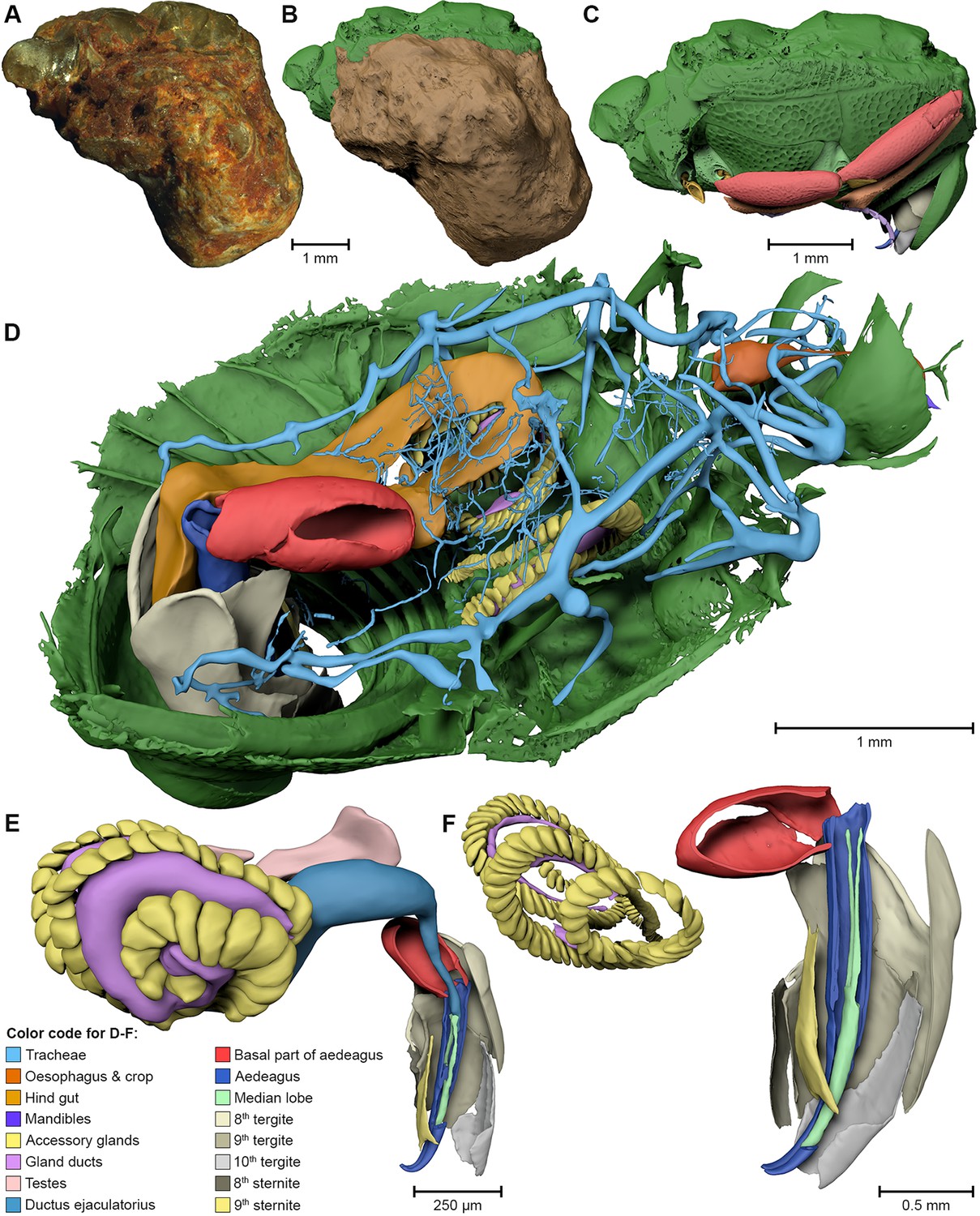
Juvenile Ovine Ex Vivo Larynges: Phonatory, Histologic, and Micro CT Based Anatomic Analyses
It is well known that the phonatory process changes during the life span. However, detailed investigations on potential factors concerned are rare. To deal with this issue, we performed extended biomechanical, macro anatomical, and histological analyses of the contributing laryngeal structures in ex vivo juvenile sheep models. Altogether twelve juvenile sheep larynges were analyzed within the phonatory experiments. Three different elongation levels and 16 different flow levels were applied to... Read more
Michael Döllinger, Olaf Wendler, Claus Gerstenberger, Tanja Grossmann, Marion Semmler, Hossein Sadeghi, and Markus Gugatschka
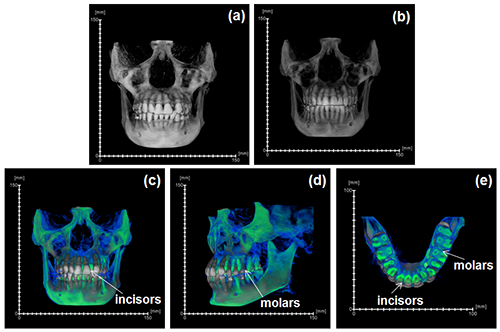
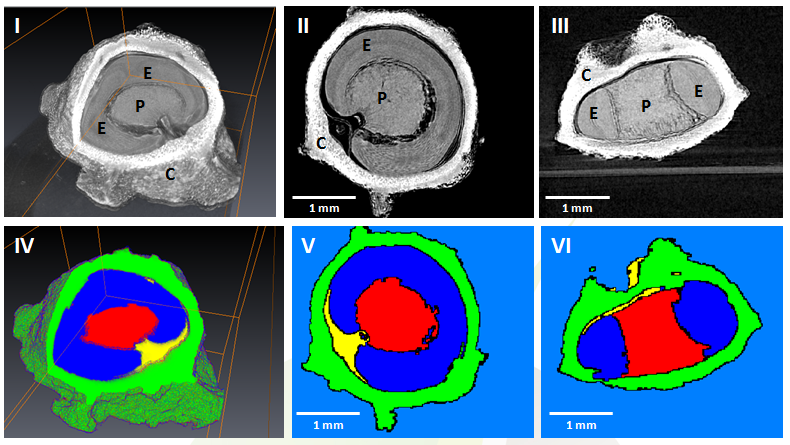
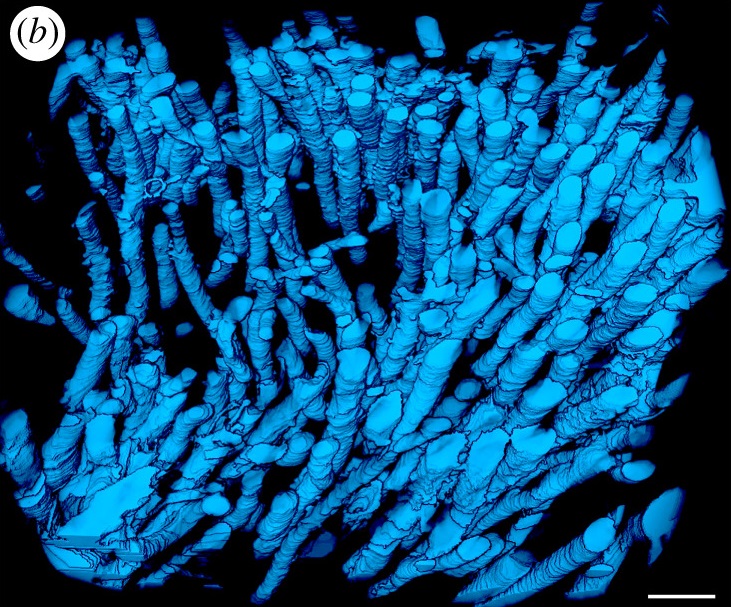
During the acts of biting and chewing, the muscles of the jaw (consisting of the masseter, temporalis, and medial pterygoid in the elevator group, and lateral pterygoid as the main depressor) generate forces that dictate jaw kinematics . The movement of jaws hinges about the temporomandibular joint and are brought together by the muscles attached to respective bones through bone-tendon interfaces known as entheses . Thus, chewing forces affect aspects of craniofacial structure as well as bo... Read more
Kyle H.-Y. Chan, fourth-year undergraduate student in Molecular and Cell Biology, and Public Health at UC Berkeley, FeiFei Yang, Ph.D., postdoctoral scholar in the Laboratory of Multiscale Biomechanics and Biomineralization, School of Dentistry, UCSF, and Sunita P. Ho, Ph.D., Division of Biomaterials and Bioengineering, Department of Preventive and Restorative Dental Sciences, School of Dentistry, University of California San Francisco
GEVES uses Avizo software to study and control plant seeds
At GEVES, Microtomography (micro-CT), which is a technique using X-rays to investigate internal anatomy and morphology of organisms without destruction, is applied to plant seed quality control and phenotyping. Several applications have been developed using micro-CT coupled with Avizo software development, such as for example in the Measurements of internal and external sugar beet seed structures for seed phenotyping
Read more
Ghassen Trigui, Laurence Le Corre, Dominique Honoré and Karima Boudehri-Giresse - 2D/3D Imaging - R&D team, GEVES
Microbial-tubeworm associations in a 440 million year old hydrothermal vent community
Microorganisms are the chief primary producers within present-day deep-sea hydrothermal vent ecosystems, and play a fundamental role in shaping the ecology of these environments. (…) The oldest known hydrothermal vent community that includes metazoans is preserved within the Ordovician to early Silurian Yaman Kasy massive sulfide deposit, Ural Mountains, Russia. (…) A re-examination of these fossils using a range of microscopy, chemical analysis and nano-tomography techniques re... Read more
Magdalena N. Georgieva , Crispin T. S. Little , Russell J. Bailey , Alexander D. Ball and Adrian G. Glover
External and internal morphological characters of extant and fossil organisms are crucial to establishing their systematic position, ecological role and evolutionary trends. (…) We found well-preserved three-dimensional anatomy in mineralized arthropods from Paleogene fissure fillings and demonstrate the value of these fossils by utilizing digitally reconstructed anatomical structure of a hister beetle. The new anatomical data facilitate a refinement of the species diagnosis and allowed... Read more
Achim H Schwermann, Tomy dos Santos Rolo, Michael S Caterino, Gunter Bechly, Heiko Schmied, Tilo Baumbach, Thomas van de Kamp
The paper proposes a new experimental methodology, based on ultrasonic measurements, that aims at evaluating the anisotropic damage in woven semi-crystalline polymer composites through new damage indicators. Due to their microstructure, woven composite materials are characterized by an anisotropic evolution of damage induced by different damage mechanisms occurring at the micro or mesoscopic scales. In this work, these damage modes in polyamide 6.6/6-woven glass fiber reinforced composites ha... Read more
Pascal Pomarède, Fodil Meraghni, Laurent Peltier, Stéphane Delalande, Nico F. Declercq
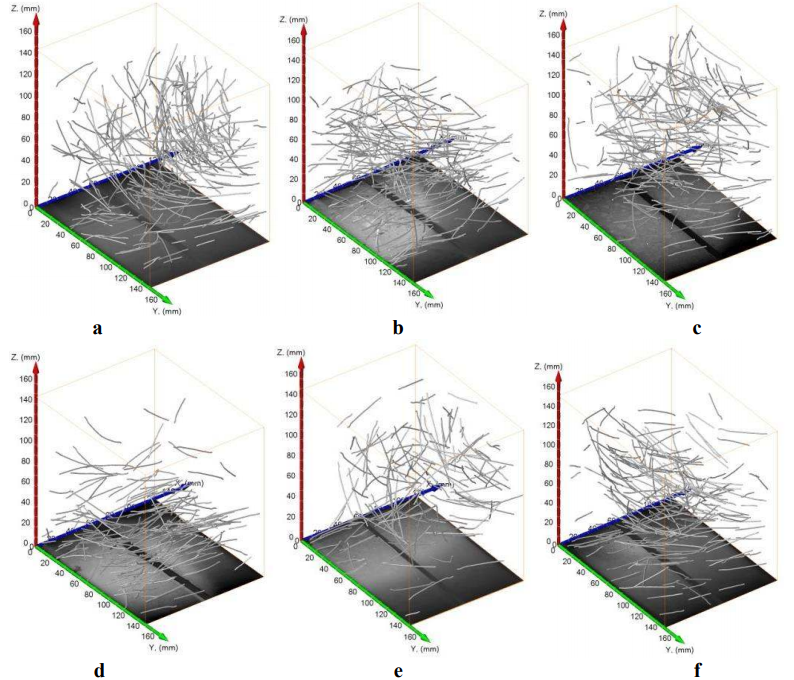
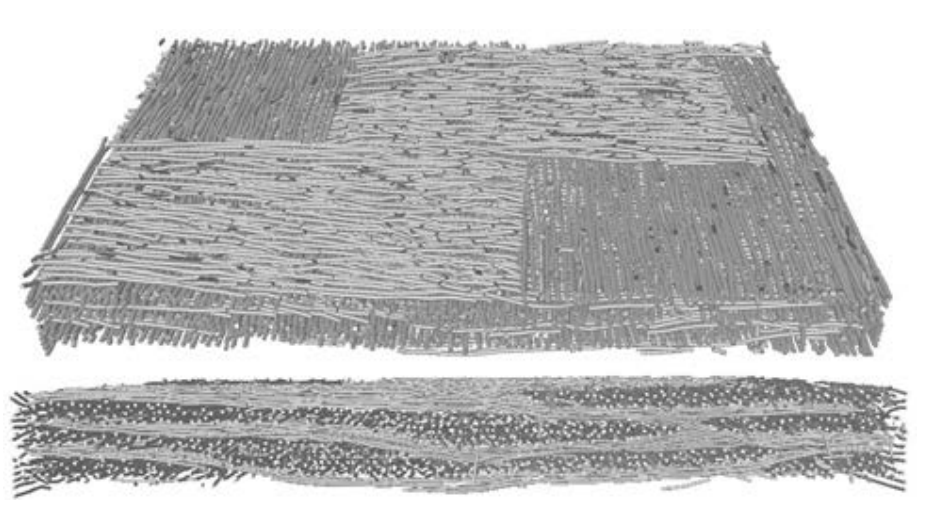
In this paper a study concerning an automatic determination of distribution of steel fibres in self-compacting concrete (SCC) is presented. The determination of fibre distribution is required to assess any relationship between those features and casting methods of concrete elements. Concrete beams with steel fibres of various types and casting methods were examined. Involved methods were computed tomography imaging followed by image analysis. After image analysis a label map consisting of all... Read more
T. Ponikiewski, J. Golaszewski, M. Rudzki, M. Bugdol