Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
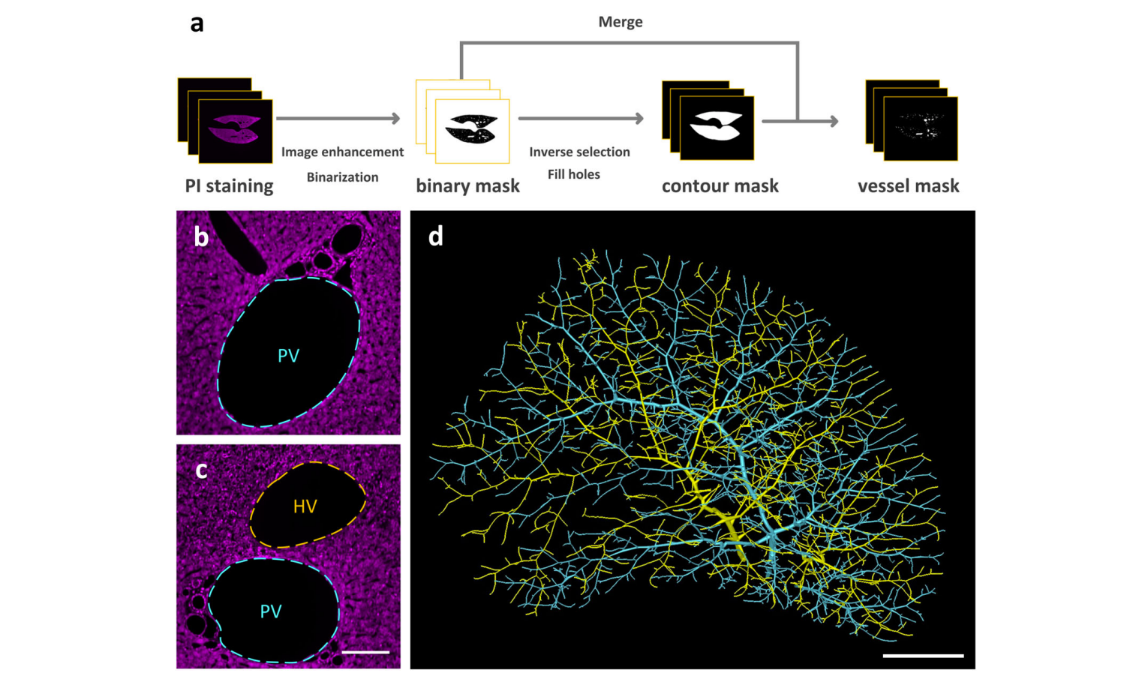
Multiscale reconstruction of various vessels in the intact murine liver lobe
The liver contains a variety of vessels and participates in miscellaneous physiological functions. While past studies generally focused on certain hepatic vessels, we simultaneously obtained all the vessels and cytoarchitectural information of the intact mouse liver lobe at single-cell resolution. […] providing a technology roadmap for studying the fine hepatic vascular structures and their spatial relationship, which will help research into liver diseases and evaluation of medical effi... Read more
Qi Zhang, Anan Li, Siqi Chen, Jing Yuan, Tao Jiang, Xiangning Li, Qingming Luo,Zhao Feng & Hui Gon
In recent years new methodologies and workflow pipelines for acquiring correlated fluorescence microscopy and volume electron microscopy datasets have been extensively described and made accessible to users of different levels. Post-acquisition image processing, and particularly correlation of the optical and electron data in a single integrated three-dimensional framework can be key for extracting valuable information, especially when imaging large sample volumes such as whole cells or tissu... Read more
Allon Weiner
A fully integrated, three-dimensional fluorescence to electron microscopy correlative workflow
While fluorescence microscopy provides tools for highly specific labeling and sensitive detection, its resolution limit and lack of general contrast has hindered studies of cellular structure and protein localization. Recent advances in correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM), including the fully integrated CLEM workflow instrument, the Thermo Scientific CorrSight with MAPS, have allowed for a more reliable, reproducible, and quicker approach to correlate three-dimensional time-lapse... Read more
Claudia S. Lopez, Cedric Bouchet-Marquis, Christopher P. Arthur, Jessica L. Riesterer, Gregor Heiss, Guillaume Thibault, Lee Pullan, Sunjong Kwon, Joe W. Gray
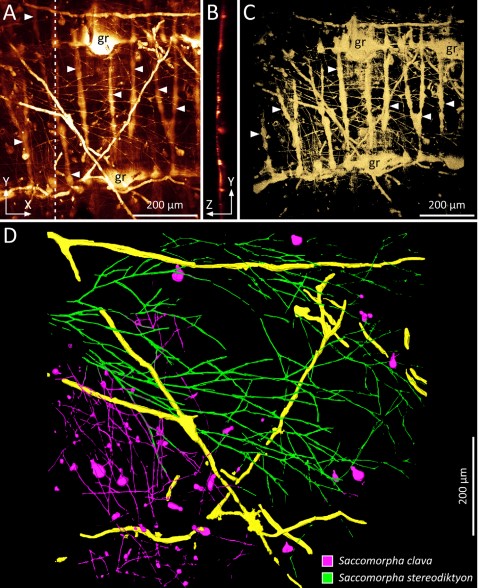
Microscopic organisms that penetrate calcareous structures by actively dissolving the carbonate matrix, namely microendoliths, have an important influence on the breakdown of marine carbonates.
Microscopic organisms that penetrate calcareous structures by actively dissolving the carbonate matrix, namely microendoliths, have an important influence on the breakdown of marine carbonates. The study of these microorganisms and the bioerosion traces they produce is crucial for understanding ... Read more
Philipp-Konrad Schätzle, Max Wisshak, Andreas Bick, André Freiwald, Alexander Kieneke
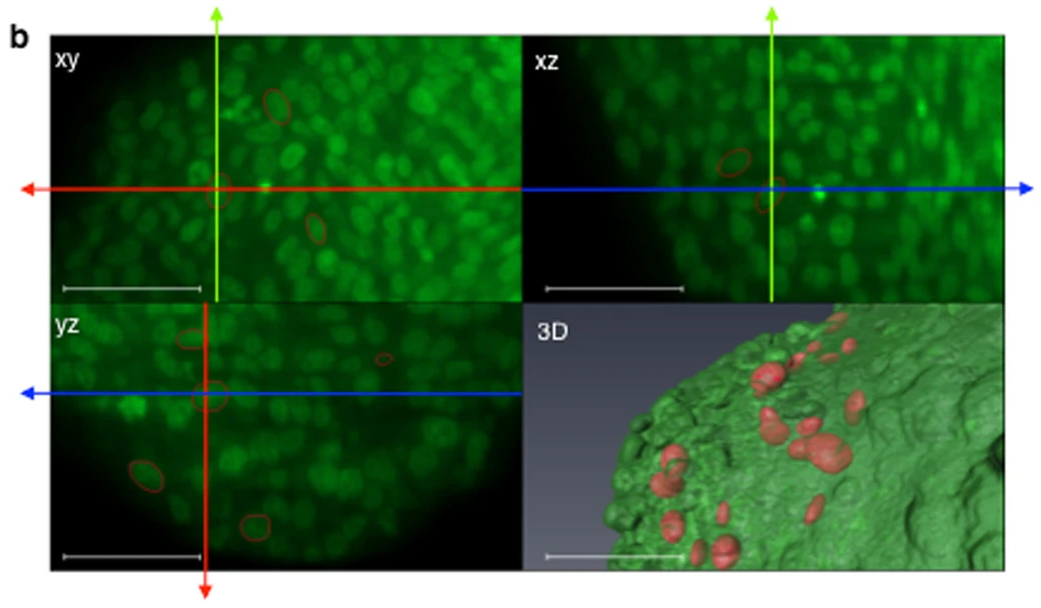
Impact of physical confinement on nuclei geometry and cell division dynamics in 3D spheroids
Multicellular tumour spheroids are used as a culture model to reproduce the 3D architecture, proliferation gradient and cell interactions of a tumour micro-domain. However, their 3D characterization at the cell scale remains challenging due to size and cell density issues. In this study, we developed a methodology based on 3D light sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) image analysis and convex hull calculation that allows characterizing the 3D shape and orientation of cell nuclei relative to ... Read more
Annaïck Desmaison, Ludivine Guillaume, Sarah Triclin, Pierre Weiss, Bernard Ducommun & Valérie Lobjois
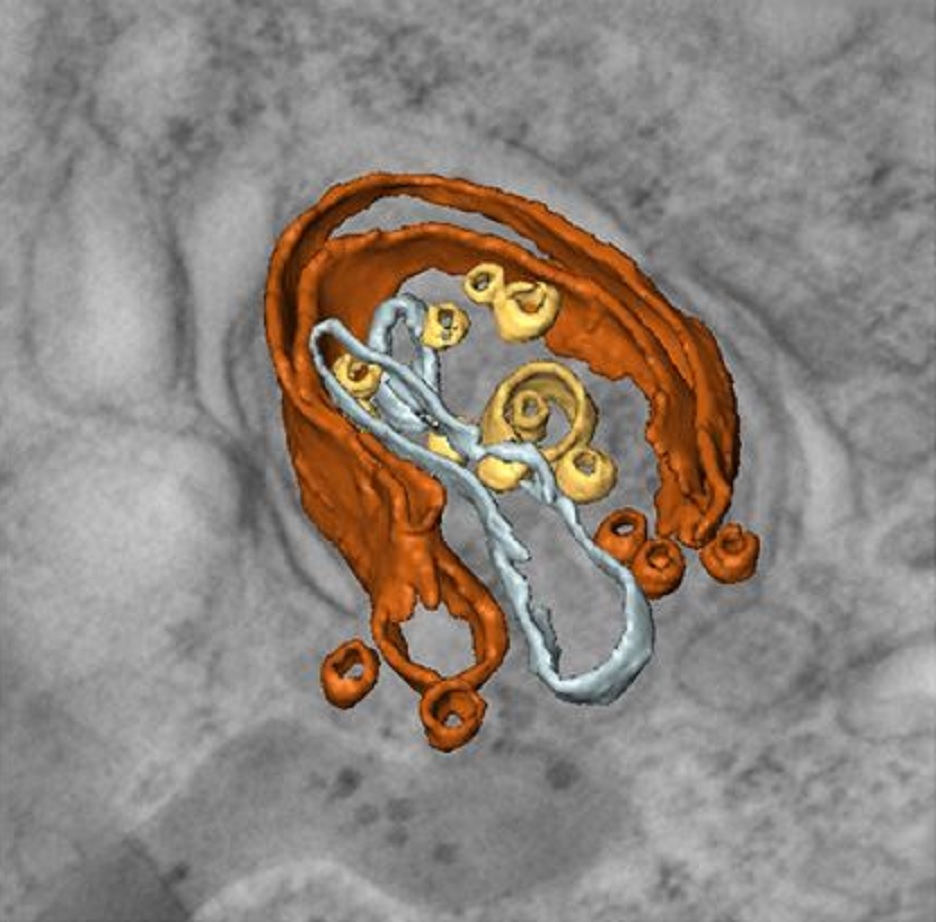
Macroautophagy is morphologically characterized by autophagosome formation. Autophagosomes are double-membraned vesicles that sequester cytoplasmic components for further degradation in the lysosome. Basal autophagy is paramount for intracellular quality control in post-mitotic cells but, surprisingly, the number of autophagosomes in post-mitotic neurons is very low, suggesting that alternative degradative structures could exist in neurons…
Read more
Maria Rosario Fernandez-Fernandez, Desire Ruiz-Garcia, Eva Martin-Solana, Francisco Javier Chichon, Jose L. Carrascosa, Jose-Jesus Fernandez
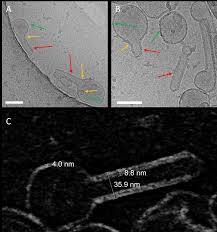
Influenza A matrix protein M1 is sufficient to induce lipid membrane deformation
The matrix protein M1 of the Influenza A virus is considered to mediate viral assembly and budding at the plasma membrane (PM) of infected cells. In order for a new viral particle to form, the PM lipid bilayer has to bend into a vesicle towards the extracellular side. Studies in cellular models have proposed that different viral proteins might be responsible for inducing membrane curvature in this context (including M1), but a clear consensus has not been reached. In this study, we use a comb... Read more
Ismail Dahmani, Kai Ludwig, Salvatore Chiantia
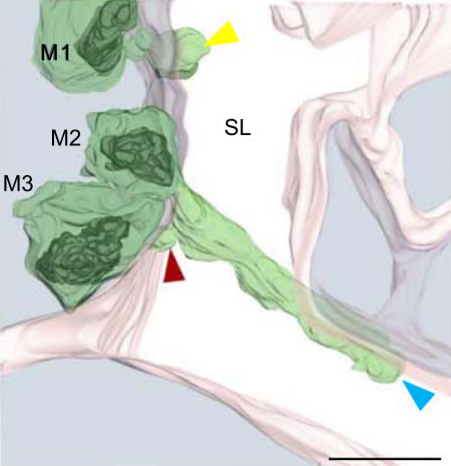
Multiple membrane extrusion sites drive megakaryocyte migration into bone marrow blood vessels
Platelets, cells central to hemostasis and thrombosis, are formed from parent cell megakaryocytes. Although the process is highly efficient in vivo, our ability to generate them in vitro is still remarkably inefficient. We proposed that greater understanding of the process in vivo is needed and used an imaging approach, intravital correlative light electron microscopy, to visualize platelet generation in bone marrow in the living mouse. In contrast to current understanding, we found that most... Read more
Edward Brown, Leo M Carlin, Claus Nerlov, Cristina Lo Celso, Alastair W Poole
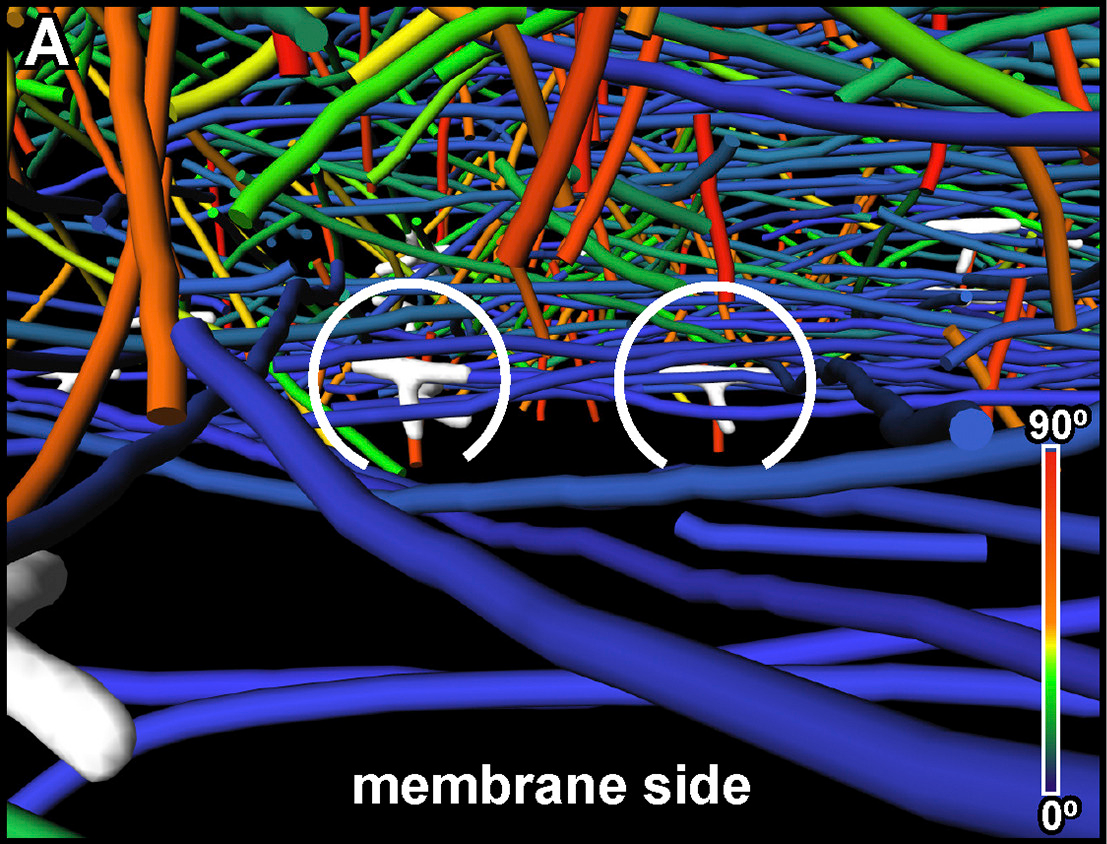
The Architecture of Traveling Actin Waves Revealed by Cryo-Electron Tomography
Actin waves are dynamic supramolecular structures involved in cell migration, cytokinesis, adhesion, and neurogenesis. Although wave-like propagation of actin networks is a widespread phenomenon, the actin architecture underlying wave propagation remained unknown. In situ cryo-electron tomography of Dictyostelium cells unveils the wave architecture and provides evidence for wave progression by de novo actin nucleation. Subtomogram averaging reveals the structu... Read more
Marion Jasnin, Florian Beck, Mary Ecke, Yoshiyuki Fukuda, Antonio Martinez-Sanchez, Wolfgang Baumeister, Günther Gerisch
Multiscale Co‐reconstruction of Lung Architectures and Inhalable Materials Spatial Distribution
Pulmonary diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, lower respiratory infections, and lung cancer are listed in the top ten causes of deaths globally with more than 10 million mortality per year. Apart from oral administration, the Dry Powder Inhalation (DPI) for pulmonary administration provides an important alternative route for targeted treatment of these pulmonary diseases. […] Furthermore, there is a growing demand on und... Read more
Xian Sun, Xiaochuan Zhang, Xiaohong Ren, Hongyu Sun, Li Wu, Caifen Wang, Xiaohui Ye, Peter York, Zhaobing Gao, Hualiang Jiang, Jiwen Zhang, Xianzhen Yin
The importance of context in regulation of gene expression is now an accepted principle; yet the mechanism by which the microenvironment communicates with the nucleus and chromatin in healthy tissues is poorly understood. A functional role for nuclear and cytoskeletal architecture is suggested by the phenotypic differences observed between epithelial and mesenchymal cells…
Read more
Danielle M. Jorgens, Jamie L. Inman, Michal Wojcik, Claire Robertson, Hildur Palsdottir, Wen-Ting Tsai, Haina Huang, Alexandre Bruni-Cardoso, Claudia S. López, Mina J. Bissell, Ke Xu, Manfred Auer
Determining the bacterial cell biology of planctomycetes
Bacteria of the phylum Planctomycetes have been previously reported to possess several features that are typical of eukaryotes, such as cytosolic compartmentalization and endocytosis-like macromolecule uptake. However, recent evidence points towards a Gram-negative cell plan for Planctomycetes, although in-depth experimental analysis has been hampered by insufficient genetic tools…
Read more
Christian Boedeker, Margarete Schüler, Greta Reintjes, Olga Jeske, Muriel C. F. van Teeseling et al.
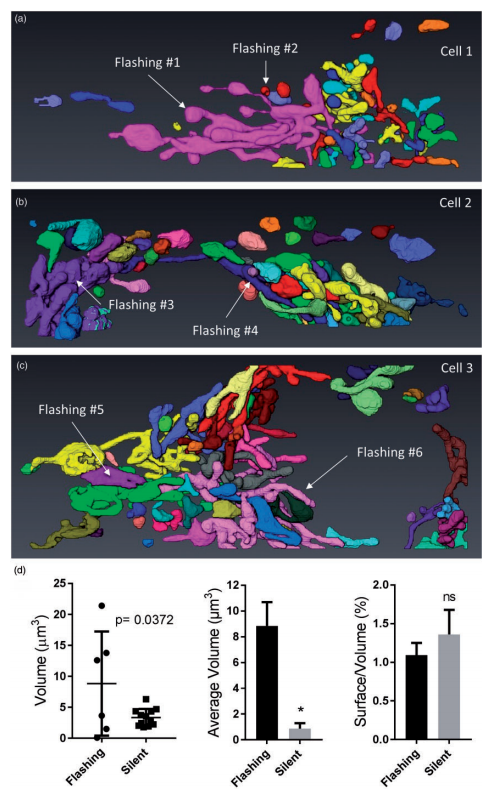
Ultrastructural Characterization of Flashing Mitochondria
Mitochondria undergo spontaneous transient elevations in matrix pH associated with drops in mitochondrial membrane potential. These mitopHlashes require a functional respiratory chain and the profusion protein optic atrophy 1, but their mechanistic basis is unclear. To gain insight on the origin of these dynamic events, we resolved the ultrastructure of flashing mitochondria by correlative light and electron microscopy. HeLa cells expressing the matrix-targeted pH probe mitoSypHer were screen... Read more
Manon Rosselin, Paula Nunes-Hasler, and Nicolas Demaurex
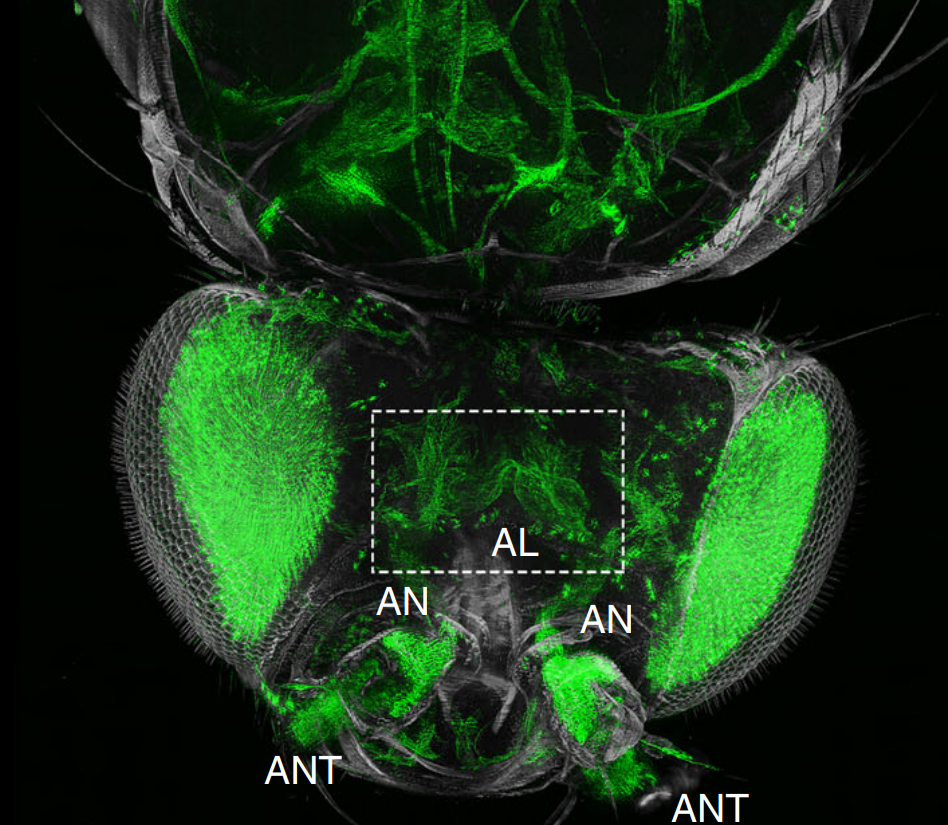
The fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, is an important experimental model to address central questions in neuroscience at an organismic level. However, imaging of neural circuits in intact fruit flies is limited due to structural properties of the cuticle. Here we present a novel approach combining tissue clearing, ultramicroscopy, and data analysis that enables the visualisation of neuronal networks with single-cell resolution from the larval stage up to the adult Drosophila. (…) This... Read more
Marko Pende, Klaus Becker, Martina Wanis, Saiedeh Saghafi, Rashmit Kaur, Christian Hahn, Nika Pende, Massih Foroughipour, Thomas Hummel & Hans-Ulrich Dodt
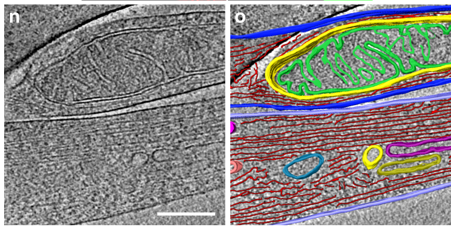
Correlative cryo-electron microscopy reveals the structure of TNTs in neuronal cells
The orchestration of intercellular communication is essential for multicellular organisms. One mechanism by which cells communicate is through long, actin-rich membranous protrusions called tunneling nanotubes (TNTs), which allow the intercellular transport of various cargoes, between the cytoplasm of distant cells in vitro and in vivo. Here, we use correlative FIB-SEM, light- and cryo-electron microscopy approaches to elucidate the structural organization of neuronal TNTs. Our data indicate ... Read more
Anna Sartori-Rupp, Diégo Cordero Cervantes, Anna Pepe, Karine Gousset, Elise Delage, Simon Corroyer-Dulmont, Christine Schmitt, Jacomina Krijnse-Locker & Chiara Zurzolo
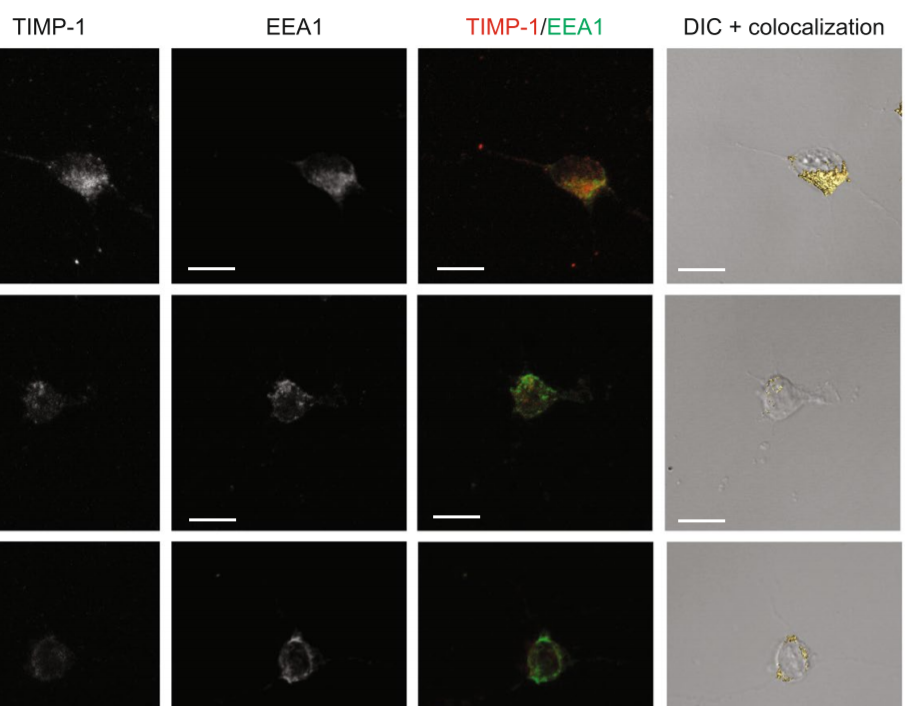
The tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) exerts inhibitory activity against matrix metalloproteinases and cytokine-like effects. We previously showed that TIMP-1 reduces neurite outgrowth in mouse cortical neurons and that this cytokine-like effect depends on TIMP-1 endocytosis mediated by the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP-1). To gain insight into the interaction between TIMP-1 and LRP-1, we considered conformational changes that occur when a ligand bind... Read more
Laurie Verzeaux, Nicolas Belloy, Jessica Thevenard-Devy, Jérôme Devy, Géraldine Ferracci, Laurent Martiny, Stéphane Dedieu, Manuel Dauchez, Hervé Emonard, Nicolas Etique & Emmanuelle Devarenne-Charpentier
Immunofluorescence tomography is a high-resolution 3-D reconstruction method based on methacrylate embedding and serial-sectioning, where 2-D images of immuno-stained serial-sections are computationally aligned into image stacks, and the 3-D volume rendered. Butyl-Methyl Methacrylate (BMMA) plastic was adopted as it preserves excellent tissue morphology and can be de-plasticized easily using an organic solvent, which enables immuno-staining of serial-sections without antibody penetration issu... Read more
Parfitt, Geraint J
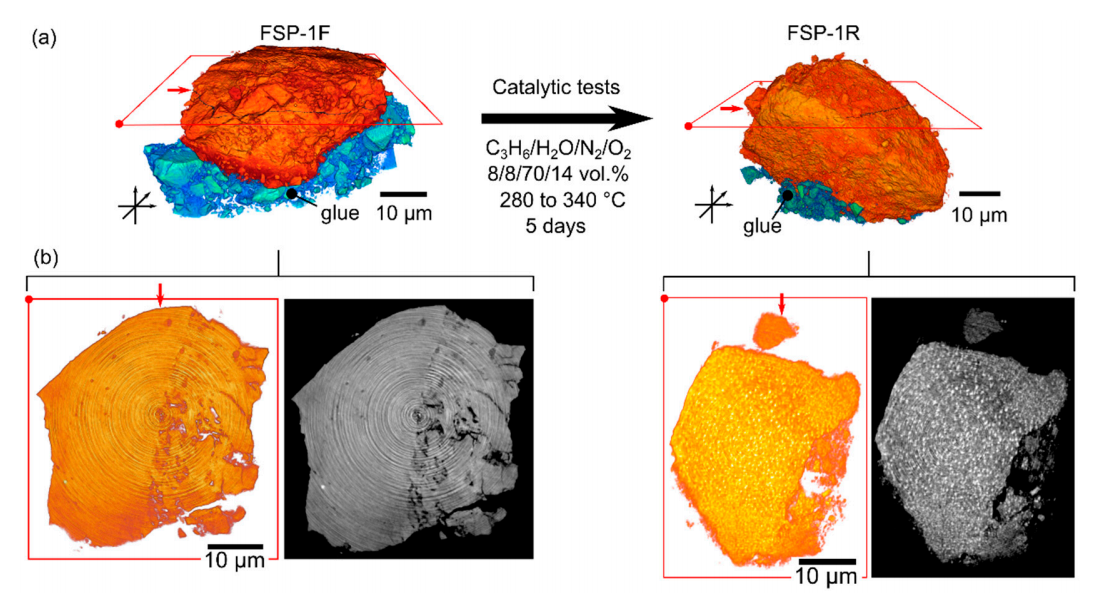
Structural Evolution of Highly Active Multicomponent Catalysts for Selective Propylene Oxidation
Multicomponent Bi-Mo-Fe-Co oxide catalysts prepared via flame spray pyrolysis were tested for selective propylene oxidation, showing high conversion (>70%) and selectivity (>85%) for acrolein and acrylic acid at temperatures of 330 ◦C. During extended time-on-stream tests (5–7 days), the catalysts retained high activity while undergoing diverse structural changes. This was evident on: (a) the atomic scale, using powder X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray absorption spectros... Read more
Paul Sprenger, Thomas L Sheppard, Jussi-Petteri Suuronen, Abhijeet Gaur, Federico Benzi and Jan-Dierk Grunwaldt
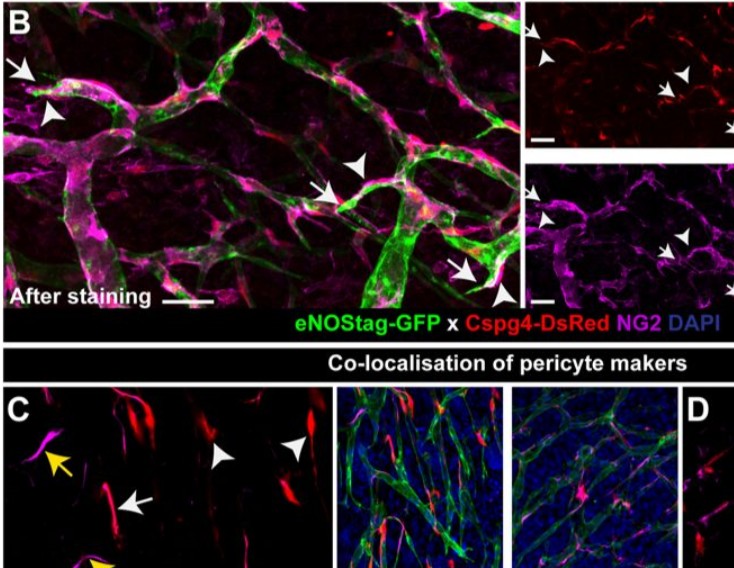
Endothelial cells and pericytes are integral cellular components of the vasculature with distinct interactive functionalities. To study dynamic interactions between these two cells we created two transgenic animal lines. A truncated eNOS (endothelial nitric oxide synthase) construct was used as a GFP tag for endothelial cell evaluation and an inducible Cre-lox recombination, under control of the Pdgfrb (platelet derived growth factor receptor beta) promoter, was created for pericyte assessmen... Read more
Ann L. B. Seynhaeve, Douwe Oostinga, Rien van Haperen, Hanna M. Eilken, Susanne Adams, Ralf H. Adams & Timo L. M. ten Hagen
Chronic cigarette smoke exposure drives spiral ganglion neuron loss in mice
Tobacco use is associated with an increased risk of hearing loss in older individuals, suggesting cigarette smoke (CS) exposure may target the peripheral auditory organs. However, the effects of CS exposure on general cochlear anatomy have not previously been explored.
Here we compare control and chronic CS exposed cochleae from adult mice to assess changes in structure and cell survival. Two-photon imaging techniques, including the imaging of second harmonic generation (SHG) and two-p... Read more
Stephen T. Paquette, Ryan P. Dawes, Isaac K. Sundar, Irfan Rahman, Edward B. Brown & Patricia M. White
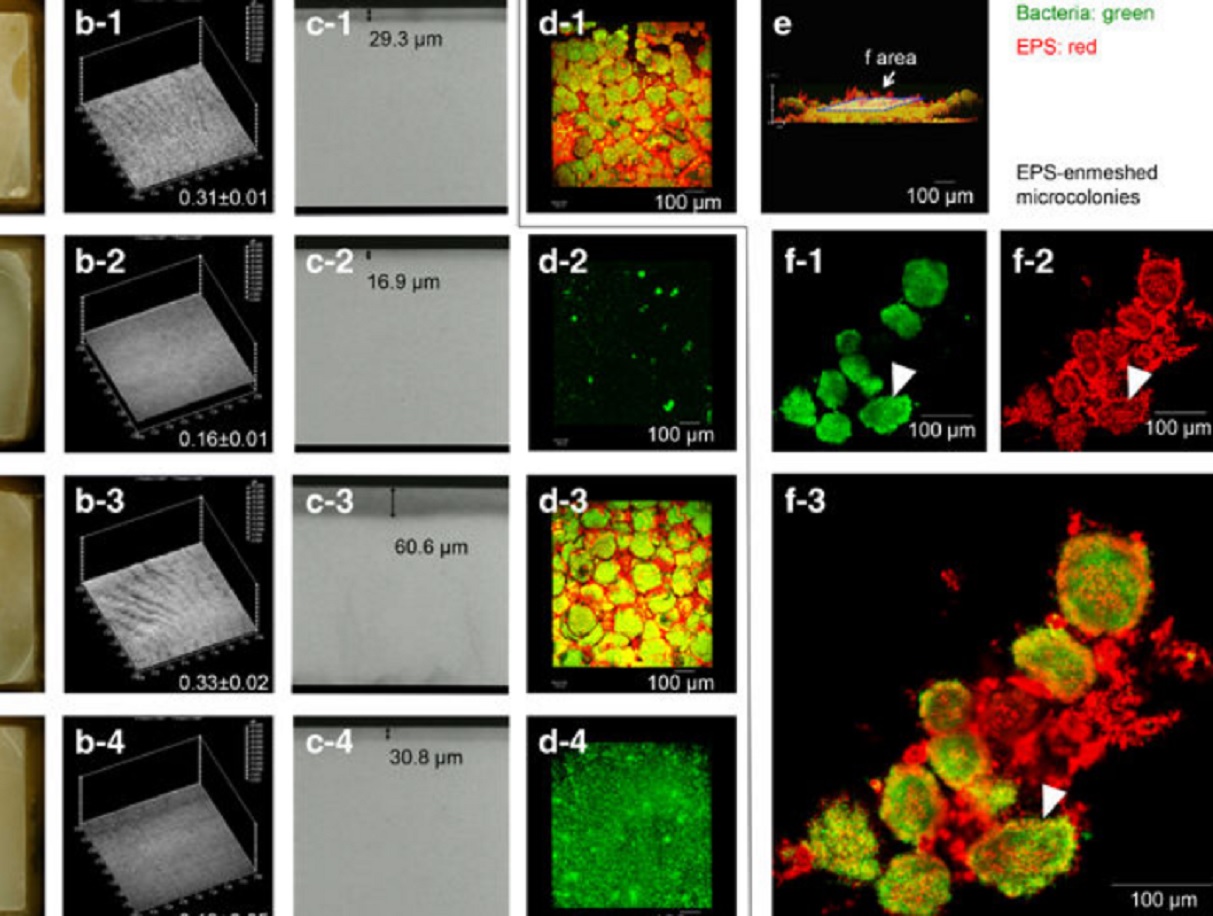
Acidic microenvironments created by bacterial clusters thriving in a polysaccharide matrix could be behind localized tooth decay. Jin Xiao of the University of Rochester Medical Center and Geelsu Hwang of the University of Pennsylvania with colleagues in the US mapped acidity changes across tooth enamel caused by the microstructure of dental plaque: a film of bacteria and the polysaccharide matrix they secrete. Using fluorescence microscopy, they studied the 3D architecture of plaque that for... Read more
Jin Xiao, Anderson T Hara, Dongyeop Kim, Domenick T Zero, Hyun Koo et al.