Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
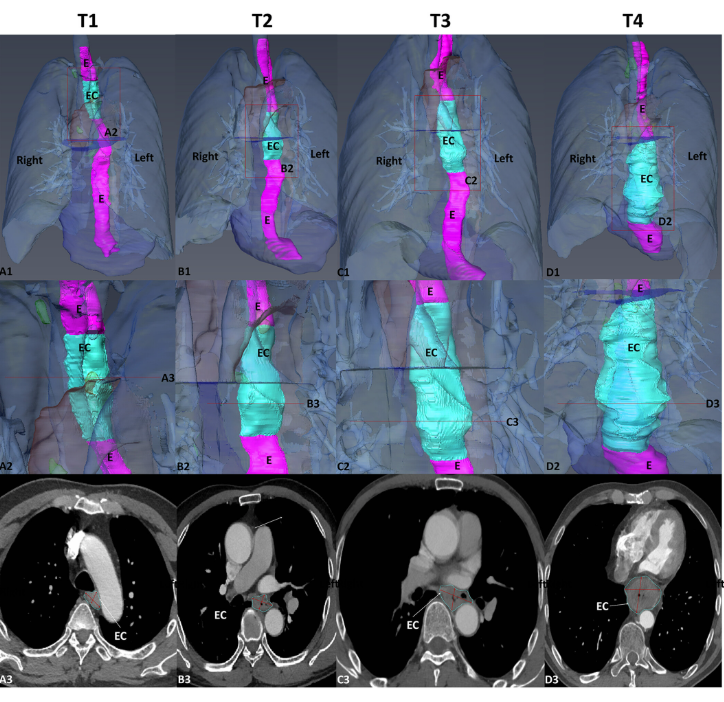
Objectives
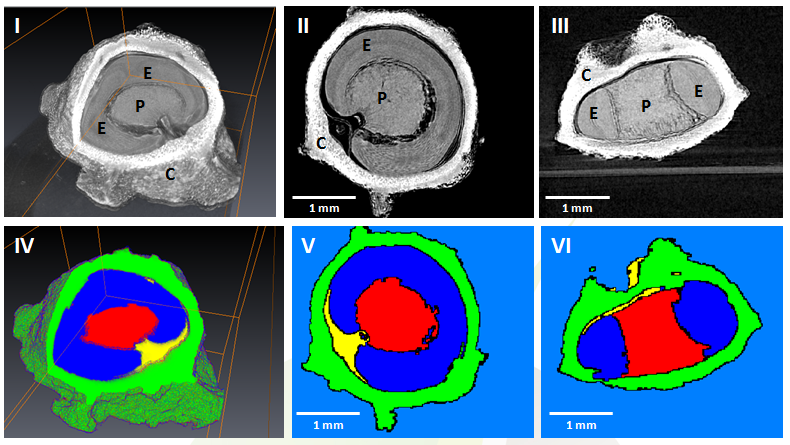
To statistically study the 3D shape of oesophageal cancer (EC) and its spatial relationships based on computed tomography angiography (CTA) 3D reconstruction, to determine its relationship with T-stages, and to create an optimal T-stage diagnosis protocol based on CTA calculation.
Runyuan Wang, Xiaoqin Zhang, Wei Wu, Jinfeng Ma, Jincheng Chen, Zhu Zhang, Liqun Liu, Shanshan Xu, Ximei Cao, Yi Wu, Huilin Cui
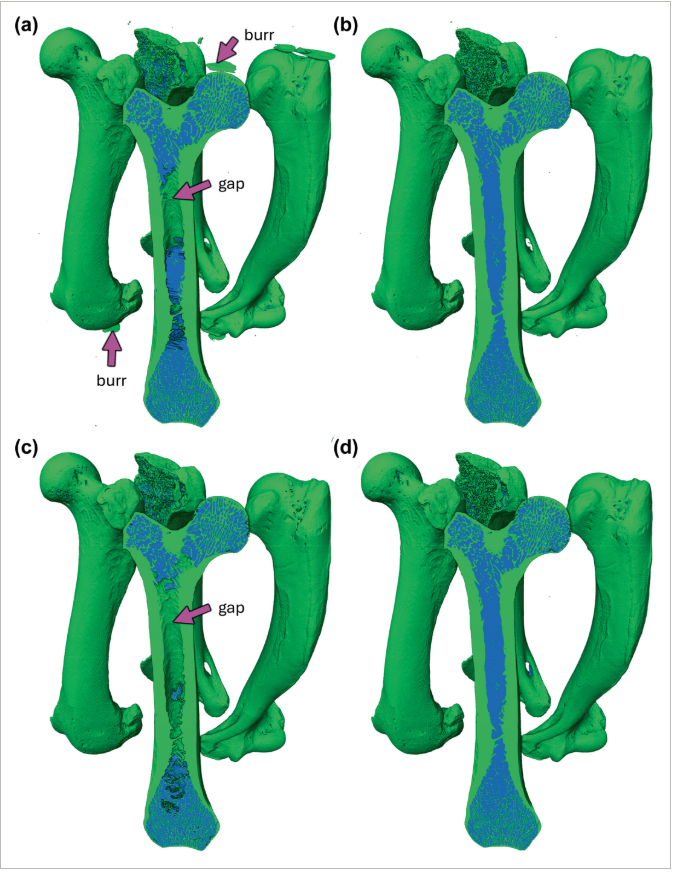
Computed tomography (CT) enables rapid imaging of large-scale studies of bone, but those datasets typically require manual segmentation, which is time-consuming and prone to error. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) offer an automated solution, achieving superior performance on image data. In this methodology-focused paper, we used CNNs to train segmentation models from scratch on 2D and 3D patches from micro-CT scans of otter long bones. These new models, collectively called BONe (Bone One... Read more
Andrew H. Lee, Julian M. Moore, Brandon Vera Covarrubias, Leigha M. Lynch
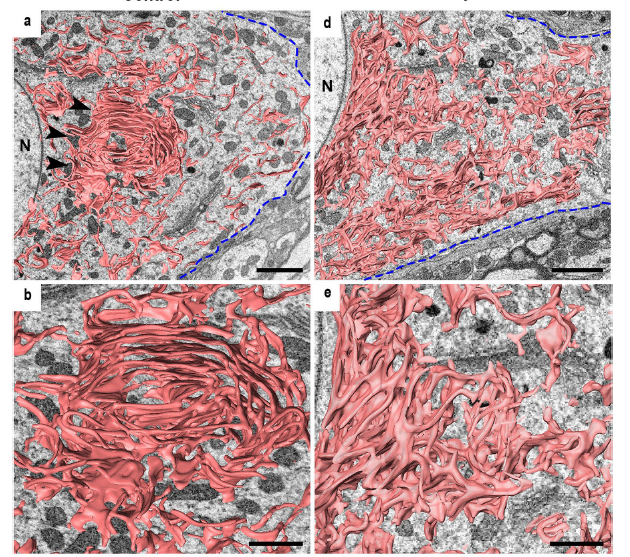
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) extends throughout a cell and plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Changes in ER shape could provide a clue to explore the mechanisms that underlie the fate determination of neurons after
axon injury because the ER drastically changes its morphology under neuronal stress to maintain cellular homeostasis and
recover from damage. Because of their tiny structures and richness in the soma, the detailed morphology of the ER and... Read more
Mahmoud Elgendy,Hiromi Tamada, Takaya Taira, Yuma Iio, Akinobu Kawamura, Ayusa Kunogi, Yuka Mizutani, Hiroshi Kiyama
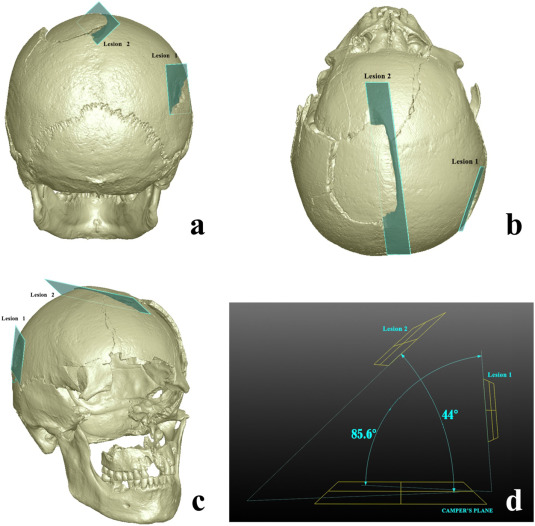
Human skeletal remains from archaeological contexts occasionally present signs of traumatic injuries from weapons, revealing, for example, the degree of interpersonal violence, the type of weapon and the sequence of events of a specific historical context.
Traumatic lesions are generally analyzed using macroscopic and microscopic methods, which are not necessarily integrated in the same study. In this study, we employed a multi-analytical approach to determine i... Read more
Antonino Vazzana, Lucia Martina Scalise, Mirko Traversari, Carla Figus, Salvatore Andrea Apicella, Laura Buti, Gregorio Oxilia, Rita Sorrentino, Silvia Pellegrini, Chiara Matteucci, Lucio Calcagnile, Raffaele Savigni, Robin N.M.Feeney, Giorgio Gruppioni, Stefano Benazziah
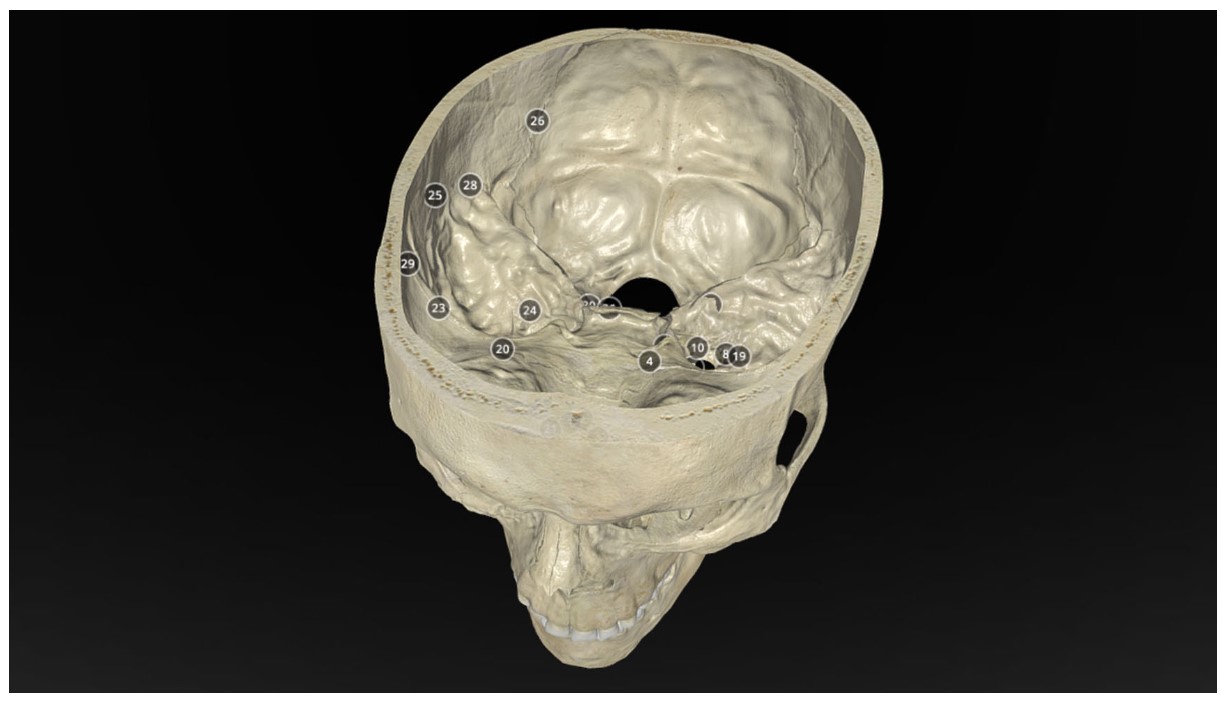
Operative Anatomy of the Human Skull: A Virtual Reality Expedition
Benjamin K Hendricks, MD Akash J Patel, MD Jerome Hartman Mark F Seifert, PhD Aaron Cohen-Gadol, MD, MSc, MBA
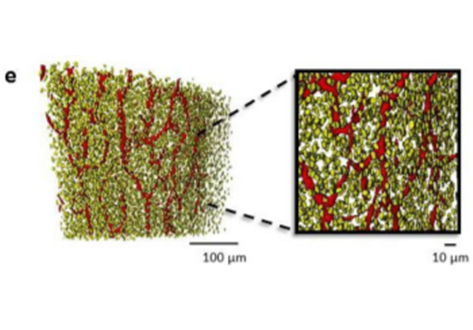
Cortical bone is permeated by a system of pores, occupied by the blood supply and osteocytes. With ageing, bone mass reduction and disruption of the microstructure are associated with reduced vascular supply. Insight into the regulation of the blood supply to the bone could enhance the understanding of bone strength determinants and fracture healing. Using synchrotron radiation-based computed tomography, the distribution of vascular canals and osteocyte lacunae was assessed in murine cortica... Read more
J.A. Núñez; A. Goring; B. Javaheri; H. Razi; D. Gomez-Nicola; E. Hesse; A.A. Pitsillides; P.J. Thurner; P. Schneider; E. Clarkin
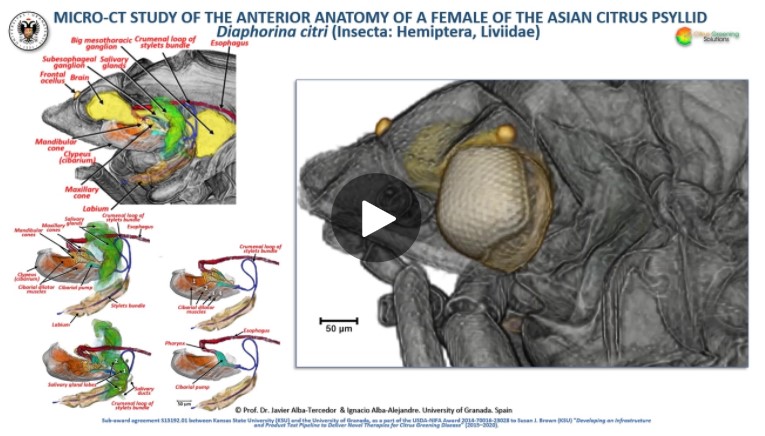
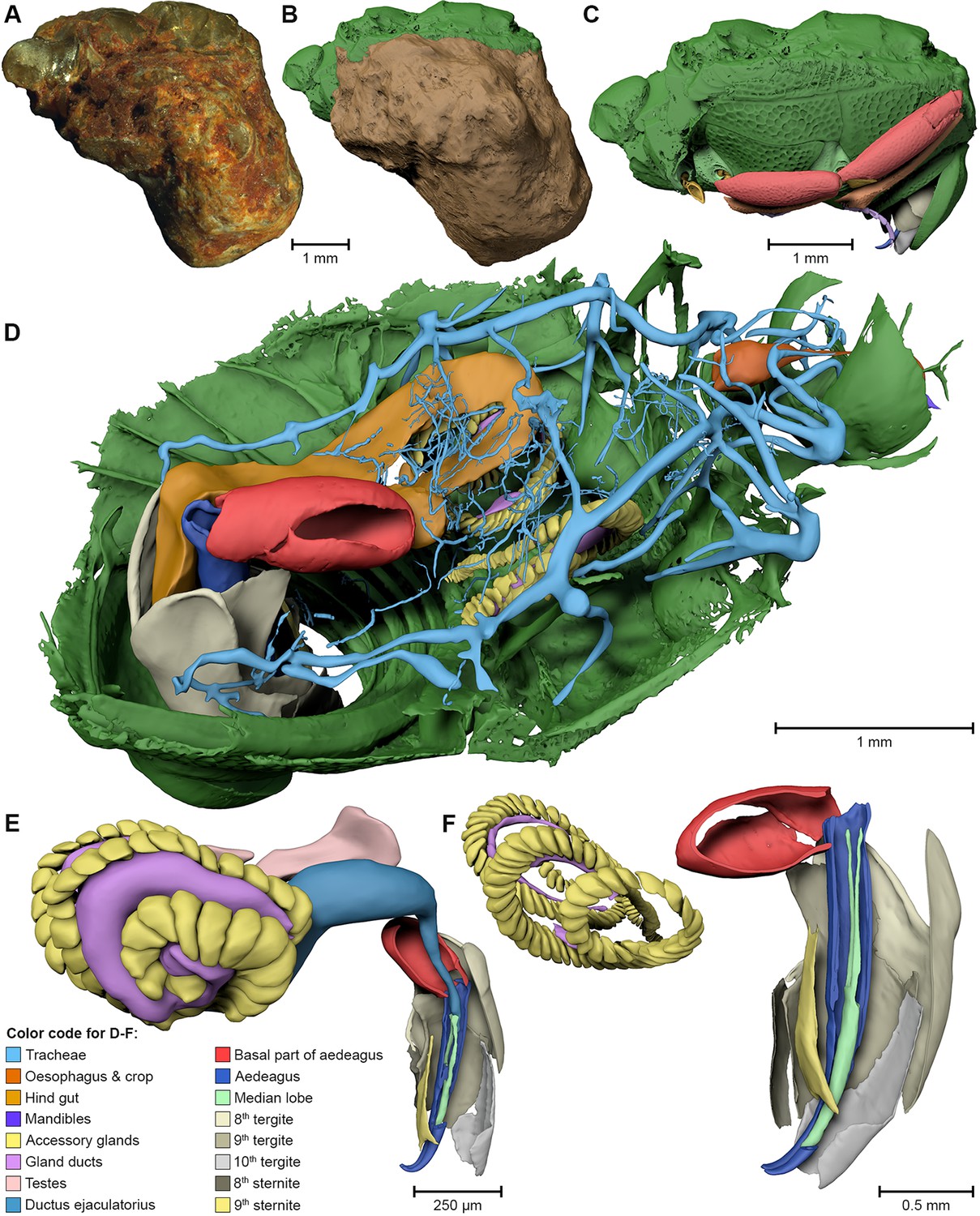
The Asian citrus psyllid (ACP), Diaphorina citri, is a harmful pest of citrus trees that transmits Candidatus Liberibacter spp. which causes Huanglongbing (HLB) (citrus greening disease); this is considered to be the most serious bacterial disease of citrus plants.
Here we detail an anatomical study of the external and internal anatomy (excluding the reproductive system) using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT). This is the first complete 3D micro-CT reconstruction o... Read more
Javier Alba-Tercedor, Wayne B. Hunter & Ignacio Alba-Alejandre
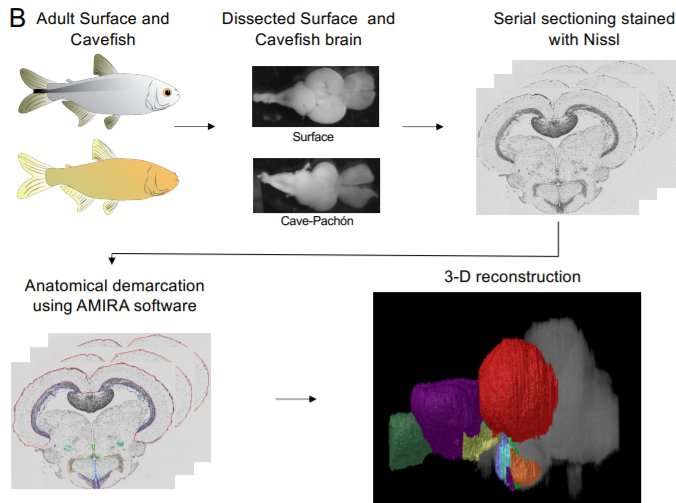
A shift in environmental conditions impacts the evolution of complex developmental and behavioral traits. The Mexican cavefish, Astyanax mexicanus, is a powerful model for examining the evolution of development, physiology, and behavior because multiple cavefish populations can be compared to an extant and ancestral-like surface population of the same species. Many behaviors have diverged in cave populations of A. mexicanus, and previous studies have shown that cavefish ha... Read more
Cody Loomis, View ORCID ProfileRobert Peuß, James Jaggard, Yongfu Wang, Sean McKinney, Stephen Raftopoulos, Austin Raftopoulos, Daniel Whu, Matthew Green, Suzanne E. McGaugh, Nicolas Rohner, Alex C. Keene, Erik R. Duboue
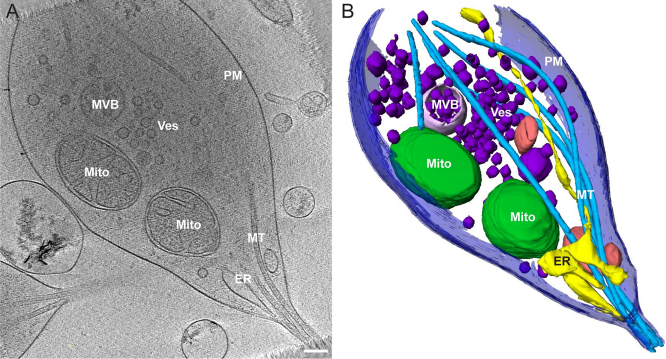
Morphology of mitochondria in spatially restricted axons revealed by cryo-electron tomography
Neurons project axons to local and distal sites and can display heterogeneous morphologies with limited physical dimensions that may influence the structure of large organelles such as mitochondria. Using cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET), we characterized native environments within axons and presynaptic varicosities to examine whether spatial restrictions within these compartments influence the morphology of mitochondria. Segmented tomographic reconstructions revealed distinctive morphologi... Read more
Tara D. Fischer, Pramod K. Dash, Jun Liu, M. Neal Waxham
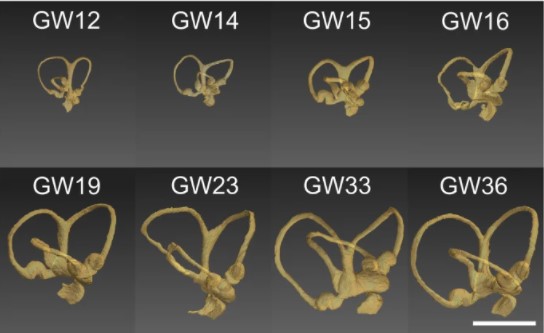
Progressive transformation of the otic placode into the functional inner ear during gestational development in humans leads to the acquisition of hearing perception via the cochlea and balance and spatial orientation via the vestibular organ.
Using a correlative approach involving micro-computerized tomography (micro-CT), transmission electron microscopy and histological techniques we were able to examine both the morphological and cellular changes associated with human inner ear devel... Read more
Lejo Johnson Chacko, David Wertjanz, Consolato Sergi, Jozsef Dudas, Natalie Fischer, Theresa Eberharter, Romed Hoermann, Rudolf Glueckert, Helga Fritsch, Helge Rask-Andersen, Anneliese Schrott-Fischer & Stephan Handschuh
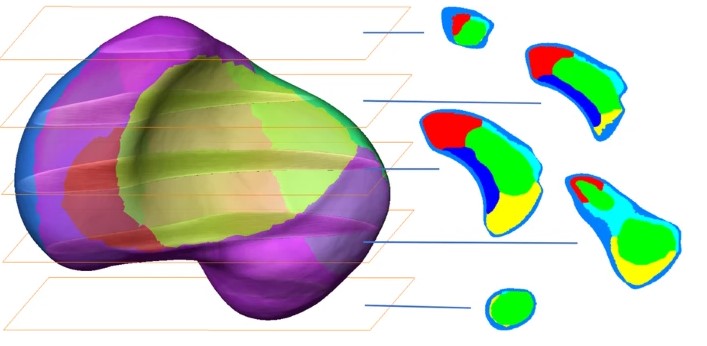
3D computational anatomy of the scaphoid and its waist for use in fracture treatment
A detailed understanding of scaphoid anatomy helps anatomic fracture reduction and optimal screw position. Therefore, we analyzed the size and shape variations of the cartilage and osseous surface, the distribution of volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD), and if the vBMD values differ between a peripheral and a central screw pathway?
Forty-three fresh frozen hand specimens (17 females, 26 males) were analysed with high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) ... Read more
Marc-Daniel Ahrend, Teun Teunis, Hansrudi Noser, Florian Schmidutz, Geoff Richards, Boyko Gueorguiev & Lukas Kamer
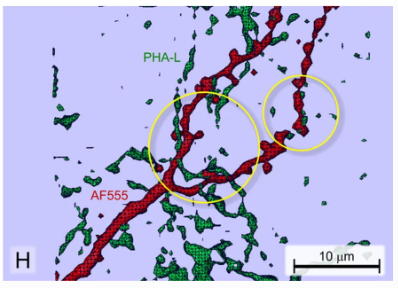
Neuroanatomical tract-tracing techniques that did go viral
Neuroanatomical tracing methods remain fundamental for elucidating the complexity of brain circuits. During the past decades, the technical arsenal at our disposal has been greatly enriched, with a steady supply of fresh arrivals. This paper provides a landscape view of classical and modern tools for tract-tracing purposes. Focus is placed on methods that have gone viral, i.e., became most widespread used and fully reliable.
Read more
Jose L. Lanciego; Floris G. Wouterlood
GEVES uses Avizo software to study and control plant seeds
At GEVES, Microtomography (micro-CT), which is a technique using X-rays to investigate internal anatomy and morphology of organisms without destruction, is applied to plant seed quality control and phenotyping. Several applications have been developed using micro-CT coupled with Avizo software development, such as for example in the Measurements of internal and external sugar beet seed structures for seed phenotyping
Read more
Ghassen Trigui, Laurence Le Corre, Dominique Honoré and Karima Boudehri-Giresse - 2D/3D Imaging - R&D team, GEVES
Aetosauria is a clade of heavily armored, quadrupedal omnivorous to herbivorous archosaurs known from the Late Triassic across what was the supercontinent of Pangea. Their abundance in many deposits relative to the paucity of other Triassic herbivores indicates that they were key components of Late Triassic ecosystems. However, their evolutionary relationships remain contentious due, in large part, to their extensive dermal armor, which often obstructs observation of internal skeletal anatomy... Read more
Devin K. Hoffman, Andrew B. Heckert, Lindsay E. Zanno
External and internal morphological characters of extant and fossil organisms are crucial to establishing their systematic position, ecological role and evolutionary trends. (…) We found well-preserved three-dimensional anatomy in mineralized arthropods from Paleogene fissure fillings and demonstrate the value of these fossils by utilizing digitally reconstructed anatomical structure of a hister beetle. The new anatomical data facilitate a refinement of the species diagnosis and allowed... Read more
Achim H Schwermann, Tomy dos Santos Rolo, Michael S Caterino, Gunter Bechly, Heiko Schmied, Tilo Baumbach, Thomas van de Kamp
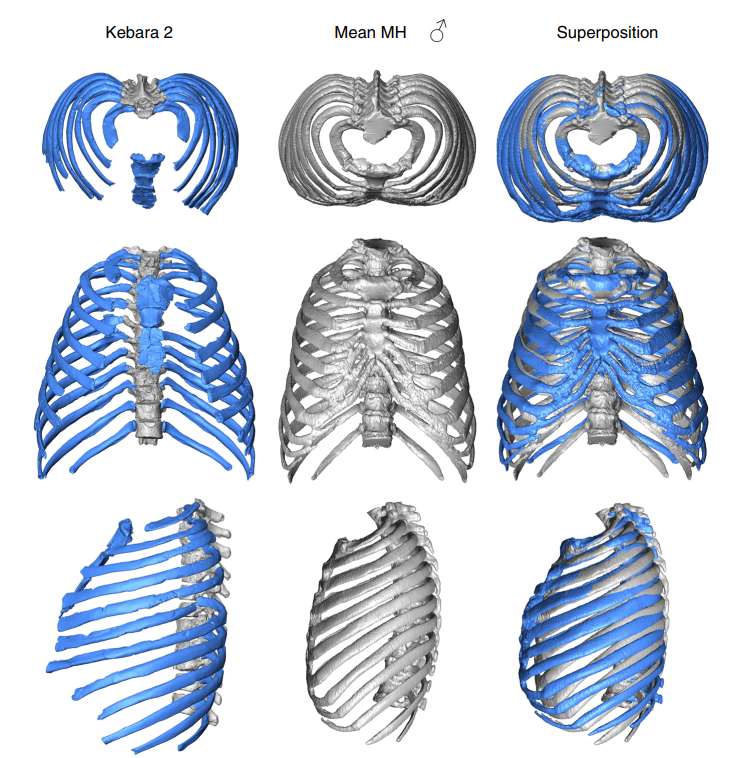
3D virtual reconstruction of the Kebara 2 Neandertal thorax
The size and shape of the Neandertal thorax has been debated since the first discovery of Neandertal ribs more than 150 years ago, with workers proposing different interpretations ranging from a Neandertal thoracic morphology that is indistinguishable from modern humans, to one that was significantly different from them. Here, we provide a virtual 3D reconstruction of the thorax of the adult male Kebara 2 Neandertal. Our analyses reveal that the Kebara 2 thorax is significantly different but ... Read more
Asier Gomez-Olivencia, Alon Barash, Daniel Garcia-Martinez, Mikel Arlegi, Patricia Kramer, Markus Bastir, Ella Been
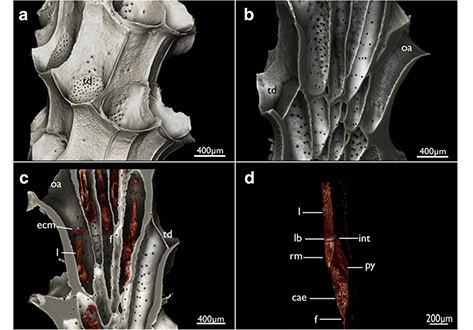
Cyclostome bryozoans are an ancient group of marine colonial suspension-feeders comprising approximately 700 extant species. Previous morphological studies are mainly restricted to skeletal characters whereas data on soft tissues obtained by state-of-the-art methods are still lacking. In order to contribute to issues related to cyclostome ground pattern reconstruction, we analyzed the morphology of the neuromuscular system Cinctipora elegans by means of immunocytochemical staining,... Read more
Thomas F. Schwaha, Stephan Handschuh, Andrew N. Ostrovsky, Andreas Wanninger
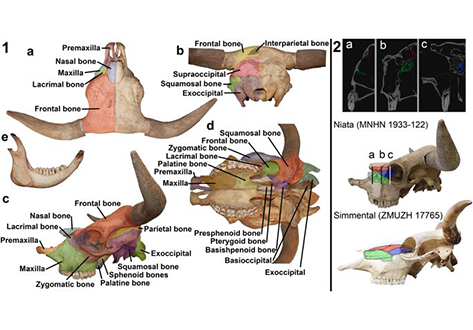
The Niata was a cattle variety from South America that figured prominently in writings on evolution by Charles Darwin. Its shortened head and other aspects of its unusual morphology have been subject of unsettled discussions since Darwin’s time. Here, we examine the anatomy, cranial shape, skull biomechanics, and population genetics of the Niata. Our results show that the Niata was a viable variety of cattle and exhibited anatomical differences to known chondrodysplastic forms. In cranial s... Read more
Kristof Veitschegger, Laura A. B. Wilson, Beatrice Nussberger, Glauco Camenisch, Lukas F. Keller, Stephen Wroe, Marcelo R. Sánchez-Villagra
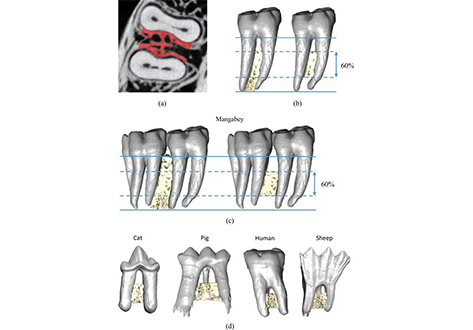
Mechanical adaptation of trabecular bone morphology in the mammalian mandible
Alveolar bone, together with the underlying trabecular bone, fulfils an important role in providing structural support against masticatory forces. Diseases such as osteoporosis or periodontitis cause alveolar bone resorption which weakens this structural support and is a major cause of tooth loss. However, the functional relationship between alveolar bone remodelling within the molar region and masticatory forces is not well understood. This study investigated this relationship by comparing m... Read more
Peter J. Watson, Laura C. Fitton, Carlo Meloro, Michael J. Fagan, Flora Gröning
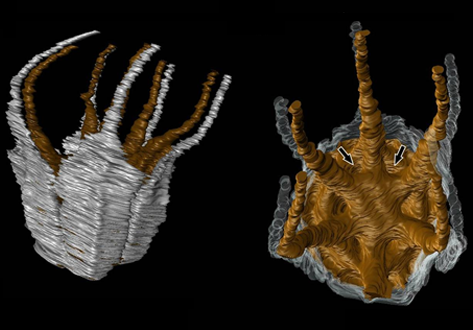
Angiosperm-dominated floras of the Late Cretaceous are essential for understanding the evolutionary, ecological, and geographic radiation of flowering plants.
The Late Cretaceous–early Paleogene Deccan Intertrappean Beds of India contain angiosperm-dominated plant fossil assemblages known from multiple localities in central India. Numerous monocots have been documented from these assemblages, providing a window into an important but poorly understood time in their diversification. On... Read more
Kelly K.S. Matsunaga, Selena Y. Smith, Steven R. Manchester, Dashrath Kapgate, Deepak Ramteke, Amin Garbout, and Herminso Villarraga-Gómez
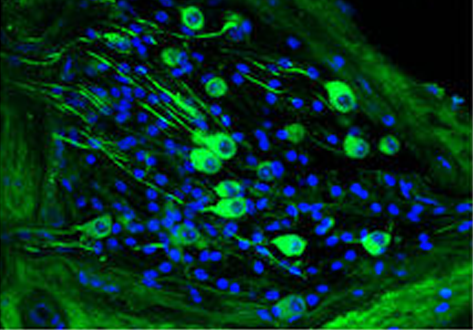
Chronic cigarette smoke exposure drives spiral ganglion neuron loss in mice
Tobacco use is associated with an increased risk of hearing loss in older individuals, suggesting cigarette smoke (CS) exposure may target the peripheral auditory organs. However, the effects of CS exposure on general cochlear anatomy have not previously been explored.
Here we compare control and chronic CS exposed cochleae from adult mice to assess changes in structure and cell survival. Two-photon imaging techniques, including the imaging of second harmonic generation (SHG) and two-p... Read more
Stephen T. Paquette, Ryan P. Dawes, Isaac K. Sundar, Irfan Rahman, Edward B. Brown & Patricia M. White