Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
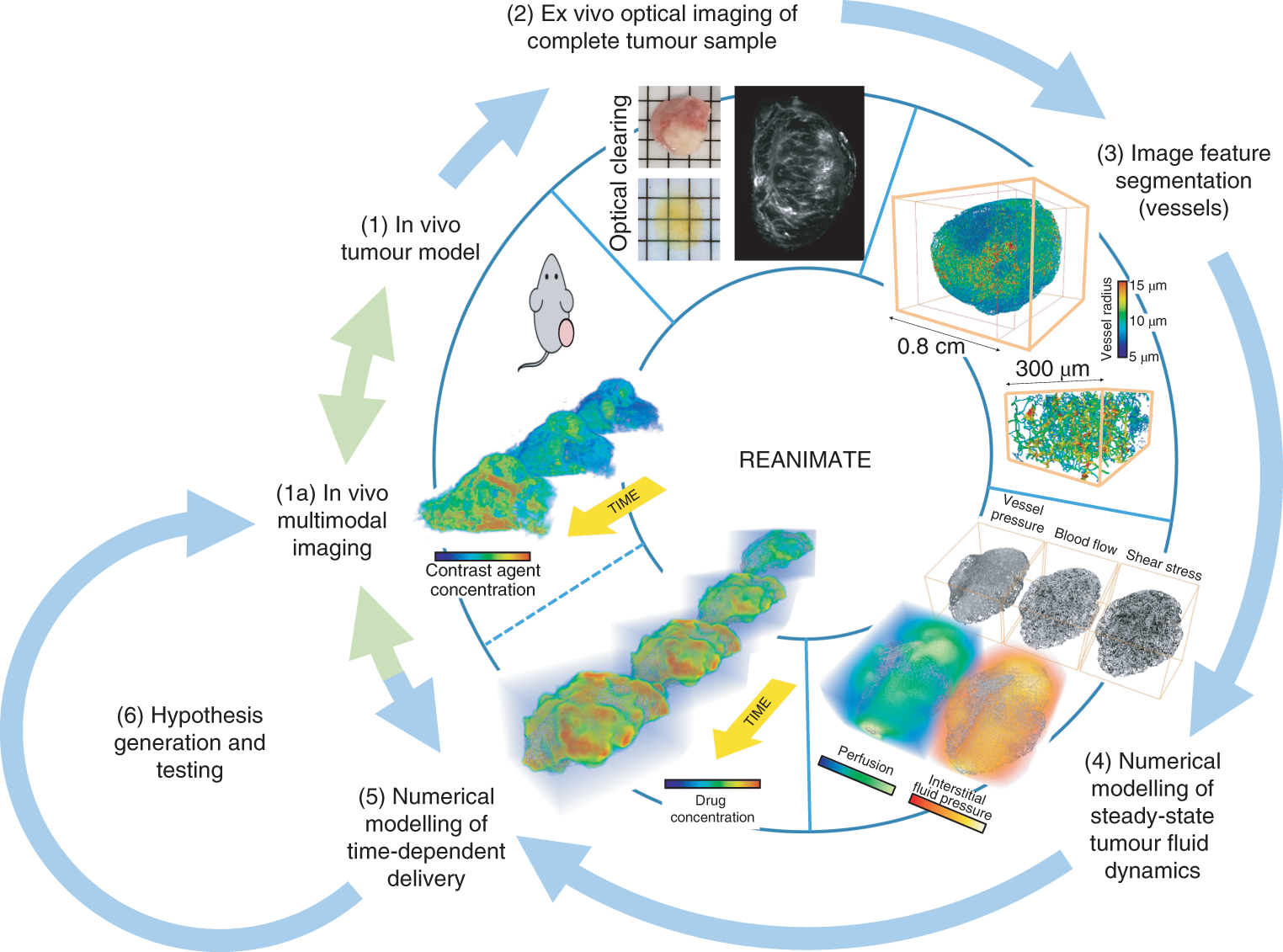
Understanding the uptake of a drug by diseased tissue, and the drug’s subsequent spatiotemporal distribution, are central factors in the development of effective targeted therapies. However, the interaction between the pathophysiology of diseased tissue and individual therapeutic agents can be complex, and can vary across tissue types and across subjects. Here, we show that the combination of mathematical modelling, high-resolution optical imaging of intact and optically cleared tumour tiss... Read more
Angela d’Esposito, Paul W. Sweeney, Morium Ali, Magdy Saleh, Rajiv Ramasawmy, Thomas A. Roberts, Giulia Agliardi, Adrien Desjardins, Mark F. Lythgoe, R. Barbara Pedley, Rebecca Shipley and Simon Walker-Samuel
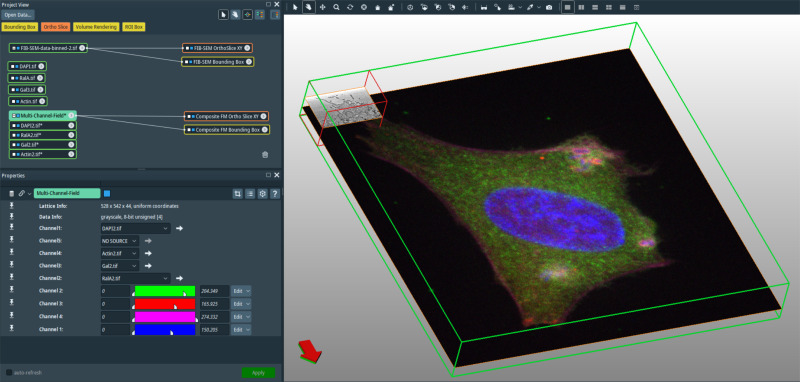
In recent years new methodologies and workflow pipelines for acquiring correlated fluorescence microscopy and volume electron microscopy datasets have been extensively described and made accessible to users of different levels. Post-acquisition image processing, and particularly correlation of the optical and electron data in a single integrated three-dimensional framework can be key for extracting valuable information, especially when imaging large sample volumes such as whole cells or tissu... Read more
Allon Weiner
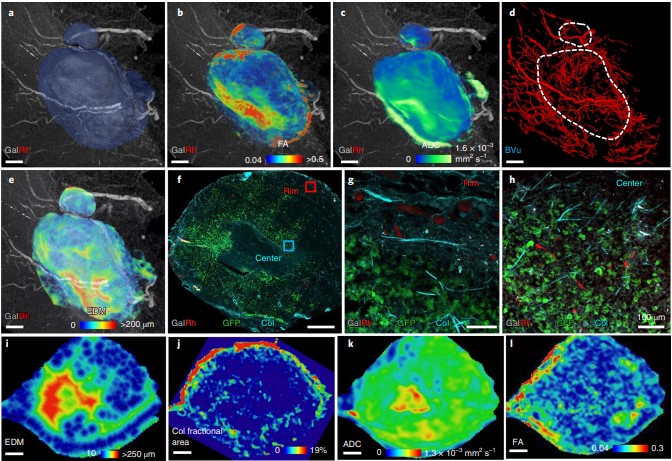
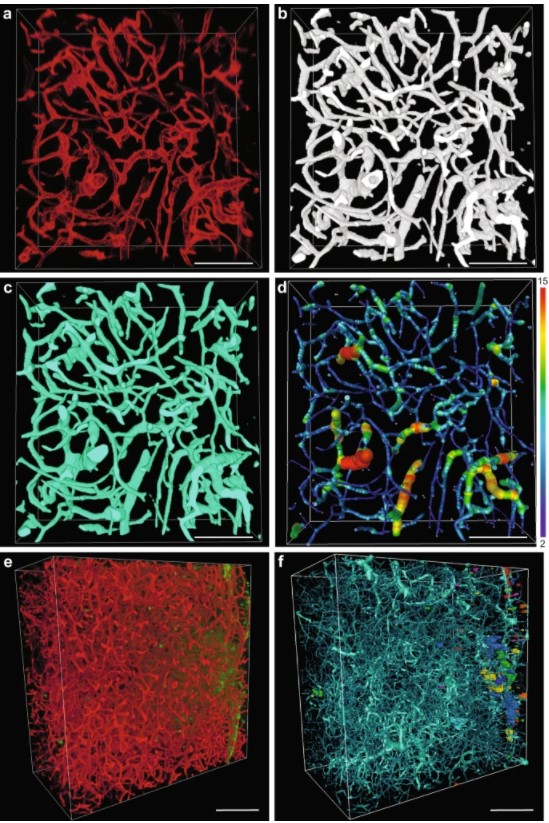
Despite advances in imaging, image-based vascular systems biology has remained challenging because blood vessel data are often available only from a single modality or at a given spatial scale, and cross-modality data are difficult to integrate.
Therefore, there is an exigent need for a multimodality pipeline that enables ex vivo vascular imaging with magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography and optical microscopy of the same sample, while permitting imaging with complementary c... Read more
Akanksha Bhargava, Benjamin Monteagudo, Priyanka Kushwaha, Janaka Senarathna, Yunke Ren, Ryan C. Riddle , Manisha Aggarwal and Arvind P. Pathak
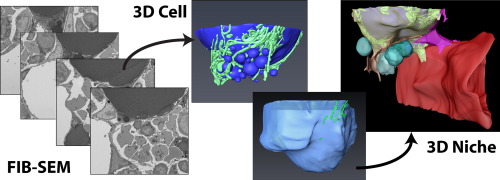
Characterization of the bone marrow adipocyte niche with three-dimensional electron microscopy
Unlike white and brown adipose tissues, the bone marrow adipocyte (BMA) exists in a microenvironment containing unique populations of hematopoietic and skeletal cells.
To study this microenvironment at the subcellular level, we performed a three-dimensional analysis of the ultrastructure of the BMA niche with focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB-SEM). This revealed that BMAs display hallmarks of metabolically active cells including polarized lipid deposits, a dense mitoch... Read more
Hero Robles, SungJae Park, Matthew S. Joens, James A.J. Fitzpatrick, Clarissa S. Craft, Erica L. Scheller
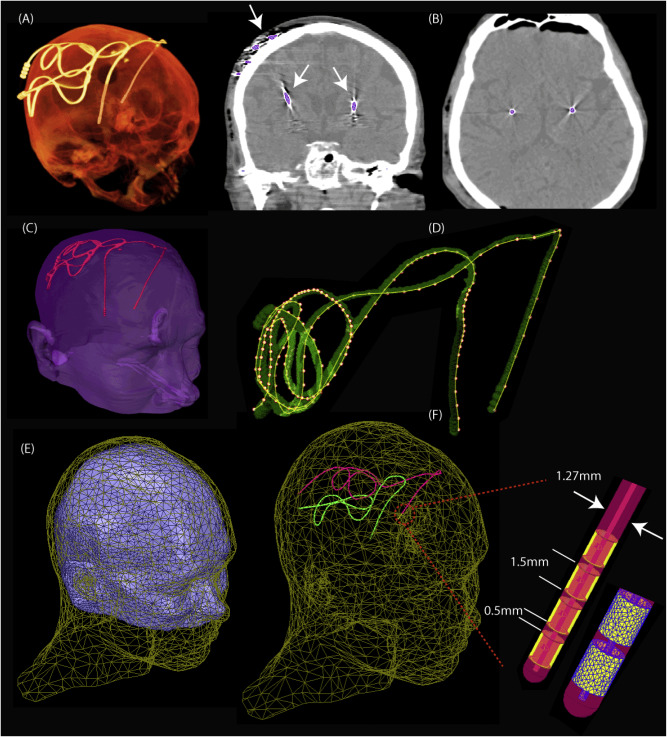
Access to MRI is limited for patients with DBS implants due to safety hazards, including radiofrequency heating of tissue surrounding the leads. Computational models provide an exquisite tool to explore the multi-variate problem of RF implant heating. We used a computational approach to assess RF heating around tips of bilateral DBS leads during MRI at 1.5T and 3T using realistic DBS lead models. A substantial difference was found between the SAR and temperature rise at the tip of right and l... Read more
Laleh Golestanirad, John Kirsch, Giorgio Bonmassar, Sean Downs, Behzad Elahi, Alastair Martin, Maria-Ida Iacono, Leonardo M. Angelone, Boris Keil, Lawrence L. Wald, Julie Pilitsis
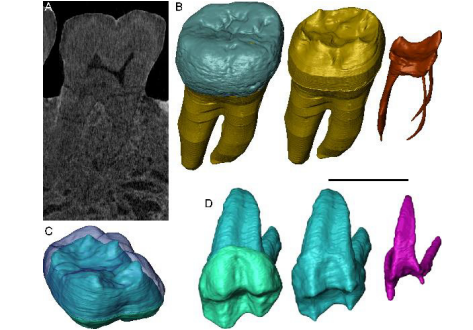
Exploring hominin and non-hominin primate dental fossil remains with neutron microtomography
Fossil dental remains are an archive of unique information for paleobiological studies. Computed microtomography based on Xray microfocus sources (X-µCT) and Synchrotron Radiation (SR-µCT) allow subtle quantification at the micron and sub-micron scale of the meso- and microstructural signature imprinted in the mineralized tissues, such as enamel and dentine, through highresolution “virtual histology”. Nonetheless, depending on the degree of alterations undergone during fossiliza... Read more
Clément Zanolli, Laboratory AMIS, UMR 5288, University of Toulouse III - Paul Sabatier, France, and al.
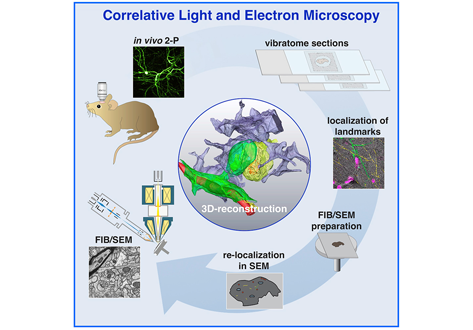
Label-free 3D-CLEM using endogenous tissue landmarks
We demonstrate feasibility of the workflow by combining in vivo 2-photon microscopy and focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB/SEM) to dissect the role of astrocytic coverage in the persistence of dendritic spines.
Emerging 3D correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM) approaches enable studying neuronal structure-function relations at unprecedented depth and precision. However, established protocols for the correlation of light and electron micrographs rely ... Read more
Manja Luckner,Steffen Burgold, Severin Filser, Maximilian Scheungrab, Yilmaz Niyaz, Eric Hummel, Gerhard Wanner, Jochen Herms
Endosseous oral implant is applied for orthodontic anchorage in subjects with multiple tooth agenesis. Its effectiveness under orthodontic loading has been demonstrated clinically and experimentally. This study investigates the deformation and stress on the bone and implant for different bite forces by three-dimensional (3D) finite element (FE) methods. A numerical simulation of deformation and stress distributions around implants was used to estimate the survival life for implants. The model... Read more
Hsin-Chung Cheng, Boe-Yu Peng, May-Show Chen, Chiung-Fang Huang, Yi Lin, and Yung-Kang Shen
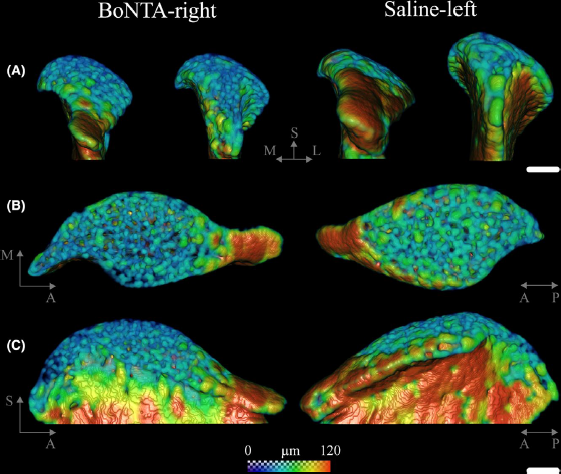
Masseter muscle function influences mandibular bone homeostasis. As previously reported, bone resorption markers increased in the mouse mandibular condyle two days after masseter paralysis induced with botulinum toxin type A (BoNTA), followed by local bone loss.
This study aimed to evaluate the bone quality of both the mandibular condyle and alveolar process in the mandible of adult mice during the early stage of a BoNTA‐induced masseter muscle atrophy, using a combined 3D histomorpho... Read more
Julián Balanta‐Melo, María Angélica Torres‐Quintana, Maximilian Bemmann, Carolina Vega, Constanza González, Kornelius Kupczik, Viviana Toro‐Ibacache, Sonja Buvinic
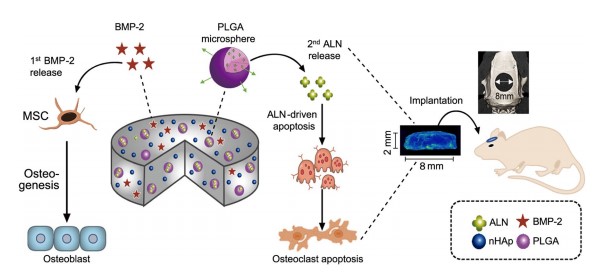
The clinical use of bioactive molecules in bone regeneration has been known to have side effects, which result from uncontrolled and supraphysiological doses.
In this study, we demonstrated the synergistic effect of two bioactive molecules, bone morphogenic protein-2 (BMP-2) and alendronate (ALN), by releasing them in a sequential manner. Collagen-hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds functionalized using BMP-2 are loaded with biodegradable microspheres where ALN is encapsulated.
Th... Read more
Dongtak Lee, Maierdanjiang Wufuer, Insu Kim, Tae Hyun Choi , Byung Jun Kim , Hyo Gi Jung, Byoungjun Jeon, Gyudo Lee, Ok Hee Jeon, Hak Chang & Dae Sung Yoon
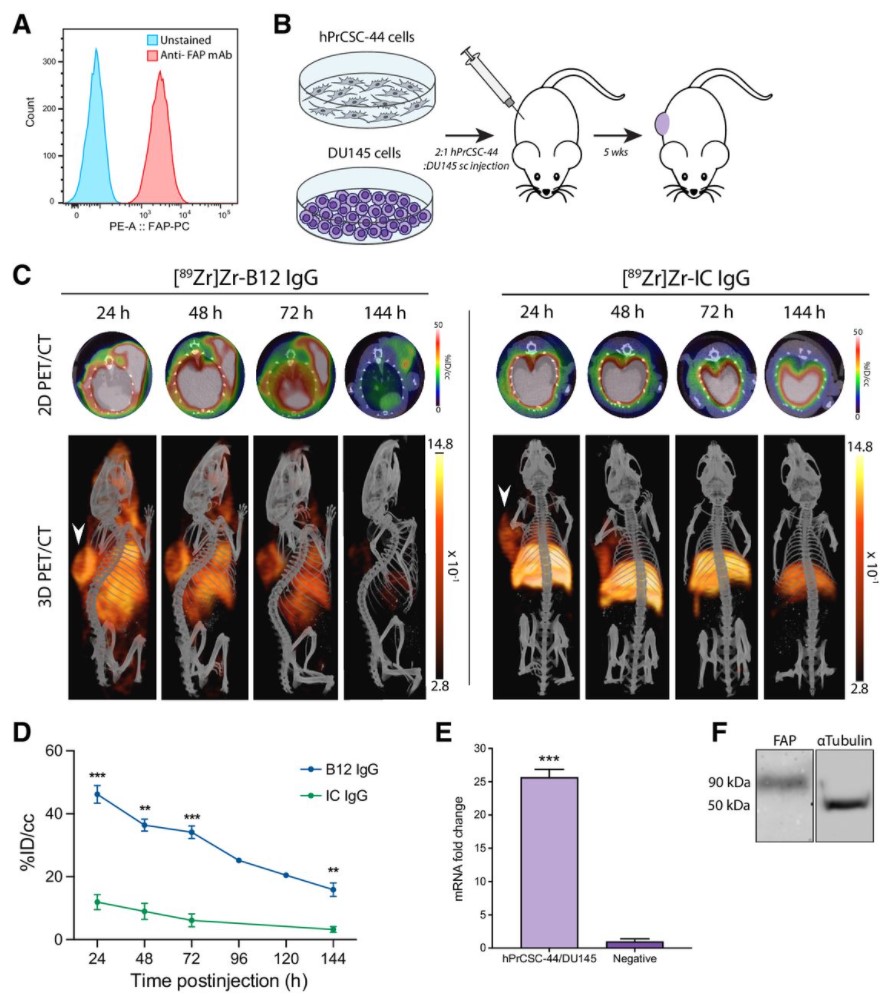
Malignant cells are surrounded by a complex and supportive tumor microenvironment that consists of immune cells, extracellular matrix, vasculature, and fibroblasts. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) are the major cell type in the reactive stroma and are known to promote tumorigenesis and metastasis. Fibroblast activation protein alpha (FAP) is a transmembrane serine protease expressed by CAFs in the microenvironment of epithelial tumors.
Meta-analysis of FAP expression and clinical ... Read more
Hallie M. Hintz, Joseph P. Gallant, Donald J. Vander Griend, Ilsa M. Coleman, Peter S. Nelson and Aaron M. LeBeau
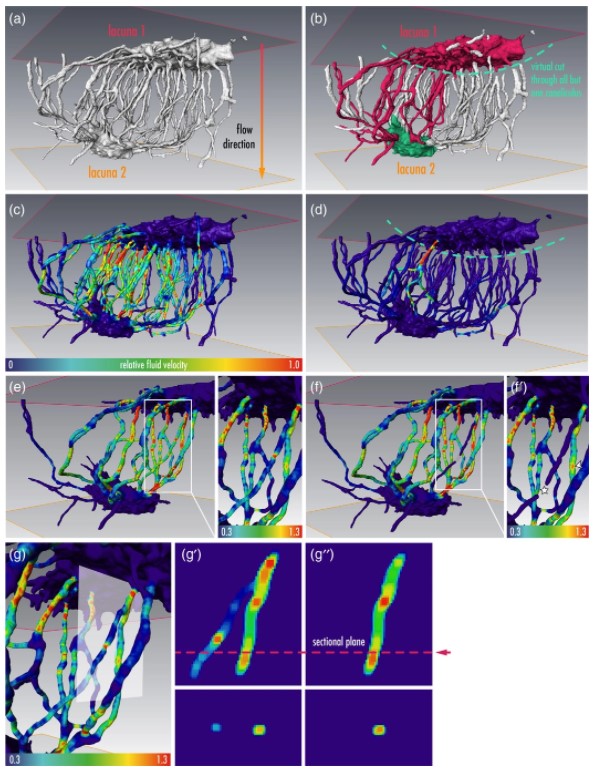
Osteocytes are the most frequent bone cells connected with each other through cell processes within tiny tubular-shaped canaliculi. The so-called osteocyte lacunar-canalicular network (LCN) plays a crucial role in bone remodeling and mineral homeostasis. Given the critical nature of these functions, it is herein hypothesized that the LCN must be structurally “overengineered” to provide network resilience.
This hypothesis is tested by characterizing canalicular networks in human bon... Read more
Emely Bortel, Liam M Grover, Neil Eisenstein, Christian Seim, Heikki Suhonen, Alexandra Pacureanu, Peter Westenberger, Kay Raum, Max Langer, Francoise Peyrin, Owen Addison, Bernhard Hesse
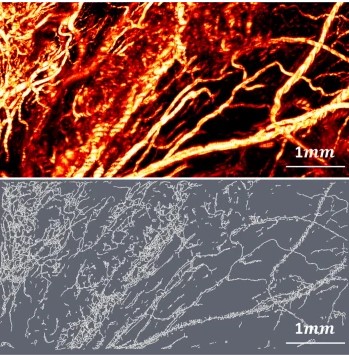
Precise methods for quantifying drug accumulation in brain tissue are currently very limited, challenging the development of new therapeutics for brain disorders. Transcardial perfusion is instrumental for removing the intravascular fraction of an injected compound, thereby allowing for ex vivo assessment of extravasation into the brain. However, pathological remodeling of tissue microenvironment can affect the efficiency of transcardial perfusion, which has been largely overlooked.
We... Read more
Serhii Kostrikov, Kasper B. Johnsen, Thomas H. Braunstein, Johann M. Gudbergsson, Frederikke P. Fliedner, Elisabeth A. A. Obara, Petra Hamerlik, Anders E. Hansen, Andreas Kjaer, Casper Hempel & Thomas L. Andresen
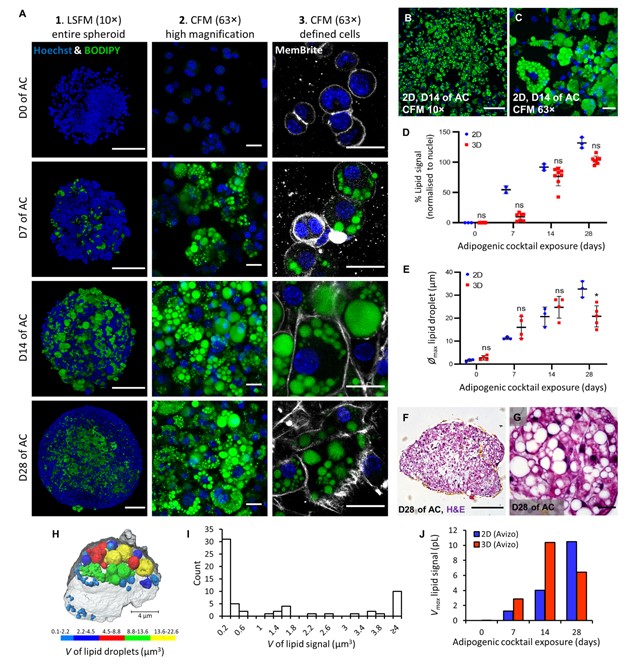
Adipose models have been applied to mechanistic studies of metabolic diseases (such as diabetes) and the subsequent discovery of new therapeutics. However, typical models are either insufficiently complex (2D cell cultures) or expensive and labor intensive (mice/in vivo). To bridge the gap between these models and in order to better inform pre-clinical studies we have developed a drug-responsive 3D model of white adipose tissue (WAT).
Here, spheroids (680 ± 60 μm) comp... Read more
Alexander D Graham, Rajesh Pandey, Viktoriya S Tsancheva, Alessia Candeo, Stanley W Botchway, Alasdair J Allan, Lydia Teboul4, Kamel Madi, Tahkur S Babra, Louisa A K Zolkiewski, Xuan Xue, Liz Bentley, Joan Gannon, Sam N Olof and Roger D Cox
Optical Resolution Photoacoustic Microscopy of Ovary and Fallopian Tube
Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death among gynecological cancers, but is poorly amenable to preoperative diagnosis. In this study, we investigate the feasibility of “optical biopsy,” using high-optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy (OR-PAM) to quantify the microvasculature of ovarian and fallopian tube tissue. The technique is demonstrated using excised human ovary and fallopian tube specimens imaged immediately after surgery.
This report describes the first applicatio... Read more
Bin Rao, Xiandong Leng, Yifeng Zeng, Yixiao Lin, Ruimin Chen, Qifa Zhou, Andrea R. Hagemann, Lindsay M. Kuroki, Carolyn K. McCourt, David G. Mutch, Matthew A. Powell, Ian S. Hagemann & Quing Zhu
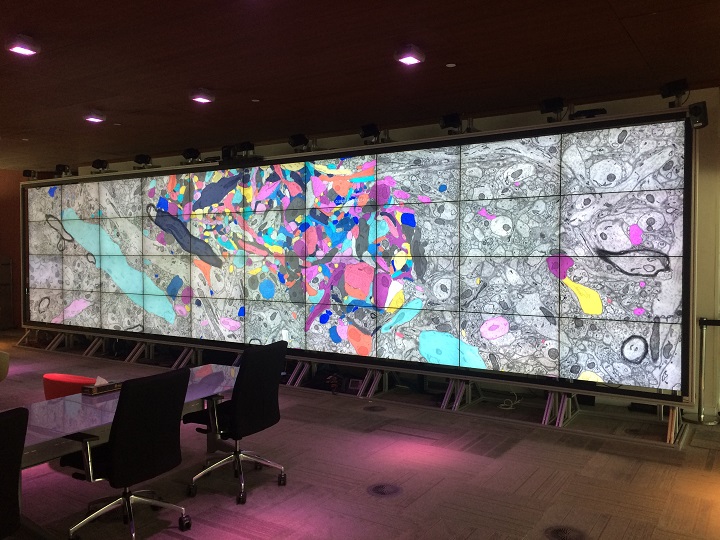

Insights into data with the KAUST Visualization Core Lab
Through collaboration, the KAUST Visualization Core Lab (KVL) team augments the efforts and domain expertise of KAUST researchers by providing complimentary technical knowledge with exploratory visualization and analytic tools.
KVL’s multi-year collaboration with KAUST Distinguished Professor P. Magistretti and research scientist C. Calì’s KAUST-EPFL Alliance for Integrative Modelling of Brain Energy Metabolism project—itself a collaboration with the Swiss Blue Br... Read more
By the KAUST Visualization Core Lab team and Caitlin Clark
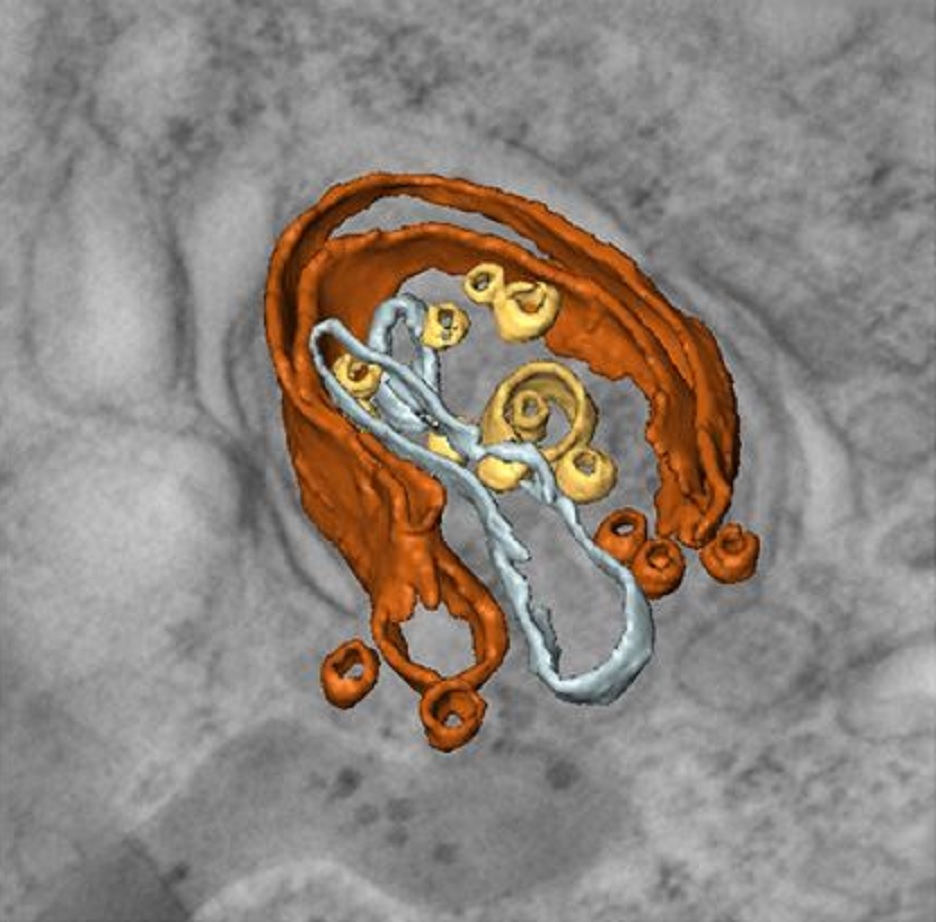
Macroautophagy is morphologically characterized by autophagosome formation. Autophagosomes are double-membraned vesicles that sequester cytoplasmic components for further degradation in the lysosome. Basal autophagy is paramount for intracellular quality control in post-mitotic cells but, surprisingly, the number of autophagosomes in post-mitotic neurons is very low, suggesting that alternative degradative structures could exist in neurons…
Read more
Maria Rosario Fernandez-Fernandez, Desire Ruiz-Garcia, Eva Martin-Solana, Francisco Javier Chichon, Jose L. Carrascosa, Jose-Jesus Fernandez
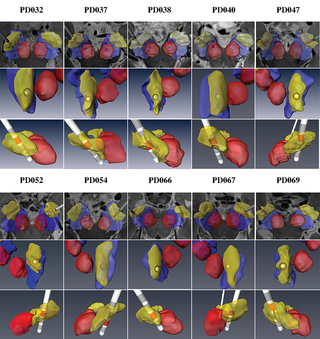
Patient-specific anatomical model for deep brain stimulation based on 7 Tesla MRI
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) requires accurate localization of the anatomical target structure, and the precise placement of the DBS electrode within it. Ultra-high field 7 Tesla (T) MR images can be utilized to create patient-specific anatomical 3D models of the subthalamic nuclei (STN) to enhance pre-surgical DBS targeting as well as post-surgical visualization of the DBS lead position and orientation. We validated the accuracy of the 7T imaging-based patient-specific model of the STN and m... Read more
Yuval Duchin, Reuben R. Shamir, Remi Patriat, Jinyoung Kim, Jerrold L. Vitek, Guillermo Sapiro, Noam Harel
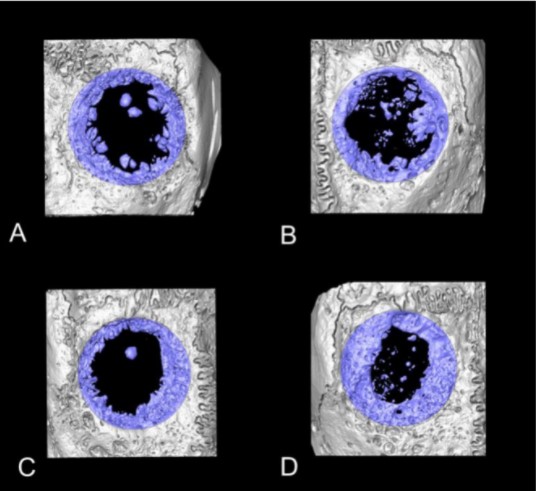
Collagen-Based Matrices for Osteoconduction: A Preclinical In Vivo Study
The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of additional hydroxyapatite (HA) in collagen-based matrices (CM) and membrane placement on bone formation in calvarial defects.
Critical size defects in the calvaria of 16 New Zealand White Rabbits were randomly treated with CM or mineralized collagen-based matrices (mCM). Half of the sites were covered with a collagen membrane. Animals were euthanized after 12 weeks of healing. The samples were studied by micro-CT and histology. New... Read more
Hiroki Katagiri, Yacine El Tawil, Niklaus P. Lang, Jean-Claude Imber, Anton Sculean, Masako Fujioka-Kobayashi and Nikola Saulacic
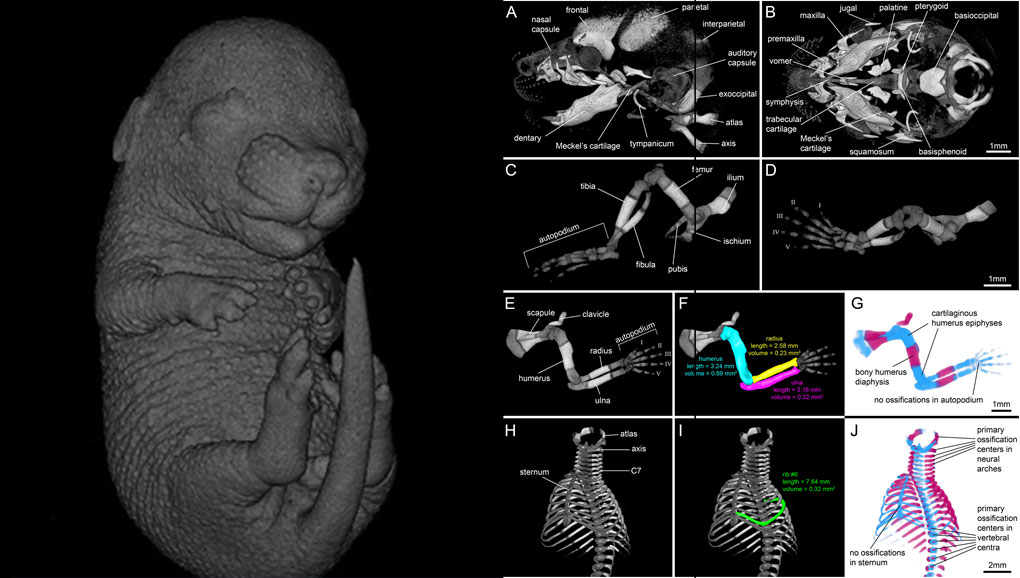
For decades, clearing and staining with Alcian Blue and Alizarin Red has been the gold standard to image vertebrate skeletal development. Here, we present an alternate approach to visualise bone and cartilage based on X-ray microCT imaging, which allows the collection of genuine 3D data of the entire developing skeleton at micron resolution.
Our novel protocol is based on ethanol fixation and staining with Ruthenium Red, and efficiently contrasts cartilage matrix, as demonstrated in wh... Read more
Simone Gabner, Peter Böck, Dieter Fink, Martin Glösmann, Stephan Handschuh
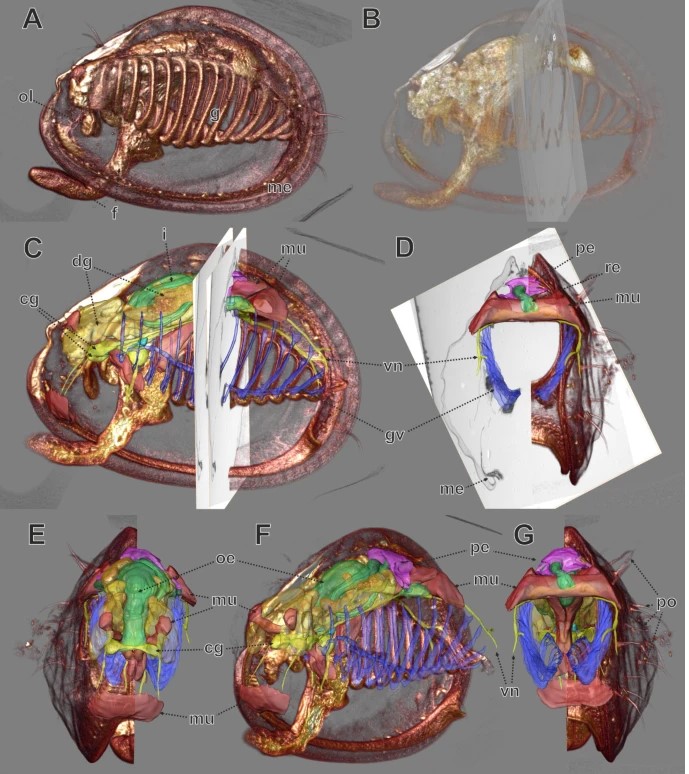
In biomedical research, a huge variety of different techniques is currently available for the structural examination of small specimens, including conventional light microscopy (LM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), microscopic X-ray computed tomography (microCT), and many others. Since every imaging method is physically limited by certain parameters, a correlative use of complementary methods often yields a significant broader range of inform... Read more
Stephan Handschuh, Natalie Baeumler, Thomas Schwaha & Bernhard Ruthensteiner