Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
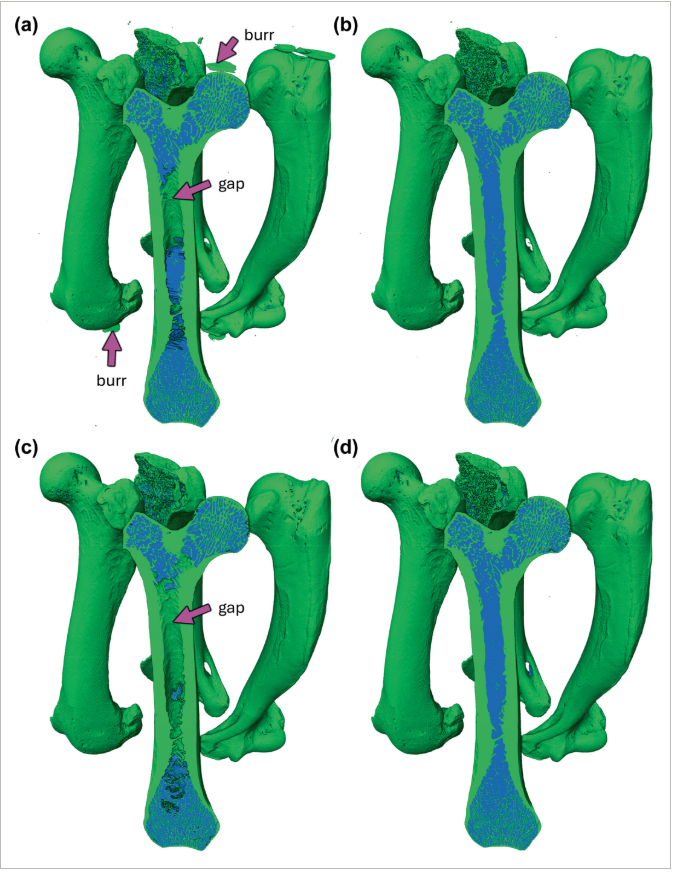
Computed tomography (CT) enables rapid imaging of large-scale studies of bone, but those datasets typically require manual segmentation, which is time-consuming and prone to error. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) offer an automated solution, achieving superior performance on image data. In this methodology-focused paper, we used CNNs to train segmentation models from scratch on 2D and 3D patches from micro-CT scans of otter long bones. These new models, collectively called BONe (Bone One... Read more
Andrew H. Lee, Julian M. Moore, Brandon Vera Covarrubias, Leigha M. Lynch
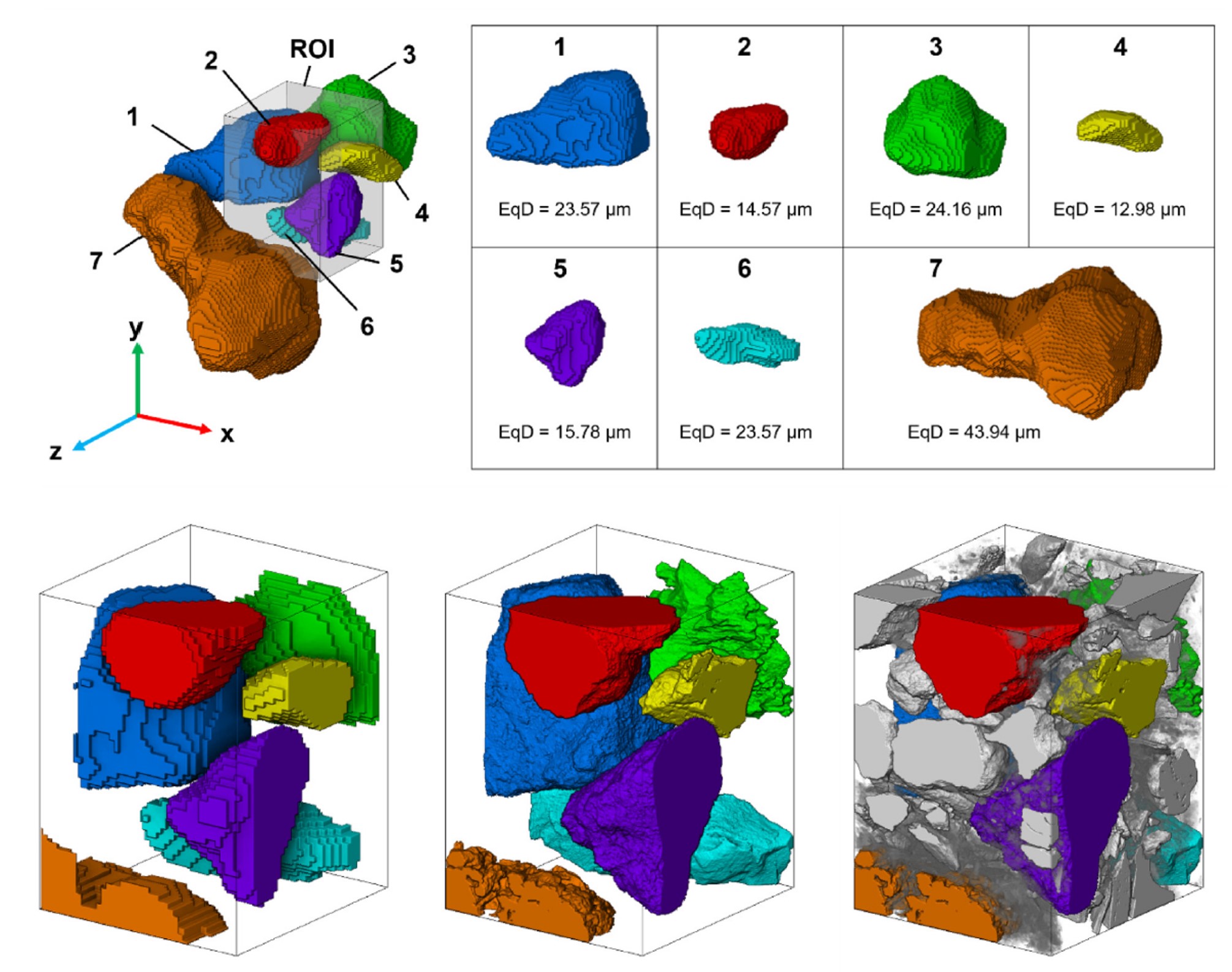
The behavior of loess is controlled by its microstructure, consisting of silt sized skeleton particles and complex bonding structures formed by clay-sized particles. Achieving a deep understanding and precise modelling of loess behavior necessitates comprehensive knowledge of the realistic 3D microstructure.
- Innovative 3D analysis of loess microstructure using μXCT and FIB-SEM.
- Detailed visualizat... Read more
B. Yu, T.A. Dijkstra, W. Fan, I.J. Smalley, Y.N. Wei, L.S. Deng
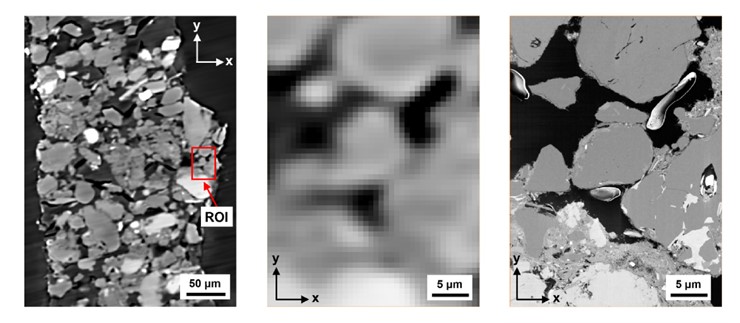
3D loess microstructure of loess, including skeleton particles as well as inter-particle bonding structures, was characterized through a correlative approach using μXCT and FIB-SEM
Loess, a Quaternary wind-blown deposit, is a problem soil that gives rise to frequent geohazards such as landslides and water-induced subsidence. The behavior of loess is controlled by its microstructure, consisting of silt sized
skeleton particles and complex bonding structures formed by clay-sized p... Read more
B. Yu, T.A. Dijkstra, W. Fan, I.J. Smalley, Y.N. Wei, L.S. Deng
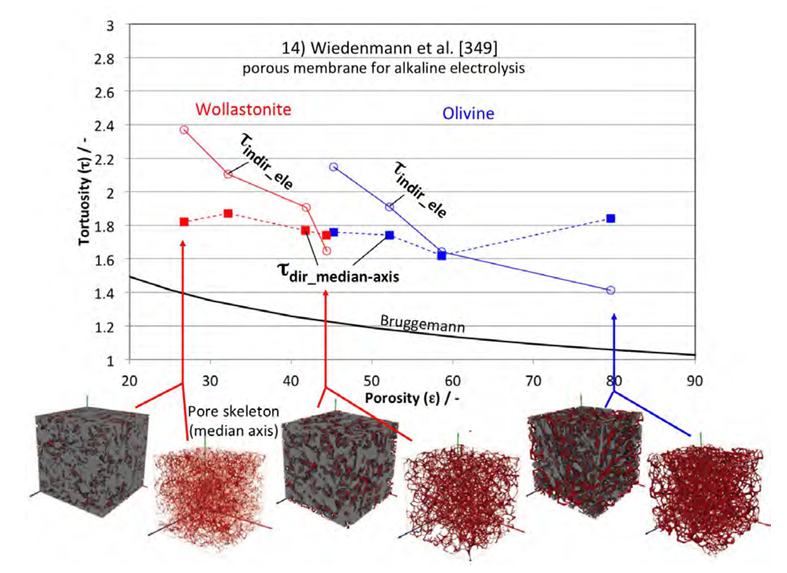
This study provides a comprehensive review of tortuosity and its impact on the transport properties of porous media. It discusses the classical theories and equations related to tortuosity for flow, conduction, and diffusion. The study also highlights the evolution of these theories and their connection to methodologies such as tomography and 3D image analysis. In order to clarify the topic, a new classification scheme and nomenclature for different types of tortuosity are proposed. The study... Read more
Holzer, L. *1, Marmet, P. 1, Fingerle, M. 2, Wiegmann, A. 2, Neumann, M. 3, Schmidt, V. 3
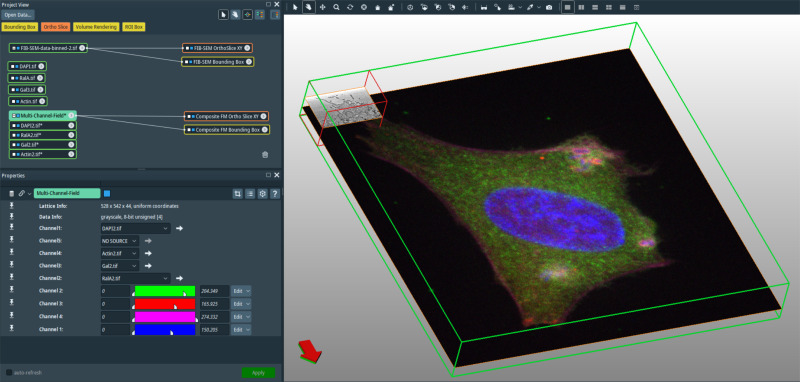
In recent years new methodologies and workflow pipelines for acquiring correlated fluorescence microscopy and volume electron microscopy datasets have been extensively described and made accessible to users of different levels. Post-acquisition image processing, and particularly correlation of the optical and electron data in a single integrated three-dimensional framework can be key for extracting valuable information, especially when imaging large sample volumes such as whole cells or tissu... Read more
Allon Weiner
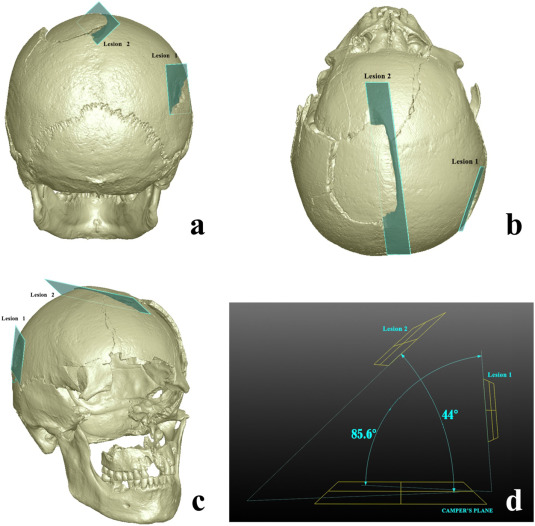
Human skeletal remains from archaeological contexts occasionally present signs of traumatic injuries from weapons, revealing, for example, the degree of interpersonal violence, the type of weapon and the sequence of events of a specific historical context.
Traumatic lesions are generally analyzed using macroscopic and microscopic methods, which are not necessarily integrated in the same study. In this study, we employed a multi-analytical approach to determine i... Read more
Antonino Vazzana, Lucia Martina Scalise, Mirko Traversari, Carla Figus, Salvatore Andrea Apicella, Laura Buti, Gregorio Oxilia, Rita Sorrentino, Silvia Pellegrini, Chiara Matteucci, Lucio Calcagnile, Raffaele Savigni, Robin N.M.Feeney, Giorgio Gruppioni, Stefano Benazziah
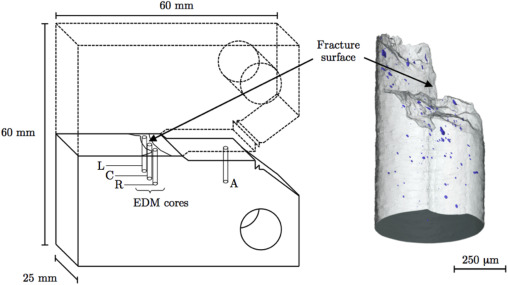
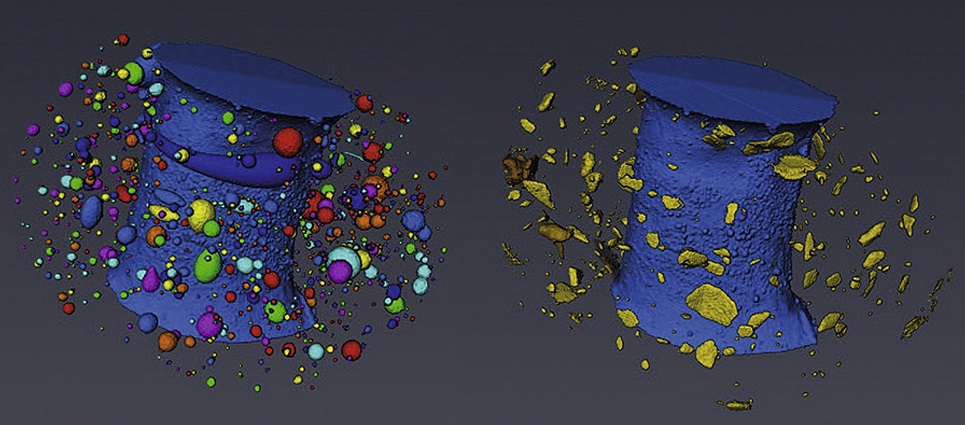
X-ray computed tomography (XCT) has been shown to reveal the true extent of ductile damage below the fracture surface of failed test specimens, which is often significantly underestimated when probed using 2D serial sectioning techniques and a microscope, since a single plane of material may only exhibit only a handful of resolvable voids.
In contrast XCT offers the capability to generate large datasets consisting of hundreds, if not thousands, of individually resolvable voids, where e... Read more
A. J. Cooper ; O. C. G. Tuck ; T. L. Burnett ; A. H. Sherry
The usefulness of desktop Micro-CT scanners for the study of archaeological artefacts is demonstrated in a non-destructive study of manufacturing methods of Roman and Early Medieval monochrome and polychrome glass beads. Differences in glass colours show up in these scans as differences in attenuation. The presence and distribution of bubbles and various inclusions (metal, opacifier) are also well visible. Shaft shapes and patterns of bubbles inside the glass make it possible in most cases to... Read more
D.J.M.Ngan-Tillard, D.J.Huisman, F.Corbella, A.Van Nass
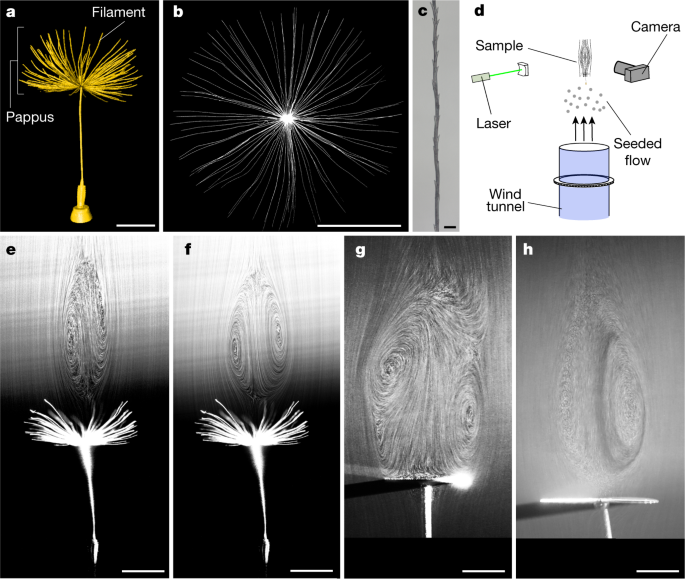
A separated vortex ring underlies the flight of the dandelion
Wind-dispersed plants have evolved ingenious ways to lift their seeds. The common dandelion uses a bundle of drag-enhancing bristles (the pappus) that helps to keep their seeds aloft. This passive flight mechanism is highly effective, enabling seed dispersal over formidable distances; however, the physics underpinning pappus-mediated flight remains unresolved. Here we visualized the flow around dandelion seeds, uncovering an extraordinary type of vortex. This vortex is a ring of recirculating... Read more
Cathal Cummins, Madeleine Seale, Alice Macente, Daniele Certini, Enrico Mastropaolo, Ignazio Maria Viola, Naomi Nakayama
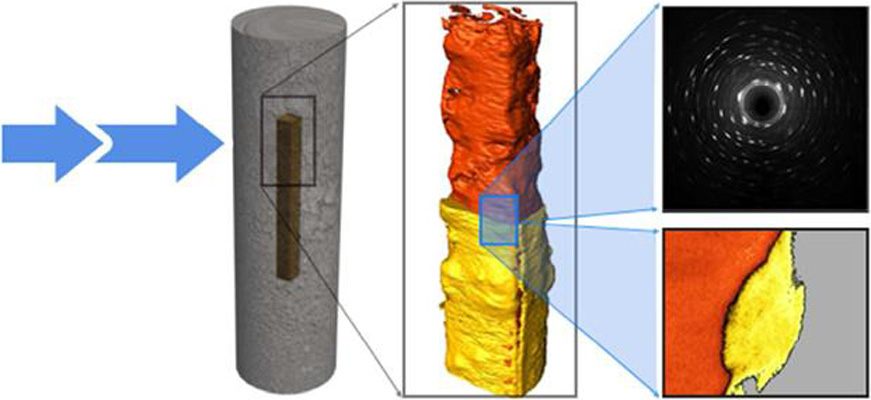
Nuclear waste viewed in a new light; a synchrotron study of uranium encapsulated in grout
How do you characterise the contents of a sealed nuclear waste package without breaking it open?
This question is important when the contained corrosion products are potentially reactive with air and radioactive. Synchrotron X-rays have been used to perform micro-scale in-situ observation and characterisation of uranium encapsulated in grout; a simulation for a typical intermediate level waste storage packet. X-ray tomography and X-ray powder diffraction generated both qualitative and ... Read more
C.A. Stitt, M. Hart, N.J. Harker, K.R. Hallam, J. MacFarlane, A. Banos, C. Paraskevoulakos, E. Butcher, C. Padovani, T.B. Scott
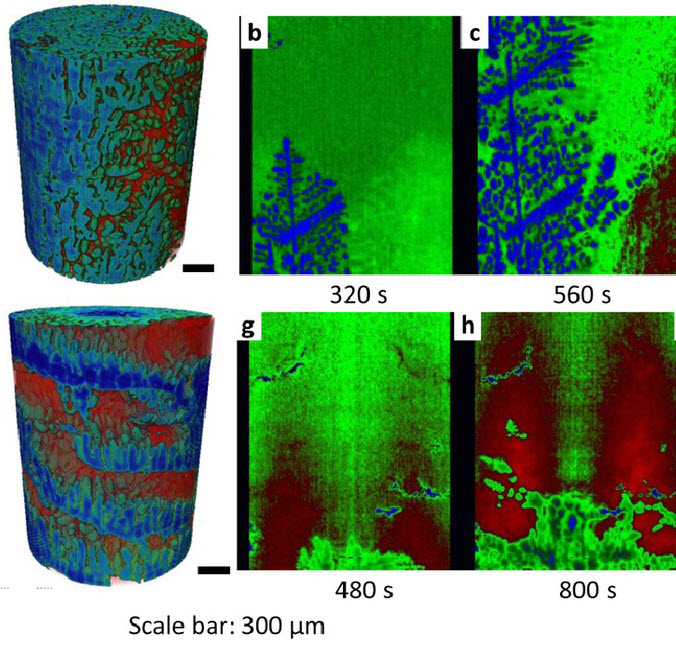
Revealing the mechanisms by which magneto-hydrodynamics disrupts solidification microstructures
A key technique for controlling solidification microstructures is magneto-hydrodynamics (MHD), resulting from imposing a magnetic field to solidifying metals and alloys. Applications range from bulk stirring to flow control and turbulence damping via the induced Lorentz force. Over the past two decades the Lorentz force caused by the interaction of thermoelectric currents and a magnetic field, a MHD phenomenon known as Thermoelectric Magnetohydrodynamics (TEMHD), was also shown to drive inter... Read more
B. Cai, A. Kao, E. Boller, O.V. Magdysyuk, R.C. Atwood, N.T. Vo, K. Pericleous, P.D. Lee
The prevailing electrode fabrication method for lithium-ion battery electrodes includes calendering at high pressures to densify the electrode and promote adhesion to the metal current collector.
However, this process increases the tortuosity of the pore network in the primary transport direction and imposes severe tradeoffs between electrode thickness and rate capability. With the aim of understanding the impact of pore tortuosity on electrode kinetics, and enabling cell designs with ... Read more
Benjamin Delattre, Ruhul Amin, Jonathan Sander, Joël De Coninck, Antoni P. Tomsia and Yet-Ming Chiang
Metal-Organic Framework Crystal-Glass Composites
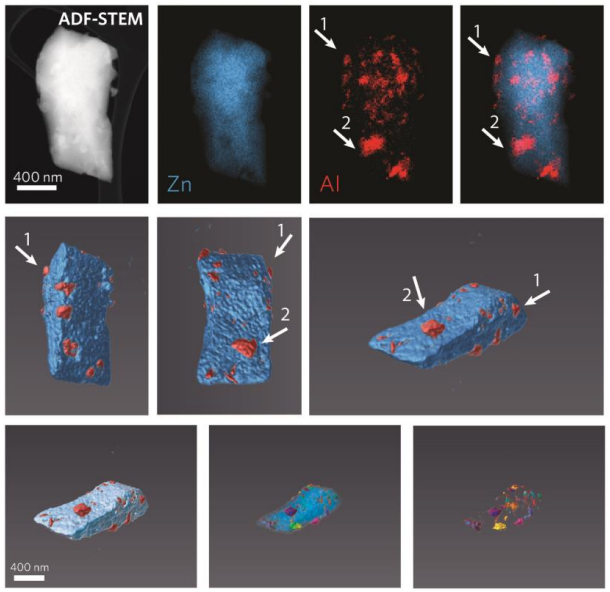
The majority of research into metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) focuses on their crystalline nature. However, in recent research the vitrification of a number of MOFs has been revealed. We propose that the solid-liquid phase transitions involved in MOF-glass formation can provide unique opportunities for the creation of a new class of functional, stable and porous composite materials. Described herein is the design, synthesis, and characterisation of novel metal-organic framework (MOF) crystal-... Read more
Jingwei Hou, Christopher W. Ashling, Sean M. Collins, Andraž Krajnc, Chao Zhou, Louis Longley, Duncan N. Johnstone, Philip A. Chater, Shichun Li, François-Xavier Coudert, David A. Keen, Paul A. Midgley, Gregor Mali, Vicki Chen, Thomas Bennett
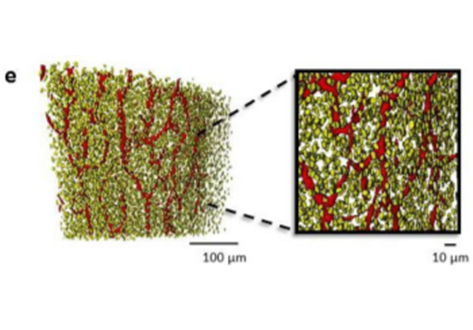
Cortical bone is permeated by a system of pores, occupied by the blood supply and osteocytes. With ageing, bone mass reduction and disruption of the microstructure are associated with reduced vascular supply. Insight into the regulation of the blood supply to the bone could enhance the understanding of bone strength determinants and fracture healing. Using synchrotron radiation-based computed tomography, the distribution of vascular canals and osteocyte lacunae was assessed in murine cortica... Read more
J.A. Núñez; A. Goring; B. Javaheri; H. Razi; D. Gomez-Nicola; E. Hesse; A.A. Pitsillides; P.J. Thurner; P. Schneider; E. Clarkin
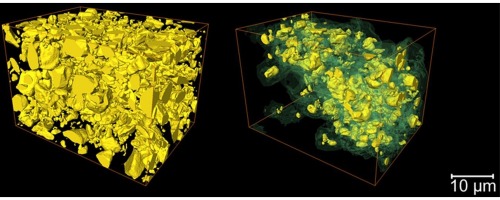
The microstructural degradation of a composite silicon electrode at different stages in its cycle life was investigated in 3D using X-ray nano-computed tomography. A reconstructed volume of 36 μm × 27 μm × 26 μm from the composite electrode was imaged in its pristine state and after 1, 10 and 100 cycles. Particle fracturing and phase transformation was observed within the electrode with increased cycling. In addition, a distinct, lower X-ray attenuating phase was clearly resolved,... Read more
Oluwadamilola O. Taiwo, Melanie Loveridge, Shane D.Beattie, Donal P.Finegan, Rohit Bhagat, Daniel J.L.Brett, Paul R.Shearing
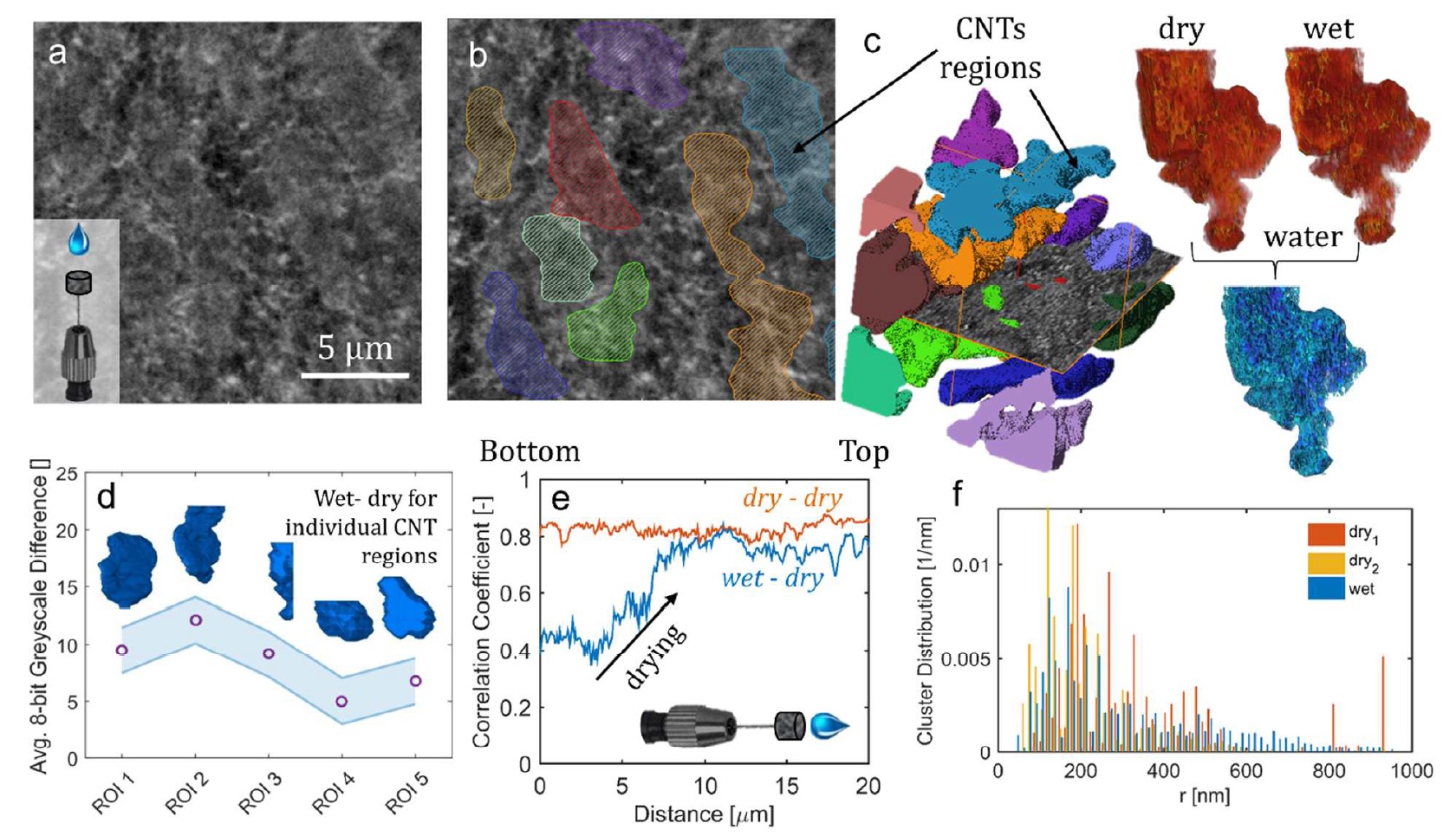
This work describes the performance improvement of a polymer electrolyte fuel cell with a novel class of microporous layers (MPLs) that incorporates hydrophilic additives: one with 30 μm aluminosilicate fibers and another with multiwalled carbon nanotubes with a domain size of 5 μm. Higher current densities at low potentials were observed for cells with the additive-containing MPLs compared to a baseline cell with a conventional MPL, which correlate with improvements in water management. Th... Read more
Dusan Spernjak, Rangachary Mukundan, Rodney L. Borup, Liam Connolly, Benjamin Zackin, Vincent De Andrade, Michael Wojcik, Dilworth Y. Parkinson, David Jacobson, Daniel Seth Hussey, Karren L More, Thomas Chan, Adam Z Weber, and Iryna V. Zenyuk
Label-free 3D-CLEM using endogenous tissue landmarks
We demonstrate feasibility of the workflow by combining in vivo 2-photon microscopy and focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB/SEM) to dissect the role of astrocytic coverage in the persistence of dendritic spines.
Emerging 3D correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM) approaches enable studying neuronal structure-function relations at unprecedented depth and precision. However, established protocols for the correlation of light and electron micrographs rely ... Read more
Manja Luckner,Steffen Burgold, Severin Filser, Maximilian Scheungrab, Yilmaz Niyaz, Eric Hummel, Gerhard Wanner, Jochen Herms
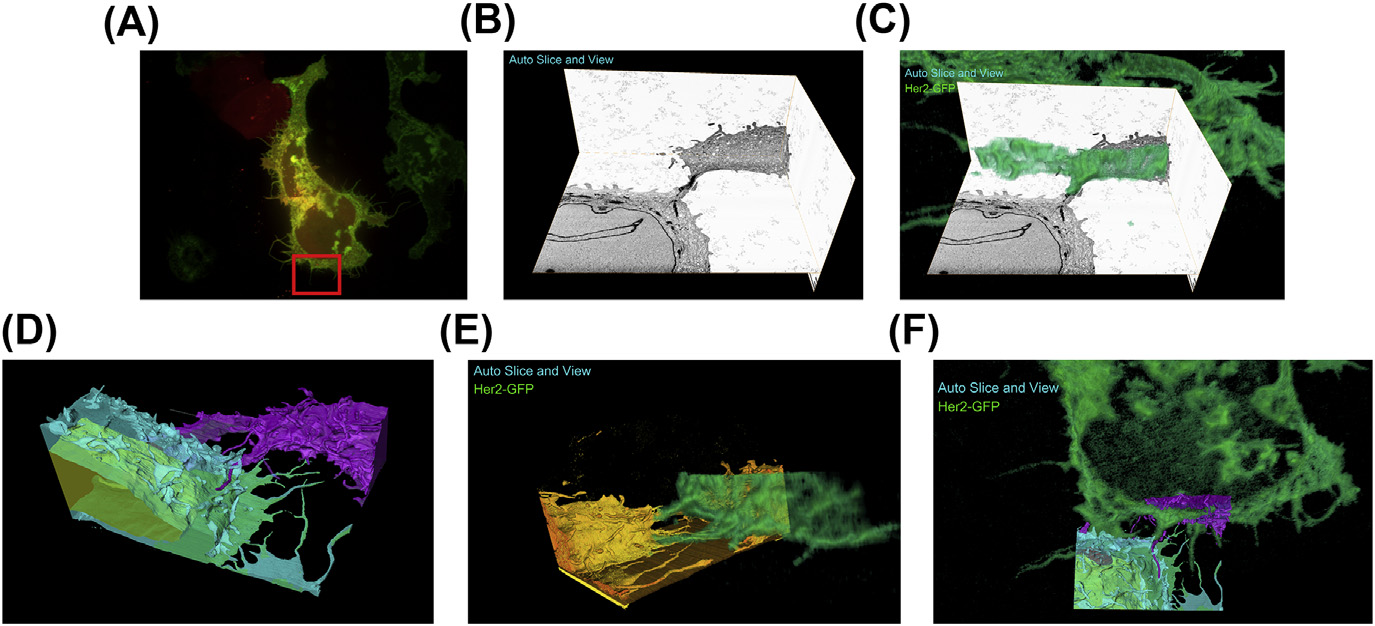
A fully integrated, three-dimensional fluorescence to electron microscopy correlative workflow
While fluorescence microscopy provides tools for highly specific labeling and sensitive detection, its resolution limit and lack of general contrast has hindered studies of cellular structure and protein localization. Recent advances in correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM), including the fully integrated CLEM workflow instrument, the Thermo Scientific CorrSight with MAPS, have allowed for a more reliable, reproducible, and quicker approach to correlate three-dimensional time-lapse... Read more
Claudia S. Lopez, Cedric Bouchet-Marquis, Christopher P. Arthur, Jessica L. Riesterer, Gregor Heiss, Guillaume Thibault, Lee Pullan, Sunjong Kwon, Joe W. Gray
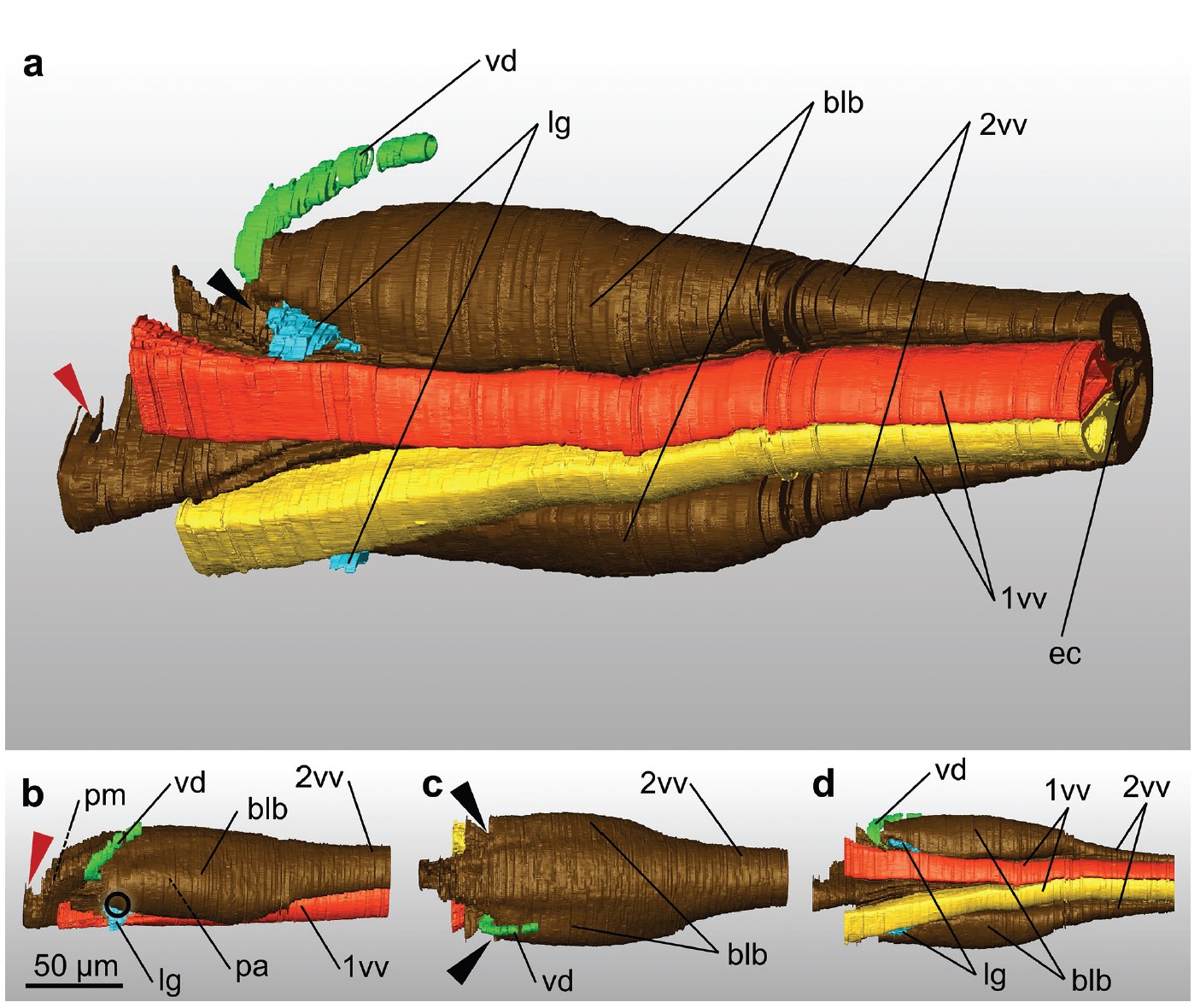
Ovipositor of the braconid wasp Habrobracon hebetor: structural and functional aspects
The Braconidae are a megadiverse and ecologically highly important group of insects. The vast majority of braconid wasps are parasitoids of other insects, usually attacking the egg or larval stages of their hosts. The ovipositor plays a crucial role in the assessment of the potential host and precise egg laying. We used lightand electron-microscopic techniques to investigate all inherent cuticular elements of the ovipositor (the female 9th abdominal tergum, two pairs of valvifers, and three p... Read more
Michael Csader, Karin Mayer, Oliver Betz, Stefan Fischer, Benjamin Eggs
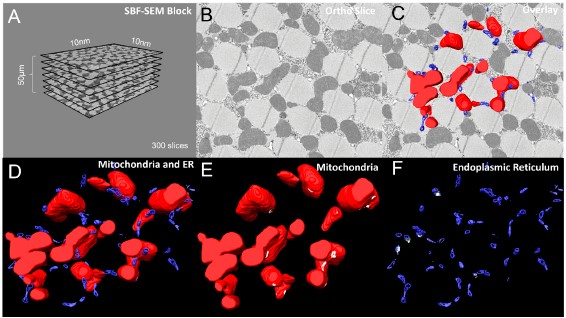
Protocols for Generating Surfaces and Measuring 3D Organelle Morphology Using Amira
High-resolution 3D images of organelles are of paramount importance in cellular biology. Although light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) have provided the standard for imaging cellular structures, they cannot provide 3D images.
However, recent technological advances such as serial block-face scanning electron microscopy (SBF-SEM) and focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM) provide the tools to create 3D images for the ultrastructural analysis of org... Read more
Edgar Garza-Lopez, Zer Vue, Prasanna Katti, Kit Neikirk, Michelle Biete, Jacob Lam, Heather K. Beasley, Andrea G. Marshall, Taylor A. Rodman, Trace A. Christensen, Jeffrey L. Salisbury, Larry Vang, Margaret Mungai, Salma Ash Shareef, Sandra A. Murray, Jianqiang Shao, Jennifer Streeter, Brian Glancy, Renata O. Pereira1, E. Dale Abel, and Antentor Hinton, Jr.

The molecular basis for sarcomere organization in vertebrate skeletal muscle
Sarcomeres are force-generating and load-bearing devices of muscles. A precise molecular picture of how sarcomeres are built underpins understanding their role in health and disease. Here, we determine the molecular architecture of native vertebrate skeletal sarcomeres by electron cryo-tomography.
Our reconstruction reveals molecular details of the three-dimensional organization and interaction of actin and myosin in the A-band, I-band, and Z-disc and demonstrates that α-actinin cros... Read more
Zhexin Wang, Michael Grange, Thorsten Wagner, Ay Lin Kho, Mathias Gautel, Stefan Raunser