Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
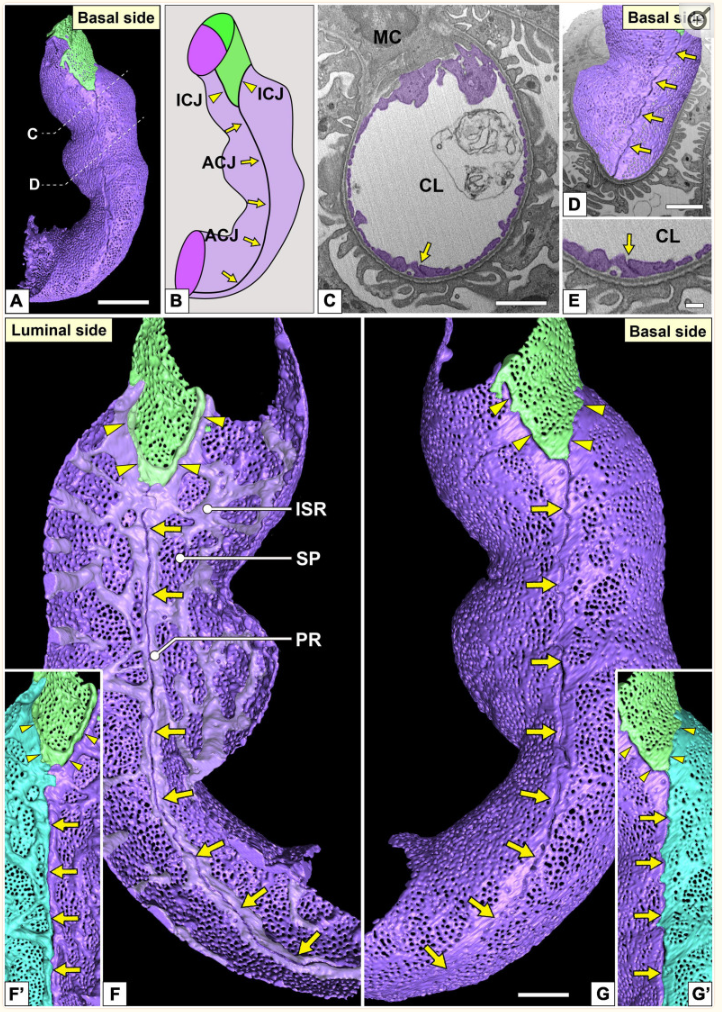
Three-Dimensional Architecture of Glomerular Endothelial Cells Revealed by FIB-SEM Tomography
Focused-ion beam-scanning electron microscopic (FIB-SEM) tomography enables easier acquisition of a series of ultrastructural, sectional images directly from resin-embedded biological samples. In this study, to clarify the three-dimensional (3D) architecture of glomerular endothelial cells (GEnCs) in adult rats, we manually extracted GEnCs from serial FIB-SEM images and reconstructed them on an Amira reconstruction software. The luminal and basal surface structures were clearly visualized in ... Read more
Yuto Kawasaki, Yasue Hosoyamada, Takayuki Miyaki, Junji Yamaguchi, Soichiro Kakuta, Tatsuo Sakai, and Koichiro Ichimura
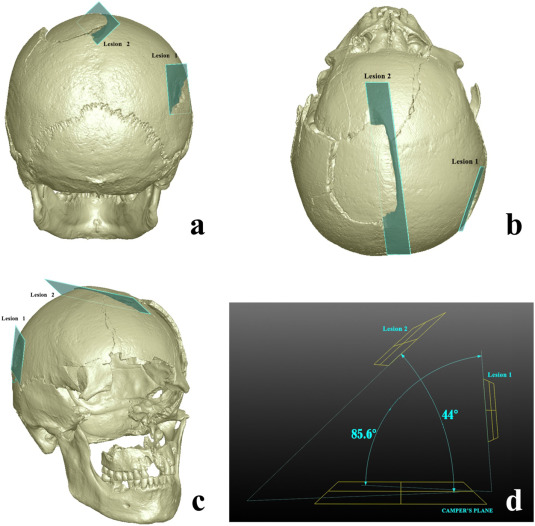
Human skeletal remains from archaeological contexts occasionally present signs of traumatic injuries from weapons, revealing, for example, the degree of interpersonal violence, the type of weapon and the sequence of events of a specific historical context.
Traumatic lesions are generally analyzed using macroscopic and microscopic methods, which are not necessarily integrated in the same study. In this study, we employed a multi-analytical approach to determine i... Read more
Antonino Vazzana, Lucia Martina Scalise, Mirko Traversari, Carla Figus, Salvatore Andrea Apicella, Laura Buti, Gregorio Oxilia, Rita Sorrentino, Silvia Pellegrini, Chiara Matteucci, Lucio Calcagnile, Raffaele Savigni, Robin N.M.Feeney, Giorgio Gruppioni, Stefano Benazziah
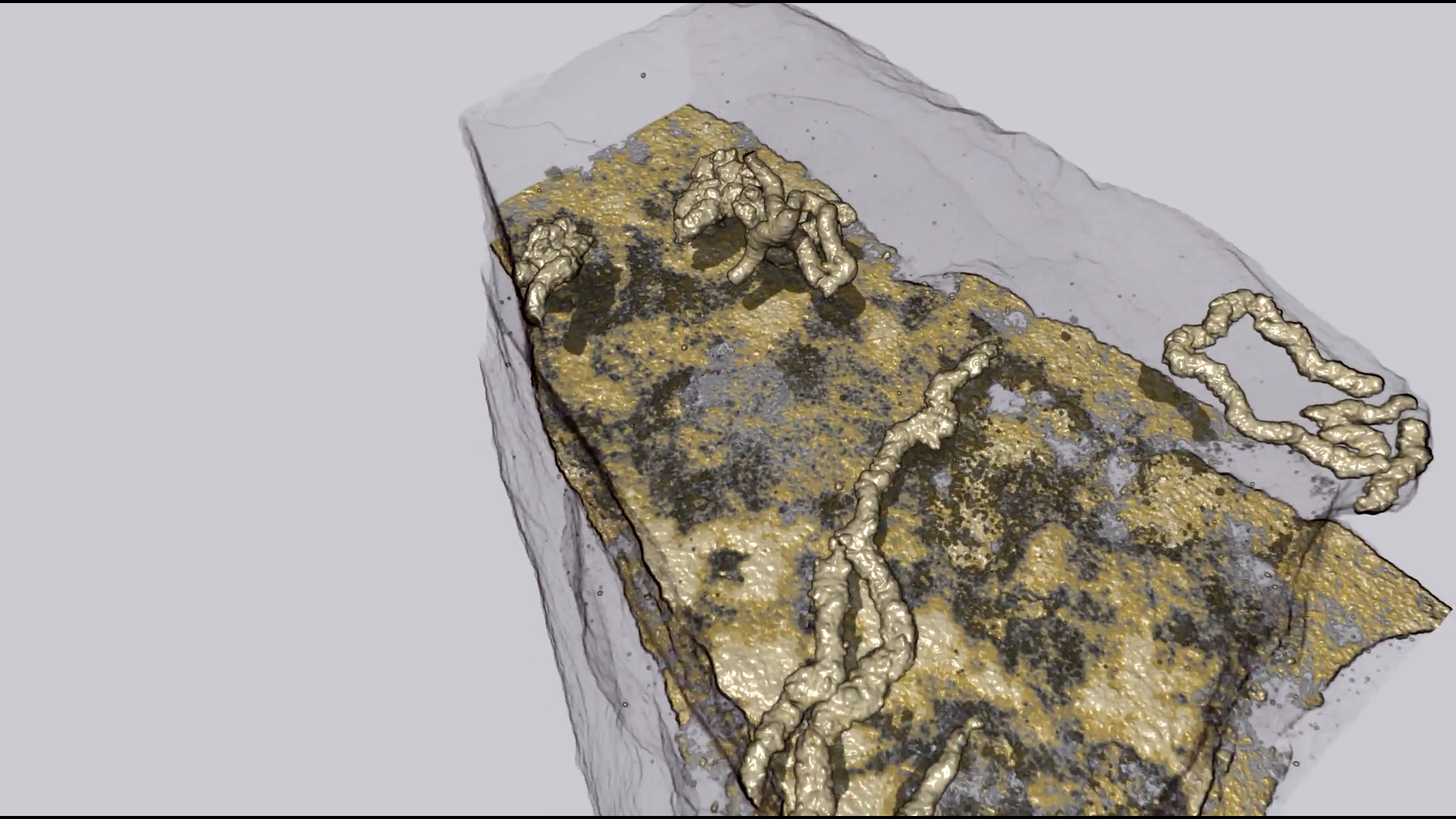
Organism motility in an oxygenated shallow-marine environment 2.1 billion years ago
Evidence for macroscopic life in the Paleoproterozoic Era comes from 1.8 billion-year-old (Ga) compression fossils [Han TM, Runnegar B (1992) Science 257:232–235; Knoll et al. (2006) Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 361:1023–1038], Stirling biota [Bengtson S et al. (2007) Paleobiology 33:351–381], and large colonial organisms exhibiting signs of coordinated growth from the 2.1-Ga Francevillian series, Gabon. Here we report on pyritized string-shaped structures from... Read more
Abderrazak El Albani, M. Gabriela Mangano, Luis A. Buatois, Stefan Bengtson, Armelle Riboulleau, Andrey Bekker, Kurt Konhauser, Timothy Lyons, Claire Rollion-Bard, Olabode Bankole, Stellina Gwenaelle Lekele Baghekema, Alain Meunier, Alain Trentesaux, Arnaud Mazurier, Jeremie Aubineau, Claude Laforest, Claude Fontaine, Philippe Recourt, Ernest Chi Fru, Roberto Macchiarelli, Jean Yves Reynaud, François Gauthier-Lafaye, and Donald E. Canfield
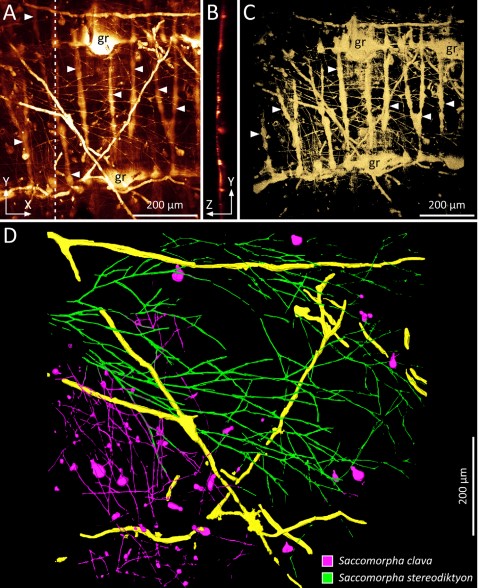
Microscopic organisms that penetrate calcareous structures by actively dissolving the carbonate matrix, namely microendoliths, have an important influence on the breakdown of marine carbonates.
Microscopic organisms that penetrate calcareous structures by actively dissolving the carbonate matrix, namely microendoliths, have an important influence on the breakdown of marine carbonates. The study of these microorganisms and the bioerosion traces they produce is crucial for understanding ... Read more
Philipp-Konrad Schätzle, Max Wisshak, Andreas Bick, André Freiwald, Alexander Kieneke
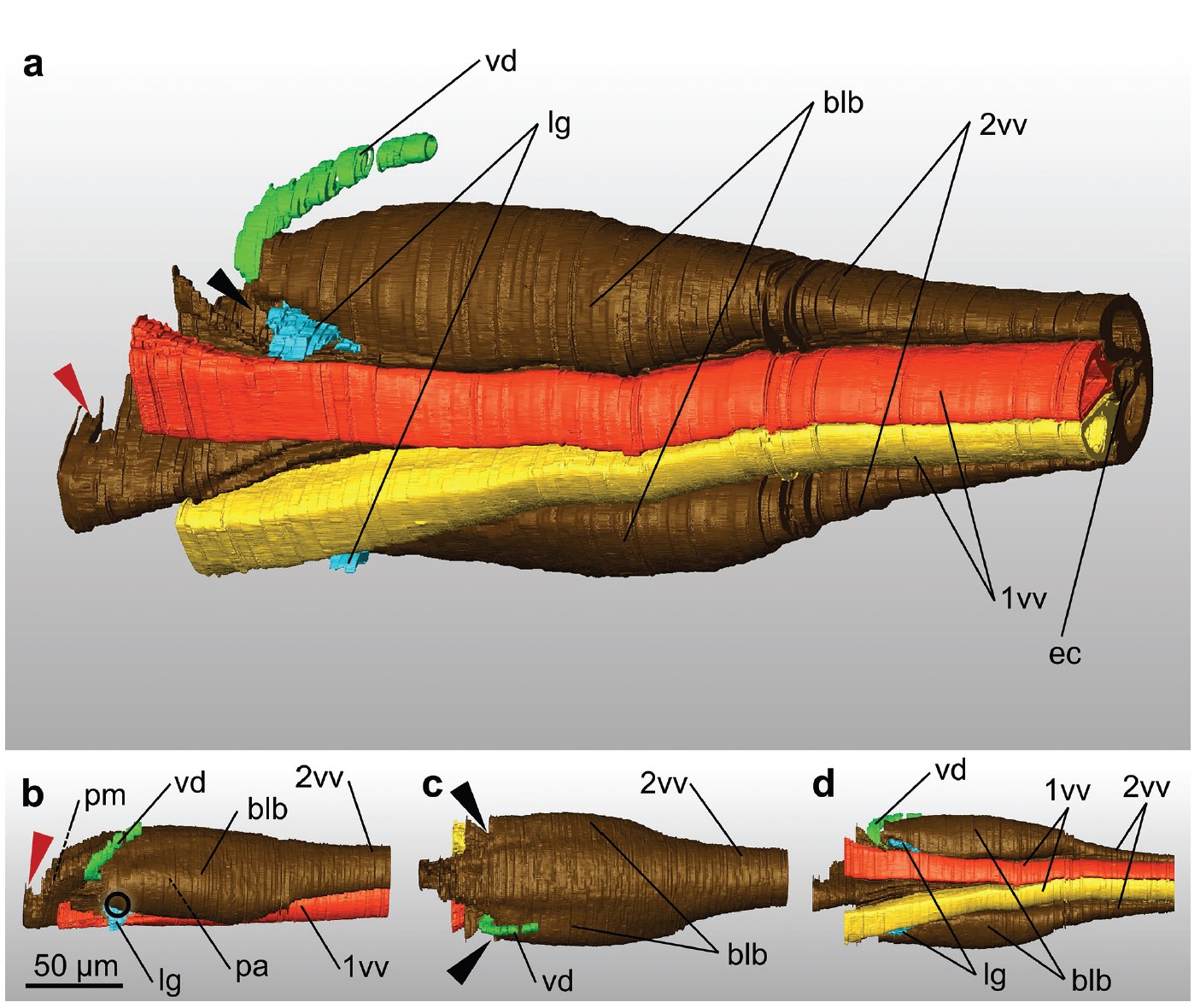
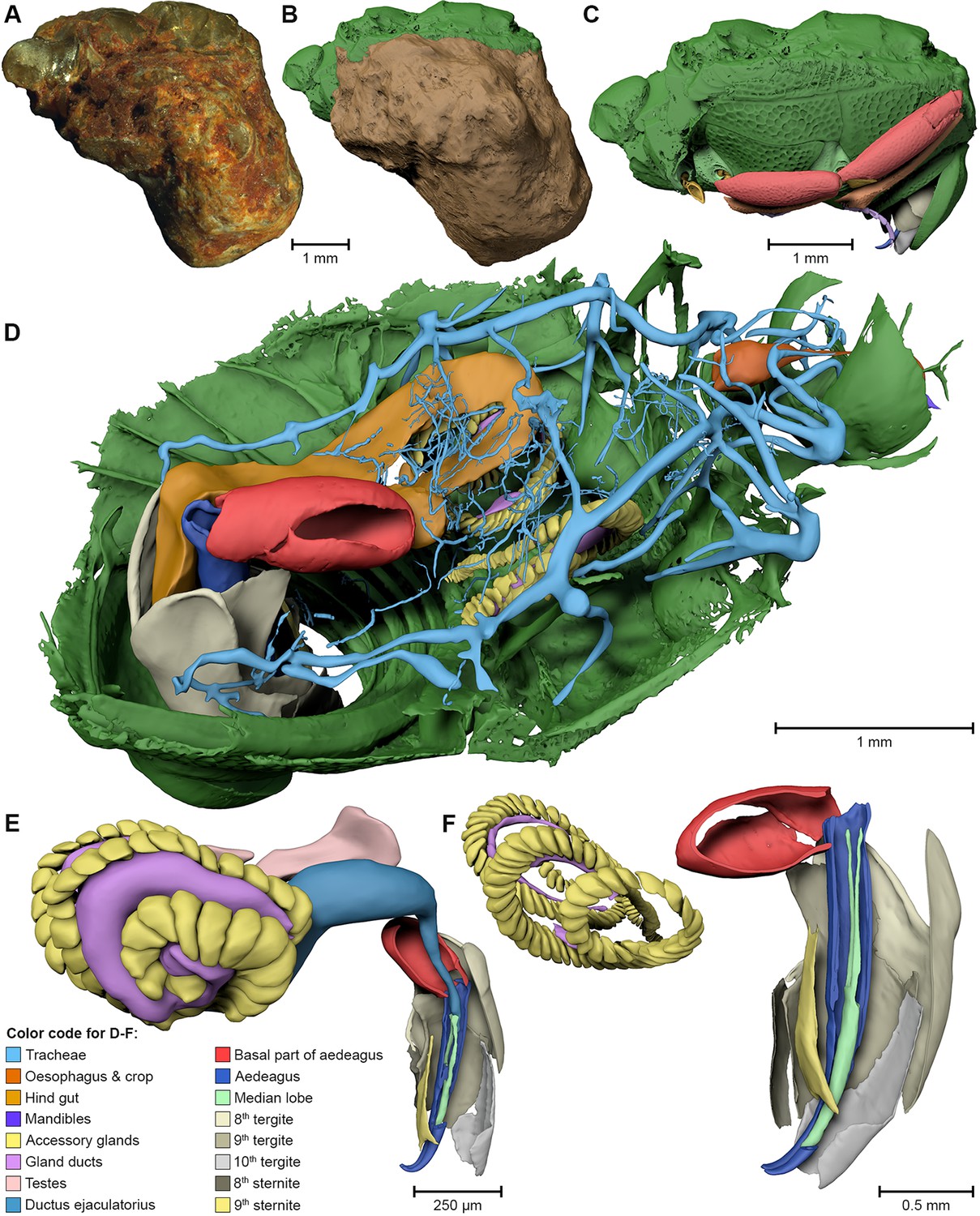
Ovipositor of the braconid wasp Habrobracon hebetor: structural and functional aspects
The Braconidae are a megadiverse and ecologically highly important group of insects. The vast majority of braconid wasps are parasitoids of other insects, usually attacking the egg or larval stages of their hosts. The ovipositor plays a crucial role in the assessment of the potential host and precise egg laying. We used lightand electron-microscopic techniques to investigate all inherent cuticular elements of the ovipositor (the female 9th abdominal tergum, two pairs of valvifers, and three p... Read more
Michael Csader, Karin Mayer, Oliver Betz, Stefan Fischer, Benjamin Eggs
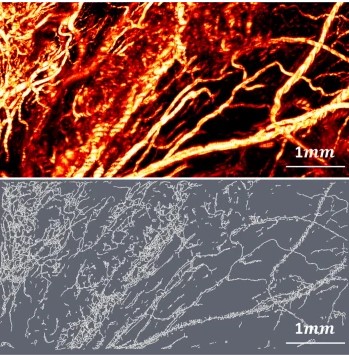
Optical Resolution Photoacoustic Microscopy of Ovary and Fallopian Tube
Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death among gynecological cancers, but is poorly amenable to preoperative diagnosis. In this study, we investigate the feasibility of “optical biopsy,” using high-optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy (OR-PAM) to quantify the microvasculature of ovarian and fallopian tube tissue. The technique is demonstrated using excised human ovary and fallopian tube specimens imaged immediately after surgery.
This report describes the first applicatio... Read more
Bin Rao, Xiandong Leng, Yifeng Zeng, Yixiao Lin, Ruimin Chen, Qifa Zhou, Andrea R. Hagemann, Lindsay M. Kuroki, Carolyn K. McCourt, David G. Mutch, Matthew A. Powell, Ian S. Hagemann & Quing Zhu
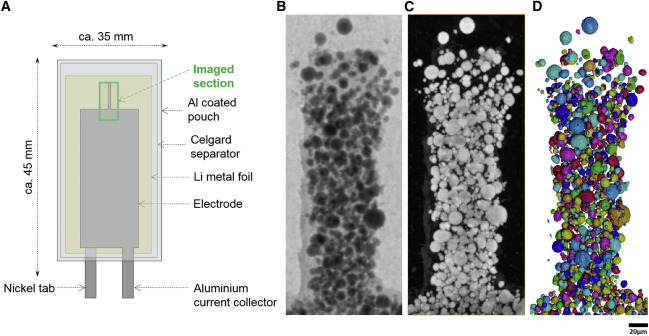
Nickel-rich transition metal oxide materials […] are of great interest for achieving immediate improvements in the energy density of Li-ion batteries and for risk reduction within the Li-ion battery supply chain.
[…] An increase in Ni content in NMC materials leads to accelerated degradation […]. This potentially complicates their adoption in applications requiring extended cycle life such as in electric vehicles.
Recent developments in X-ray characterization to... Read more
ChunTan, Andrew S.Leach, Thomas M.M. Heenan, Huw Parks, Rhodri Jervis, Johanna Nelson Weker, Daniel J.L. Brett, Paul R.Shearing
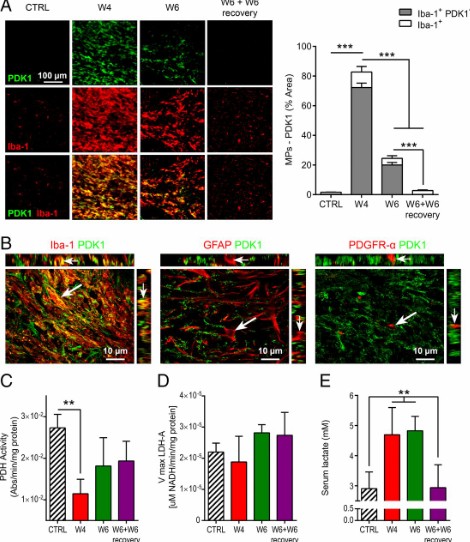
Proinflammatory mononuclear phagocytes (MPs) play a crucial role in the progression of multiple sclerosis (MS) and other neurodegenerative diseases. Despite advances in neuroimaging, there are currently limited available methods enabling noninvasive detection of MPs in vivo. Interestingly, upon activation and subsequent differentiation toward a proinflammatory phenotype MPs undergo metabolic reprogramming that results in increased glycolysis and production of lactate. Hyperpolarized (HP)
Caroline Guglielmetti, Chloé Najac, Alessandro Didonna, Annemie Van der Linden, Sabrina M. Ronen, and Myriam M. Chaumeil
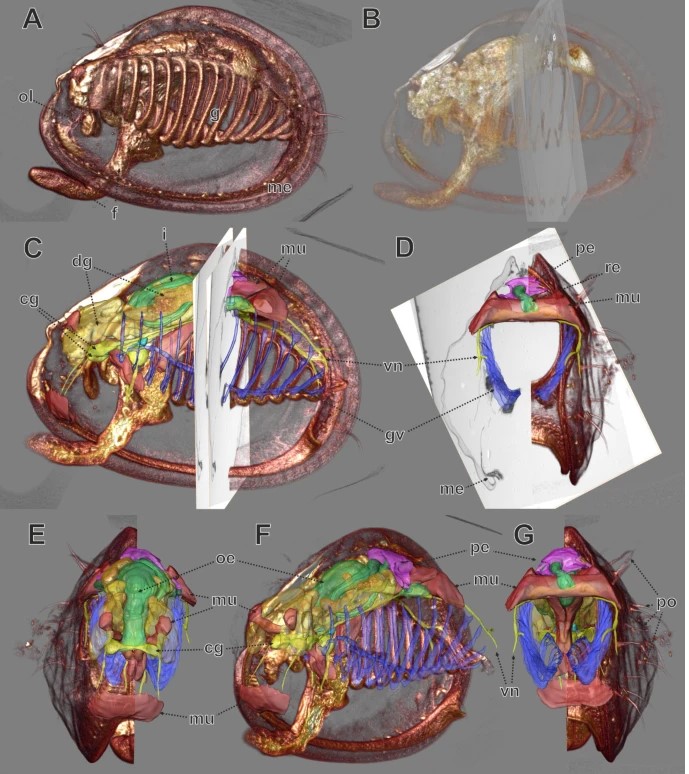
In biomedical research, a huge variety of different techniques is currently available for the structural examination of small specimens, including conventional light microscopy (LM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), microscopic X-ray computed tomography (microCT), and many others. Since every imaging method is physically limited by certain parameters, a correlative use of complementary methods often yields a significant broader range of inform... Read more
Stephan Handschuh, Natalie Baeumler, Thomas Schwaha & Bernhard Ruthensteiner
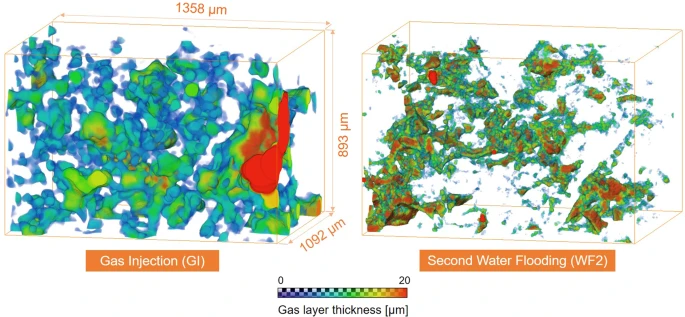
Pore-scale mechanisms of CO2 storage in oilfields
Rapid implementation of global scale carbon capture and storage is required to limit temperature rises to 1.5 °C this century. Depleted oilfields provide an immediate option for storage, since injection infrastructure is in place and there is an economic benefit from enhanced oil recovery. To design secure storage, we need to understand how the fluids are configured in the microscopic pore spaces of the reservoir rock. We use high-resolution X-ray imaging to study the flow of oil, water and ... Read more
Abdulla Alhosani, Alessio Scanziani, Qingyang Lin, Ali Q. Raeini, Branko Bijeljic & Martin J. Blunt
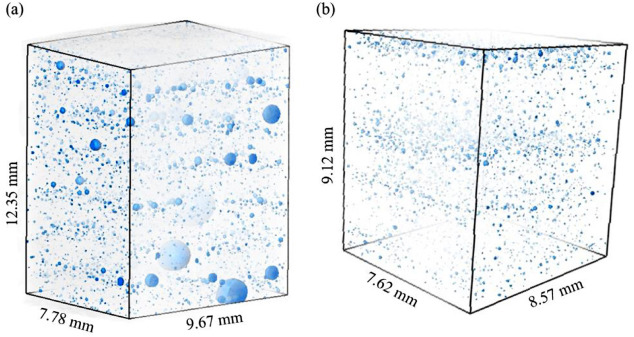
Hot-wire arc additive manufacturing of aluminum alloy with reduced porosity and high deposition rate
Wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) technology has attracted considerable interest in large-scale metallic components, but porosity and low deposition rate are the two dominating technical challenges in WAAM of aluminum alloy. In order to effectively solve these problems, a novel method of hot-wire arc additive manufacturing is used to fabricate aluminum alloy. Systematic studies are carried out to investigate the formation mechanism of the pores, the macro/microstructures, as well as the ... Read more
Rui Fu, Shuiyuan Tang, Jiping Lu, Yinan Cui, Zixiang Li, Haoru Zhang, Tianqiu Xu, Zhuo Chen, Changmeng Liu
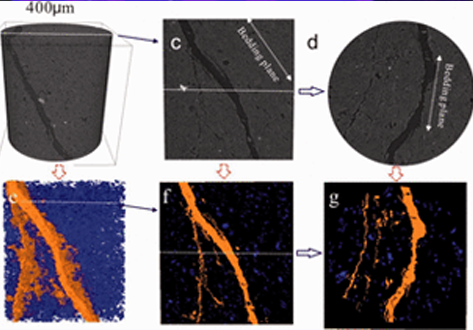
Experimental study on the cracking process of layered shale using X-ray microCT
The cracking process in Longmaxi formation shale was experimentally studied during uniaxial compressive loading. Both the evolution of the three-dimensional fracture network and the micromechanics of failure in the layered shale were examined as a function of the inclination angle of the bedding plane. To visualize the cracking process, the test devices presented here used an industrial X-ray CT scanner that enabled scanning during the uniaxial compressive loading. Scanning electron microscop... Read more
Institue of Geomechanic, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Laboratory of Shale Oil & Gas, Beijing, China
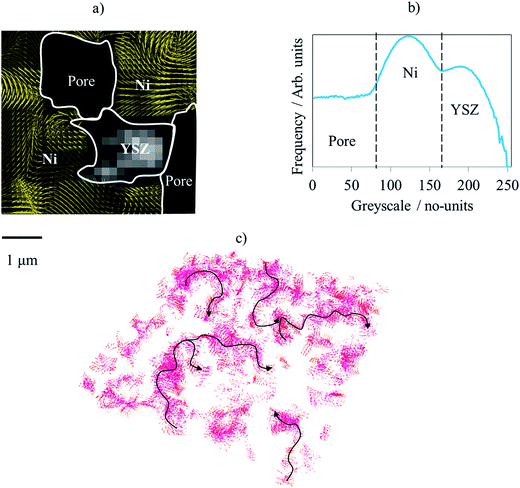
Evaluating microstructure evolution in an SOFC electrode using digital volume correlation
Degradation mechanisms within solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) during thermal cycling limit operational start-up times and cell lifetime, and must therefore be better understood and mitigated. This work explores such mechanisms using digital volume correlation (DVC) techniques applied to lab-based X-ray tomograms where the microstructural evolution is evaluated during the operational cycling of a Ni–YSZ/YSZ cell. To emulate reduced start-up times, five tomograms were collected over four operat... Read more
T. M. M. Heenan, X. Lu,, D. P. Finegan,, J. Robinson, F. Iacoviello, J. J. Bailey, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
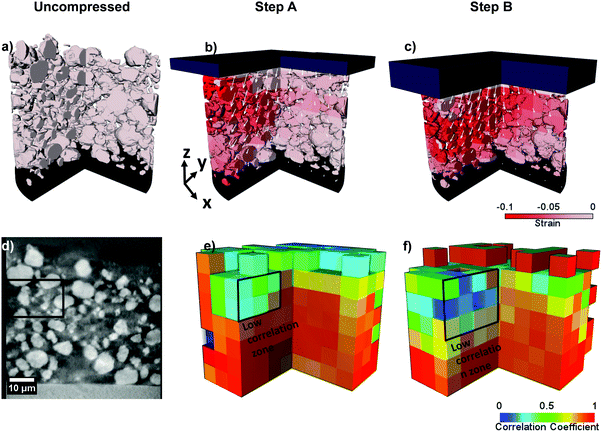
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries operate via electrochemical reactions between positive and negative electrodes, formed by complex porous microstructures. An improved understanding of these materials can lead to a greater insight into the link between microscopic electrode morphology and macroscopic performance. The practice of calendering electrodes after manufacturing has been widely used to increase the volumetric energy density and improve the electrical contact between electrode... Read more
S. R. Daemi,X. Lu, D. Sykes, J. Behnsen, C. Tan, A. Palacios-Padros, J. Cookson, E. Petrucco, P. J. Withers, D. J. L. Brett and P. R. Shearing
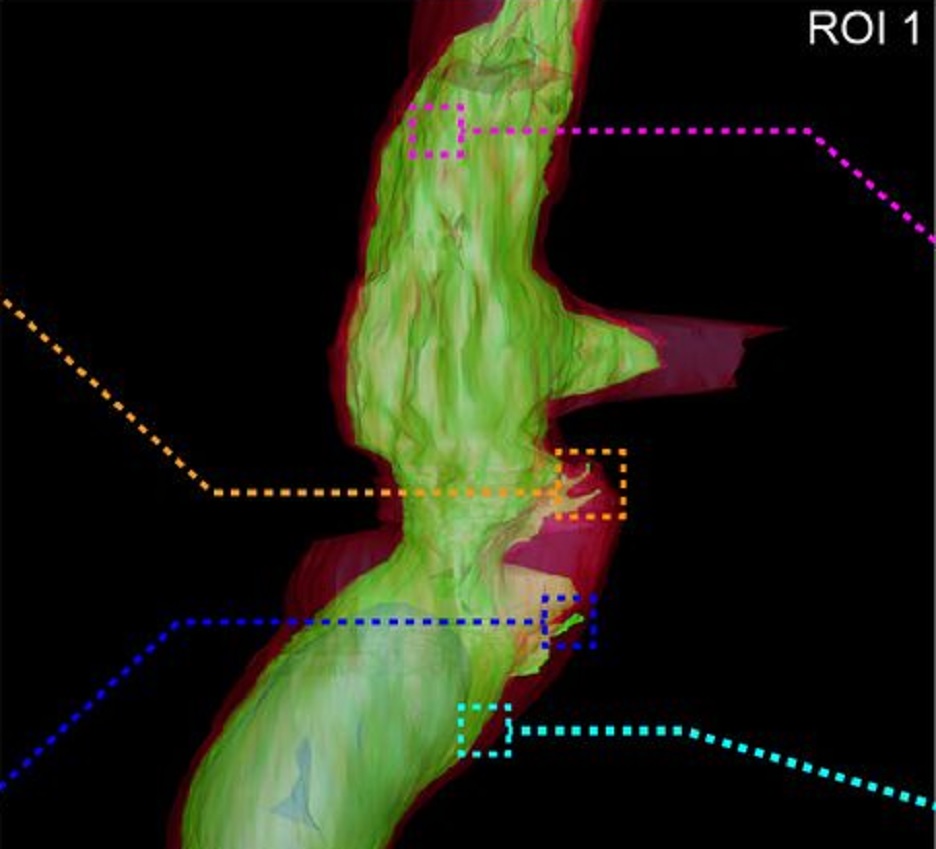
Fast and precise targeting of single tumor cells in vivo by multimodal correlative microscopy
Intravital microscopy provides dynamic understanding of multiple cell biological processes, but its limited resolution has so far precluded structural analysis. Because it is difficult to capture rare and transient events, only a few attempts have been made to observe specific developmental and pathological processes in animal models using electron microscopy. The multimodal correlative approach that we propose here combines intravital microscopy, microscopic X-ray computed tomography and thr... Read more
Matthia A. Karreman, Luc Mercier, Nicole L. Schieber, Gergely Solecki, Guillaume Allio, Frank Winkler, Bernhard Ruthensteiner, Jacky G. Goetz, Yannick Schwab
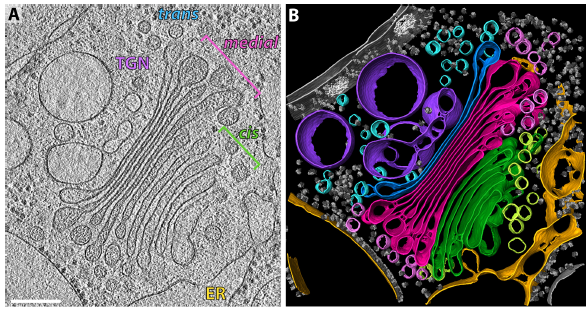
The structure of the COPI coat determined within the cell
COPI-coated vesicles mediate trafficking within the Golgi apparatus and from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum. Here, we applied cryo-focused ion beam milling, cryo-electron tomography and subtomogram averaging to determine the native structure of the COPI coat within vitrified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells. The native algal structure resembles the in vitro mammalian structure, but additionally reveals cargo bound beneath beta’–COP. We find that all coat components disassemble... Read more
Yury S Bykov, Miroslava Schaffer, Svetlana O Dodonova, Sahradha Albert, Jurgen M Plitzko, Wolfgang Baumeister, Benjamin D Engel, John AG Briggs
In biomedical research, a huge variety of different techniques is currently available for the structural examination of small specimens, including conventional light microscopy (LM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), microscopic X-ray computed tomography (microCT), and many others. Since every imaging method is physically limited by certain parameters, a correlative use of complementary methods often yields a significant broader range of inform... Read more
Stephan Handschuh, Natalie Baeumler, Thomas Schwaha and Bernhard Ruthensteiner

2 BILLION years old fossils appear to represent a first experiment in megascopic multicellularity
The Paleoproterozoic Era witnessed crucial steps in the evolution of Earth’s surface environments following the first appreciable rise of free atmospheric oxygen concentrations ∼2.3 to 2.1 Ga ago, and concomitant shallow ocean oxygenation. Combined microtomography, geochemistry, and sedimentary analysis suggest a biota fossilized during early diagenesis. The emergence of this biota follows a rise in atmospheric oxygen, which is consistent with the idea that surface oxygenation allowe... Read more
Abderrazak El Albani, Laboratoire HYDRASA, UMR 6269 CNRS-INSU, Université de Poitiers, France
External and internal morphological characters of extant and fossil organisms are crucial to establishing their systematic position, ecological role and evolutionary trends. (…) We found well-preserved three-dimensional anatomy in mineralized arthropods from Paleogene fissure fillings and demonstrate the value of these fossils by utilizing digitally reconstructed anatomical structure of a hister beetle. The new anatomical data facilitate a refinement of the species diagnosis and allowed... Read more
Achim H Schwermann, Tomy dos Santos Rolo, Michael S Caterino, Gunter Bechly, Heiko Schmied, Tilo Baumbach, Thomas van de Kamp
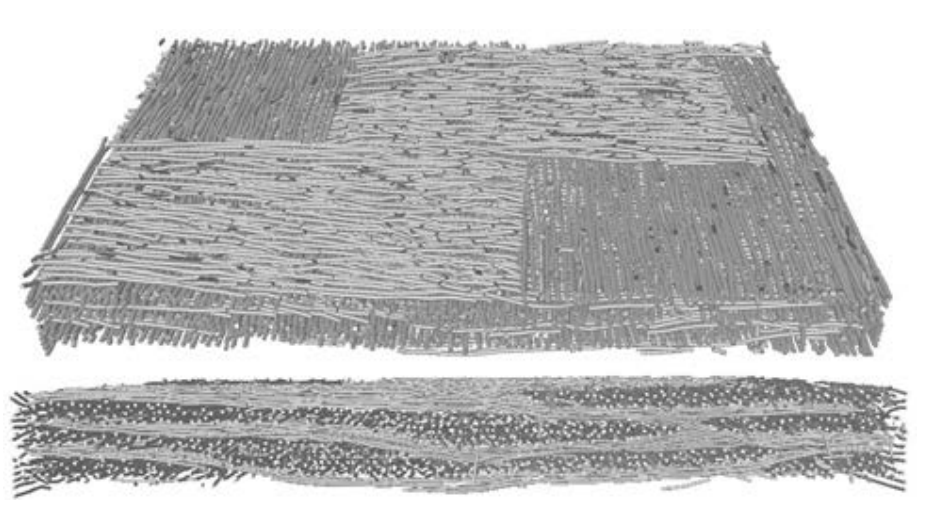
The paper proposes a new experimental methodology, based on ultrasonic measurements, that aims at evaluating the anisotropic damage in woven semi-crystalline polymer composites through new damage indicators. Due to their microstructure, woven composite materials are characterized by an anisotropic evolution of damage induced by different damage mechanisms occurring at the micro or mesoscopic scales. In this work, these damage modes in polyamide 6.6/6-woven glass fiber reinforced composites ha... Read more
Pascal Pomarède, Fodil Meraghni, Laurent Peltier, Stéphane Delalande, Nico F. Declercq
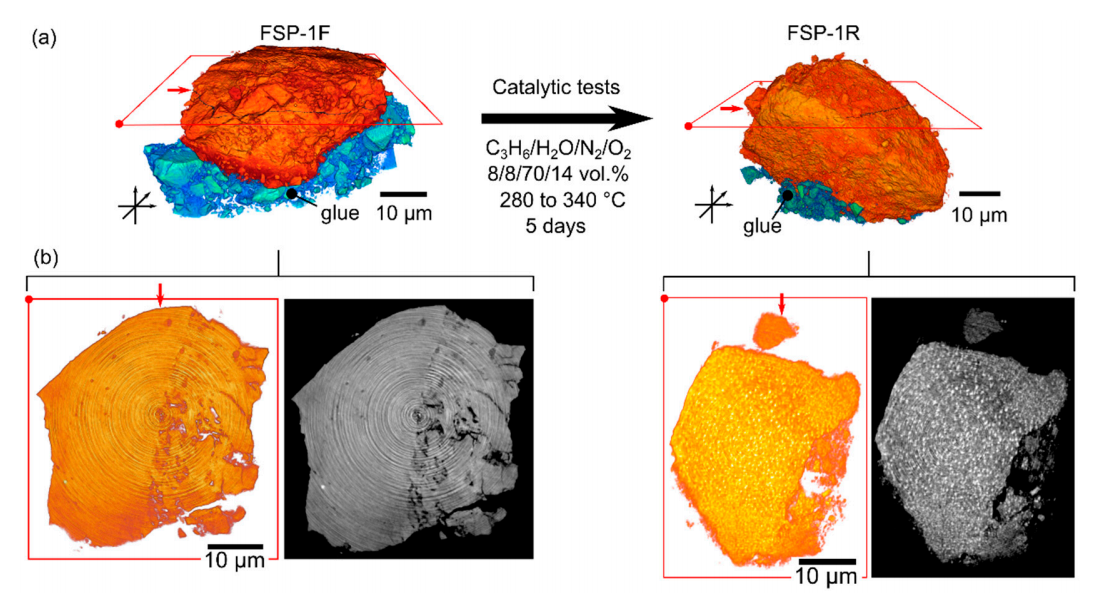
Structural Evolution of Highly Active Multicomponent Catalysts for Selective Propylene Oxidation
Multicomponent Bi-Mo-Fe-Co oxide catalysts prepared via flame spray pyrolysis were tested for selective propylene oxidation, showing high conversion (>70%) and selectivity (>85%) for acrolein and acrylic acid at temperatures of 330 ◦C. During extended time-on-stream tests (5–7 days), the catalysts retained high activity while undergoing diverse structural changes. This was evident on: (a) the atomic scale, using powder X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray absorption spectros... Read more
Paul Sprenger, Thomas L Sheppard, Jussi-Petteri Suuronen, Abhijeet Gaur, Federico Benzi and Jan-Dierk Grunwaldt