Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
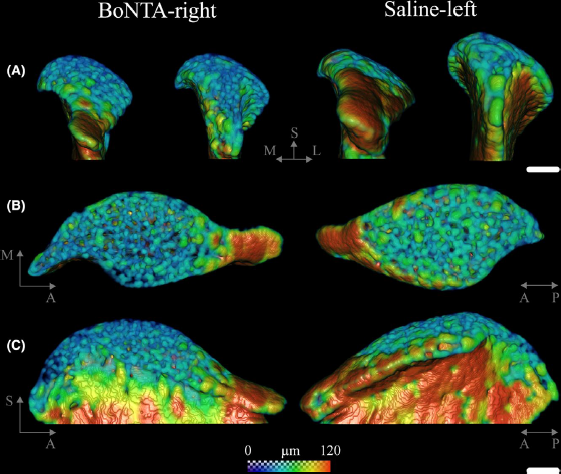
Masseter muscle function influences mandibular bone homeostasis. As previously reported, bone resorption markers increased in the mouse mandibular condyle two days after masseter paralysis induced with botulinum toxin type A (BoNTA), followed by local bone loss.
This study aimed to evaluate the bone quality of both the mandibular condyle and alveolar process in the mandible of adult mice during the early stage of a BoNTA‐induced masseter muscle atrophy, using a combined 3D histomorpho... Read more
Julián Balanta‐Melo, María Angélica Torres‐Quintana, Maximilian Bemmann, Carolina Vega, Constanza González, Kornelius Kupczik, Viviana Toro‐Ibacache, Sonja Buvinic
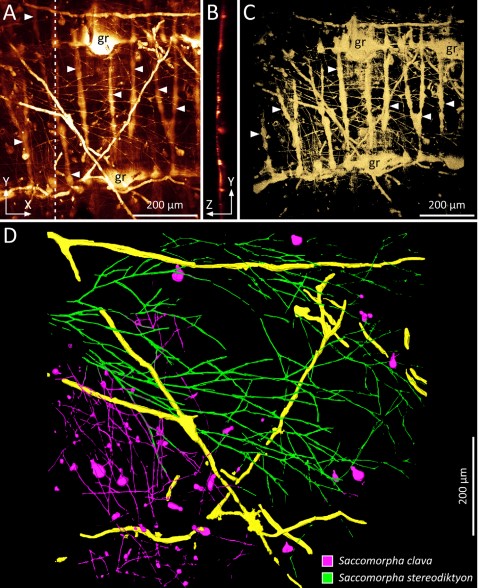
Microscopic organisms that penetrate calcareous structures by actively dissolving the carbonate matrix, namely microendoliths, have an important influence on the breakdown of marine carbonates.
Microscopic organisms that penetrate calcareous structures by actively dissolving the carbonate matrix, namely microendoliths, have an important influence on the breakdown of marine carbonates. The study of these microorganisms and the bioerosion traces they produce is crucial for understanding ... Read more
Philipp-Konrad Schätzle, Max Wisshak, Andreas Bick, André Freiwald, Alexander Kieneke
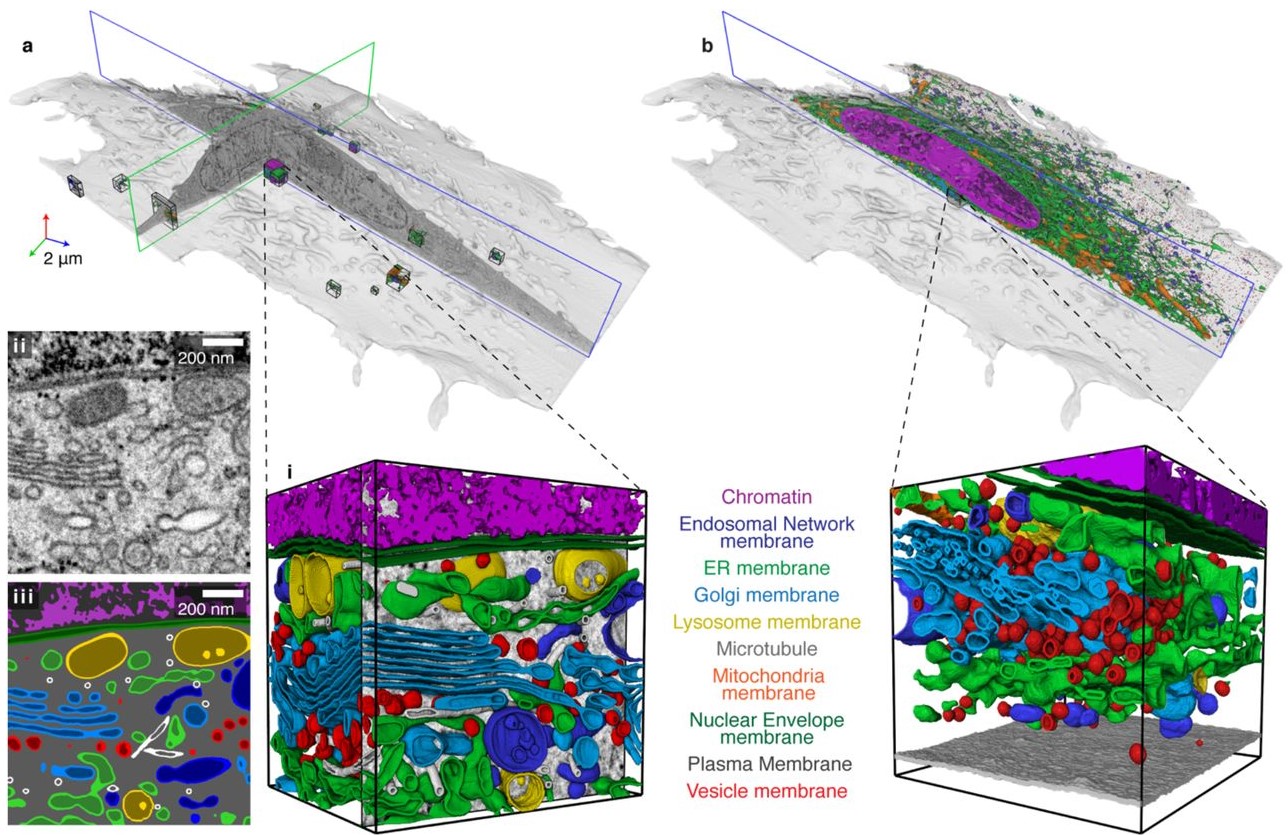
Automatic whole cell organelle segmentation in volumetric electron microscopy
Cells contain hundreds of different organelle and macromolecular assemblies intricately organized relative to each other to meet any cellular demands. Obtaining a complete understanding of their organization is challenging and requires nanometer-level, three-dimensional reconstruction of whole cells. Even then, the immense size of datasets and large number of structures to be characterized requires generalizable, automatic methods.
To meet this challenge, we developed an analy... Read more
Larissa Heinrich, Davis Bennett, David Ackerman, Woohyun Park, John Bogovic, View ORCID ProfileNils Eckstein, Alyson Petruncio, Jody Clements, C. Shan Xu, Jan Funke, Wyatt Korff, Harald F. Hess, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Stephan Saalfeld, Aubrey V. Weigel, COSEM Project Team
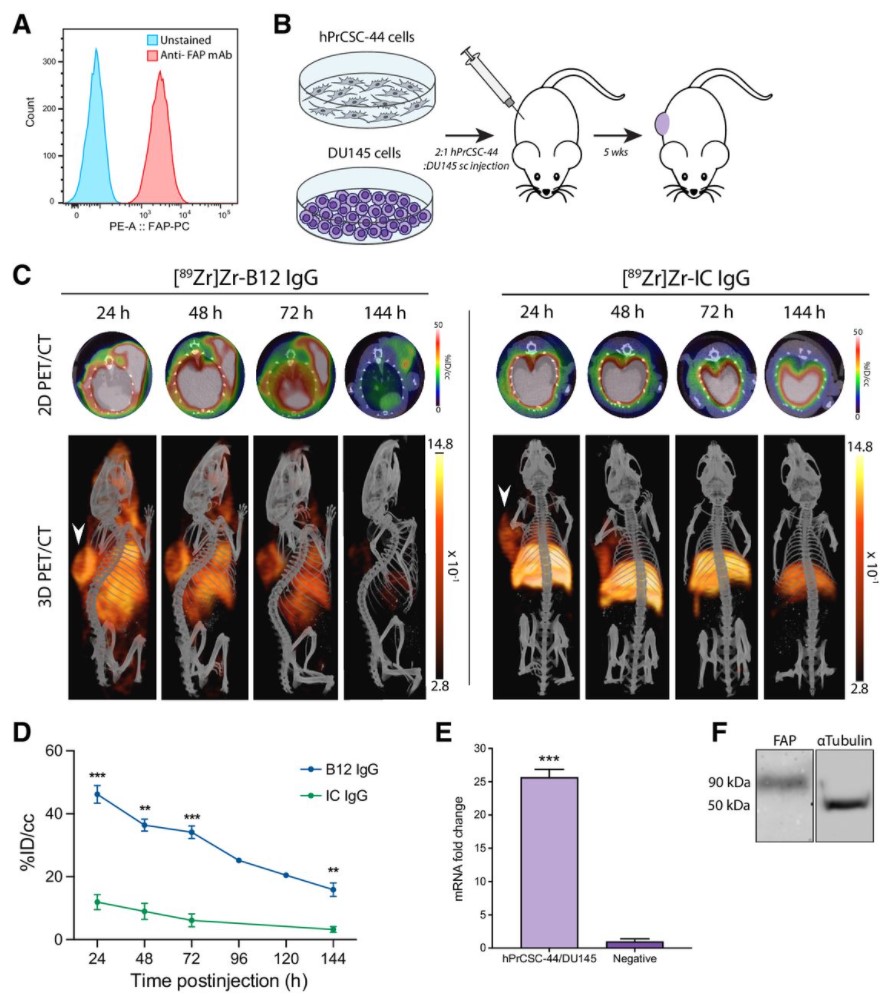
Malignant cells are surrounded by a complex and supportive tumor microenvironment that consists of immune cells, extracellular matrix, vasculature, and fibroblasts. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) are the major cell type in the reactive stroma and are known to promote tumorigenesis and metastasis. Fibroblast activation protein alpha (FAP) is a transmembrane serine protease expressed by CAFs in the microenvironment of epithelial tumors.
Meta-analysis of FAP expression and clinical ... Read more
Hallie M. Hintz, Joseph P. Gallant, Donald J. Vander Griend, Ilsa M. Coleman, Peter S. Nelson and Aaron M. LeBeau
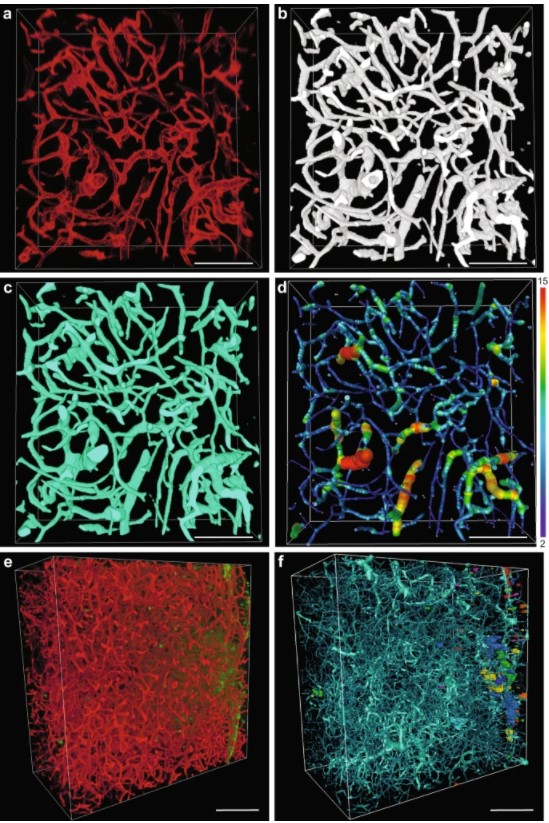
Precise methods for quantifying drug accumulation in brain tissue are currently very limited, challenging the development of new therapeutics for brain disorders. Transcardial perfusion is instrumental for removing the intravascular fraction of an injected compound, thereby allowing for ex vivo assessment of extravasation into the brain. However, pathological remodeling of tissue microenvironment can affect the efficiency of transcardial perfusion, which has been largely overlooked.
We... Read more
Serhii Kostrikov, Kasper B. Johnsen, Thomas H. Braunstein, Johann M. Gudbergsson, Frederikke P. Fliedner, Elisabeth A. A. Obara, Petra Hamerlik, Anders E. Hansen, Andreas Kjaer, Casper Hempel & Thomas L. Andresen
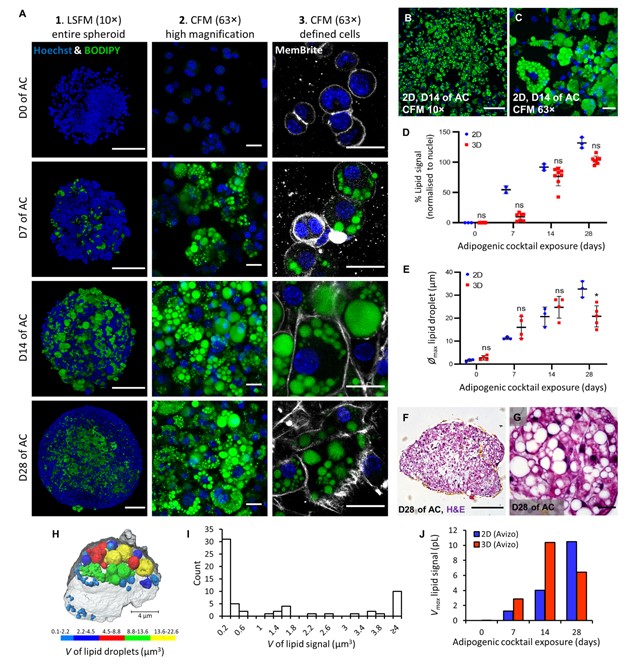
Adipose models have been applied to mechanistic studies of metabolic diseases (such as diabetes) and the subsequent discovery of new therapeutics. However, typical models are either insufficiently complex (2D cell cultures) or expensive and labor intensive (mice/in vivo). To bridge the gap between these models and in order to better inform pre-clinical studies we have developed a drug-responsive 3D model of white adipose tissue (WAT).
Here, spheroids (680 ± 60 μm) comp... Read more
Alexander D Graham, Rajesh Pandey, Viktoriya S Tsancheva, Alessia Candeo, Stanley W Botchway, Alasdair J Allan, Lydia Teboul4, Kamel Madi, Tahkur S Babra, Louisa A K Zolkiewski, Xuan Xue, Liz Bentley, Joan Gannon, Sam N Olof and Roger D Cox
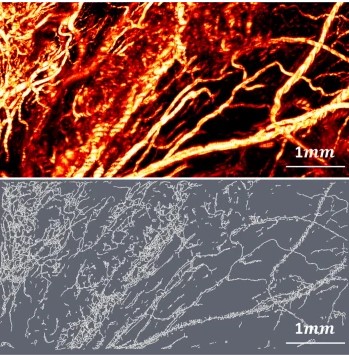
Optical Resolution Photoacoustic Microscopy of Ovary and Fallopian Tube
Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death among gynecological cancers, but is poorly amenable to preoperative diagnosis. In this study, we investigate the feasibility of “optical biopsy,” using high-optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy (OR-PAM) to quantify the microvasculature of ovarian and fallopian tube tissue. The technique is demonstrated using excised human ovary and fallopian tube specimens imaged immediately after surgery.
This report describes the first applicatio... Read more
Bin Rao, Xiandong Leng, Yifeng Zeng, Yixiao Lin, Ruimin Chen, Qifa Zhou, Andrea R. Hagemann, Lindsay M. Kuroki, Carolyn K. McCourt, David G. Mutch, Matthew A. Powell, Ian S. Hagemann & Quing Zhu
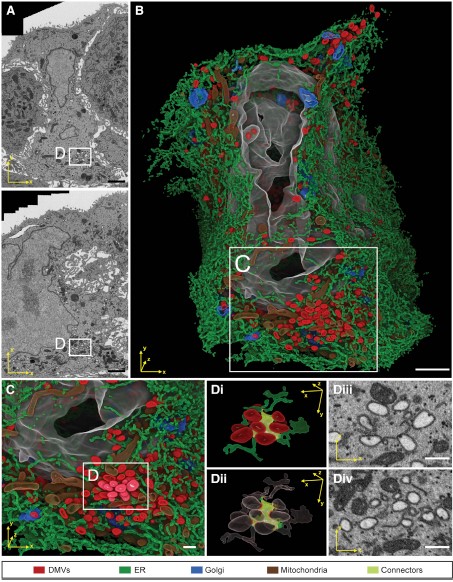
Integrative Imaging Reveals SARS-CoV-2-Induced Reshaping of Subcellular Morphologies
Cortese et al. use integrative imaging techniques to generate a publicly available repository of morphological alterations induced by SARS-CoV-2 in lung cells. Accumulation of ER-derived double-membrane vesicles, the viral replication organelle, occurs concomitantly with cytoskeleton remodeling and Golgi fragmentation. Pharmacological alteration of cytoskeleton dynamics restricts viral replication and spread.
Pathogenesis induced by SARS-CoV-2 is thought to result from both an inflamma... Read more
Mirko Cortese, Ji-Young Lee, Berati Cerikan, ..., Laurent Chatel-Chaix, Yannick Schwab, Ralf Bartenschlager
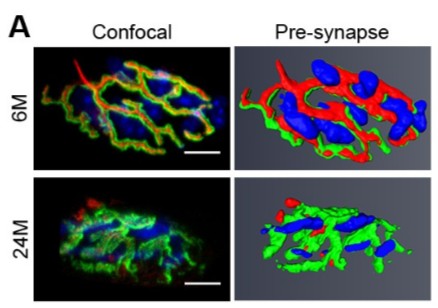
Loss of adult skeletal muscle stem cells drives age-related neuromuscular junction degeneration
Neuromuscular junction degeneration is a prominent aspect of sarcopenia, the age-associated loss of skeletal muscle integrity. Previously, we showed that muscle stem cells activate and contribute to mouse neuromuscular junction regeneration in response to denervation (Liu et al., 2015). Here, we examined gene expression profiles and neuromuscular junction integrity in aged mouse muscles, and unexpectedly found limited denervation despite a high level of degenerated neuromuscular junctions. In... Read more
Wenxuan Liu, Alanna Klose, Sophie Forman, Nicole D Paris, Lan Wei-LaPierre, Mariela Cortés-Lopéz, Aidi Tan, Morgan Flaherty, Pedro Miura, Robert T Dirksen, Joe V Chakkalakal
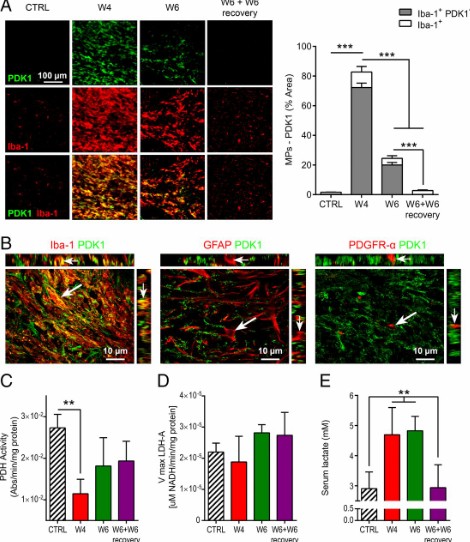
Proinflammatory mononuclear phagocytes (MPs) play a crucial role in the progression of multiple sclerosis (MS) and other neurodegenerative diseases. Despite advances in neuroimaging, there are currently limited available methods enabling noninvasive detection of MPs in vivo. Interestingly, upon activation and subsequent differentiation toward a proinflammatory phenotype MPs undergo metabolic reprogramming that results in increased glycolysis and production of lactate. Hyperpolarized (HP)
Caroline Guglielmetti, Chloé Najac, Alessandro Didonna, Annemie Van der Linden, Sabrina M. Ronen, and Myriam M. Chaumeil
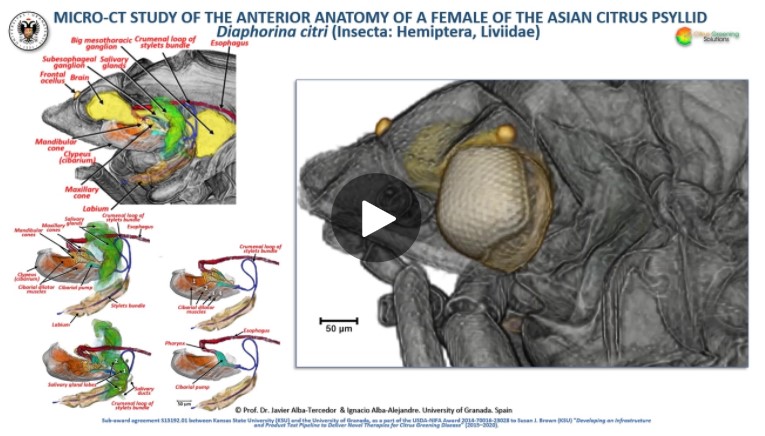
The Asian citrus psyllid (ACP), Diaphorina citri, is a harmful pest of citrus trees that transmits Candidatus Liberibacter spp. which causes Huanglongbing (HLB) (citrus greening disease); this is considered to be the most serious bacterial disease of citrus plants.
Here we detail an anatomical study of the external and internal anatomy (excluding the reproductive system) using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT). This is the first complete 3D micro-CT reconstruction o... Read more
Javier Alba-Tercedor, Wayne B. Hunter & Ignacio Alba-Alejandre
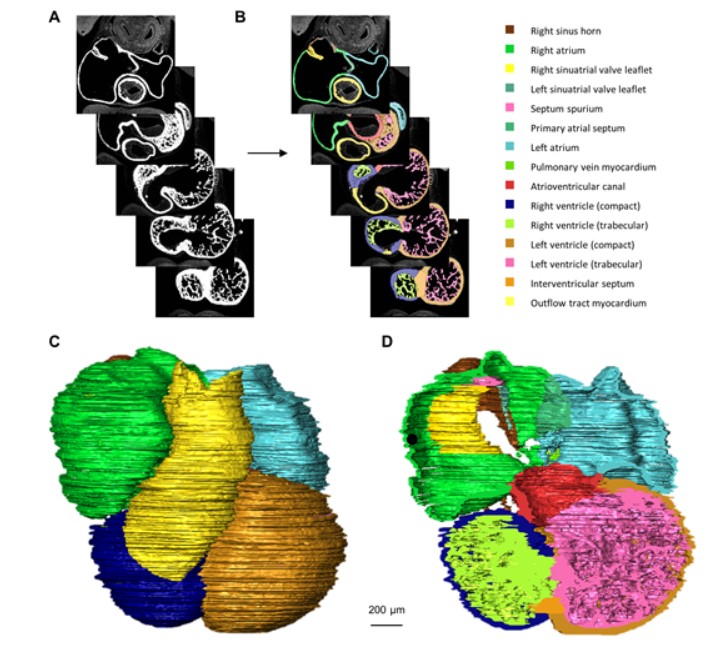
Quantified growth of the human embryonic heart
The size and growth patterns of the components of the human embryonic heart have remained largely undefined.
To provide these data, three-dimensional heart models were generated from immunohistochemically stained sections of ten human embryonic hearts ranging from Carnegie stage 10 to 23. Fifty-eight key structures were annotated and volumetrically assessed. Sizes of the septal foramina and atrioventricular canal opening were also measured. The heart grows exponentially throughout embr... Read more
Jaeike W. Faber, Jaco Hagoort, Antoon F. M. Moorman, Vincent M. Christoffels, Bjarke Jensen
Patient-specific anatomical model for deep brain stimulation based on 7 Tesla MRI
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) requires accurate localization of the anatomical target structure, and the precise placement of the DBS electrode within it. Ultra-high field 7 Tesla (T) MR images can be utilized to create patient-specific anatomical 3D models of the subthalamic nuclei (STN) to enhance pre-surgical DBS targeting as well as post-surgical visualization of the DBS lead position and orientation. We validated the accuracy of the 7T imaging-based patient-specific model of the STN and m... Read more
Yuval Duchin, Reuben R. Shamir, Remi Patriat, Jinyoung Kim, Jerrold L. Vitek, Guillermo Sapiro, Noam Harel
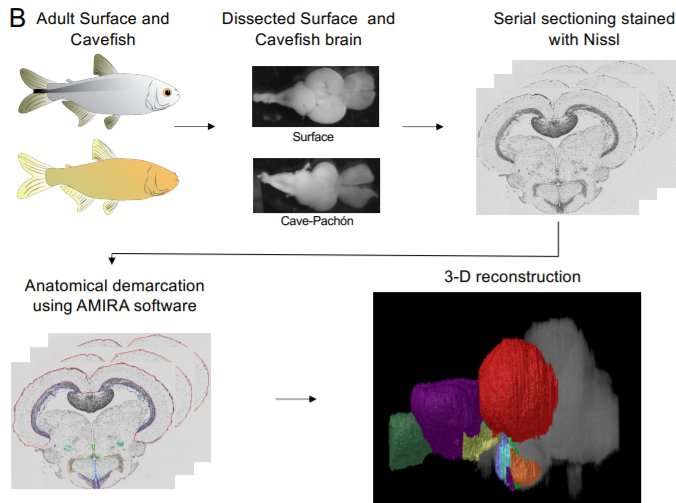
A shift in environmental conditions impacts the evolution of complex developmental and behavioral traits. The Mexican cavefish, Astyanax mexicanus, is a powerful model for examining the evolution of development, physiology, and behavior because multiple cavefish populations can be compared to an extant and ancestral-like surface population of the same species. Many behaviors have diverged in cave populations of A. mexicanus, and previous studies have shown that cavefish ha... Read more
Cody Loomis, View ORCID ProfileRobert Peuß, James Jaggard, Yongfu Wang, Sean McKinney, Stephen Raftopoulos, Austin Raftopoulos, Daniel Whu, Matthew Green, Suzanne E. McGaugh, Nicolas Rohner, Alex C. Keene, Erik R. Duboue
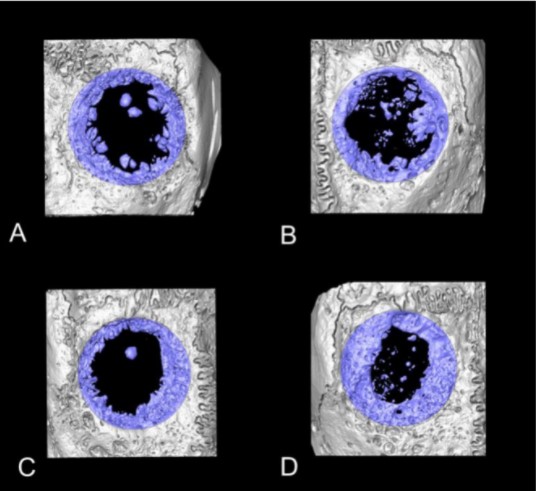
Collagen-Based Matrices for Osteoconduction: A Preclinical In Vivo Study
The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of additional hydroxyapatite (HA) in collagen-based matrices (CM) and membrane placement on bone formation in calvarial defects.
Critical size defects in the calvaria of 16 New Zealand White Rabbits were randomly treated with CM or mineralized collagen-based matrices (mCM). Half of the sites were covered with a collagen membrane. Animals were euthanized after 12 weeks of healing. The samples were studied by micro-CT and histology. New... Read more
Hiroki Katagiri, Yacine El Tawil, Niklaus P. Lang, Jean-Claude Imber, Anton Sculean, Masako Fujioka-Kobayashi and Nikola Saulacic
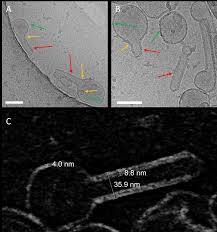
Influenza A matrix protein M1 is sufficient to induce lipid membrane deformation
The matrix protein M1 of the Influenza A virus is considered to mediate viral assembly and budding at the plasma membrane (PM) of infected cells. In order for a new viral particle to form, the PM lipid bilayer has to bend into a vesicle towards the extracellular side. Studies in cellular models have proposed that different viral proteins might be responsible for inducing membrane curvature in this context (including M1), but a clear consensus has not been reached. In this study, we use a comb... Read more
Ismail Dahmani, Kai Ludwig, Salvatore Chiantia
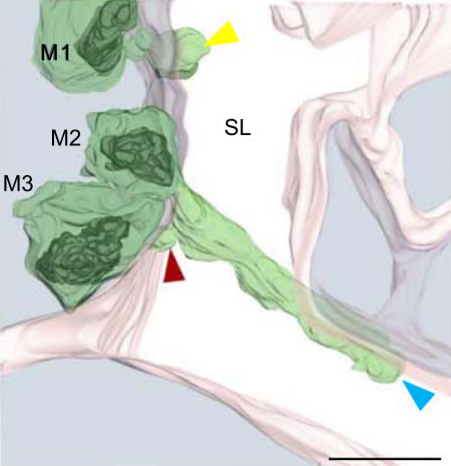
Multiple membrane extrusion sites drive megakaryocyte migration into bone marrow blood vessels
Platelets, cells central to hemostasis and thrombosis, are formed from parent cell megakaryocytes. Although the process is highly efficient in vivo, our ability to generate them in vitro is still remarkably inefficient. We proposed that greater understanding of the process in vivo is needed and used an imaging approach, intravital correlative light electron microscopy, to visualize platelet generation in bone marrow in the living mouse. In contrast to current understanding, we found that most... Read more
Edward Brown, Leo M Carlin, Claus Nerlov, Cristina Lo Celso, Alastair W Poole
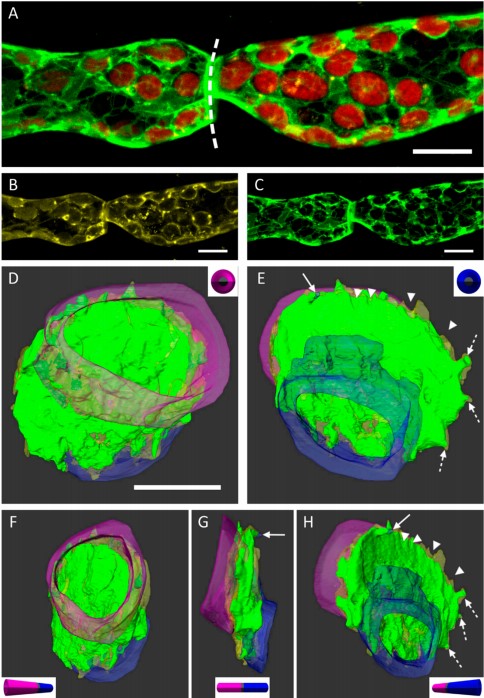
3D Dissection of Structural Membrane-Wall Contacts in Filamentous Moss Protonemata
Cell-to-cell contact is essential for communication and development of multicellular organisms. A prerequisite is the passage through membranes. That way, molecular exchange and information flow is regulated via hormones, membrane proteins and pores.
In plants, the rigid cell walls prevent large membrane contact areas between protoplasts. Only plasmodesmata, minute channels between adjacent cells, form direct connections. Often, molecular data of the proteins involved are manifold but t... Read more
Dominik Harant and Ingeborg Lang
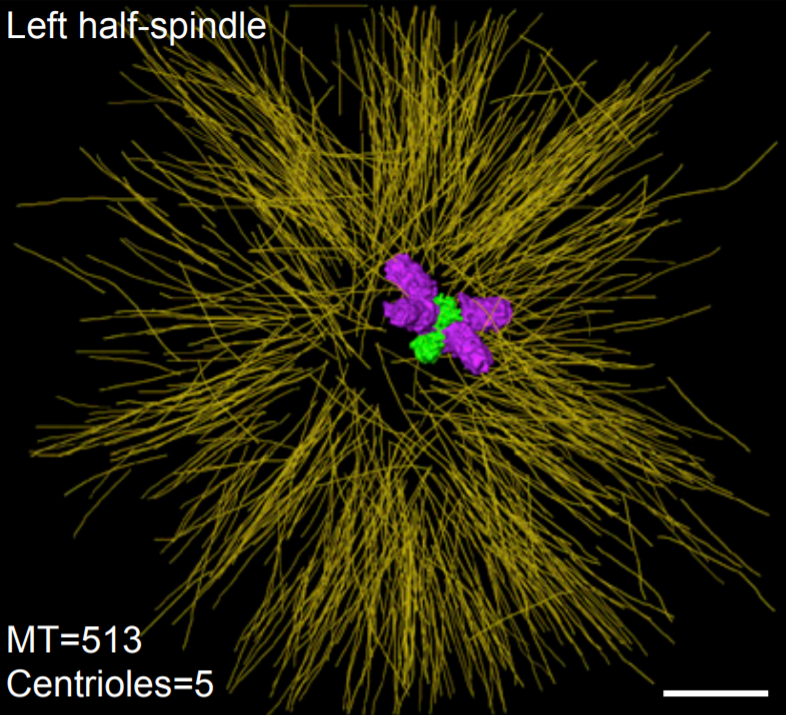
Asymmetric Centriole Numbers at Spindle Poles Cause Chromosome Missegregation in Cancer
Chromosomal instability is a hallmark of cancer and correlates with the presence of extra centrosomes, which originate from centriole overduplication.
Overduplicated centrioles lead to the formation of centriole rosettes, which mature into supernumerary centrosomes in the subsequent cell cycle. While extra centrosomes promote chromosome missegregation by clustering into pseudo-bipolar spindles, the contribution of centriole rosettes to chromosome missegregation is unknown. We us... Read more
Marco R.Cosenza, Anna Cazzola, Annik Rossberg, Nicole L. Schieber, Gleb Konotop, Elena Bausch, Alla Slynko, Tim Holland-Letz, Marc S.Raab, Taronish Dubash, Hanno Glimm, Sven Poppelreuther, Christel Herold-Mende, Yannick Schwab, Alwin Krämer
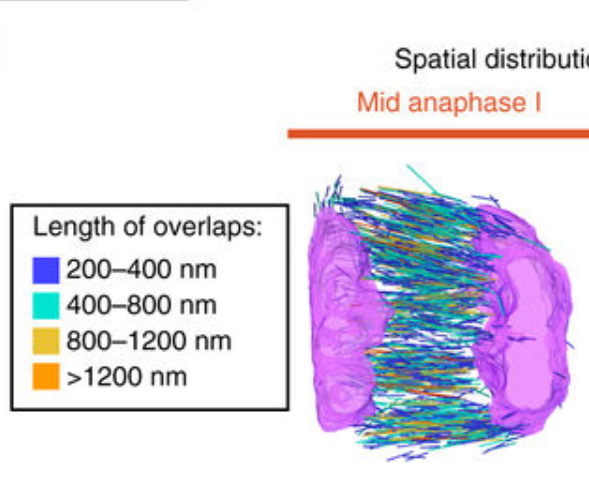
Chromosome segregation occurs by microtubule pushing in oocytes
During cell division, spindle microtubules ensure an equal repartition of chromosomes between the two daughter cells. While the kinetochore-dependent mechanisms that drive mitotic chromosome segregation are well understood, in oocytes of most species atypical spindles assembled in absence of centrosomes entail poorly understood mechanisms of chromosome segregation. In particular, the structure(s) responsible for force generation during meiotic chromosome separation in oocytes is unclear. Usin... Read more
Kimberley Laband, Rémi Le Borgne, Frances Edwards, Marine Stefanutti, Julie C. Canman, Jean-Marc Verbavatz, Julien Dumont

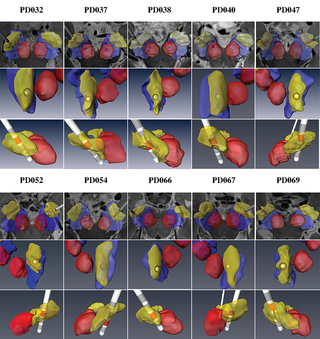
Each pulmonary segment is an anatomical and functional unit. However, it is fundamentally difficult to precisely distinguish every pulmonary segment using the conventional pulmonary intersegmental planes from computed tomography images. Building arteriopulmonary segments is likely to be an effective way to identify pulmonary segments.
The three-dimensional reconstructed images showed the branches of the pulmonary artery ramified up to their eighth order covering the entire lung as well... Read more
Huijie Gao, Chao Liu