Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
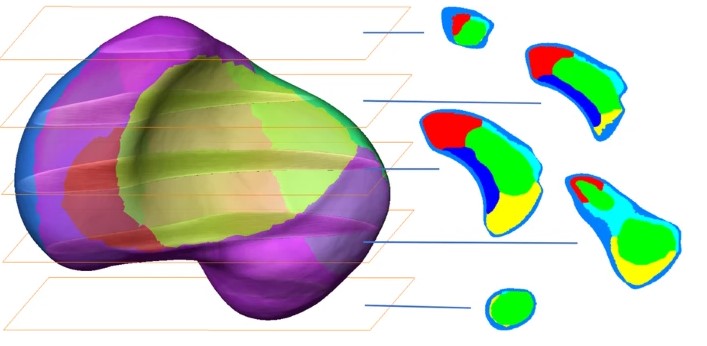
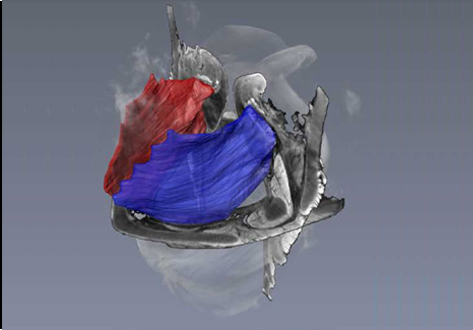
3D computational anatomy of the scaphoid and its waist for use in fracture treatment
A detailed understanding of scaphoid anatomy helps anatomic fracture reduction and optimal screw position. Therefore, we analyzed the size and shape variations of the cartilage and osseous surface, the distribution of volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD), and if the vBMD values differ between a peripheral and a central screw pathway?
Forty-three fresh frozen hand specimens (17 females, 26 males) were analysed with high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) ... Read more
Marc-Daniel Ahrend, Teun Teunis, Hansrudi Noser, Florian Schmidutz, Geoff Richards, Boyko Gueorguiev & Lukas Kamer
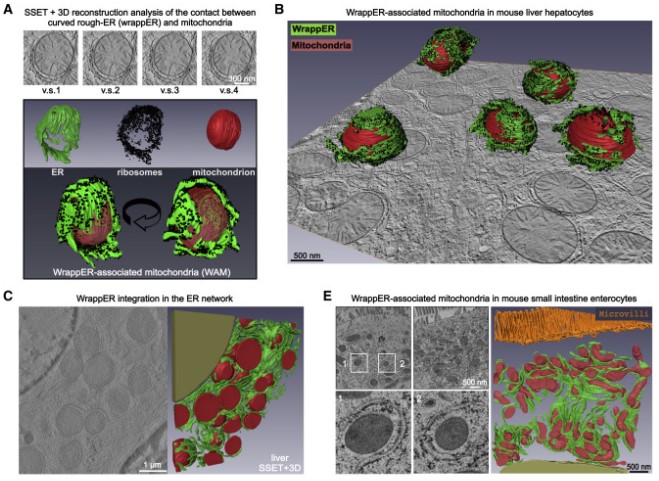
Mitochondria-rough-ER contacts in the liver regulate systemic lipid homeostasis
In this work, we studied mitochondria-rER contacts in vivo by serial section electron tomography (SSET) and 3D reconstruction analysis of cryo-fixed mouse tissue samples. We characterized this inter-organelle association as mitochondria tightly wrapped by sheets of curved rER (wrappER). Further, we used multi-omics and genetic approaches to obtain evidence that the wrappER is a distinct intracellular compartment and demonstrate the importance of wrappER-mitochondria contacts for v... Read more
Irene Anastasia, Nicolò Ilacqua, Andrea Raimondi, Philippe Lemieux, Rana Ghandehari-Alavijeh, Guilhem Faure, Sergei L. Mekhedov, Kevin J. Williams, Federico Caicci, Giorgio Valle, Marta Giacomello, Ariel D. Quiroga, Richard Lehner, Michael J. Miksis, Katalin Toth, Thomas Q. de Aguiar Vallim, Eugene V. Koonin, Luca Scorrano, Luca Pellegrini
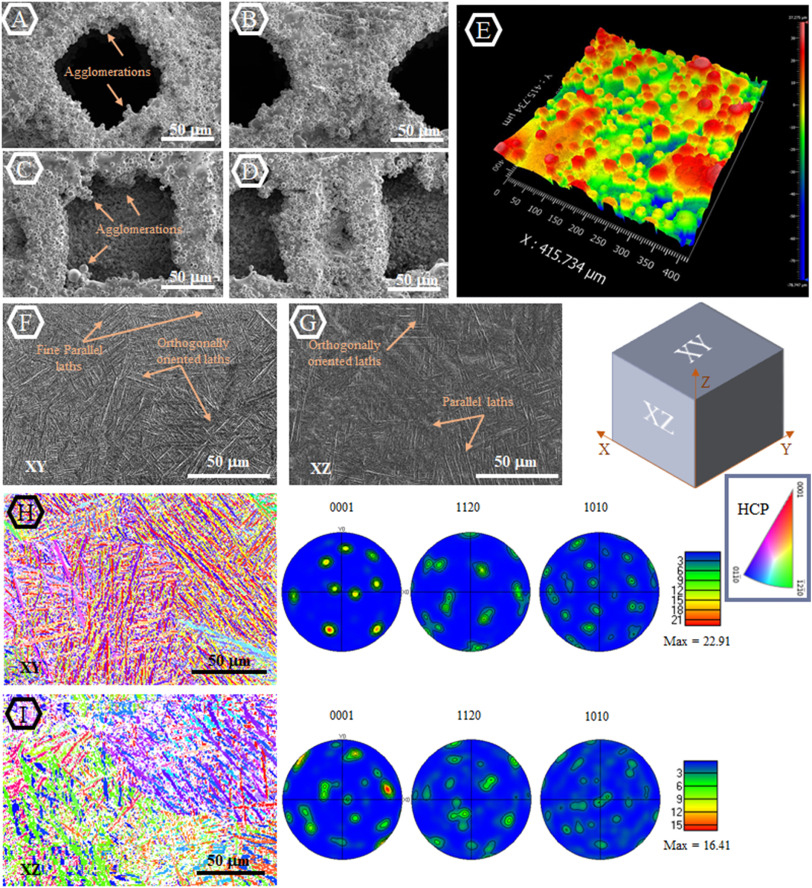
Material synthesis techniques have been historically used to engineer the mechanical and biological properties of biomaterials. Despite the overall success of this approach in different fronts […] there are still major unaddressed challenges due to the limited range of material properties that can be obtained through such synthesis techniques […]. Recent advances in additive manufacturing (AM) have initiated a new paradigm, which could facilitate better control of mechanical and b... Read more
Maryam Tilton, Alireza Borjali, Aaron Isaacson, Kartik Mangudi Varadarajan, Guha P.Manogharan
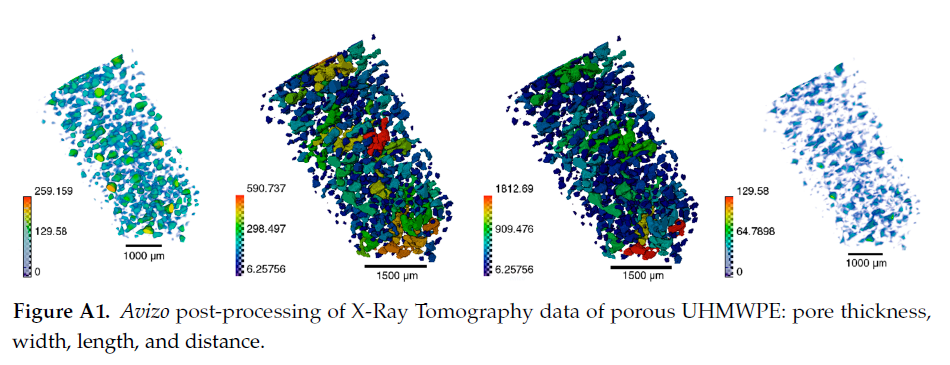
Since its invention and commercialization in the 1950s, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) has been known as a high-performance polymer successfully applied in diverse engineering systems ranging from strong ropes for naval demands and wear-resistant liners in bearings, transportation belts and heavy trucks in mines and quarries, through the lining of chemical vessels and disposable bags in bioreactors, to sophisticated products such as orthopaedic implants and replacements of ... Read more
Eugene S. Statnik, Codrutza Dragu, Cyril Besnard, Alexander J.G. Lunt, Alexey I. Salimon, Aleksey Maksimkin and Alexander M. Korsunsky
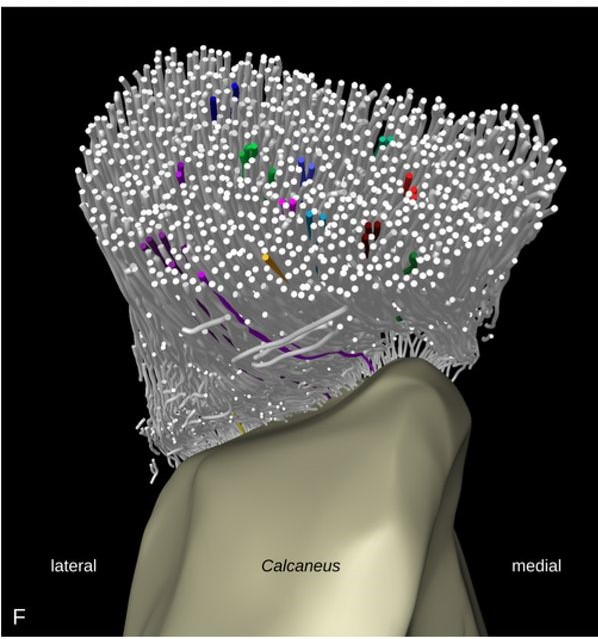
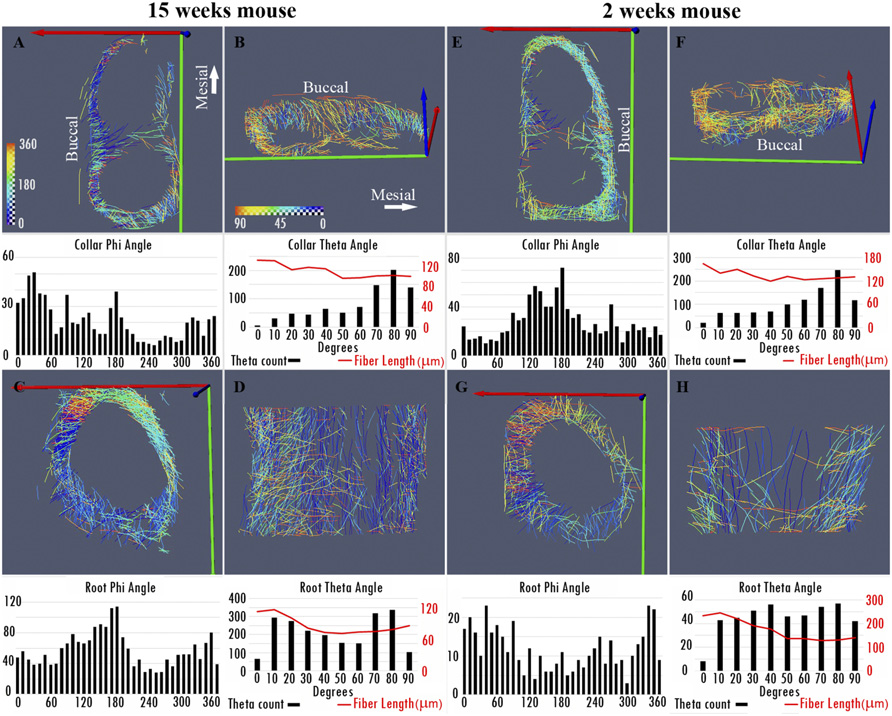
Tracking tendon fibers to their insertion – a 3D analysis of the Achilles tendon enthesis in mice
Tendon insertions to bone are heavily loaded transitions between soft and hard tissues. The fiber courses in the tendon have profound effects on the distribution of stress along and across the insertion. We tracked fibers of the Achilles tendon in mice in micro-computed tomographies and extracted virtual transversal sections. The fiber tracks and shapes were analyzed from a position in the free tendon to the insertion with regard to their mechanical consequences. The fiber number was found to... Read more
Julian Sartori, Heiko Stark
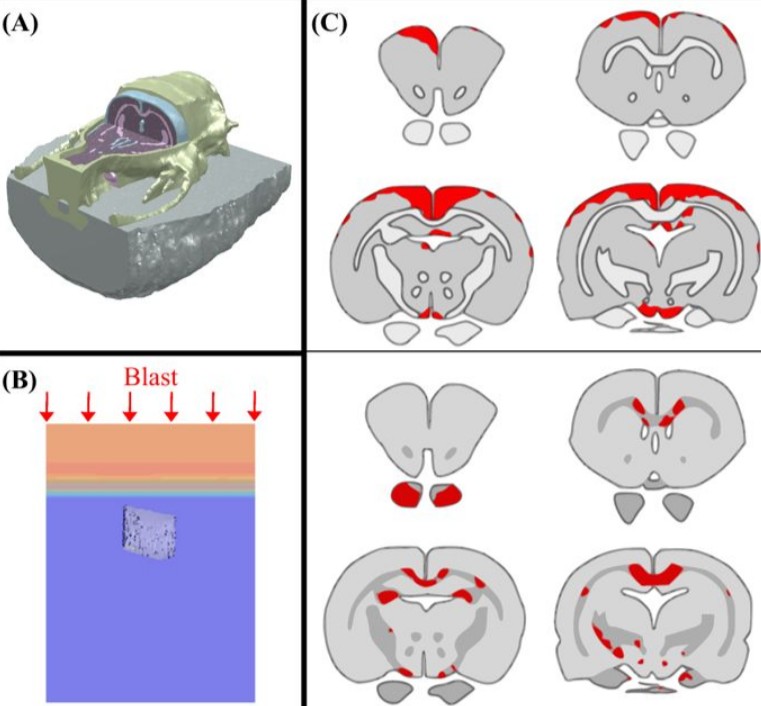
Cognition based bTBI mechanistic criteria; a tool for preventive and therapeutic innovations
Blast-induced traumatic brain injury has been associated with neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders. To date, although damage due to oxidative stress appears to be important, the specific mechanistic causes of such disorders remain elusive. Here, to determine the mechanical variables governing the tissue damage eventually cascading into cognitive deficits, we performed a study on the mechanics of rat brain under blast conditions. To this end, experiments were carried out to analyse... Read more
Daniel Garcia-Gonzalez, Nicholas S. Race, Natalie L. Voets, Damian R. Jenkins, Stamatios N. Sotiropoulos, Glen Acosta, Marcela Cruz-Haces, Jonathan Tang, Riyi Shi & Antoine Jérusalem
Biodegradable materials, such as collagen scaffolds, are used extensively in clinical medicine for tissue regeneration and/or as an implantable drug delivery vehicle. However, available methods to study biomaterial degradation are typically invasive, destructive, and/or non-volumetric. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate a new method for nondestructive, longitudinal, and volumetric measurement of collagen scaffold degradation. Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) were covalently ... Read more
Tyler A. Finamore, Tyler E. Curtis, James V. Tedesco, Kathryn Grandfield, Ryan K. Roeder
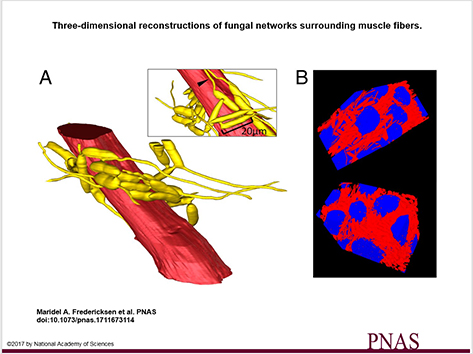
3D visualization and deep-learning reveal complex parasite networks in behaviorally manipulated ants
Microbial parasites may behave collectively to manipulate their host’s behavior. We examine adaptations of a microbial parasite in its natural environment: the body of its coevolved and manipulated host.
Electron microscopy and 3D reconstructions of host and parasite tissues reveal that this fungus invades muscle fibers throughout the ant’s body but leaves the brain intact, and that the fungal cells connect to form extensive networks.
Read more
Maridel A. Fredericksena, Yizhe Zhangb, Missy L. Hazenc, Raquel G. Loretoa,d, Colleen A. Mangoldd,e, Danny Z. Chenb, and David P. Hughes, Department of Entomology, Pennsylvania State University
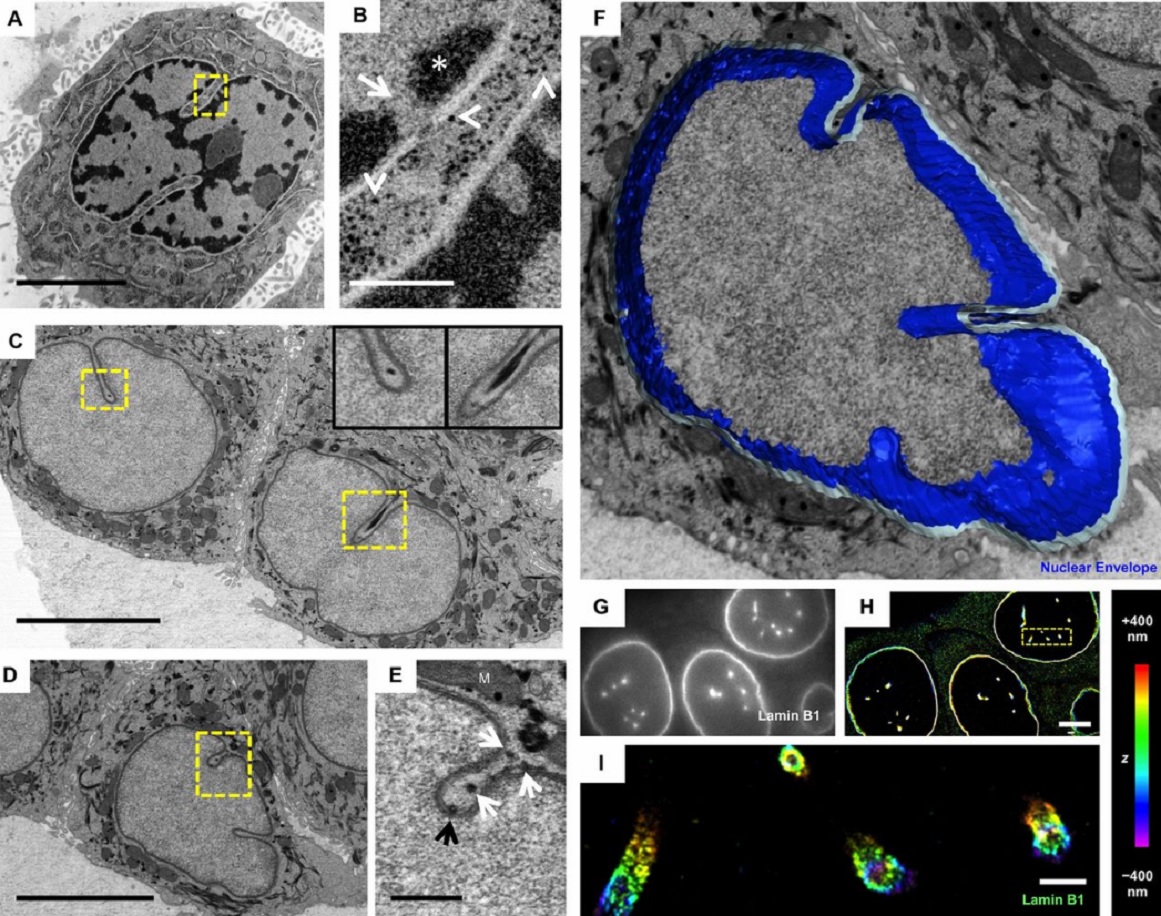
The importance of context in regulation of gene expression is now an accepted principle; yet the mechanism by which the microenvironment communicates with the nucleus and chromatin in healthy tissues is poorly understood. A functional role for nuclear and cytoskeletal architecture is suggested by the phenotypic differences observed between epithelial and mesenchymal cells…
Read more
Danielle M. Jorgens, Jamie L. Inman, Michal Wojcik, Claire Robertson, Hildur Palsdottir, Wen-Ting Tsai, Haina Huang, Alexandre Bruni-Cardoso, Claudia S. López, Mina J. Bissell, Ke Xu, Manfred Auer
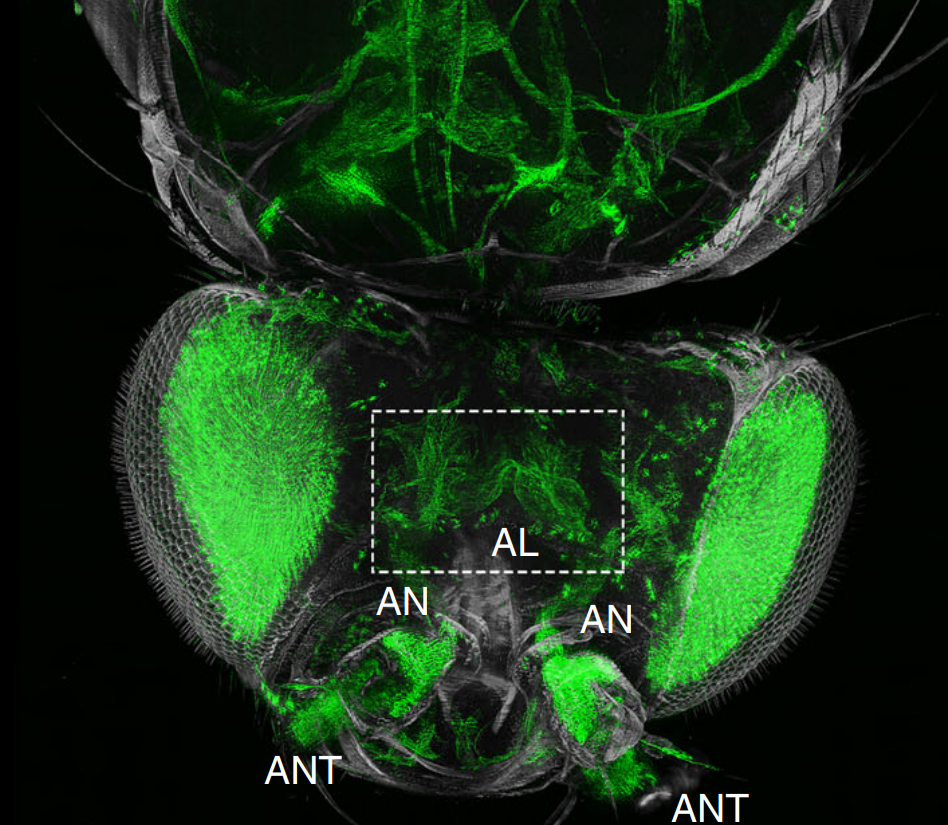
The fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, is an important experimental model to address central questions in neuroscience at an organismic level. However, imaging of neural circuits in intact fruit flies is limited due to structural properties of the cuticle. Here we present a novel approach combining tissue clearing, ultramicroscopy, and data analysis that enables the visualisation of neuronal networks with single-cell resolution from the larval stage up to the adult Drosophila. (…) This... Read more
Marko Pende, Klaus Becker, Martina Wanis, Saiedeh Saghafi, Rashmit Kaur, Christian Hahn, Nika Pende, Massih Foroughipour, Thomas Hummel & Hans-Ulrich Dodt
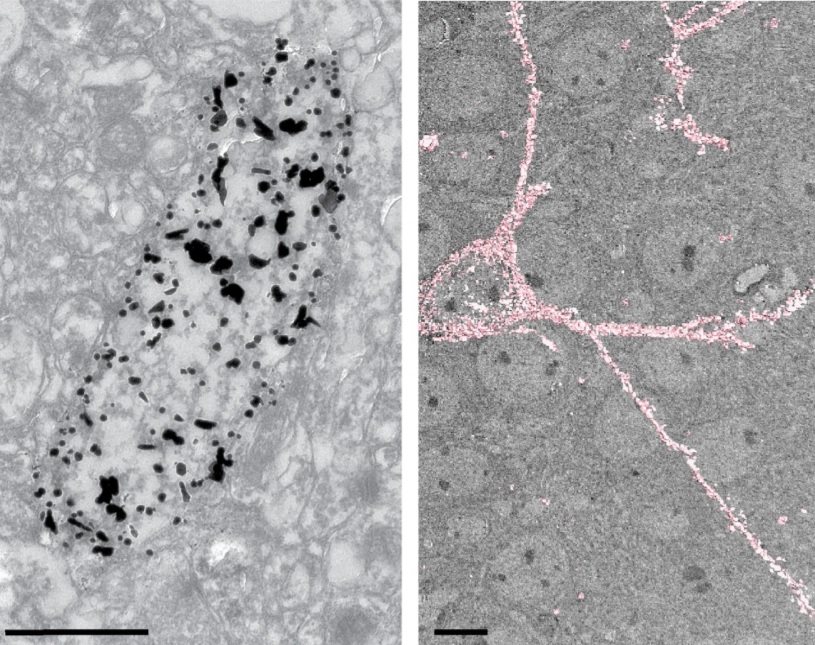
Analysis of neuronal arborization and connections is a powerful tool in fundamental and clinical neuroscience. Changes in neuronal morphology are central to brain development and plasticity and are associated with numerous diseases. Golgi staining is a classical technique based on a deposition of metal precipitate in a random set of neurons. Despite their versatility, Golgi methods have limitations that largely precluded their use in advanced microscopy. We combined Golgi staining with fluore... Read more
Katlijn Vints, Dorien Vandael, Pieter Baatsen, Benjamin Pavie, Frank Vernaillen, Nikky Corthout, Vasily Rybakin, Sebastian Munck & Natalia V. Gounko
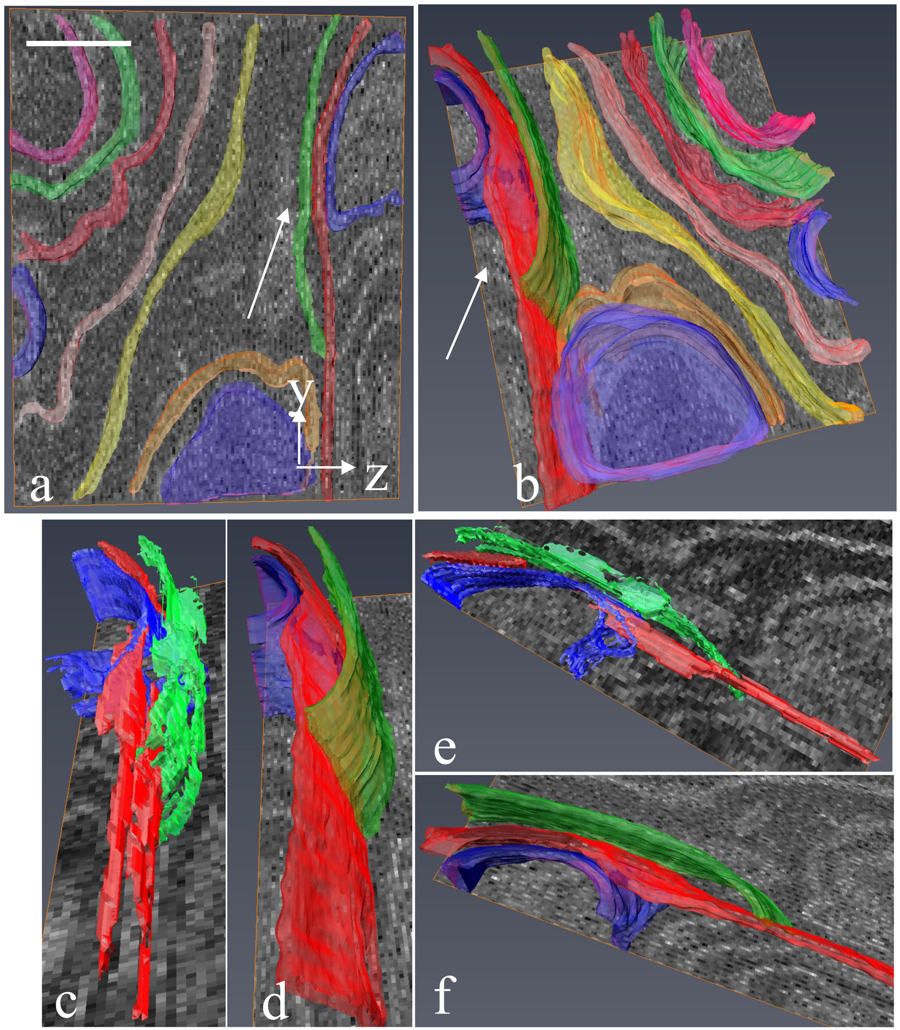
Serial block-face electron microscopy (SBEM) provides nanoscale 3D ultrastructure of embedded and stained cells and tissues in volumes of up to 107 µm3. In SBEM, electrons with 1–3 keV energies are incident on a specimen block, from which backscattered electron (BSE) images are collected with x, y resolution of 5–10 nm in the block-face plane, and successive layers are removed by an in situ ultramicrotome. Sp... Read more
Q. He, M. Hsueh, G. Zhang, D. C. Joy & R. D. Leapman
Juvenile Ovine Ex Vivo Larynges: Phonatory, Histologic, and Micro CT Based Anatomic Analyses
It is well known that the phonatory process changes during the life span. However, detailed investigations on potential factors concerned are rare. To deal with this issue, we performed extended biomechanical, macro anatomical, and histological analyses of the contributing laryngeal structures in ex vivo juvenile sheep models. Altogether twelve juvenile sheep larynges were analyzed within the phonatory experiments. Three different elongation levels and 16 different flow levels were applied to... Read more
Michael Döllinger, Olaf Wendler, Claus Gerstenberger, Tanja Grossmann, Marion Semmler, Hossein Sadeghi, and Markus Gugatschka
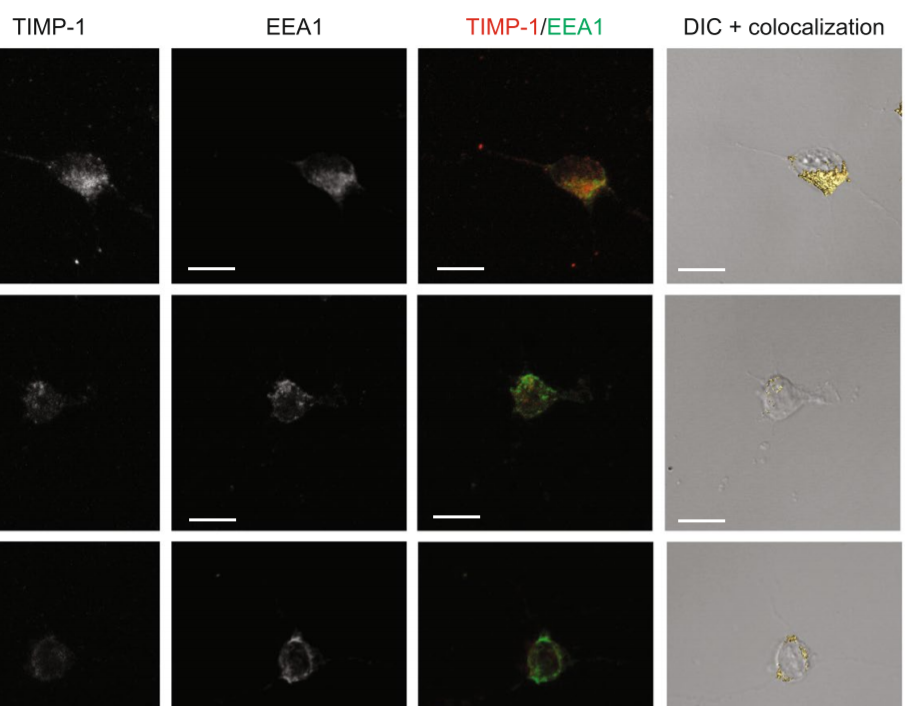
The tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) exerts inhibitory activity against matrix metalloproteinases and cytokine-like effects. We previously showed that TIMP-1 reduces neurite outgrowth in mouse cortical neurons and that this cytokine-like effect depends on TIMP-1 endocytosis mediated by the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP-1). To gain insight into the interaction between TIMP-1 and LRP-1, we considered conformational changes that occur when a ligand bind... Read more
Laurie Verzeaux, Nicolas Belloy, Jessica Thevenard-Devy, Jérôme Devy, Géraldine Ferracci, Laurent Martiny, Stéphane Dedieu, Manuel Dauchez, Hervé Emonard, Nicolas Etique & Emmanuelle Devarenne-Charpentier
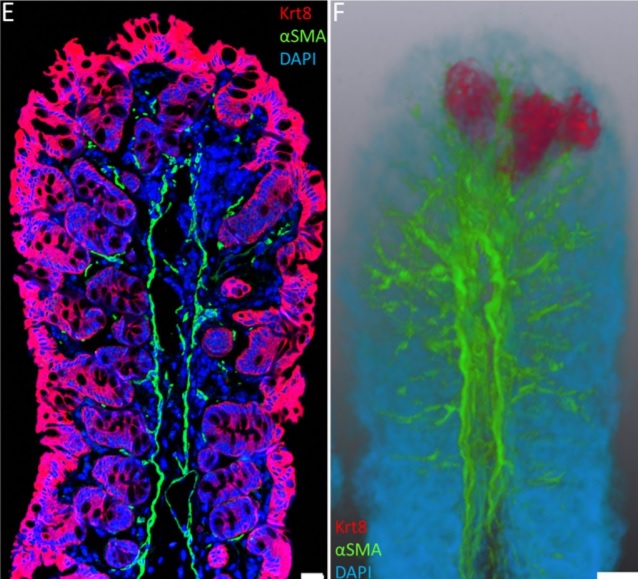
Immunofluorescence tomography is a high-resolution 3-D reconstruction method based on methacrylate embedding and serial-sectioning, where 2-D images of immuno-stained serial-sections are computationally aligned into image stacks, and the 3-D volume rendered. Butyl-Methyl Methacrylate (BMMA) plastic was adopted as it preserves excellent tissue morphology and can be de-plasticized easily using an organic solvent, which enables immuno-staining of serial-sections without antibody penetration issu... Read more
Parfitt, Geraint J
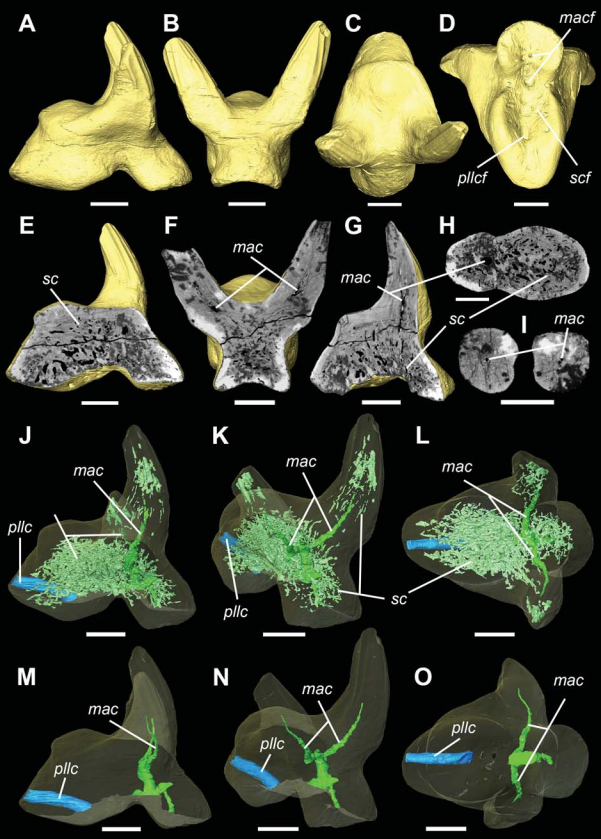
Vascular structure of the earliest shark teeth
Here we use synchrotron tomography to characterise dental vasculature in the oldest known tooth-bearing sharks, Leonodus carlsi Mader, 1986 and Celtiberina maderi Wang, 1993. Three dimensional reconstruction of the vascular system and microstructure of both taxa revealed a complex and dense network of canals, including horizontal, ascending and secondary bifurcated canals, as well as histological features consistent with an osteodont histotype. However, L. carlsi and C. maderi also exhibit si... Read more
Carlos Martinez-Perez, Alba Martin-Lazaro, Humberto G Ferron, Martina Kirstein, Philip C.J. Donoghue, Hector Botella
Nonuniformity in ligaments is a structural strategy for optimizing functionality
Ligaments serve as compliant connectors between hard tissues. In that role, they function under various load regimes and directions. The 3D structure of ligaments is considered to form as a uniform entity that changes due to function. The periodontal ligament (PDL) connects the tooth to the bone and sustains different types of loads in various directions. Using the PDL as a model, employing a fabricated motorized setup in a microCT, we demonstrate that the fibrous network structure with... Read more
Gili R. S. Naveh, Jonathan E. Foster, Tomas M. Silva Santisteban, Xianrui Yang, and Bjorn R. Olsen
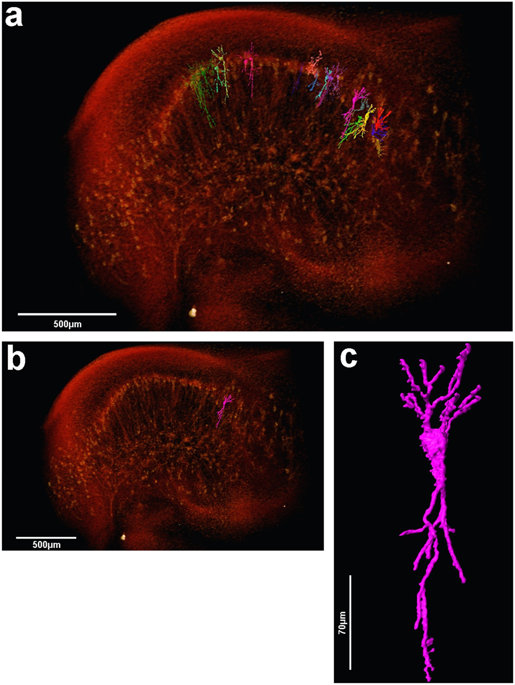
The assessment of neuronal number, spatial organization and connectivity is fundamental for a complete understanding of brain function. However, the evaluation of the three-dimensional (3D) brain cytoarchitecture at cellular resolution persists as a great challenge in the field of neuroscience. In this context, X-ray microtomography has shown to be a valuable non-destructive tool for imaging a broad range of samples, from dense materials to soft biological specimens, arisen as a new method fo... Read more
Matheus de Castro Fonseca, Bruno Henrique Silva Araujo, Carlos Sato Baraldi Dias, Nathaly Lopes Archilha, Dionísio Pedro Amorim Neto, Esper Cavalheiro, Harry Westfahl Jr, Antônio José Roque da Silva, Kleber Gomes Franchini
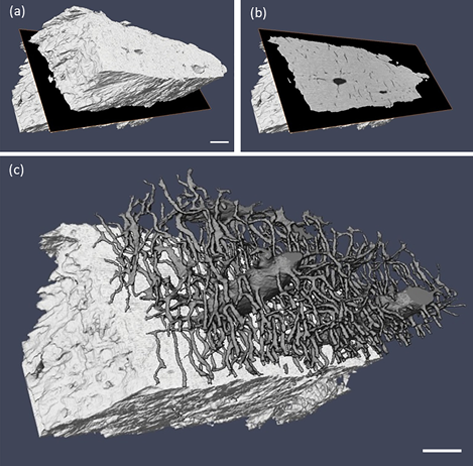
Ptychographic X-ray computed tomography (PXCT) is a quantitative imaging modality that non-destructively maps the 3D electron density inside an object with tens of nanometers spatial resolution. This method provides unique access to the morphology and structure of the osteocyte lacuno-canalicular network (LCN) and nanoscale density of the tissue in the vicinity of an osteocyte lacuna. Our findings indicate that PXCT can non-destructively provide detailed, nanoscale information on the 3D org... Read more
Antonia Ciani, Hechmi Toumi, Stéphane Pallu, Esther H.R.Tsai, Ana Diaz, Manuel Guizar-Sicairos, Mirko Holler, Eric Lespessailles, Cameron M.Kewish | Synchrotron Soleil, France
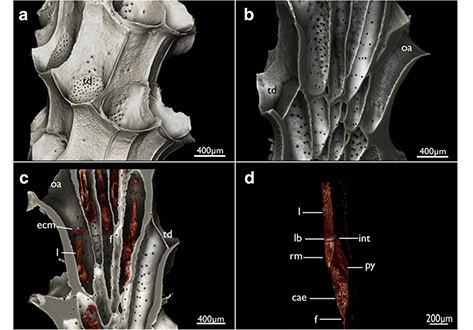
Cyclostome bryozoans are an ancient group of marine colonial suspension-feeders comprising approximately 700 extant species. Previous morphological studies are mainly restricted to skeletal characters whereas data on soft tissues obtained by state-of-the-art methods are still lacking. In order to contribute to issues related to cyclostome ground pattern reconstruction, we analyzed the morphology of the neuromuscular system Cinctipora elegans by means of immunocytochemical staining,... Read more
Thomas F. Schwaha, Stephan Handschuh, Andrew N. Ostrovsky, Andreas Wanninger
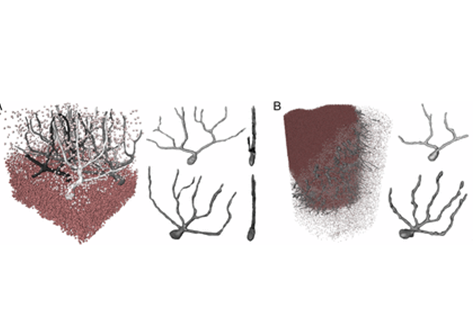
Three-dimensional virtual histology of human cerebellum by X-ray phase-contrast tomography
To quantitatively evaluate brain tissue and its corresponding function, knowledge of the 3D cellular distribution is essential. The gold standard to obtain this information is histology, a destructive and labor-intensive technique where the specimen is sliced and examined under a light microscope, providing 3D information at nonisotropic resolution. To overcome the limitations of conventional histology, we use phase-contrast X-ray tomography with optimized optics, reconstruction, and image an... Read more
Mareike Töpperwien, Franziska van der Meer, Christine Stadelmann, and Tim Salditt